
Research on Consumer Purchase Intention of Different Social
Presence in Live Broadcast based on GLS Structural Equation Mode
Long Zheng
Department of Business Administration, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Keywords: Live Broadcast Marketing, Structural Equation Model, Warm Presence, Quasi-Social Interaction.
Abstract: The development of enterprise information technology provides more ways and means for enterprises to carry
out marketing management, and the development of live broadcast information technology provides more
ways and supports for customers to participate in enterprise consumption. The development of webcasting
technology can display commodities in multiple directions, providing a good idea for the e-commerce
circulation industry. This paper adopts the quasi-social interaction theory, collects data through
questionnaires, on-site interviews and tracking sales records in the live broadcast of enterprises, analyzes the
collected data based on statistical software such as SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 22.0, and uses GLS to build a
structural equation model effects and mediation effects. Through empirical analysis, it is found that different
presences in e-commerce live broadcasts have a positive impact on customer purchase intention, and the
mediating effect of quasi-social interaction is significant. Among them, the dimensions of communication
presence and warm presence have an important impact on social interaction, which in turn affects customers.
Purchase Intention. On this basis, suggestions are put forward to improve the effect of webcasting.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
Since Taobao took the lead in launching an online
live broadcast marketing platform positioned as
"consumer live broadcast" in 2016, major online e-
commerce platforms have successively launched
their own online live broadcast services. In the past
year, it has become a new bright spot in the growth of
online consumption (China Internet Network
Information Center, 2019). According to reports,
during the "Double Eleven" period in 2019, more
than 100,000 merchants opened live broadcasts on
Taobao's single platform; in the opening 63 minutes,
the transaction volume guided by Taobao's live
broadcast has exceeded that of the "Double Eleven"
in 2018; % of merchants have gained new growth
through live streaming. The combined impact of the
outbreak of the new crown epidemic in 2020 and the
long holiday has caused a surge in the number of live
broadcast users and usage time. According to a
research report released by Media Research, from
2019 to 2020, about 43.2% of Chinese consumers
expressed their willingness to choose live broadcast
e-commerce for online shopping; compared with
other e-commerce models, live broadcast e-
commerce has a shorter propagation path and higher
efficiency with higher advantages, the transaction
scale of China's live broadcast e-commerce is
expected to reach 916 billion yuan in 2020.
As a medium of instant recording, webcasting can
quickly spread images and sounds through various
communication technologies, and users rely on
instant messages, likes, and gift giving to interact
with anchors and audiences, creating a virtual
immersive feeling (Chen, Lin, 2018). In the study,
scholars use Co-presence (CP) and Social Presence
(SP) to describe the degree to which individuals feel
the virtual co-presence of others in the online
environment (Bulu, 2012) and the interpersonal
relationships established virtually. degree of
prominence (Short, et al, 1976, Zhang, Chen, 2017).
The co-presence and social presence of live webcasts
make consumers no longer an "isolated island"
isolated from other buyers, but placed in an online
shopping situation where others watch and buy
together virtually. Following the viewpoints of
previous scholars, this paper divides the social
presence in webcasting into situational presence,
warm presence and communication presence around
Zheng, L.
Research on Consumer Purchase Intention of Different Social Presence in Live Broadcast based on GLS Structural Equation Mode.
DOI: 10.5220/0011156000003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 33-40
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
33

the aspects of consumer awareness, emotion and
cognition. Existing social psychology and marketing
research shows that people's activities are often
influenced by the presence of others, such as
consumers' attention, the pursuit of commodity
variety, and consumption decisions are often
influenced by social interactions from family
members, friends, salespeople, and even strangers.
impact (Chatterjee, et al, 2017, Park, et al, 2017,
WHITE and ARGO 2011). Previous research on
conformity consumption mainly focused on offline
consumption scenarios (Bearden, et al, 1994,
Gardner, et al, 2020) and online graphic consumption
scenarios (Ying, et al, 2016, Chen, Gao, 2013). In
particular, the impact of the exact presence in the
context of webcasting on consumers' purchase
intention remains to be explored.
1.2 Theory and Literature Review
1.2.1 Definition
Social presence (Social Presence) describes a real
perception of people's intimacy, enthusiasm,
friendliness or social interaction with others in a
virtual environment, that is, the degree to which they
perceive that they are in the same space with others
(Xie, et al, 2019). By combing domestic and foreign
scholars' literature, this study found that many
scholars have defined social presence from different
research perspectives. This article will expound from
four perspectives: media characteristics, co-presence,
psychological involvement and behavioral fit.
(1) Based on media characteristics.
Communication media can convey rich social cues to
users, which can help users gain a sense of social
presence. Some scholars who study social presence
from the perspective of media characteristics believe
that social presence is an attribute of the media itself.
(2) Based on the perspective of co-presence. Co-
presence refers to the degree to which a user
perceives a space-time coexistence with others.
Goffman (1959) believes that social presence is the
degree to which users perceive the simultaneous
presence of others through the medium, which is a
psychological feeling. Although people are currently
not in the same location as users who live far away,
they can be connected through a certain
communication medium and feel each other's
existence, and this existence is warm and friendly
(Sallnas, et al, 2000).
(3) Based on the perspective of psychological
involvement. Psychological involvement means that
users feel the efforts of others in the process of
interaction to the extent that they will devote
themselves to changing their emotions and mentality
due to the emotional state of other users. From a
psychological point of view, Mehrabian (Mehrabian,
1967) believes that social presence is the user's
perceived closeness, intimacy and immediacy with
others. The research of Savicki (Savicki, 2000)
defines social presence as the psychological feeling
that users perceive the existence of other people, and
will produce mutual understanding and
consideration. Based on the research background of
social e-commerce, Dai Jianping (Dai, 2018) defined
social presence as consumers' perception and
identification with other consumers in the shopping
platform, thus generating a sense of shopping
immersion.
(4) Based on the behavioral fit angle. Behavioral
fit describes interdependence and interaction, making
their own decisions based on the behavior of others,
and sometimes generating value co-creation
behaviors. Social presence is the degree of
interdependence between users and others and will
engage in social interactions through multiple
channels (Palmer, 1995).
All in all, scholars focus on different angles, and
there is no unified definition. Some scholars believe
that social presence is an attribute of social media,
and social presence is different due to different
technologies. Some scholars also emphasize that
social presence is the psychological perception of
people when they interact with other people. This
paper argues that social presence is a combination of
technology and psychological perception, including
both technical and psychological factors. Technical
factors provide support for users to obtain a sense of
social presence, but technology is auxiliary and also
contains social value, mainly including scene
presence and communication presence in the live
broadcast room, while psychological perception is
mainly warm presence, social presence The
generation of sense is inseparable from the user's
psychological perception (Teng, Yan, Yang, 2013).
Combined with the live broadcast marketing
background, this paper believes that the sense of
social presence is the degree of co-existence and
significant interpersonal relationship between
consumers and the anchor and other consumers in the
interaction of the live broadcast platform, and it is the
fit with other participants in emotion, cognition and
consciousness.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
34

1.2.2 Dimensional Division of Social
Presence
By sorting out the research content of the dimension
of social presence, it is found that scholars divide
social presence into different dimensions based on
different research situations, and there are single-
dimensional and multi-dimensional perspectives in
the current research on social presence. This paper
adopts a multi-dimensional perspective of social
presence. With the development of Internet
technology, the social clues that the media can
convey are becoming more and more abundant, and
the user's control over the media is continuously
strengthened. Single-dimensional social presence
cannot well explain the interaction between users and
other participants, so many scholars need to conduct
multi-dimensional research on social presence based
on their own research backgrounds.
Biocca et al. (Biocca, et al, 2001) believed that the
two dimensions could not meet the research needs
very well, so they divided social presence into
consumers' perception of being with others, the
degree of psychological involvement between
themselves and others, and the degree of their own
behavior and others' behavior. The impact of these
three dimensions on consumers is a gradual process.
Tu (Tu, 2002) divided social presence into social
scenes, online communication and interaction based
on online education scenarios, and explored the
impact of the three on user learning performance.
With the advancement of technology and changes in
consumers' shopping concepts, the dimensions of
social presence are also being improved due to the
continuous development of research needs. Later,
scholars became very interested in virtual
communities. Shen et al. (Shen, et al, 2008) believed
that social presence not only includes consumer
cognition, but also emotion, and further divided
social presence into three dimensions: consciousness,
emotion and cognition. Based on the online
community scenario, Lu et al. (Lu, et al, 2016)
divided social presence into web pages, others, and
communication social presence, and it would affect
the level of consumer trust. For the research on the
platform economy, social presence not only includes
scene stimuli but also character stimuli, which can be
divided into situation, communication and warm
presence. These three dimensions all significantly
affect customer loyalty (Li, et al, 2019). Witmer et al.
(Witmer, et al, 2005) used exploratory factor analysis
to divide the social presence perceived by individuals
through various channels into four dimensions: the
degree of individual inner involvement, the degree of
individual psychological immersion, the degree of
individual sensory fidelity and the degree of interface
quality.
All in all, with the continuous development of
social technology, in the fields of online education, e-
commerce and human-computer interaction, the
single-dimensional perspective can no longer meet
the research needs. Scholars mostly study the sense
of social presence from a multi-dimensional
perspective, and multi-dimensional division can be
accurately compared. It fully describes the user
experience and guides the design of the platform
system more effectively. With the explosive
development of live broadcast marketing and the
improvement of consumers' emotional needs when
shopping, social presence has gradually become an
important research topic. Combined with the specific
live broadcast situation, this paper adopts Li Xuexin
et al.’s (Li, 2019) research on the presence of a
specific platform economy, and divides the social
presence into situational presence, communication
presence and warm presence.
1.2.3 Related Research in the Field of Social
Presence Live Broadcasting
In the field of online marketing, with the rise of online
shopping, research on social presence has been on the
rise since the beginning of the 21st century, and has
reached a new height with the rise of live streaming
and other forms of delivery. The definition of social
presence has undergone a series of developments.
Scholars Hassanein and Head (Scholars, Head, 2007)
believe that social presence refers to the sense of
warmth and sociality that consumers feel when they
are shopping online due to interacting with others
who are online at the same time; Eroglu (Eroglu,
2001) believes that consumers are shopping in online
stores. When shopping online, a sense of social
presence will naturally arise. This sense of social
presence can be used to indicate the extent to which
consumers can experience shopping in a physical
store when they shop online; in the study of live-
streaming shopping marketing, Xie Ying et al.
Presence refers to the sense of realism, intimacy and
familiarity that comes naturally from the real-time
interaction between anchors and consumers, and
between consumers and consumers in live broadcast
platforms. The closer the connection between
consumers, consumers and consumers, as if face-to-
face communication, the more significant the
interpersonal relationship; The weaker the
relationship (Peck, 2016).
Research on Consumer Purchase Intention of Different Social Presence in Live Broadcast based on GLS Structural Equation Mode
35

2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Social Presence in Live Shopping
Scenarios
Social presence is a manifestation of people's
psychological states, often associated with virtual
reality scenarios. In the field of marketing, scholars
combine social presence with consumer behavior to
conduct research. Shen's research believes that social
presence is a network medium that enables customers
to perceive the psychological state of the existence of
others. Lee's research considers social presence to be
a true assessment of the psychological presence of
other parties involved. Lu Hongbing's research shows
that social presence is associated with the presence
and feelings of other participants, an emotional and
cognitive fit. However, the research on social
presence in the field of marketing has not formed a
unified definition. Combined with the interactive
relationship between producers and consumers in the
platform economy, this study defines social presence
in the platform economy as the degree to which
customers perceive the existence of other relevant
parties during the process of customers using the
platform, and it is accompanied by the interaction
between customers and other parties. Communication
and emotional interaction between the parties
involved. In the field of mobile internet marketing,
scholars have also conducted research on the
dimensions of social presence. Through research on
online communities, Lu found that the social
presence of online communities consists of web
social presence, others' social presence, and
communication social presence. composed of three
dimensions. Xie Ying et al. analyzed the social
presence in live broadcast marketing and believed
that the social presence in live broadcast marketing
included three dimensions: coexistence presence,
communication presence and emotional presence.
Based on the previous research results, this study
draws on the research results of Xie Ying and Li
Xuexin, etc., and divides the social presence under
the platform economy into three dimensions:
situational presence, communication presence, and
warm presence. From the perspectives of consumer
awareness, emotion and cognition, the social
presence in the platform economy can stimulate
customers' happy mood in the process of using the
platform through the three dimensions of situation,
communication and warmth.
2.2 Social Presence and Consumer
Purchase Intention
The theory of social influence shows that when an
individual feels the greater the number of other
people, the greater the influence on the individual will
be. Therefore, in the process of using the platform,
the situation displayed by the platform and the
positive communication with other relevant parties
will have an impact on the customer's feelings and
preferences. The purchase behavior of customers in
the live broadcast will be affected by the
environment, and the purchase intention will continue
to increase due to the special preference for a certain
product or service, and then the final consumption
will be completed. When customers use the platform,
if the scene displayed by the platform can effectively
stimulate the customer's sense of presence, and the
information exchange provided by the platform for
customers and related parties can bring customers a
warm feeling, it will help to promote customer’s
purchase behaviour. In summary, the following
research hypotheses are put forward:
H1a: Situational presence has a direct and
significant impact on consumer purchase intention.
H1b: Communication presence has a direct and
significant impact on consumer purchase intention.
H1c: Warm presence has a direct and significant
impact on consumers' purchase intention.
2.3 The Mediating Role of Quasi-Social
Interaction
The theory of social interaction shows that the
customer's favorability and loyalty can be further
improved through the interaction between the two
parties, thereby reducing information asymmetry.
The various aspects of the situation displayed on the
platform and the degree of information presentation
can be told to the seller through interaction, and the
social presence can be given to the customer by
giving the customer a sense of presence. More
information, and then promote customers to engage
in quasi-social interaction with anchors and sellers,
thereby increasing their willingness to buy.
Previous academic research has mainly
established the antecedent variables of quasi-social
interaction from the perspectives of interactive
communication and emotional connection. In this
context, situational presence acts as a tool support to
help customers integrate into the live broadcast scene;
communication presence is what customers can
perceive. It is the main way to communicate with the
anchor; the sense of warmth and presence acts as
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
36

emotional support, which is mainly reflected in the
way the anchor expresses, the public welfare nature
of the products sold in the anchor’s live broadcast
room, and the embodiment of corporate social
responsibility; Moreover, there are many studies on
quasi-social interaction to customer purchase
intention. Based on previous studies, the following
hypotheses are proposed:
H2a: quasi-social interaction mediates the
relationship between situational presence and
consumer purchase intention.
H2b: quasi-social interaction mediates the
relationship between communicative presence and
consumer purchase intention.
H2c: quasi-social interaction mediates the
relationship between warm presence and consumer
purchase intention.
2.4 Samples and Data
The survey mainly adopts the Internet questionnaire
survey method, relying on the professional network
survey platform to distribute and collect the formal
questionnaires of this study, and a total of 230
samples were received. A total of 32 invalid samples,
such as irregular filling, too short time, and highly
similar questions and answers, were eliminated to
form 198 final valid samples. The effective recovery
rate of the survey samples was 86.09%. In the valid
sample: 82 males (41.41%) and 116 females
(58.59%); in terms of education level, 83 are junior
college and below (41.92%), and 61 are bachelor
degree (accounting for 58.59%). 30.81%), 54 with a
master’s degree or above (accounting for 27.27%); in
terms of age distribution, 72 persons under the age of
20 (accounting for 36.36%), 68 persons aged 21-30
(accounting for 34.34%), 37persons aged 31-40
(18.69%), and 21 people over the age of 40 (10.61%).
2.5 Variables and Measurements
According to the sorting and summary of relevant
research literature on social presence in the academic
circle, combined with the relevant characteristics of
live broadcast scenarios, and on the basis of drawing
on mature scales in related researches on social
presence and consumer purchase intentions at home
and abroad, the research institute compiled this
research. Dosage meter. At the same time, in order to
ensure the accuracy of the expression of the
measurement items, according to the suggestions of
relevant marketing experts, the test items of some
variables have been revised. All scale variables were
measured using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 means
completely disagree and 5 means completely agree.
The independent variable social presence is
divided into three dimensions: scenario,
communication and warm presence. For the
measurement of social presence in live shopping on
the corresponding platform, reference is made to the
research of Lv Hongbing and Xie Ying, etc., and the
feedback from marketing experts is combined to
determine the final scenario. There are three
dimensions of presence, communication presence
and warm presence. Among them, the situational
presence adopts "scenarios where I can feel the
contact with people during the use of the platform",
"I can perceive the existence of other relevant parties
during the use of the platform", and "the other
relevant parties can Perceived my presence” three
items to measure; communication presence is
measured by “I can have a social feeling in the
process of using the platform”, “I can exchange
information with other relevant parties in the process
of using the platform” "Two items are used to
measure; the sense of warmth and presence is
measured by "I can experience a kind of human
enthusiasm in the process of using the platform", "It
can affect my mood in the process of using the
platform", "During the process of using the platform"
Other interested parties understand my needs" three
items to measure. Quasi-social interaction follows the
current mainstream measurement scale. Consumers’
willingness to buy uses “If I want to buy related
products, I am more likely to buy them in the live
broadcast”, “I am willing to buy related products in
the live broadcast”, “When someone asks me where
to buy a product is more appropriate, I will
Recommend live shopping”, “I will continue to buy
products in the live broadcast in the future” and other
four items to measure.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, AM OS23.0 and SPSS22.0 software
were used to measure the reliability and validity of
the scale. The internal consistency of the total scale
was Cronbach's a value of 0.899, which was in line
with the conditions. Sexual analysis, the results are as
follows:
Table 1. Reliability analysis results.
Variables Alpha Cronbach based on
normalization
terms
Items
Situational 0.892 0.893 3
Research on Consumer Purchase Intention of Different Social Presence in Live Broadcast based on GLS Structural Equation Mode
37
presence
Communication
presence
0.901 0.902 2
Warmth presence 0.891 0.891 3
Quasi-social
interaction
0.882 0.885 4
purchase intention 0.908 0.908 4
Table 2: Validity analysis results.
KMO and Bartlett's test
KMO Sampling Suitability Quantity. .835
Bartlett's sphericity test Approximate
chi-square
1605.154
de
g
rees of freedom
66
salience .000
According to the statistical results in Tables 1 and
2, the reliability and validity of the scale used in this
paper meet the requirements. The reliability analysis
results of each variable in the model show that the
Cronbach's coefficients is greater than 0.8, indicating
that the reliability effect is very high; the coefficient
of factor analysis results is 0.835 (0.000***), which
has good validity.
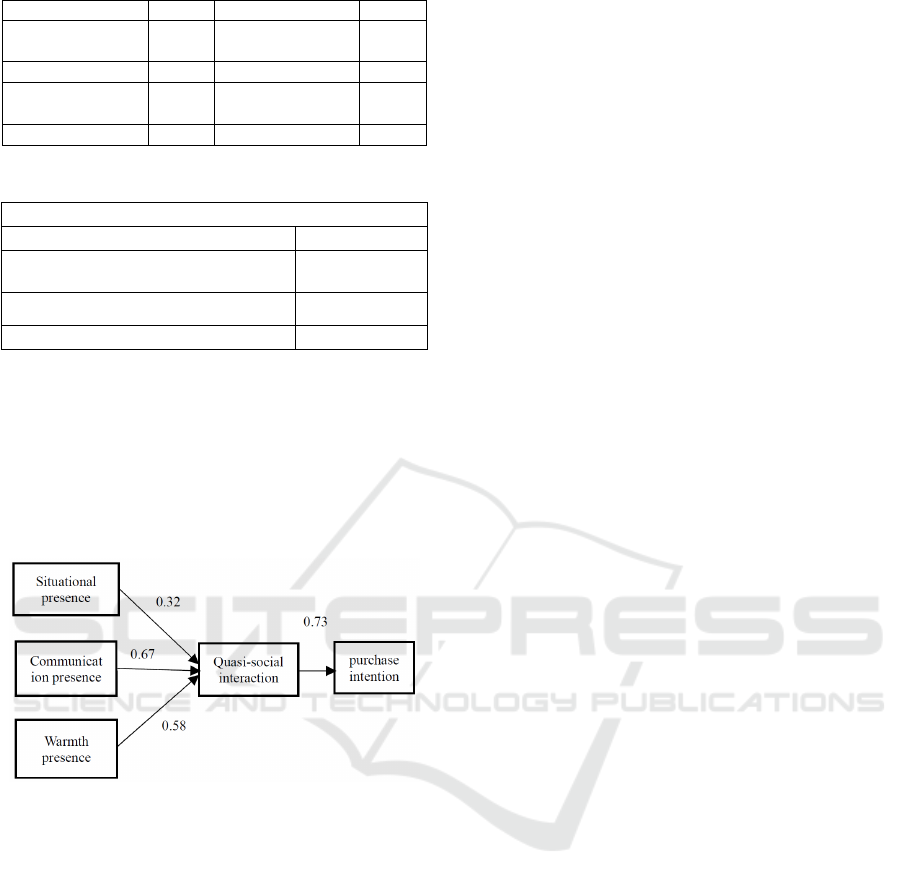
Figure 1: Research Model.
4 CONCLUSIONS
4.1 Research Conclusions
In this paper, generalized least squares analysis of
variance (GLS) was used to construct a structural
equation model to test the main and mediating effects.
As shown in Figure 1, the model includes exogenous
variables context, communication and warm
presence, endogenous mediator variables quasi-
social interaction, and endogenous variables purchase
intention. In this paper, Bootstrapping method and
coefficient multiplication method are used to verify
the mediating effect. The results are shown in the
figure: the direct effect of situational presence on
social interaction is significant (0.32***), the direct
effect of communication presence on social
interaction is significant (0.67**) *), the direct effect
of warm presence on social interaction was
significant (0.58***). Among the non-standardized
indirect effects, Bias-Corrected 95% confidence
interval 0 < Lower < Upper (0 < 0.15 < 0.73) and z >
1.96 (z =2.76), that is, the mediating effect exists, and
quasi-social interaction act as a partial intermediary.
From the results of the structural model, it can be
seen that situational presence, communication
presence, and warm presence have a direct and
significant impact on social interaction, among which
communication presence has the highest correlation
with social interaction, which indicates that in live
shopping, anchors, sellers Appropriate
communication with customers can enhance
customers’ favorability through the intermediary of
quasi-social interaction, thereby promoting customer
purchases; the correlation coefficient of situational
presence aligning with social interaction is only
0.32***, indicating that the corresponding situation
in live shopping is very important. The influence of
the customer's interaction with the anchor to the final
purchase behavior is relatively limited, which may be
related to the customer's personal factors, such as
different preferences for scenarios. In this case, the
company can further investigate the customer's
characteristics, such as discounts, promotions and
other activities. The impact of warm presence on the
society is high, reaching 0.58***, indicating that the
willingness to interact between customers and
anchors can be further improved through emotional
methods. Enterprises can strengthen corresponding
emotional methods or launch corporate social
responsibility and Caring for the society and other
products and services to live broadcast, improve the
conversion rate of order purchases.
In a word, the relationship between the
communication dimension of social presence and
quasi-social interaction is significant, indicating that
the presence brought by live broadcast platform
communication can maximize customers’ purchase
intention by strengthening the intermediary form of
interaction between buyers and sellers (Burtch et
al.,2017). Through emotional means, the customer's
willingness to interact and purchase will be
improved, and the two feel the quasi-social
interaction in the social presence and then have a
major impact on the customer's purchase intention.
4.2 Marketing Suggestions
The implications and suggestions for platform
companies from this study are as follows:
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
38

1. Platform companies attract a large number of
users through the "burning money" model for positive
network effects. In this process, attention should be
paid to the improvement of user experience by social
presence. By improving the customer's favorable
impression of the platform, the occurrence of multi-
attribution of customers is reduced, so as to avoid the
reduction of active users of the platform due to
frequent changes of platforms by customers, thereby
avoiding the generation of negative network effects.
2. The platform company should establish
communication and information exchange channels
for customers and other relevant parties, so as to
facilitate customers to obtain information and reduce
the risk of information uncertainty to customers. At
the same time, in the process of customers using the
platform, platform companies pay attention to the
construction of a warm social presence, and should
give customers a warm feeling, so that customers can
meet their psychological needs while consuming.
3. It is the key goal of platform companies to
improve customers' awareness and trust in the
platform. As a trading market for customers and
product service providers, platform companies are
very necessary to ensure the authenticity of the
information of customers and product service
providers. By establishing a good trust mechanism
and taking communication presence as an important
social presence, reducing transaction costs and
transaction risks caused by information uncertainty in
live shopping will help customers to rely on the
platform and be able to Provide customers'
willingness to recommend the platform, thereby
contributing to the formation of positive network
effects.
4.Effectively improve consumers' sense of social
presence, especially for the situation, communication
and warm presence in the current situation, mainly
around the following points;
(1) enhance consumers' sense of presence in the
situation. Situational presence refers to the degree to
which consumers can perceive the virtual presence of
other people (hosts, product salespeople, and other
consumers) while watching a live broadcast. The
premise for consumers to perceive the existence of
others is to allow consumers to experience a feeling
close to the real offline shopping (Lu and Liu et al.,
2020). Merchants can enhance consumer awareness
and social presence in terms of information display,
live broadcast atmosphere and real-time interaction.
(2) enhance consumers' sense of presence in
communication. Communication presence is the
degree to which consumers perceive that virtual
presence of others will have an effect on them, and
can communicate verbally and ideologically with the
host. Due to information asymmetry, consumers are
often caught in a helpless predicament when
shopping online. The premise of Communication
social presence is that users in the live broadcast room
can provide consumers with purchasing suggestions.
(3) enhance consumers' sense of warmth and
presence. Warm presence is the degree to which
consumers perceive the emotions and moods of
others (anchors, product salespersons, and other
consumers) when watching live broadcasts. Today's
consumers are not simply for material needs, more
and more consumers regard online shopping as a
hobby, focusing on social, personal expression and
emotional needs. Merchants can improve consumers'
emotional social presence from the level of
communication style and emotional symbol setting.
4.3 Research Limitations
Based on the relevant research on social presence,
which is divided into the dimensions of situational
presence, communication presence and warm
presence according to the economy of a specific live
broadcast platform, this study discusses the influence
of social presence on consumers' purchase intention
in the process of live broadcast marketing, the
specific content includes the direct influence of
consumers' purchase intention in various dimensions
of social presence, etc. Although this paper follows
the scientific and standardization of academic
research, the research results obtained have certain
contributions in theory and business practice, but due
to the influence of subjective and
objective conditions,
this paper still has the following shortcomings:
(1) The study sample is limited. The sample data
in this paper is mainly collected through the
distribution of questionnaires on the Internet. Due to
resource constraints such as time and financial
resources, the sample size is relatively small, making
the results of the study relatively unconvincing. The
questionnaires are mainly online. Due to time and
space constraints, the respondents will have some
confusion when filling out the questionnaires, but
because they are not around, they cannot solve the
questions on the spot, which easily makes the final
results of the respondents deviate from the research
purpose. Influence the scientific nature of academic
research.
(2) Future research should not only focus on
empirical research, but should pay attention to
diversified research methods, and can carry out case
studies, experimental research and other methods;
conduct longitudinal research on consumer behavior
Research on Consumer Purchase Intention of Different Social Presence in Live Broadcast based on GLS Structural Equation Mode
39

in live broadcast rooms, observe dynamic changes in
consumer behavior, and enrich the research results.
4.4 Future Research
(1) To explore the emotional mechanism of social
presence in the process of live broadcast marketing
affecting herd consumption. Although the feeling of
warmth and presence focuses on the live broadcast
platform and its characteristics to generate an
emotional experience, it is essentially the process of
consumers' cognition of the live broadcast
environment to their emotions. At present, most
scholars have actively carried out the cognitive
mechanism of the influence of social presence on
herd consumption in the process of live broadcast
marketing, and investigated the herd consumption
behavior of consumers due to the influence of
information, but lack of discussion on the emotional
mechanism. The presence of others affects our
decision-making, often reducing our rational thinking
and improving some simple behaviors. In the live
broadcast room, consumers make purchase decisions
based on the word-of-mouth information of the
anchor and other consumers, which are simple task
behaviors, while purchasing decisions based on
product specifications, materials, and manufacturing
processes are complex task behaviors. So far, no
research has explored how social presence in live
marketing affects herd consumption through
consumer emotional mechanisms. Therefore, future
research can focus on exploring emotional
mechanisms and enrich the theory of social presence.
(2) Subsequent research can refine product
categories and explore whether different products
have a common psychological mechanism that
stimulates purchases to verify the applicability of the
model under different categories. In practical
applications, there is still a certain intermediary path
between social presence and purchase intention. In
the follow-up, we can continue to explore consumer
psychology from psychological intervention, so as to
help anchors mobilize consumers' sense of
participation and improve the conversion rate of
purchase orders.
REFERENCES
Biocca, F. (2001). Will simulation sickness slow down the
diffusion of virtual environment technology [J].
Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments,
1(3): 334-343.
Chatterjee P, Chollet B, Trendel O. (2017). From
conformity to reactance: Contingent role of network
centrality in consumer-to-consumer influence[J].
Journal of Business Research, 75(JUN.):86-94.
Huang N, Hong Y, Burtch G. (2017). Social network
integration and user content generation: Evidence from
natural experiments[J]. MIS Quarterly, 41(4):1035-
1058.
Li Xuexin, Huang Weijie, Guo Chen. (2019). The influence
of social presence on customer loyalty under the
platform economy [J]. Economic Theory and Practice,
33 (1) 95-101.
Lu B, Fan W, Zhou M. (2016). Social presence, trust, and
social commerce purchase intention: An empirical
research [J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 56(Mar.):
225-237.
Meng Lu, Liu Fengjun, Chen Siyun, et al. (2020). Can I
Arouse You: A Study on the Influence Mechanism of
Different Types of Live Streaming Influencer
Information Source Characteristics on Consumers'
Purchase Intention [J]. Nankai Management Review,
(1): 13-27
Park E, Rishika R, Janakiraman R, et al. (2017). Social
Dollars in Online Communities: The Effect of Product,
User and Network Characteristics[J]. Journal of
Marketing 7:16-27.
Peck J, Wiggins J. (2006). It Just Feels Good: Customers'
Affective Response to Touch and Its Influence on
Persuasion[J]. Journal of Marketing, 70(4):56-69.
Sallnas, E. L. (2000). Effects of communication mode on
social presence, virtual presence, and performance in
collaborative virtual environments[J]. Teleoperators
and Virtual Environments, 14(4): 434-449.
Savicki, Singh, J. & Sabol, B. (2000). Consumer trust,
value, and loyalty in relational exchanges[J]. Journal of
Marketing, 66(1): 15-37.
Shen, J. (2012). Social comparison, social presence, and
enjoyment in the acceptance of social shopping
websites[J]. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research,
13(3), 198–212.
Tu, C. H. (2002). On-line learning migration: From social
learning theory to social presence theory in a CMC
environment[J]. Journal of Network and Computer
Application, 2(3): 27-37.
Xie Y, Chen M, Lai H, et al. (2016). Neural Basis of Two
Kinds of Social Influence: Obedience and
Conformity[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroence, 10:37-
52.
Xie Ying, Li Chunqing, Gao Peng, et al. (2018). The
influence of social presence in live broadcast marketing
on online conformity consumption and its mechanism
of action—a behavioral and neurophysiological
perspective [J]. Advances in Psychological Science,
(6): 990-1004.
Zhang K, Chen X. (2017). Herding in a P2P lending market:
Rational inference OR irrational trust? [J]. Electronic
Commerce Research and Applications 6:45-53.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
40
