
Maturity Assessment for Implementing Digital Technologies
in SMEs
Li Pan
Institute of Economics and Management, National Research Tomsk State University, 36 Lenin Ave, Tomsk, Russia
Keywords: Digital Technology, Maturity Assessment, Reference Framework, Labor Productivity, Economic
Profitability.
Abstract: More and more companies have been tapping into digital technologies to improve their labor productivity and
economic profitability. To assess the maturity level of implementing digital technologies is paramount for
SMEs to embark on the digital transformation journey. There is a lack of maturity assessment reference on
implementing digital technologies in SMEs. Through defining a set of digital technology indices, this paper
proposes a maturity assessment reference framework for SMEs to implement digital technologies. By using
the proposed reference framework, the maturity assessment is conducted for two case study companies. The
maturity assessment helps the two companies to clearly understand their current status of digital technology
implementation and confidently know how to move forward on the digital transformation journey so that their
labor productivity and economic profitability can be further improved and their businesses can be more
competitive in the digital economy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital technologies have become imperative for
working, learning, entertaining, socializing, shopping
and accessing everything from healthcare to culture
and life style. Specially, in the COVID-19 pandemic,
the digital technologies have been radically changing
and shaping the world and economy, which are the
disruptive innovation since ever. In 2020, affected by
the epidemic, the major economies in the world
showed negative growth. Against this trend, the
digital economy with digital technologies as an
important driving force, increased by 3% year on
year, becoming a key force to effectively hedge the
epidemic and boost the global economy (CAICT,
2021).
The utilization of digital technologies is an
effective way to improve labor productivity and
economic profitability. The digital technologies such
Mobile, Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT),
Artificial Intelligence (AI) have facilitated sharing
economy, crowdsourcing, and network collaboration
to reconstruct the labor and production relationships.
The new transaction and consumption models
redefine the business models, organizational models
and working modes, which have a positive impact on
productivity and profitability of enterprises.
According to the research of American consulting
institutions, the labor productivity of the enterprises
with high information utilization rate is
about 60~90%
higher than that of the enterprises with low
information utilization rate. In the service industry,
the contribution rate of capital utilization of digital
economy to the industry is 2~3 times higher than that
of traditional capital utilization (The State
Information Center, 2018).
Digital technologies also have a deep impact on
the number and quality of employment and how work
is organized. From 2006 to 2016, of the 380 million
additional jobs in the OECD region, about 40% came
from higher digital-intensive industries. From 2011 to
2017, for every 10 additional jobs created in Europe,
four were ICT work-intensive jobs (OECD, 2019). In
the digital economy, workers increasingly need to
adapt their skills to new requirements, especially for
generic skills such as communication, teamwork,
problem solving, and creativity. Digital technologies
also offer new opportunities for how they work. The
increase in flexible work and employee discretion in
the work model is the key to the digital development
of work style (Greenan, Napolitano, 2021).
In the post-epidemic era, embracing digital
technologies has been becoming essential for many
Pan, L.
Maturity Assessment for Implementing Digital Technologies in SMEs.
DOI: 10.5220/0011157300003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 61-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

businesses. Among them, SMEs play a central role in
this shift, representing about 90% of the world and
providing more than 50% of jobs. In OECD
countries,
SMEs account for 75 percent of jobs in the sectors
most severely affected by the epidemic, and micro-
enterprises with fewer than 10 employees account for
about 30 percent of jobs in those industries. In
emerging economies, formal SMEs account for 40%
of GDP, creating 7 of the 10 jobs (OECD, 2021).
Therefore, SMEs using digital technologies to
innovate the production modes and management
concepts, and promote sustainable development are
the key to unleashing the global economic potential.
In fact, there is few research on digital technologies
for SMEs, and the digitalization of many companies
is still in the initial stage, and most companies know
little about digital technologies and have no clue
about how to implement digital technologies to
survive. It motivates the study of this paper to
propose the maturity assessment reference
framework to assist companies to embark on the
digitalization journey.
The paper is organized as follows. Section II will
conduct the literature review. Section III will propose
the maturity assessment reference framework.
Section IV will conduct the case studies for two
companies by applying the proposed maturity
assessment reference framework. Section V will
conclude the paper with remarks.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
This section reviews the literature on digital
technologies and digital transformation maturity
assessment models, and identifies the research gaps
in the literature, which motivate the research works in
this paper.
The essence of digital transformation is that
organizations use the corresponding digital
technologies to respond to changes, which is the
source of disruption. In this process, digital
technologies play a central role in the creation and
reinforcement of disruption that occurs in the society
and industry. Digital technologies create the drive
that drives organizations to implement responses to
gain or maintain their competitive advantages. Vial
classified 282 digital transformation documents and
found that most digital technologies are related to
social, analysis, mobile, Internet of Things, cloud
(Vial, 2019), consistent with Zhu et al. on 865 digital
transformation documents from 2000 to 2020 and
moreover, digital platforms are an important category
(Zhu, Ge, Wang, 2021). The business competition
increasingly relies on the ability to use digital
technologies. In defining digital technologies, Vial
observed that combinations of technologies are
particularly relevant in the context of digital
transformation. For example, the ability to implement
algorithmic decisions may depend on the ability of
companies to analyze big data collected by
individuals using social media through their mobile
phones. In the study of Zhu et al. on the thriving stage
from 2018 to 2020 of the digital transformation
literature, the research on digital technologies
compared to digital business strategy, digital
transformation of manufacturing (Industry 4.0),
digital enterprise architecture and other fields is the
least (Vial, 2019).
The findings by DeStefano et al. suggested that
younger companies using cloud computing are more
likely to increase jobs and sales, and that cloud
computing and fiber-optic infrastructure enable
younger companies to scale up without increasing
their geographic footprint. In addition, cloud
computing improves employee mobility between
institutions within the enterprise. Cloud technology
reduces fixed IT costs for enterprises, and can
technically replace their own IT devices, facilitating
start-ups to grow (DeStefano, Kneller & Timmis
2020). From the perspective of the strategic choice of
Russian enterprises, Lezina et al. diagnosed the
digital maturity preparation model of system
management, company structure, business process,
data management and personnel preparation through
the form of questionnaires. The model created by the
authors is universal and targeted at all kinds of
enterprises (Lezina, et al, 2019). Yezhebay et al. used
the SWOT analysis method to define the
characteristics of advantages and disadvantages for
SMEs in Kazakhstan, and developed the digital
maturity model for SMEs in Kazakhstan. The model
consists of six dimensions that are strategy,
leadership, personnel, product, operations and
technology, and the corresponding 15 sub-
dimensions (Yezhebay, et al, 2021).
In the literature, the maturity models for SME
digitalization are mostly based on the Industry 4.0
model. The most maturity models did not consider the
specific requirements and challenges of SMEs and
cannot reflect the actual status of digital technologies
in SMEs (Mittal, et al, 2018). As such, SMEs are
unable to use those maturity models to assess their
digital technology level. Thus, it is significant to
create an appropriate maturity assessment framework
for SMEs to assess their maturity level for
implementing digital technologies and make a right
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
62

decision while embarking on the digitalization
journey.
In this paper, through defining a set of digital
technology indices, a maturity assessment reference
framework is proposed for SMEs to assess their
maturity level for implementing digital technologies.
By applying maturity assessment reference
framework, SMEs are able to understand their current
status of digital technology implementation and clear
about how to move forward on the digital
transformation journey so that their labor
productivity and economic profitability can be further
improved and their businesses can be more
competitive in the digital economy.
3 MATURITY ASSESSEMNT
REFERENCE FRAMEWORK
The research indicates that mobile technology, social
media, cloud computing and data security are the first
digital technologies that SMEs consider to adopt
(DELL, 2021). During the outbreak of COVID-19 in
China at the beginning of 2020, the Internet of Things
(IoT) and Artificial Intelligent (AI) technologies are
more conducive to production recovery. The research
data shows that SMEs using high-level digital
technologies can mobilize internal and external
resources faster to promote production recovery and
digital response (
Renmin University of China, 2020).
Mobile Technology is the technology that goes
where the user goes. It consists of portable two-way
communications devices, computing devices and the
networking technology that connects them. Mobile
Technology is typified by internet-enabled devices
like smartphones, tablets and watches. The adoption
of Mobile Technology by SMEs can improve the
efficiency of mobile and collaborative working.
Leveraging various forms of social media can
improve product promotion, outreach and
conversion, and facilitate SME business model
optimization within the constraints of a company's
size and financial status. Through mobile applications
or by providing a digital workplace, employees can
perform decentralized online tasks (crowd work)
(Wood, et al, 2019).
Cloud Computing Technology gives users access
to storage, files, software, and servers through their
internet-connected devices: computers, smartphones,
tablets, and wearables. Cloud computing providers
store and process data in a location that’s separate
from end users. Cloud Computing is the ability to
store and access data and programs over the internet
instead of on a hard drive. This means businesses of
any size can harness powerful software and IT
infrastructure to become bigger, leaner, and more
agile, as well as compete with much larger
companies. Regardless of the size of the business,
cloud computing is a major technological priority.
For SMEs in particular, it is the basis for future
changes in the form of work and the reshaping of
business processes (CISCO, 2020). The emergence of
the epidemic has accelerated the development of
cloud services such as telecommuting and
videoconferencing. Cloud technologies allow
workers to connect from everywhere at any time,
login their organization’s information system, access
shared documents, and exchange information about
their work in an easy way. Employees become more
and better informed that promote workers’ discretion,
autonomy and empowerment, usually entail lower
direct supervision and control over employees. In
return, workers are required to interact, communicate,
and cooperate more (Wood, et al, 2019).
Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical
objects “things” that are embedded with sensors,
software, and other technologies for the purpose of
connecting and exchanging data with other devices
and systems over the internet. The potential economic
value that the Internet of Things can release is huge.
The greatest potential for value creation in the factory
setting will be optimizing operations in
manufacturing—making the various day-to-day
management of assets and people more efficient.
Internet of things facilitates several advantages in
day-to-day life in the business sector. For example, as
devices of IoT interact and communicate with each
other and do a lot of tasks, then they minimize human
effort (Behura, et al, 2022).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a wide-ranging
branch of computer science concerned with building
smart machines capable of performing tasks that
typically require human intelligence. AI is used for
enterprises to drive modern decisions. Advanced AI
technologies such as machine learning, deep learning,
computer vision, and natural language processing
while basic technologies include data management,
digital assistants, and robotic process automation
(ThoughtLab, 2020).
With four digital technologies Mobile, Cloud
Computing, IoT and AI, the maturity assessment
reference framework is proposed in Table 1. For each
technology, there are three levels and six grades to
describe its maturity. For each grade at every level, a
set of reference indices are defined in each grade to
assess the technology maturity and determine the
corresponding maturity point. For example, there are
Maturity Assessment for Implementing Digital Technologies in SMEs
63
four reference indices defined for Mobile Technology
in Grade 1, and two reference indices are defined in
Grade 2. Grade 1 is the lowest grade where the
company is in a very preliminary state for
implementing the respective technology. Grade 6 is
the highest grade where the company is fully mature
in terms of implementing the respective technology.
The four digital technologies are presented in the
order of advance in the reference framework. Mobile
is the primary digital technology and AI is the
advanced digital technology.
Table 1. Reference framework for implementing digital technology maturity assessments in SMEs
4 CASE STUDIES
In this section, we use the maturity assessment
reference framework proposed in Section III to assess
the maturity for implementing the digital
technologies in two case study companies, Company
A and Company B. Company A is a manufacturing
company which produces dried fruits, bread, sea-
buckthorn juice and other foods with 30 employees
including 10 administrative personnel and 20
workshop workers. Since the pandemic in 2020, the
company has used various social media such as
WeChat, Mini Programs, Douyin to sell its products.
The sales of sea buckthorn juice is now number one
in China on the Douyin platform. Company B is a
new media company whose main business is video
shooting, promoting and branding through new
media. It also helps other companies to advertise their
products in the new media space and develop their
live streaming businesses. The company currently has
6 people.
According to the maturity assessment reference
framework proposed in Section III, by interviewing
the technical heads of the two companies, we
obtained the points in Table II, where 1 represents all
the indices defined in the corresponding grade are
met, 2/3 represents two of three indices are met, and
0 represents none of indices are met. The maturity
score S is calculated by (1).
𝑆=
∑
𝑤
𝑝
(1)
where 𝑤
=
is the weight assigned to Grade i, and
𝑝
is the point obtained in the corresponding grade
for the respective technology, 𝑖 = 1, 2, … , 6.
Mobile Cloud Computing IoT AI
Grade 1
•
Internet/wireless connection
•
Paperless documents
•
Networked computers/machines
•
Product Platform (Social media)
•
Data storage in the cloud
•
Files shared in the cloud
•
Single node/device
• Low cost and low complexity
•
Developing plans for AI
Grade 2
•
Product Platform (Website)
•
Product d igital spe c ifica tions
•
Public c loud
•
Community cloud
• Single node/device
• Low volume
•
Local data
• Building internal support for AI
(working closely with business
teams to identify use cases)
•
Simple rule based decision
Grade 3
•
CRM
•
O rd er management Syste m
•
Pub lic cloud environment
•
Mobile workplace
•
Community cloud
•
Single node/device
•
Big volume of data
• Intensive computng
•
Machine learning
• Computer vision
Grade 4
•
ERP
•
Financial management system
•
Hybrid cloud environment
•
Collaborative office
•
Expanding on the cloud
•
Data cybersecurity
•
Multiple e nd node s/device s
•
Big volume of data
• Intensive computng
• Multiple Lo ca l d ata
•
Local analysis
•
Bring in a richer set of data to
drives higher AI performance
(psychographic, geospatial and
real-time)
•
ML based decision
Grade 5
•
Multi- screen office
•
Product branding and Digital
mark eting
•
Digital business process
•
Hybrid cloud
•
Data cybersecurity
•
IaaS
•
Multiple e nd node s/device s
• Coordinator node/device
• Multiple Infinite sensing netwo rk
• Natural language processing
• Deep learning
• Using AI for parts of business
Grade 6
•
5G connection
•
Secure cloud environment
•
Cloud Optimisation
•
Services Secure cloud
•
SaaS
•
PaaS
•
Multiple indep e ndent e nd
nodes/devices
•
Visualize d applicatio ns
• Widely using AI to generate to
transform business
• Training and hiring people
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Digital
Tochnoligies
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
64
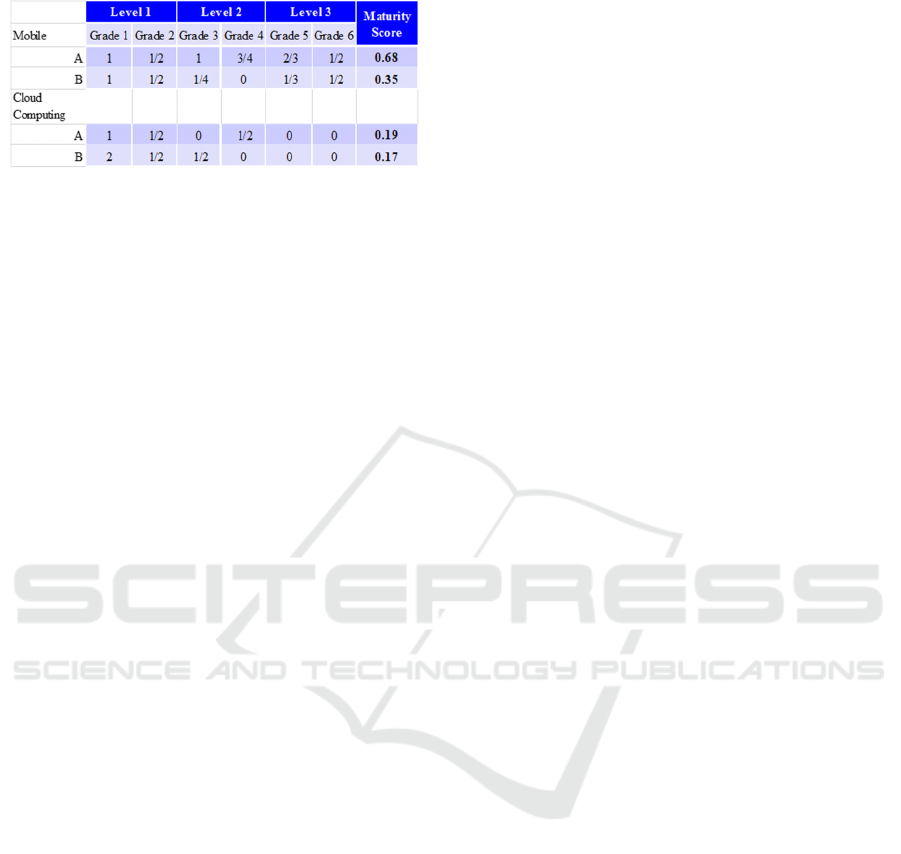
Table 2. Assessment Results.
Based on the maturity scores in Table 2, we are
able to know which digital technology the company
has been implementing at which maturity level. From
Table 2, in Company A, Mobile and Cloud
Computing technologies have been implemented
with maturity levels 0.68 (i.e., 68%) and 0.19 (i.e.,
19%), respectively. In Company B, and Cloud
Computing technologies have been implemented
with maturity levels 0.35 (i.e., 35%) and 0.17 (i.e.,
17%), respectively. From our interviews with these
two companies, Company A indicated that IoT
technology has been considered but not yet
implemented, and AI technology is not very relevant
for its business. Company B does not consider to
implement IoT and AI technologies at this moment.
We noted a lack of understanding of IoT and AI in
both companies, which led to missing strategic
considerations. This may be also due to the current
scale of their businesses. Although these two
companies in our case studies are not involved in IoT
and AI technologies, it’s valid for us to keep these
two technologies in the reference framework. Those
companies with larger sizes or more advanced
development may engage in IoT and AI, where the
reference framework will be applicable.
For SMEs under great pressure to survive, from
the perspective of saving operational costs, we
recommend to share technologies, data, human
resources, marketing channels, infrastructure and
other resources by using a shared platform.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The use of digital technologies has become a critical
turning point for all businesses. SMEs have not fully
embraced digital technologies due to their constraints
on survival, costs and sizes. This paper created the
maturity assessment reference framework for SMEs
to assess the maturity level of digital technology
implementation. By conducting the case studies for
the two companies, the proposed reference
framework is applied to provide an opportunity for
the companies to understand their current states of
digital technology adoption and subsequent
development. In the near future, we shall be
conducting more case studies for companies from
various industries and apply the proposed maturity
assessment reference framework to assess their
maturity of digital technology implementation and
provide them decision support for their embarking on
the digital transformation journey so as to further
improve their labor productivity and economic
profitability and maintain their competitiveness in the
digital economy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The author would like to thank the two case study
companies for their valuable information and
feedback.
REFERENCES
Behura A, Satpathy S, Mohanty S N, et al. (2022) Internet
of Things: Basic Concepts and Decorum of Smart
Services. In: Nandan Mohanty S., Chatterjee J.M.,
Satpathy S. (Eds), Internet of Things and Its
Applications. Springer, Cham, Switzerland. pp. 3-36.
CAICT (2021). White Paper on the Global Digital
Economy.http://www.caict.ac.cn/kxyj/qwfb/bps/20210
8/P020210913403798893557.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec
2021
CISCO (2020). Asia Pacific SME Digital Maturity Report.
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/global/zh_cn/solutions/
small-business/digitalmaturity/cisco-smb-digital-
maturity-ebook.pdf. Accessed 23 Dec 2021
DELL (2021). White Paper of the Digital Initialization
Index in SMEs.
https://i.dell.com/sites/csdocuments/App-
Merchandizing_Documents/zh/cn/DELLDigitalization
WP%202.0_Lite.pdf?ref=cptl_white-
paper2tiles1rows1_cta_primary_. Accessed 23 Dec
2021
DeStefano T., Kneller R. & Timmis J. (2020). Cloud
computing and firm growth. J. Munich Society for the
Promotion of Economic Research, CESifo Working
Paper No. 8306
Greenan N. & Napolitano S. (2021). Why Do Employees
Participe in Innovation? Skills and Organisational
Design Issues and the Ongoing Technological
Transformation. J. halshs-03270141v
Lezina T., Stoianova O, Ivanova V, et al. (2019).
Assessment the company’s readiness for digital
transformation: Clarifying the issue. In: International
Conference on Digital Economy. Beirut. pp. 3-14.
Mittal S, Khan M A, Romero D, et al. (2018). A critical
review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity
models: Implications for small and medium-sized
Maturity Assessment for Implementing Digital Technologies in SMEs
65

enterprises (SMEs). J. Journal of manufacturing
systems, 49: 194-214.
OECD (2019). Measuring the Digital Transformation: A
Roadmap for the Future. OECD Publishing, Paris.
OECD (2021). OECD SME and Entrepreneurship Outlook
2021. OECD Publishing, Paris.
Renmin University of China. (2020) COVID-19 and Digital
Transformation of Chinese Small and Medium
Enterprises.https://www.rmbs.ruc.edu.cn/uploadfile/ed
/upload/file/20200311/1583923008453554.pdf.Access
ed 25 Dec 2021
The State Information Center. (2018). A profound impact
of the digital economy on social and economic
development.http://www.sic.gov.cn/News/611/9743.ht
m. Accessed 22 Dec 2021
ThoughtLab. (2020). AI: From Data to ROI.
https://thoughtlabgroup.com/ wp-content/ uploads/
2020/09/ai-from-data-to-roi-codex5984.pdf. Accessed
21 Dec 2021
Vial, G. (2019). Understanding digital transformation: A
review and a research agenda. J. The journal of strategic
information systems, 28(2): 118-144.
Wood, A. J., Graham M, Lehdonvirta V, et al. (2019). Good
gig, bad gig: autonomy and algorithmic control in the
global gig economy. J. Work, Employment and
Society, 33(1): 56-75.
Yezhebay A, Sengirova V, Igali D, et al. (2021). Digital
Maturity and Readiness Model for Kazakhstan SMEs.
In International Conference on Smart Information
Systems and Technologies. Nur-Sultan.
Zhu X., Ge S. & Wang N. (2021). Digital transformation:
A systematic literature review. J. Computers &
Industrial Engineering, 162, 107774.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
66
