
Research on the Influence of Equity Pledge of Controlling
Shareholders on Enterprise Innovation: Based on the Real Surplus
Management Perspective
Guangqiang Han and Yingxue Wang
School of Economics, Bohai University, Jinzhou, Liaoning, China
Keywords: Equity Pledge, Real Surplus Management, Enterprise Innovation, Mechanism Analysis, Intermediary Effect.
Abstract: The article samples Chinese A-share listed companies from 2007 to 2020, and verifies the relationship
between the controlling shareholder equity pledge, surplus management and enterprise innovation by using
empirical research methods. The study found that the implementation of equity pledge by the controlling
shareholders will reduce the degree of innovation of enterprises, and the real surplus management will play a
partial intermediary role in the relationship between the two. The research conclusion is helpful to improve
the economic consequence theory of equity pledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Fifth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central
Committee proposed that the 14th Five-Year Plan
period must be innovation-driven and high-quality
supply. Although research and innovation will lead to
a large increase in enterprise costs in the short term,
it is related to the long-term development of
enterprises. According to the statistics of wind
database, as of November 26,2021, the number of
pledged shares in the A-share market is 429.87 billion
shares, and the equity pledge situation is generally
more common. When the controlling shareholder
makes a large proportion of the equity pledge to
finance, motivated to maintain control, it tends to use
its own control for various surplus management
activities, so as to stabilize the stock price. Cutting
innovation investment is an effective method of real
surplus management.
Some scholars have analyzed the relationship
between equity pledge and enterprise innovation
from the perspective of internal control, management
risk preference and institutional environment. From
the perspective of real surplus management, this
paper discusses the impact of equity pledge on
enterprise innovation, which provides a richer
perspective.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESES
AREPRESENTED
2.1 Equity Pledge and Enterprise
Innovation
Most scholars believe that equity pledge and
enterprise innovation are a linear negative
correlation. For example, Zhang Ruijun et al (2017)
believe that the negative relationship between the
controlling shareholder equity pledge and the
enterprise R & D investment (Zhang, et al, 2017),
while Li Changqing et al (2018) believes that such
will only occur when the equity pledge rate is higher
and the closer to the liquidation line (Li, et al, 2018).
Wenwen et al. (2018) believe that the equity pledge
of the controlling shareholders in the high-tech
industry has a stronger inhibitory effect on enterprise
innovation than (Wen, et al, 2018).Some scholars
believe that the relationship between the two is
nonlinear. Xu Weilong et al (2020) believe that with
the increase of the pledge ratio, the innovation ability
increases first and then reduces the (Xu, et al, 2020).
Based on this, we propose the hypotheses 1a,1b:
H1a: Equity pledge of major shareholders is
negatively related to enterprise innovation.
510
Han, G. and Wang, Y.
Research on the Influence of Equity Pledge of Controlling Shareholders on Enterprise Innovation based on the Real Surplus Management Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0011188900003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 510-514
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

H1b: Equity pledge of major shareholders and
enterprise innovation is not a linear negative
relationship.
2.2 Equity Pledge and Surplus
Management
Surplus management activities are a relatively
common legal market value management behavior in
listed companies, which is divided into accrued
surplus management and real surplus management.
Sun Haitao et al. (2020) believe that the companies
that make the equity pledge will take more real
surplus management activities to adjust the surplus
(Sun, et al, 2020). Li Xiaodong et al (2020) also
believe that the equity pledge of major shareholders
is significantly negatively related to the degree of
accrued surplus management, and significantly
positively related to the degree of real surplus
management(Li, et al, 2020).The equity pledge of the
controlling shareholder that has been released within
the year has no significant impact on the real surplus
management degree of the company (Xie, et al, 2018)
.Based on this, the hypothesis 2 is proposed:
H2: The equity pledge of major shareholders has
a positive relationship with the real surplus
management.
2.3 Surplus Management and
Enterprise Innovation
Once the enterprise has the need for surplus
management activities, it will pay special attention to
the large expenses in the surplus management
activities. Long payback and costly R & D innovation
activities will be reduced by surplus management
activities. When the degree of surplus management is
reduced, the agency problems and financing
constraints are reduced, so that the enterprise
innovation behavior can be significantly improved
(Yu, et al, 2018). Businesses with R & D expenses
will engage in surplus management for real R & D
trading activities(Xiao, Zhou, 2012).The innovation
strategy of enterprises is divided into radical and
conservative types. The higher the real surplus
management degree of the enterprise, the lower the
intensity of its R & D expenditure, and the enterprise
will adopt a more conservative innovation strategy
(Dai 2016).
In general, equity pledge has led to an increase in
surplus management, and real surplus management
will be based on cutting corporate innovation. In this
way, the action path of "equity pledge, one real
surplus management and one enterprise innovation"
is formed. Thus, we propose the hypothesis that the
3:
H3: If H1a is established, the real surplus
management plays an intermediary role between
equity pledge and enterprise innovation.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
3.1 Sample Selection and Data Sources
All the data in this paper are from GuoTai'an, and the
equity pledge data of major shareholders at the end of
2007-2020 is obtained through manual sorting.
Surplus management requires data from the previous
two years, which began in 2005.Excluding the
financial industry, missing data, and ST, *ST, and PT,
all continuous variables were processed with
Winsorize.
3.2 Variable-Definition
3.2.1 Explanatory Variable
The explanatory variable is the major shareholder's
equity pledge. According to the existing literature,
through the sorting of the pledge data of the current
year, the judgment standard is whether there is an
equity pledge by the major shareholder at the end of
the year, and the value is 1, and the value is 0. It does
not include the samples released in the current year.
Enterprises that did not update the pledge data in the
current year are consistent with the equity pledge in
previous years.
3.2.2 Explained Variable
The ratio of R & D investment and operating income
is taken as a measure of enterprise innovation:
Radint= Total enterprise R & D expenditure /
operating income
(1)
The larger the calculated Radint value indicates
that the higher the enthusiasm of the enterprise to
implement the enterprise innovation.
3.2.3 Mediating Variable
This paper uses real surplus management data from
GuoTaian database, represented by DREM. The
calculated DREM value is greater than zero and the
greater the degree of upward real surplus
management; the DREM value is less than zero and
Research on the Influence of Equity Pledge of Controlling Shareholders on Enterprise Innovation based on the Real Surplus Management
Perspective
511

the smaller, the higher the degree of downward real
surplus management.
3.2.4 Controlled Variable
Based on previous research results related to equity
pledge and earnings management, the following
variables are used as control variables: (1) Nature of
property rights (SOE): Based on whether it is a state-
owned enterprise, the value is 1 if it is a state-owned
enterprise, and 0 if it is not. (2) Shareholding ratio of
the largest shareholder (Top1): This variable is used
to represent the concentration of ownership. It is
measured by the proportion of the shares held by the
largest shareholder to the total shares of the listed
company. Generally, the larger the proportion, the
higher the degree of equity concentration. (3) Audit
quality (Big4): The Big Four accounting firms are
relatively authoritative accounting firms. It is
measured according to whether the listed company is
audited by the Big Four accounting firm at the end of
the year. (4) Size of the company (Size): The size of
the company is measured by taking the natural
logarithm of the company's total assets. The larger the
indicator is, the larger the company is. (5) Growth
rate of operating income (Growth): It is used to
express the development ability of the enterprise. It is
measured by dividing the operating income of the
current year by the operating income of the previous
year and subtracting one. (6) Number of directors
(Board): Indicates the size of the board of directors of
the listed company, which is measured by taking the
natural logarithm of the number of directors of the
company. (7) Tobin's Q value (Tobin): This variable
is used to measure the company's performance. It is
measured by the ratio of the company's market value
to the replacement cost of assets. At the same time,
two dummy variables of year and industry are defined
to control their effects.
3.3 Model Specification
In this paper, the stepwise test method of mediation
test is used to test whether the total effect coefficient
is significant, that is, whether there is a significant
relationship between the independent variable and the
dependent variable. If significant, proceed to
subsequent analyses, if not, mediation analysis is
terminated. Test whether the effect of the
independent variable acting on the mediating variable
is significant; if it is significant, continue the
subsequent test, otherwise stop the analysis, and the
mediating effect does not exist; test whether the effect
of the mediating variable acting on the dependent
variable is significant; if significant, continue the
subsequent test, otherwise stop the analysis, the
mediating effect does not exist; test whether the direct
effect is significant. When the first two items are
significant, if it is not significant, there is a complete
mediation effect (Judd, Kenny, 1981), otherwise
there is a partial mediation effect (Baron & Kenny
1986).
The following models are set up to conduct the
mediation effect test of assumptions 1,2 and 3, and
then use the Bootstrap method if the step-wise test is
not significant.
Hypothesis 1a、1b was verified to construct the
following multiple linear regression model:
Radinti, t=β0+β1Pledgei, t+β2Soei, t+β3Roai,
t+β4Top1i, t+β5Big4i, t+β6Sizei, t+β7Growthi,
t+β8Boaedi, t+β9Tobini, t+∑Y+∑IND+ε (2)
Hypothesis 2 was verified to construct the
following multiple linear regression model:
Pledgei, t=β0+β1DREMi, t+β2Soei, t+β3Roai,
t+β4Top1i, t+β5Big4i, t+β6Sizei, t+β7Growthi,
t+β8Boaedi, t+β9Tobini, t+∑Y+∑IND+ε (3)
To verify hypothesis 3, the following multiple
linear regression model was constructed by
combining the models (2) and (3):
Radinti, t=β0+β1Pledgei, t+β2DREMi, t+β3Soei,
t+β4Roai, t+β5Top1i, t+β6Big4i, t+β7Sizei,
t+β8Growthi, t+β9Boaedi, t+β10Tobini,
t+∑Y+∑IND+ε
(4)
4 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
The descriptive statistics of the variables in this paper
are shown in Table 2. The minimum value of R & D
investment of listed companies is 0, and the
maximum value is 251.6%. It can be seen that there
is a large gap in the innovation level of different listed
companies, and there is an extreme phenomenon of
excessive innovation investment in that year. For
example, in Junshi Biology in 2019 and 2020, this
value reached 122.06% and 112.72%. The median is
3.4%, indicating that the overall innovation level of
listed companies is low, and the innovation impetus
is insufficient. The average equity pledge ratio
(Pledge) of controlling shareholders is 44.5%,
indicating that the equity pledge situation of
controlling shareholders of listed companies is
relatively common.
The Variance Inflation Factor test refers to the
ratio of the variance when there is multicollinearity
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
512
among the explanatory variables to the variance when
there is no multicollinearity between the explanatory
variables. The larger the VIF, the more serious the
collinearity is. The judgment method shows that
when 0<VIF<10, there is no multicollinearity among
the variables. It can be seen from Table 3 that after
the VIF test, the VIF values of each variable (dummy
variable year, industry controlled) are all less than 2,
and it can be judged that there is no multicollinearity
between the variables.
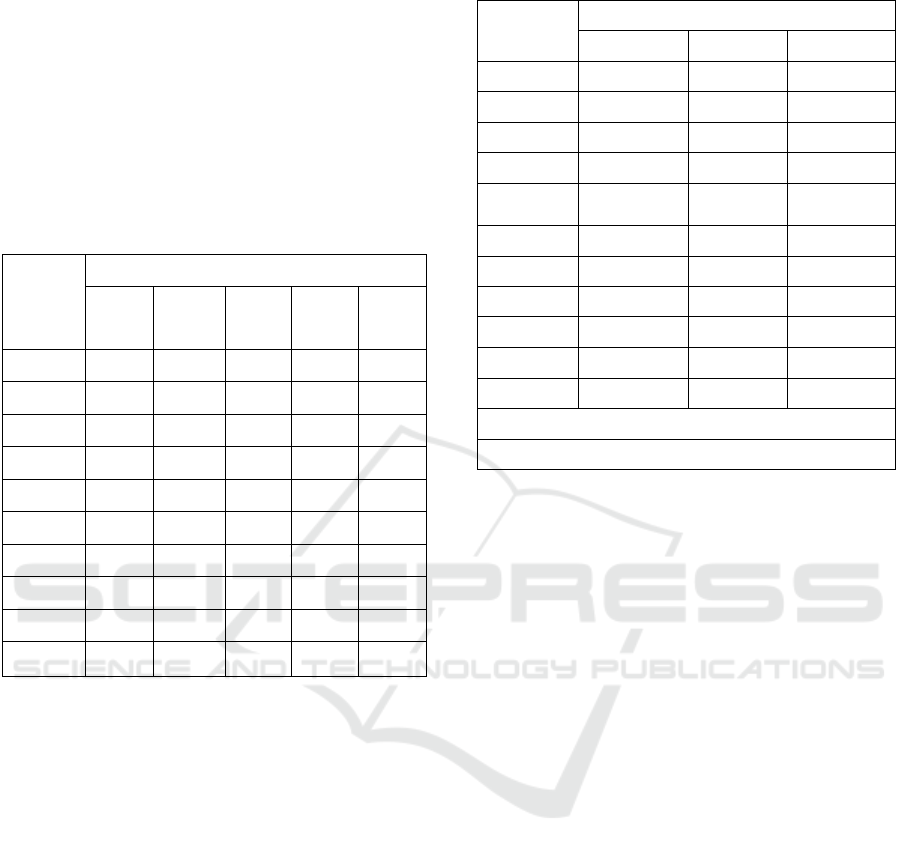
Table 1: Descriptive statistics.
Variable
Descriptive Statistical Items
Mean Median SE Min Max
Radint 0.044 0.034 0.054 0.000 2.516
Pledge 0.445 0.000 0.497 0.000 1.000
DREM -0.002 0.009 0.165 -0.652 0.496
SOE 0.344 0.000 0.475 0.000 1.000
Top1 0.335 0.316 0.137 0.085 0.729
Big4 0.048 0.000 0.213 0.000 1.000
Size 22.202 22.044 1.177 19.982 26.190
Growth 0.146 0.105 0.296 -0.493 2.276
Boar
d
2.150 2.197 0.169 1.792 2.708
Tobin 2.018 1.660 1.125 0.860 8.391
4.2 Regression Analysis
The first column of Table II reports the regression
results of the equity pledge on the innovation input
and innovation output of the first controlling
shareholder, with the regression coefficient of -0.003
at the 1% level, supporting the assumption of
H1a.The second column of Table II reports a
significant positive correlation between the equity
pledge of major shareholders and the real surplus
management at 1%, with a coefficient of 0.025,
supporting the assumption of H 2.In the third column
of Table II, after adding surplus management, equity
pledge and enterprise innovation are significantly
negatively related at 5%, and the coefficient
becomes-0.002; real surplus management and
enterprise innovation at 1%, with the coefficient of-
0.022, indicating that surplus management plays part
of the intermediary between equity pledge and
enterprise innovation. Taken together, the regression
results support the hypothesis of H 3 that there is a
partial mediation effect.
Table 2: Regression analysis.
Variable
Regression Analysis Results
Radint DREM Radint
Pledge -0.003*** 0.025*** -0.002**
(0.001) (0.003) (0.001)
DREM
-0.022***
(0.002)
controlled
variable
control control control
yea
r
control control control
trade control control control
constant 0.091*** 0.189*** 0.095***
(0.010) (0.035) (0.010)
observes 17,780 17,780 17,780
R-square
d
0.239 0.068 0.243
Standard errors in
p
arentheses
***
p
<0.01, **
p
<0.05, *
p
<0.1
5 RESEARCH CONCLUSIONS
AND RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Research Conclusions
This paper uses the data of A-share listed companies
for empirical analysis, and the following research
conclusions: the larger the equity pledge ratio of the
major shareholders, the higher the surplus
management degree, the less sufficient funds to
invest in research and development; or reduce R & D
expenditure through surplus management, the
enterprise innovation cannot be effectively
implemented.
5.2 Recommendations
Relevant countermeasures and suggestions in this
paper can be put forward from the following aspects:
First, listed enterprises should try to diversified
financing methods. Although equity pledge is a fast
and efficient financing method, financing through
equity pledge has risks. Enterprises should try
diversified financing methods to reduce the risk of
drastic fluctuations in enterprise stock prices.
Secondly, the listed enterprises should reduce the real
surplus management activities. We should give full
play to the role of internal and external supervision of
enterprises, ensure that the quality of surplus
Research on the Influence of Equity Pledge of Controlling Shareholders on Enterprise Innovation based on the Real Surplus Management
Perspective
513

information is at a relatively high level, and improve
the sustainability of enterprise development. Finally,
listed enterprises should maintain or even increase
their innovation efforts. For the long-term
development of enterprises, only continuous
innovation can have the competitiveness of the long-
term development of the enterprise. Only by making
continuous innovation, keeping up with or even
leading the trend of continuous change of the industry
can we maintain the long-term development of the
enterprise.
REFERENCES
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986) The moderator-
mediator variable distinction in social psychological
research: Conceptual, strategic and statistical
considerations. Journal of Personality and Social
Psychology, 51: 1173-1182.
Deren, X., Ke, L. (2018) Equity pledge of the controlling
shareholder and the real surplus management of the
listed company. J. Accounting Research, 39: 21-27.
Hailian, X., Meihua, Z. (2012) R & D Spending and
Surplus Management —— is based on empirical
evidence of R & D accounting policy changes [J].
Securities Market Guide, 22:48-54.
Haitao, S., Kexin, W., Yueyue, H. (2020) Influence of
major shareholder equity pledge on real surplus
management —— is based on enterprise strategic
perspective. J. Friends of the Accounting, 38: 67-74.
Judd, C. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1981) Process analysis:
estimating mediation in treatment evaluations.
Evaluation Review, 5: 602–619.
Lianchao, Y., Weiguo, Z., Qian, B. (2018) Does surplus
information quality affect enterprise innovation? [J].
Modern Finance and Economics (Journal of Tianjin
University of Finance and Economics), 38: 128-145.
Ruijun, Z., Xin, X., Chao'en, W. (2017) Major shareholder
equity pledge and enterprise innovation. J.Audit and
Economic Research, 32: 63-73.
Weilong, X., Yue, P. (2020) Study on the influence of
shareholder equity pledge on the innovation ability of
enterprises [J]. Science and technology promotes
development, 16 (12): 1603-1611.
Wen, W., Yinmo, C., Yuting, H. (2018) Research on the
Impact of Controlling shareholder Equity Pledge on
Enterprise Innovation. J. Journal of Management, 15:
998-1008.
Xia, D. (2016) Real Surplus Management with R & D
expenditure —— a GEM listed company Experience
Evidence [J]. Technology management research, 36
(04): 224-228.
Xiaodong, L., Key, Z., Jin, W. (2020) Equity pledge of
major shareholders, internal control and surplus
management [J]. Friends of the Accounting, (24): 75-
83.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
514
