
The Influence of Perceived Product Innovativeness on Customer
Commitment: An Empirical Study of TPB Theory
Zichen Wang
a
College of Innovation and Management, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Bangkok, Thailand
Keywords: Perceived Product Innovativeness, Customer Commitment, Theory of Planned Behavior.
Abstract: The study analyzes the elements that contribute to increased customer commitment in China, with the Chinese
brand Vivo as a case study. The advancement of information technology has enabled an increasing number
of people to enjoy the conveniences of the Internet at any time and from any location; the population of online
users is growing; demand for online shopping is increasing, and an increasing number of customers are
gathering information via social media platforms. At the moment, new consumer growth has stalled, and the
expense of acquiring new customers is constantly growing. Therefore, if businesses intend to succeed in the
market, they must focus on their existing target groups, preserve stickiness, and encourage existing client
devotion. After doing data analysis using SmartPLS 3 and SPSS, this study discovered that consumers'
perceived innovativeness of a product would have a positive and statistically significant influence on customer
commitment. The findings of this study are used to develop practical recommendations for e-commerce
platform-based operations and future research initiatives in this area.
1 INTRODUCTION
While the market potential is vast, the new Internet
purchasing scene is more dynamic and evolving,
competition is getting more complicated and tough,
and the introduction of a variety of social media
sources has provided shoppers with more alternatives
(Anshari, Almunawar, Lim, Al-Mudimigh, 2019).
Businesses must develop a loyal consumer base to
maintain a competitive advantage in a dynamic,
competitive environment because it is far less costly
to retain a loyal client than it is to acquire a new one.
This ensures a steady stream of earnings for the firm,
enabling it to compete more successfully in a
competitive market. Customers' ability to participate
in the enterprise value chain circulation process has a
direct impact on a business's performance in today's
competitive market (Wang 2021). This study sought
to quantify the association between perceived product
innovation and customer commitment. Whether
perceived product innovativeness has an impact on
consumer commitment is the question under
investigation in this study.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0326-336X
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theory of Planned Behavior
According to the theory of planned behavior, whether
a consumer will engage in an activity is determined
by the customer's own motivation and ability (Hsu,
Chang, Yansritakul, 2017). As seen in Figure 1. The
theory of planned behavior evolved from rational
behavior theory and is now frequently utilized to
investigate customers' behavioral intentions and
actual conduct.
Figure 1: Main variables of the theory of planned behavior.
Wang, Z.
The Influence of Perceived Product Innovativeness on Customer Commitment: An Empirical Study of TPB Theory.
DOI: 10.5220/0011168500003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 161-165
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
161

2.2 Perceived Product Innovativeness
Zhang, Sun, Liu, and Chang (Zhang, Sun, Liu,
Chang, 2020) investigated China's inventive toy
industry. Zhang et al. analyze the methods through
which consumer innovation results in consumers'
willingness to pay via perceived product innovation
and perceived value. Zhang et al. (Zhang, et al., 2020)
discover that perceived product innovation and
consumer innovation contribute to willingness to pay.
Perceived product innovation and perceived social
value are mediating factors in the link between
consumer innovation and consumer willingness to
pay. Additionally, research into the actual innovation
process has proved unequivocally that the success or
failure of new product creation is not simply
determined by the corporation but also by the
subjective opinions of customers about the product's
innovative dimension. Table 1 highlights the
definitions of perceived product innovation obtained
from prior academics in this research.
Table 1: Perceived product innovativeness definations.
eference Definition
Kim, Kim, and Hwang (2021)
The subjective view or evaluation of creative conduct based on the
subjective perception of the customer is known as consumer perceived
innovativeness.
Lowe and Alpert (2015)
It is the degree to which customers see a product as original and enhanced
over current alternatives that are referred to as perceived product
innovation.
Al-Jundi, Shuhaiber, and Augustine (2019)
Consumer perception of product innovativeness analyzes the differences
in product innovation from the consumer's viewpoint, unlike objective
study on innovative behavior.
Flores and Jansson (2021)
Perceived innovativeness refers to consumers' subjective views of product
innovation.
2.3 Consumer Commitment
Various scholarly definitions of customer
commitment are summarized and categorized in
Table 2. Even more intriguingly, the definitions of
commitment in marketing seem to be consistent from
the outset, unlike in the area of organizational
behavior, where psychological and behavioral
approaches disagree.
Table 2: Customer commitment definations.
Reference Definition
Hur, Kim, and Kim (2018)
Customer commitment is a pledge to continue a commercial connection
b
etween two o
r
more trading partners, whethe
r
implicit o
r
explicit.
Iglesias, Markovic, and Rialp (2019)
In contrast to other brands, consumer commitment may be characterized
as an emotional or psychological bond with a brand within a product
category.
Rather, Tehseen, Itoo, and Parrey (2019)
In business and organizations, customer commitment refers to the goal of
developing and maintaining a long-term, stable relationship with a
company o
r
organization.
Jacoby and Kyner (1973)
Customer commitment is defined as the long-term psychological reaction
to a brand that occurs after customers have considered one or more
competing products o
r
services.
2.4 Hypotheses
Hypotheses are presented in this study based on the
research objective and a review of the literature.
Hypothesis: Perceived product innovativeness
has a positive impact on customer commitment.
3 METHODOLOGIES
3.1 Research Structure
In accordance with Figure 2, the structure was
developed in accordance with a prior literature
analysis and the theory of planned behavior. The
framework incorporates two variables: perceived
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
162
product innovativeness and customer commitment, as
well as a hypothesis concerning the link between the
two variables and the hypothesis. Because of the
logical foundation of the idea offered in this research,
it is simpler to understand.
Figure 2: The conceptual framework of research.
3.2 Research Design
The data for this research was collected via the use of
a self-administered questionnaire. Everything from 1
(strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree) on a Likert
scale was evaluated for each of the following
constructs (strongly agree).
4 RESEARCH FINDING AND
DISCUSSION
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
The quantitative research method was used to
disseminate and collect online questionnaires using
social media platforms on the Internet in this study.
This research sent 150 questionnaires, and after
removing those that took less than 30 seconds to
complete, 98 legitimate questionnaires remained,
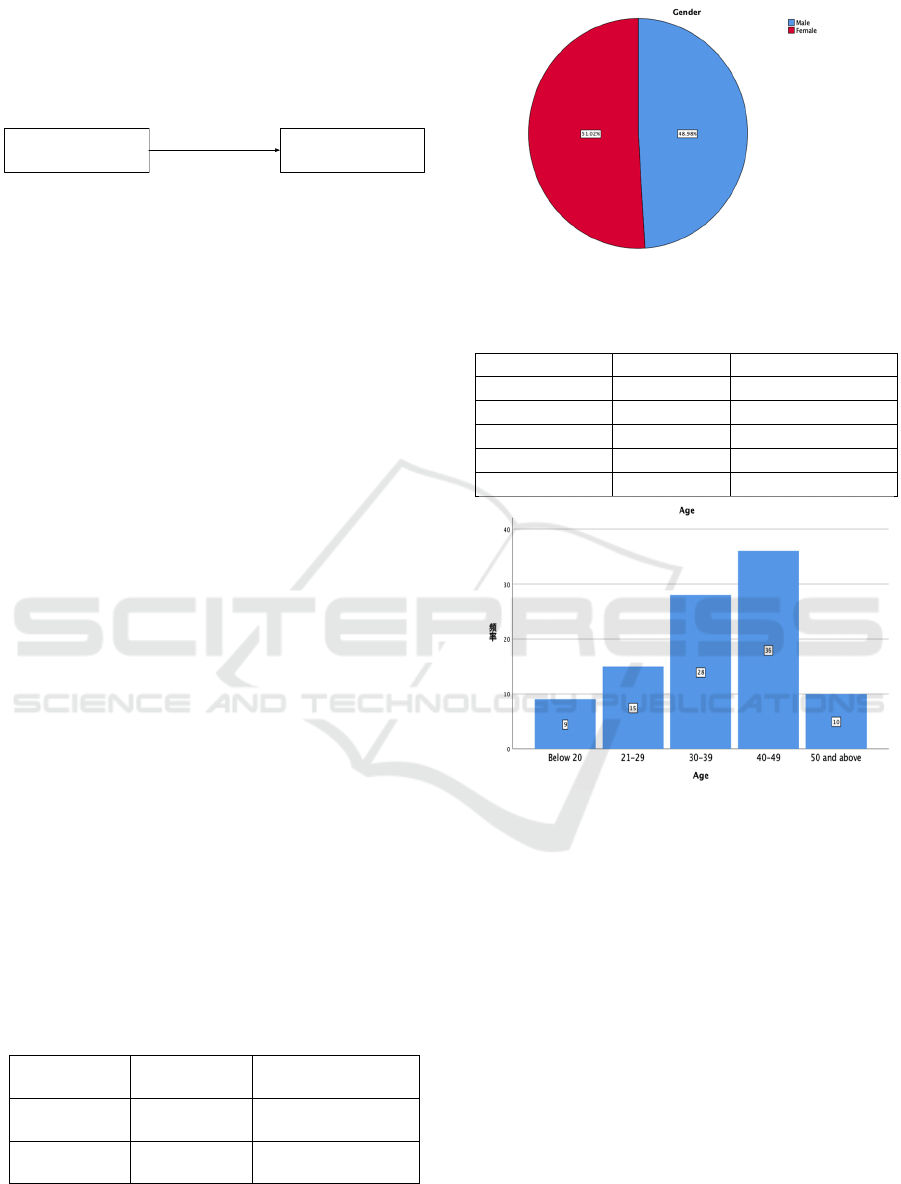
with a valid recovery rate of 65.33 percent. Table III
and Figure 3 indicate that females outnumbered men
by a little margin, with 48 males (48.98 percent of the
total) and 50 females (51.02 percent of the total
number).
According to Table 3 and Figure 4, the age
distribution of Vivo brand smartphone users is
dominated by consumers aged 40-49, with 36
individuals accounting for 36.7 percent of the total
number, and by consumers under the age of 20, with
only nine individuals accounting for 9.2 percent of
the total number.
Table 3: The Gender Distribution of Samples.
Gender Number Percentage(%)
Male 48 48.98
Female
50 51.02
Figure 3: The gender distribution of samples.
Table 4: The age distribution of samples.
Age Number Percentage(%)
Below 20 9 9.2
21-29 15 15.3
30-39 28 28.6
40-49 36 36.7
50 and above 10 10.2
Figure 4:
The age distribution of samples.
4.2 Measurement Model
As shown in Table 5, all item loadings were more
than the suggested threshold of 0.6 (Hair, Sarstedt,
Ringle, Gudergan 2018). As shown in Table I, the
results of the construct reliability test indicate that the
CR values of all items are more than the intended
threshold of 0.7. The average variance extracted
(AVE) value exceeds the suggested threshold of 0.5
for the total amount of variation in the indicators
accounted for by the latent construct (Hair, et al.,
2018). In summary, the measuring scale used in this
investigation is valid for convergence. The square
root (diagonal value) of the AVE for each structure is
larger than the associated correlation coefficient,
indicating that the structure has the proper
discriminant validity. The factor loadings and cross-
Perceived Product Innovativeness Customer Commitment
The Influence of Perceived Product Innovativeness on Customer Commitment: An Empirical Study of TPB Theory
163
loadings of the measurement model are shown in
Table 7.
Table 5: Validity and reliability for constructs.
Constructs Items Loadings
Cronbac
h's alpha
CR AVE
Customer
commitment
CC5 0.829
0.890
0.93
2
0.822
CC6 0.944
CC7 0.941
Perceived
Product
Innovativene
ss
PCI1 0.797
0.759
0.86
1
0.673
PCI10 0.802
PCI2 0.861
Table 6: Discriminant validity.
Constructs
C1 C2
Customer
commitment
0.970
Perceived
Product
Innovativeness
0.759 0.821
a. Values on the diagonal (bolded) are the square root of the AVE, while the off-
diagonals are correlations.
Table 7: Factor Loadings and Cross Loadings for the
Measurement Model.
Items Customer
commitment
Perceived Product
Innovativeness
CC5 0.829 0.750
CC6 0.944 0.650
CC7 0.941 0.642
PCI1 0.684 0.797
PCI10 0.517 0.802
PCI2 0.644 0.861
a. Values on the diagonal (bolded) are the square root of the AVE, while the off-
diagonals are correlations.
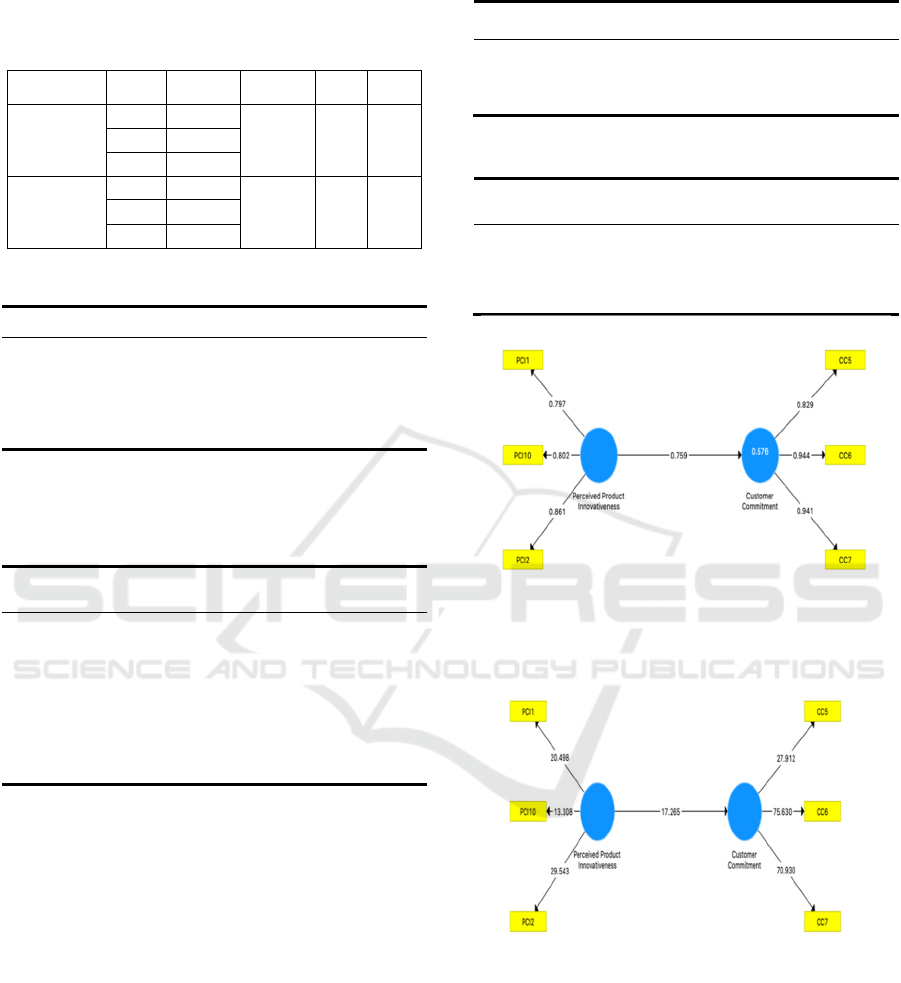
4.3 Structural Model
The findings of the data analysis performed using
SmartPLS are shown in Figures 5 and 6, respectively.
In the case of the structural model, as indicated in
Figures 5 and 6, the results of hypothesis testing may
be obtained by a study of the model. In this study, the
relationship between the components is studied.
Table 8 summarizes the findings of the structural
route analysis performed using SmartPLS. Customer
commitment was favorably and significantly
impacted by perceived product innovativeness (β =
0.759; t = 17.265; p < 0.001). As a result, hypothesis
1 was validated.
Table 8: The structural path analysis result.
Constructs
Relationship
Beta
T
Value
f
P
Values
Perceived Product
Innovativeness ->
Customer
Commitment
0.759 17.265 1.360 0.000
Table 9: Predictive relevance (Q
2
).
SSO SSE
Q² (=1-
SSE/SSO)
Customer
Commitment
354.00
0
139.27
3
0.607
Perceived Product
Innovativeness
354.00
0
234.04
8
0.339
Figure 5: Structural model assessment
Figure 6: Effect size.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research aims to determine if there is a
correlation between product innovation and customer
commitment as perceived by customers of Vivo-
branded smartphones. As a consequence of the data
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
164

breakdown described above, this chapter discusses
the results and management implications before
giving appropriate suggestions and pointing to future
study topics. According to the conclusions of this
study's data analysis, brand reputation is known to
impact consumer commitment. This conclusion is
consistent with Foroudi, Jin, Gupta, Foroudi, Kitchen
(Foroudi, Jin, Gupta, Foroudi, Kitchen, 2018) and
other researchers' findings, indicating that companies
with a strong brand reputation are more likely to
generate significant customer loyalty and recurrent
purchases of the brand's goods and services (Foroudi,
et al., 2018). Since regular customers not only help
businesses perform better they also reduce marketing
expenses, companies can increase customer loyalty
by actively innovating their product lines. This will
give them an advantage over other brands of similar
products and give customers a stake in the service
delivery process. As a way to enhance the company's
own value benefits and competitiveness, businesses
nurture loyal customers as part of their human
resource management strategy.
Research limitations and suggestions are included
in this study, which aims for rigor in its approach
design but is still vulnerable to external influences.
It is proposed that future studies might look at
other brands or sectors in order to further understand
the link between perceived product innovation and
consumer loyalty, even though this study focuses on
Vivo-branded smartphones.
REFERENCES
Anshari, M., Almunawar, M. N., Lim, S. A., & Al-
Mudimigh, A. (2019). Customer relationship
management and big data-enabled: Personalization &
customization of services. Applied Computing and
Informatics, 15(2), 94-101.
Boisvert, J., & Khan, M. S. (2021). Toward a better
understanding of the main antecedents and outcomes of
consumer-based perceived product innovativeness.
Journal of Strategic Marketing, 1-24.
Foroudi, P., Jin, Z., Gupta, S., Foroudi, M. M., & Kitchen,
P. J. (2018). Perceptional components of brand
reputation: Configuring the Symmetrical and
Asymmetrical Paths to brand fidelity and brand
purchase intention. Journal of Business Research, 89,
462-474.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Gudergan, S. P.
(2018). Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares
Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand
Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hsu, C. L., Chang, C. Y., & Yansritakul, C. (2017).
Exploring purchase intention of green skincare
products using the theory of planned behavior: Testing
the moderating effects of country of origin and price
sensitivity. Journal of Retailing and Consumer
Services, 34, 145-152.
Hur, W. M., Kim, H., & Kim, H. K. (2018). Does customer
engagement in corporate social responsibility
initiatives lead to customer citizenship behaviour? The
mediating roles of customer‐company identification
and affective commitment. Corporate Social
Responsibility and Environmental Management, 25(6),
1258-1269.
Iglesias, O., Markovic, S., & Rialp, J. (2019). How does
sensory brand experience influence brand equity?
Considering the roles of customer satisfaction,
customer affective commitment, and employee
empathy. Journal of Business Research, 96, 343-354.
Jacoby, J. & Kyner, D. B. (1973). Brand fidelity vs. repeat
purchasing behavior. Journal of Marketing Research,
10(1), 1-9.
Rather, R. A., Tehseen, S., Itoo, M. H., & Parrey, S. H.
(2019). Customer brand identification, affective
commitment, customer satisfaction, and brand trust as
antecedents of customer behavioral intention of loyalty:
An empirical study in the hospitality sector. Journal of
Global Scholars of Marketing Science, 29(2), 196-217.
Wang, Z. (2021). Experiential marketing: Will it affect
customer citizenship behavior? An empirical study of
multiple mediation model in Thailand. Journal of
Community Psychology, 49(6), 1767-1786.
Zhang, F., Sun, S., Liu, C., & Chang, V. (2020). Consumer
innovativeness, product innovation and smart toys.
Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 41,
100974.
The Influence of Perceived Product Innovativeness on Customer Commitment: An Empirical Study of TPB Theory
165
