
Application of Data Sharing Model of Investment Facilitation based
on Multi-level Blockchain
Mengxue Zuo
a
Law School, Xi’an Jiaotong University, 28 Xianning West Road, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China
Keywords: Multi-Level Blockchain, Data Sharing, Investment Facilitation, Distributed Storage, Federated Learning.
Abstract: Big data technology has been used in almost every aspect of traditional industries in recent years. Investment
facilitation involves multinational corporations, host countries, investors' home countries, investment
promotion agencies and other subjects, with their data information. How to improve the efficiency of data
storage and ensure the privacy and security of data has become a key technical issue for the wide application
of investment facilitation. The data sharing model of investment facilitation based on multi-level
blockchaincan can meet the requirements of transparency, sustainable development and high efficiency of
investment facilitation, and better help investment facilitation to realize data sharing characteristics. By
encrypting investment facilitation data and its index information, and uploading the encrypted data to the
distributed storage outside the chain and the storage on the chain respectively, and adopting multi-level
blockchain technology, the data storage efficiency is significantly improved, the security of investment
facilitation data is ensured, and the scalability of blockchain is improved. In addition, the model uses the
differential privacy technology in the parameter transmission of the federal learning module, which enhances
data privacy protection. The application of investment facilitation to scientific research, monitoring and
evaluation systems, as well as the promulgation and enforcement of host country laws, can be effectively
realized by this technical means.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with the rapid development of
information technology and the wide application of
cloud computing, new network technology and
Internet of Things equipment, international
investment is gradually transforming to digitalization
and informatization. At the same time electronic
investment data are experiencing explosive growth
and diversified development of data types.
Nowadays, data is no longer a simple data storage
medium and computing protocol, but a factor of
production, with the value of resources, and causing
legal disputes. International investment is also in the
digital revolution, rushing to embrace the blue ocean
of the digital economy. However, international
investment is a complicated issue involving many
subjects including multinational corporations, host
countries, investors' home countries, investment
promotion agencies and so on. The biggest problem
is that it is difficult to guarantee the consistency,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7888-9178
authenticity and integrity of data, and it is difficult to
resist malicious attacks. In this respect, blockchain
technology has solved the problems existing in
traditional cloud servers.
Blockchain technology is characterized by
decentralization, decent-trust and anonymity, which
is more in line with the security and privacy
protection requirements in the field of data sharing in
international investment. The emergence of smart
contracts has turned the blockchain into distributed
account book with computing power, through which
users can calculate according to a fixed computing
mode. For federated learning, participants can write
intelligent contracts to complete parameters
aggregation, allocation and other operations, so as to
avoid the single point of failure of the third-party
server in the global modeling stage. The multi-level
blockchain architecture consists of the public chain
and the alliance chain. The public chain is maintained
by the special departments of the host country, which
is responsible for the interaction between the host
Zuo, M.
Application of Data Sharing Model of Investment Facilitation based on Multi-level Blockchain.
DOI: 10.5220/0011163900003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 117-123
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
117
country and the system. At the same time, these
departments also form different alliance chains
according to different data types, and combine with
attribute database encryption to ensure data privacy.
(Malamas, Kotzanikolaou, Dasaklis, 2020)
Investment facilitation is a new issue in
international investment. It is to create a transparent
and efficient investment policy environment for
investors by improving policy transparency and
predictability, simplifying investment rules and
procedures. Investment facilitation is not the right to
amend or enact the investment laws and it has nothing
to do with investment protection, investment
promotion and investment liberalization. (Hamdani
2018) The transparency mentioned in investment
facilitation suggestions put forward by various
countries mainly includes the following aspects.
When formulating investment-related policies, the
government should provide comprehensive, clear and
timely notice. The government should ensure
effective access to information, including providing
"one-stop" consultation points or special consultation
points, and appropriate online services. The
government should also promote simplification of the
language of laws and regulations and publish the
results of periodic review of the investment
mechanism in a timely manner. From the perspective
of the host country, a core aspect of investment
facilitation is to improve the openness and
transparency of investment supervision and
management of the host government. Digital
application is the simplest and most direct way to
achieve transparency.
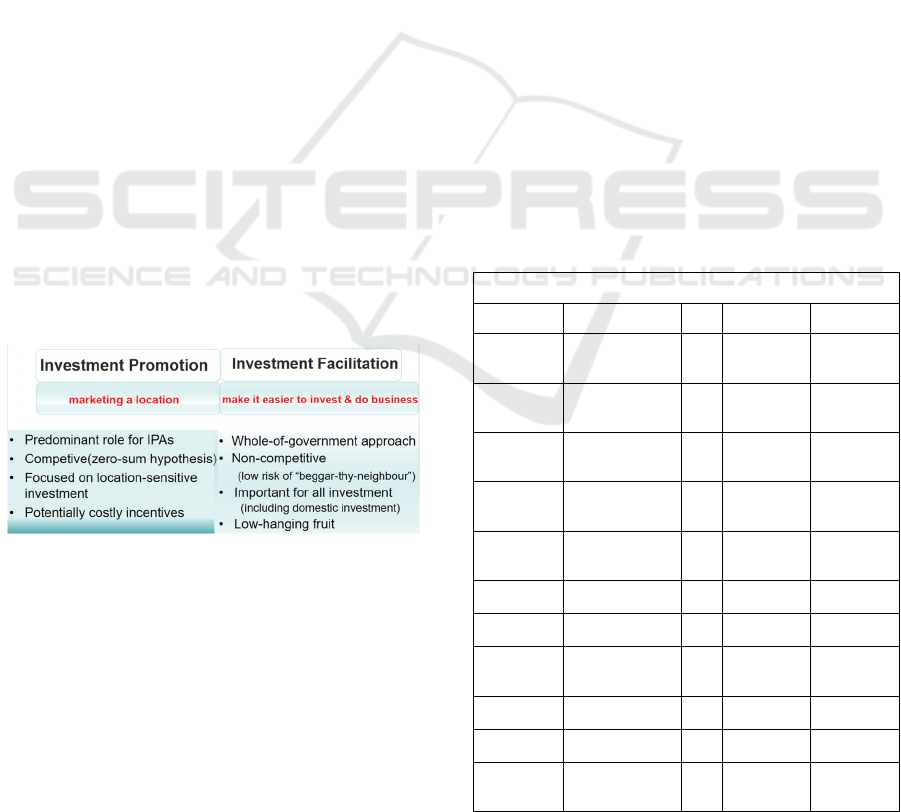
Figure 1: Scope of Investment Promotion and Facilitation.
Therefore, the most important issue is how to
implement investment facilitation under the existing
mechanisms. The research goal of this paper is to use
blockchain technology to realize the application of
investment facilitation at a wide range of levels.
Finally, it will solve the problem of mistrust among
the subjects, increase the transparency and
effectiveness of investment facilitation, and ensure
that the privacy, openness and transparency of
investment data do not conflict.
2 CHALLENGES OF
ESTABLISHMENT DATA
SHARING MODEL ON
INVESTMENT FACILITATION
2.1 Challenges in Institution
The current level of investment facilitation is low and
the depth of cooperation is shallow. Although there
are several cooperative organizations at the regional
level, the multilateral level still stays on the sidelines.
Investment facilitation belongs to an emerging
transnational legal system. Among it, global
governance has a stronger color than traditional legal
governance, but the fact is that "transnational
legislation" and "international legislation"
complement each other and move forward. The “
international legislation” based on the express or
implied mutual consent of various countries has
formed international law in the traditional sense
(international hard law), but the development of
globalization has put forward incremental
requirements for transnational legal norms, that is
international soft law formulated by various non-state
actors, which requires the introduction of the law-
making mechanism of “transnational legislation”.
Table 1: Concrete Measures of Investment Facilitation.
Concrete Measures of Investment Facilitation
UNCTRAD2017 G20 APEC2009 OECD2015
Accessibility
and
trans
p
arenc
y
Line1 √ √
Stability,
security and
p
rotection
√ √
Predictability
and
consistenc
y
Line 3 √ √
Efficiency
and
effectiveness
Line 2 √
Constructive
stakeholder
relationshi
p
s
Line 4 √ √
Use of new
technology
√
Monitoring
and review
Line 6 √ √
Enhance
international
coo
p
eration
Line 7 & Line 10 √ √
Capacity-
b
uildin
g
Line 9 √
Designate a
lead a
g
enc
y
Line 5 √
Support and
technical
assistance
Line 8
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
118

The issue of investment facilitation is at the initial
stage of consultation and joint construction by
various governance entities around the world. Among
them, transnational legislation has initially developed
a set of regional standardized rules that can be used
as reference by various countries, while inter-state
legislation is trapped by conflicts of interest
distribution and differences in preferences. First, at
the regional level, only a preliminary investment
facilitation rule framework was reached in the G20
and BRICS summits. Second, at the multilateral
level, the WTO investment facilitation proposals
promoted by developing members have not been truly
adopted. Finally, at the bilateral level, there is a lack
of clauses containing specific commitments to
investment facilitation. Among the existing more
than 3,300 international investment agreements, only
some clauses contain investment facilitation
commitments, and most of them focus on the entry
and residence of investors and the enhancement of
transparency of laws and regulations. According to
UNCTAD's statistics, only India, Indonesia, ASEAN,
Japan, China, Australia, Malaysia and other countries
have relevant clauses in investment agreements, and
the relevant content is often too simple. However, in
a state where inter-state legislation is stagnant, there
are still many domestic measures that are gradually
benchmarked against the international system. This
abnormal development is enough to attract attention.
In this situation, the data sharing platform can bring
together different stakeholders such as data subjects,
data controllers, and data users, and include different
types of data, avoiding repeated collection of data and
wasting resources. In addition, the data sharing can
ensure the uniformity of the degree of investment
facilitation and reduce the huge difference between
developed and developing countries.
2.2 Challenges in Recognition
Principles
2.2.1 Transparency Principle
The principle of transparency is the most important
and targeted principle in investment facilitation. The
APEC investment facilitation agenda requires that
every APEC economy should ensure the transparency
of relevant laws, regulations and administrative
procedures affecting the flow of goods, services, and
capital, so as to create and maintain an open and
predictable trade and investment environment. The “
G20 Global Investment Policy Guiding Principles”
also regard transparency as a principle and goal. In
the WTO legal system and the international
investment dispute settlement mechanism, the
principle of transparency is an extremely important
principle. It is applicable to almost all fields of
international investment and overcomes the
information failure in international investment.
The investment facilitation proposals put forward
by various countries in recent years also mentioned
transparency requirements, mainly including: (1) The
government should provide comprehensive, clear and
timely notifications when formulating investment-
related policies, (2) Ensure effective access to
information, Including the provision of "one-stop"
consultation points or special consultation points and
appropriate online services, (3) promoting the
simplification of the language of laws
and regulations,
(4) promptly publishing the results of periodic review
of the investment mechanism. From the perspective
of the host country, a core aspect of investment
facilitation is to improve the openness and
transparency of investment supervision and
management of the host government. The application
of digitizing is the simplest and most direct way to
achieve transparency.
2.2.2 Sustainable Development Principle
The investment facilitation plays a vital role in
promoting sustainable development. According to
UNCTAD’s calculations, developing countries are
facing an annual sustainable development goal-an
investment gap of US$2.5 trillion (Hamdani 2018).
Investment facilitation will effectively reduce the
investment gap and help developing countries
achieve sustainable development goals. Data sharing
can help developed countries and developing
countries to share interests and risks, bind interests
and risks together, rather than separate them, and
achieve sustainable goals in the investment field.
2.2.3 Efficiency Principle
The principle of high efficiency is the ultimate goal
pursued by investment facilitation, different from
investment liberalization, investment promotion and
investment protection. The ultimate goal of
investment facilitation is to improve the efficiency of
the investment process, thereby effectively reducing
investors' time and costs. The supporting measures
related to the principle of high efficiency in the
international standards proposed by APEC and
UNCTAD include: (1) reducing the time for
registration, approval, registration, taxation and other
procedures, (2) avoiding multiple discussions, (3)
reducing foreign investment needs to fill in Forms,
and encourage them to be electronic, (4) The central
Application of Data Sharing Model of Investment Facilitation based on Multi-level Blockchain
119

and local levels perform their duties and coordinate.
Application and realization of E-government, "one-
stop" services and a single window match the
demands of investment facilitation above, then
smooth deployment of follow-up work and the
improvement of safety factors.
3 TENTATIVE PLAN OF
APPLICATION OF DATA
SHARING MODEL OF
INVESTMENT FACILITATION
BASED ON MULTI-LEVEL
BLOCKCHAIN
3.1 Application Data Sharing in the
Monitoring and Evaluation System
for Investment Facilitation
In terms of performance evaluation, the Doing
Business of World Bank, the Investment Climate
Statement of US State Department and the Global
Enabling Trade Report of World Economic Forum
are all important annual report for monitoring and
evaluating the business environment and investment
environment. Among them, the most influential one
is the Doing Business, whose data has been cited by
many institutions and multinational companies.
Based on the above report, this paper designs the
performance evaluation index system of investment
facilitation based on the specific objectives and action
plans put forward by UNCTAD's Global Action
Manual on Investment Facilitation and APEC's
Action Plan on Investment Facilitation (Text of
Global Action Memu in 2001 and Text of IFAP in
2009). The ultimate goal of this performance
evaluation indicator system is to further evolve the
international standards proposed by UNCTAD and
APEC into quantifiable data, and to formulate data
that can not only reflect the performance of
environmental investment facilitation, but also reflect
the best practices of investment facilitation. Based on
the secondary and tertiary indicators demonstrated to
the world, the investment facilitation level of
countries and regions participating in international
cooperation on investment facilitation is finally
calculated. Among them, through the data sharing
platform, the evaluation reports of multiple
organizations are integrated, and the big data
software system is used to make a specific evaluation
system that meets the needs of the country or industry
according to the set standards, and the monitoring
evaluation system is implemented through big data to
track dynamic information.
3.2 Application Data Sharing in
Scientific Research for Investment
Facilitation
The League of European Research Universities
(LERU) released the Scientific Data Roadmap in
2013, which clarified the benefits and challenges of
scientific data sharing and reuse, the cost of scientific
data development, and the management of scientific
data. Skills and knowledge, as well as corresponding
training and development opportunities (LERU
2015), in order to guide LERU member universities
in the form of guidelines to carry out scientific data
management related practices. In January 2014, the
Ministry of Education, Sports and Culture of the
United Kingdom and the Ministry of Statistics
reached a data sharing agreement to promote the use
of departmental management data to conduct
research on population size, structure and migration
dynamics (POPULATION, MIGRATION, 2013).
Research on investment facilitation is currently in its
infancy so that the research level and focus of
research institutions and researchers in various
countries are different. The most representative one is
the study of the Center for Sustainable Investment at
Columbia University. The Perspective established by
this institution is an excellent platform to achieve data
sharing data on investment facilitation research.
Experts in this field around the world publish their
work report through this platform, not just mature
academic papers. Therefore, the achievements of
investment facilitation research cannot be separated
from the sharing of scientific research data in such a
short period of time. (Sauvant, 2008-2022)
3.3 Application Data Sharing in Host
Country for Investment Facilitation
Data can flow between countries in accordance with
clear, practical, and fair access and reuse rules in data
space, and access to a wider range of international
data sharing conditions while ensuring compliance
with the public interest and the legitimate interests of
data providers. These are conducive to promoting
data sharing between enterprises and governments
and promoting the structure normativeness of the
laws in host country in turn.
India set up the country’ s core institution for
investment promotion and facilitation at the federal
level——Invest India. That’s the one reason not to be
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
120

ignored to a historical high recorded for India FDI
inflows after the ongoing pandemic. For a large and
politically diverse state such as India, the potential
incompatibility of investment facilitation measures
(such as national focal points and single-window
clearance mechanisms) with its federal state structure
has been a legitimate concern, particularly given how
FDI projects inevitably require clearances from
multiple levels of subnational political entities. Yet,
Invest India virtually coordinates between federal and
provincial state agencies, both horizontally and
vertically. It therefore helps to diminish procedural
inefficiencies caused by the “ center vs. state ”
demarcation. By doing so, it attempts to fast-track all
types of licenses, approvals and clearances for
investors, without encroaching upon the
constitutionally guaranteed functional autonomy of
regional and local authorities. This not only shows the
effectiveness, but also shows that the federal state
implements investment facilitation at the domestic
law level, let alone a unified centralized state.
4 HOW TO APPLICATION OF
DATA SHARING MODEL OF
INVESTMENT FACILITATION
BASED ON MULTI-LEVEL
BLOCKCHAIN
4.1 Industrial Data Sharing Platform
The industry data sharing platform is to set up a data
sharing intermediary platform in a specific industry
or field. For example, China's unified environmental
assessment declaration and approval system has
achieved national data sharing for fixed asset
investment in China. It is conducive to the
implementation of interconnection and centralized
exchange at the national level, sharing EIA approval
data with relevant local departments through the
investment platform as needed, relying on the
investment platform to reduce the burden of project
units, the integrated management department of the
investment platform supports data sharing,
coordination and cooperation between departments
With the help of the data sharing platform, the ability
of the company is significantly improved. On this
basis, cross-border cooperation for scientific data
sharing is realized.
There are already many practices for co-
construction and sharing of scientific data according
to different industries. Such as the Center for
Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) of India
and the sharing of medical information in Kenya.
Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI) connects
with each other and shares resources by compiling
data and catalogs for research and use by Kenyan
medical institutions. The earth system science data
sharing platform in China is undertaken by the
Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural
Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of
Sciences, the Institute of Resources and Environment
of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, more than 40
well-known universities in the field of domestic
geosciences, the World Data Center, International
Mountain Center, and the University of Maryland and
other international organizations and institutions
participate in the construction and operation of this
platform. With reference to the operating mode of
these existing industry data intermediary platforms, it
is feasible to apply data sharing to investment
facilitation to a large extent.
In the application of investment facilitation,
investment can be regarded as a generalized area,
which can be specifically divided into energy
industry investment, technology investment,
infrastructure construction investment, and tertiary
industry investment. The characteristics of different
industries should be highlighted in the application of
investment facilitation. For instance, in the energy
industry, the focus of investment facilitation should
be on the transparency and process of obtaining
licenses and the social obligations undertaken by
enterprises. In technology investment, the focus of
investment facilitation should be on the security of
the technology protection platform and the
transparency of the scope of technology application.
In infrastructure construction investment, the focus of
investment facilitation should be on the degree of
openness of relevant information in the host country,
reducing corruption and promoting good
communication between the home country and the
host country.
4.2 Distributed Storage of Data in
Investment Facilitation
In addition to considering the types of investment in
different industries and fields, it is also necessary to
determine an appropriate way of organizing data, that
is, to implement the subject of investment facilitation
data sharing. One is the collaborative construction
and sharing model of international organizations. As
the name suggests, the cooperative joint construction
and sharing mode of international organizations
refers to a sharing mode in which international
Application of Data Sharing Model of Investment Facilitation based on Multi-level Blockchain
121

organizations jointly formulate related sharing
strategies on a certain research direction or research
subject under a certain agreement or treaty. The
sharing strategy which includes the scope, method
and related policies of sharing can promote the
exchange and share of data in the same field. The
cooperation methods of international organizations
include international intergovernmental cooperation
and international non-governmental cooperation.
Either way, they must follow the purpose of sharing
and be bound by a common agreement to promote the
global sharing of data and improve technology of
member states. The Organization for Economic
Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an
intergovernmental international economic
organization composed of 30 market-economy
internationals. It aims to jointly respond to the
economic, social and government governance
challenges brought about by globalization and grasp
the opportunities brought by globalization.
In addition, there is a policy-driven co-
construction and sharing model. This model refers to
the promotion of the co-construction and sharing of
scientific data under the compulsory drive of national
laws, regulations and policies. The United States is
the earliest experimenter of this model. The US
Freedom of Information Act and the Copyright Act
are the legal foundations of this model. US issued the
"Global Change Research Data Management Policy"
centered on the "full and open" scientific data sharing
policy in 1991. Through this policy, the sharing of
scientific data was promoted, thereby providing
strong guarantees for scientific research in the United
States, which ensures the realization of its strategic
goals of national development and scientific and
technological development in the 21st century (Yang,
Chen, 2014).
4.3 Refined Management by Federated
Learning
The professional and refined information data
management platform unifies the data caliber and
penetrates the investment business process. So the
basic data of investment projects get rid of the
discrete, isolated, incomplete, and unrelated state.
Based on this, the foundation of investment
management is consolidated. And the free interaction
and sharing of information and data can meet the
different needs of investment management and
decision makers for rich investment data expression,
and provide convenient support for micro-level
investment decision makers.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out targeted
management of different regions. This model limits
those participating in the joint construction and
sharing of scientific data within a certain geographic
scope, which is similar to the coordination and
sharing mode of international organizations, and the
former is relatively in scope. Smaller ones, generally
limited to a certain region or a certain country,
collectively store shared resources in a specific
location, and operate and build jointly under the joint
management and co-funding of related units.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Through the investment data sharing model based on
multi-level chains, multi-level storage on the chain
and mixed storage of IPFS under the chain are
adopted, which ensures the security of investment
facilitation data and improves the scalability of
blockchain. In the data sharing based on multilevel
blockchain, the data of the host country of investment
convenience is encrypted to prevent malicious
attackers from stealing data. For the problem of data
sharing among institutions, institutions can freely
choose whether to participate in federal learning or
not, and use local differential privacy technology to
perturb and add model parameters before sending
them. Bringing together stakeholders at all stages of
the data production and use chain can greatly
overcome information asymmetry in investment
facilitation, as well as coordination among host
countries, investors and other stakeholders, and at the
same time meet the requirements of transparency,
sustainable development and high efficiency in
investment facilitation. In the future, in terms of
specific applications, besides scientific research,
legislation of host country and monitoring and
evaluation system of investment facilitation, more
suitable fields need to be developed. In addition,
according to the characteristics of data itself, we
should attach great importance to data security, and
research in this area needs further strengthening.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author is most grateful to the Law School and the
Silk Road Institute for International and Comparative
Law of Xi’an Jiaotong University for their generous
assistance. The research was funded by the projects
of National Social Science Foundation of China
Youth Project: Multilateral Reform and Chinese
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
122

Countermeasures of International Investment
Arbitration under the Background of "One Belt and
One Road" (18CFX084)
REFERENCES
Hamdani K, “Investment facilitation at the WTO is not
investment redux,” Columbia FDI Perspectives, No.
226, May 21, 2018. Reprinted with permission from the
Columbia Center on Sustainable Investment.
LERU roadmap for research data [EB/OL]. [2015-03-09].
http: //www.leru.org /files/
publications/AP14_LERU_Roadmap_for_Research_d
ata_final.pdf.
Malamas V, Kotzanikolaou P, Dasaklis T. K, et al. A
hierarchical multi blockchain for fine grained access to
medical data [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 134393-
134412.
POPULATION AND MIGRATION, Data sharing
agreement with statistics unit: population and migration
statistics [EB/OL]., OECD Factbook 2013
https://www.oecd.org/sdd/01_Population_and_migrati
on.pdf.
Sauvant P. K, Columbia FDI Perspectives, 2008-2022
https://ccsi.columbia.edu/content/columbia-fdi-
perspectives
The full text of the UNCTAD Global Action Menu for
Investment Facilitation is available at:
https://investmentpolicy.unctad.org/uploaded-
files/document/Action%20Menu%2001-12-
2016%20EN%20light%20version.pdf. The full text of
the IFAP is available at:
https://www.apec.org/docs/default-
source/Press/Features/2009/09_cti_ieg_IFAP.pdf
Yang Y, and Chen Y, “Scientific Big Data Sharing
Research: Based on the International Scientific Data
Service Platform,” in New Century Library, 2014(03):
24-28.
Application of Data Sharing Model of Investment Facilitation based on Multi-level Blockchain
123
