
Early Warning Analysis of Company's Financial Risk based on Fuzzy
Evaluation Method
Yang Long
a
Business School, China West Normal University, Nanchong, China
Keywords: Financial Risk, Financial Early Warning, Hierarchical Analysis Method, Fuzzy Evaluation.
Abstract: With the rapid development of the automotive industry, there are more and more uncertainties in the
production and operation process, which makes the possibility of financial risks increasing day by day.
Therefore, risk identification and prevention are particularly important for enterprises, especially in the rapidly
developing and promising automotive industry. Taking Company A as an example, this paper firstly analyzes
the nature and characteristics of the industry, the company's production and operation, financial data and other
information to extract financial risk assessment indicators and establish a financial early warning indicator
system. Secondly, the financial risk early warning model is constructed by combining the hierarchical analysis
method (AHP) and fuzzy evaluation method, and finally, the established financial risk early warning model
is analyzed based on the financial data of Company A in recent years. The study aims to improve the financial
risk early warning capability of the enterprise, which is a contribution to the field.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of China's economy and
the influence of world economic integration, China's
auto industry has risen at a very impressive pace.
According to the China Association of Automobile
Manufacturers (CAAM), after sixteen years of
development, China's automobile production and
sales volume has changed from 2.07 million units in
2000 to 25.02 million units in 2016 (Hou, Peng,
2019). Undeniably, with the rapid development of the
automobile industry, there are more and more
uncertainties in its production and operation process,
and these uncertainties make the possibility of
financial risks increasing day by day. The auto
industry itself is characterized by rapid product
replacement, numerous enterprises and strong
competition, which are also increasing financial risks
in a subtle way (Hou 2019). Forty-seven percent of
Chinese companies fail because of financial
problems, and the failure is not due to the lack of
profitability, but to the lack of risk prevention and
control ability, which leads to cash flow breakage.
Therefore, the identification and prevention of risks
is particularly important for the automotive industry,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7145-2547
which is growing rapidly and has great potential for
development (Hou 2019). Among the financial risk
early warning methods, the fuzzy comprehensive
evaluation method is suitable for financial risk early
warning by converting the qualitative into
quantitative and giving a definite conclusion to the
uncertain and complex environment. This paper takes
Company A as an example to use fuzzy
comprehensive evaluation method for financial risk
early warning management research has certain
theoretical significance and practical significance.
2 THEORIES RELATED TO
FINANCIAL RISK EARLY
WA RN IN G
2.1 The Concept of Financial Risk
Early Warning
"Early warning" refers to the calculation of the
likelihood of risk occurrence based on actual data and
certain research methods, and the provision of alerts
or signals before the occurrence of risk, in order to
Long, Y.
Early Warning Analysis of Company’s Financial Risk based on Fuzzy Evaluation Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0011207900003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 669-674
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
669

prevent the occurrence of risk when conditions are
available and reduce the losses caused by risk. Early
warning of enterprise financial risk refers to the use
of theories of financial management and business
management to analyze and judge the business
activities of the enterprise based on financial and non-
financial data, so as to find out the potential risks of
the enterprise, calculate the level of risks, analyze the
reasons for the risks and give an early warning signal
to the enterprise. It enables business operators to take
appropriate preventive measures to avoid the
occurrence of dangers and reduce the losses caused
by the occurrence of risks in the enterprise (Xiong,
Zhang, 2019). To escort the production and
management decisions and the survival and
development of the enterprise.
2.2 The Function of Financial Risk
Warning
Monitoring function: The financial risk early warning
system predicts the risks that may occur in the
operation of the enterprise, based on the financial data
in the operation of the enterprise and the national
standard value of the same industry, and issues an
alarm whenever the risk reaches a certain level, so
that the enterprise decision makers can feel the
existence of risk and play a monitoring role for the
enterprise (Huang, Li, 2018).
Pulse-taking function: Based on the results of risk
analysis and evaluation, financial risk warning
identifies risk factors, finds out the reasons for the
occurrence of risk factors, and furthermore finds out
the problems against the actual situation of the
enterprise, gives the pulse of the enterprise, and
provides decision support to managers.
Treatment function: Based on the risk forecast
results, the financial risk warning identifies the risk
factors affecting the enterprise through the pulse
function, finds out the problems existing in the
enterprise operation, further proposes improvement
measures to the enterprise, and provides treatment
solutions to the managers.
Protection function: Through regular financial
risk warning, the company continuously finds out the
financial risks faced by the company, takes the pulse
of the company, provides treatment plans for the
operators, prevents and controls the occurrence of
risks in the operation, and protects the company.
3 EARLY WARNING MODEL
FOR CORPORATE FINANCIAL
RISK
3.1 Background Analysis
Company A was founded in 1984, and since the first
pickup truck was produced in 1996, the sales volume
has been growing year by year, and the market share
is in the leading position in China. And starting from
the Middle East market, it has gradually expanded
into foreign markets. Company A was listed on the
Hong Kong H-share and domestic A-share markets in
2003 and 2011, respectively.
From the analysis of Company A's production and
operation in 2016, the return on net assets in 2016 was
significantly lower. When analyzing the risk profile
in 2016, more attention needs to be paid to the reasons
for the decrease in the return on net assets and the
resulting impact on the survival and development of
the company (Yan, Wang, 2018). Identify control
measures and prevent them so that the enterprise can
gain more profits and develop more stably. Company
A has a generally high market share of each product
and the company's overall financial situation is good
(Zhang, Chen, Wang, 2017). At present, China's
automobile industry is developing rapidly and the
competition is fierce. To make the enterprise
invincible in the long run, it is not enough to manage
afterwards by analyzing the previous financial reports
alone, but to manage beforehand by combining with
regular financial risk warning.
3.2 Determination of Financial Risk
Early Warning Indicator System
Current Ratio: Current ratio is the percentage of
current assets to current liabilities. Current assets are
assets that can be realized or applied in the short term,
and current liabilities are debts that need to be repaid
in the short term, and the short term generally refers
to a business cycle. The definition shows that the
current ratio is a measure of a company's ability to
liquidate its current assets to repay its debts.
Gearing ratio: Gearing ratio is the percentage of
total liabilities to total assets. With this indicator, the
importance of capital provided by creditors can be
measured and the interests of creditors can be
protected in this way.
Total Asset Turnover: Total Asset Turnover is the
net operating income as a percentage of average total
assets. The higher the total asset turnover ratio, the
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
670
stronger the company's sales capacity and reflects the
efficiency of the company's asset operations.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Accounts
Receivable Turnover Ratio is the percentage of net
credit sales revenue to the average accounts
receivable balance. It indicates the speed of collection
of accounts receivable, that is, the speed of
conversion to cash. It also indicates how well
accounts receivable support sales revenue. A higher
accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that
accounts receivable are recovered quickly and that
the funds used for operations are turned over more
quickly.
Inventory Turnover: Inventory turnover is the cost
of goods sold as a percentage of average inventory
balance. Inventory turnover ratio indicates the speed
of inventory turnover, that is, how quickly inventory
is converted into cash or accounts receivable within a
certain period of time. The higher the inventory
turnover rate, the lower the average inventory
balance. That is, the stronger the inventory realization
ability, signifying the stronger the short-term debt
servicing ability.
Operating Profit Margin: Operating profit margin
is the percentage of operating profit to total business
revenue. The higher the operating profit margin, the
more profit the enterprise makes from sales in the
course of operation, indicating stronger profitability.
Return on total assets: Return on total assets is the
percentage of net profit to the average total assets.
The return on total assets reflects the relationship
between the effectiveness of asset utilization and
capital utilization. The higher the return on total
assets, the higher the business management level and
the stronger the competitive strength of the
enterprise.
Return on net assets: Return on net assets is the
percentage of net profit to average shareholders'
equity. The higher the return on net assets, the more
effective the utilization of assets.
Operating growth rate: Operating growth rate is
the percentage of the growth of operating revenue this
year to the total operating revenue of the previous
year. Operating growth rate reflects the growth status
and development ability of the enterprise's operating
income.
Operating profit growth rate: The operating profit
growth rate is the percentage of the total operating
profit of the previous year. The growth rate of
operating profit reflects the growth of operating profit
and development ability of this year.
Growth rate of total assets: The growth rate of
total assets is the percentage of the growth of total
assets of this year to the total assets of the beginning
of the year. The growth rate of total assets reflects the
growth and development capability of total assets.
4 EARLY WARNING ANALYSIS
OF FINANCIAL RISK OF
COMPANY A
4.1 Calculation of Financial Risk Early
Warning Indicators
After establishing the financial risk early warning
index system and early warning model of Company
A, the financial data of the company from 2012 to
2016 were applied to the financial risk early warning
to analyze the financial risk of the company.
According to the balance sheet data in Company A's
accounting annual report, the financial data from
2012 to 2016 were sorted and selected against the
financial risk early warning model, and the financial
data were organized in the table, and then the values
of each evaluation index of Company A's financial
risk were obtained as shown in Table 1.
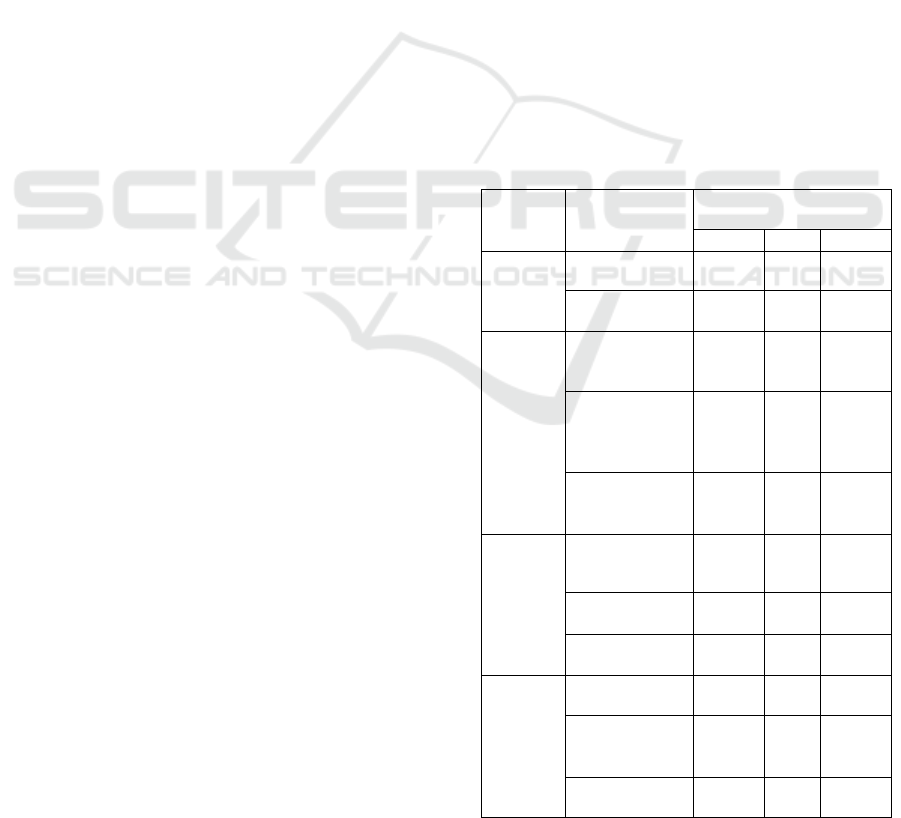
Table 1: Table of evaluation index values.
Tier 1
Indicator
s
Secondary
indicators
Early warning indicator
values
2016 2015 2014
Debt
Service
Risk
Current ratio
(%)
128.4 127 135
Gearing ratio
(%)
41.0 46.6 45.4
Operatio
nal Risk
Total assets
turnover (times)
1.23 1.06 1.02
Accounts
receivable
turnover ratio
(times)
122.31
101.
83
86.06
Inventory
turnover rate
(times)
17.47 15.0 14.5
Earnings
Risk
Operating profit
margin (%)
14.0 12.9 15.1
Return on total
assets (%)
11.5 12.1 14.1
Return on net
assets (%)
22.47 20.1 24.0
Develop
ment
Risk
Operating
growth rate (%)
12.1 21.4 10.2
Operating profit
growth rate (%)
3.56 0.40 (4.40)
Total assets
growth rate (%)
(0.28) 17.2 16.6
Early Warning Analysis of Company’s Financial Risk based on Fuzzy Evaluation Method
671
4.2 Results of Fuzzy Comprehensive
Evaluation
4.2.1 Results and Tests of Financial Risk
Early Warning Analysis in 2015.
Determining the affiliation matrix of each early
warning indicator: the standard values of enterprise
performance evaluation of the automotive vehicle
manufacturing industry in 2015 are chosen in this
paper. According to the results of Table 1, the index
affiliation matrix of 2015 year is obtained as shown
in Table 2.
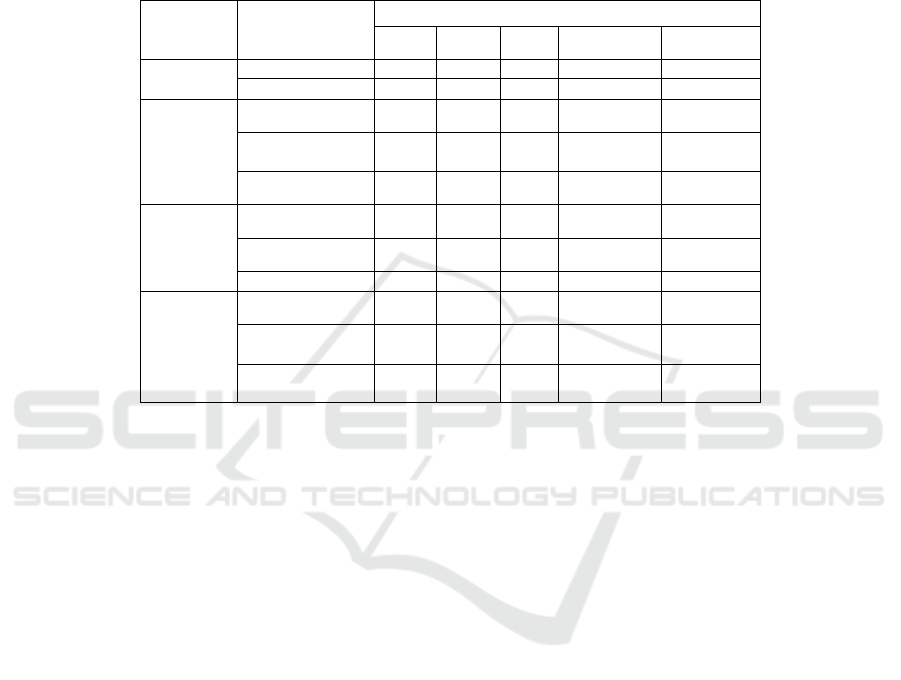
Table 2: Company A's 2015 metric affiliation matrix.
Tier 1
Indicators
Secondary
indicators
Two-level fuzzy judgment matrix
Very
safe
Safer Fair Dangerous
Very
dan
g
erous
Debt Service
Risk
Current ratio 0.94 0.06
Gearing ratio 1
Operational
Risk
Total assets
turnover
0.94 0.06
Accounts receivable
turnover ratio
1
Inventory turnover
rate
0.02 0.98
Earnings
Risk
Operating profit
mar
g
in
0.40 0.60
Return on total
assets
0.11 0.89
Return on net assets 0.77 0.23
Development
Risk
Operating growth
rate
0.75 0.25
Operating profit
growth rate
0.30 0.70
Total assets growth
rate
0.87 0.13
The first-level fuzzy synthesis evaluation of the
company's financial risk: according to the above
calculation, the relative importance weight vector
Q1=(0333,0.6667) of each secondary indicator of
company A about debt service risk, using the fuzzy
synthesis operation formula A= Qi*Ri, we get the
first-level fuzzy synthesis evaluation matrix of the
company about debt service risk:
A1=(0.6667,03133,0.0200 The first-level fuzzy
integrated evaluation matrix of the company's
operational risk is calculated as follows:
A2=(0.2322,0.1198,0.6091,0.0389,0); the weight
vector of the relative importance of the second-level
indicators of operational risk is calculated as
Q2=(0.6480, 0.2298,0.1222); the weight vector of the
relative importance of the second-level indicators of
profitability risk is calculated as follows:
A2=(0.2322,0.1198,0.6091,0.0389,0); the weight
vector of the second-level indicators of profitability
risk is calculated as Q3=(0.7380,0.0944,0.1676), the
first-level fuzzy integrated evaluation matrix of the
company regarding the profitability risk is calculated:
A3=(0.1394,0.4178,0.4428,0,0); the weight vector of
the relative importance of the second-level indicators
regarding the development risk is calculated as Q4=
(0.66602220.1111), the first-level fuzzy integrated
evaluation matrix of the company regarding the
development risk is calculated as
A3=(0.1394,0.4178,0.4428,0,0); the weight vector of
the second-level indicators regarding the
development risk is calculated as
Q4=(0.66602220.1111). The first-level fuzzy
integrated evaluation matrix A4=
(0.0967,0.5145,0.1667, 0.0667.0.1555) is calculated.
It can be seen that Company A's solvency, operating
capacity, profitability and development capacity are
within the safe range.
Second-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation:
According to the fuzzy synthesis formula: C=Q*A,
from the above calculation, the relative importance
vector Q= (0.0448,0.2674, 0.4627,0.2251) for each
first-level index of company A. The first-level fuzzy
comprehensive evaluation result A is formula (4-3),
and the second-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
result is C=(0.1782, 0.3552,0.4062,0.0254,0.0350).
The comprehensive evaluation score is calculated by
the formula Z =C*V, where V=(100,80,60,40,20),
and we get Z=72. 3, it can be seen that the financial
situation of Company A is in the range of mild risk
and is a normal operating enterprise. Among them,
the solvency reaches excellent indicators and the
financial risk is very small, but the
operating capacity,
profitability and development capacity still have
small risks, and a few indicators are not satisfactory,
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
672
especially the development capacity is slightly
poor.The early warning situation for Company A in
2015 basically matches with the actual operating
condition of the company, and the early warning
results are consistent with the current situation of the
enterprise, which can verify that the risk early
warning model constructed for Company A is
scientifically It can be verified that the risk warning
model constructed for Company A is scientific and
effective.
4.2.2 Early Warning Analysis of Financial
Risks in 2016.
Determine the subordination matrix of each early
warning indicator: based on the financial risk
evaluation index values calculated from the 2016
financial statements, the subordination matrix R is
obtained by referring to the 2016 enterprise
performance evaluation standard values of the
automotive vehicle manufacturing industry set by the
Bureau of Financial Supervision and Evaluation of
the State-owned Assets Supervision and
Administration Commission of the State Council,
corresponding to the judgment set V= {v1, v2,...
,vm}= (safe, mild, moderate, severe, serious} to find
out the affiliation matrix R. In this paper, we choose
the enterprise performance evaluation standard
values of the automotive vehicle manufacturing
industry in 2016, and finally get the index affiliation
matrix for 2016 as shown in Table 3.
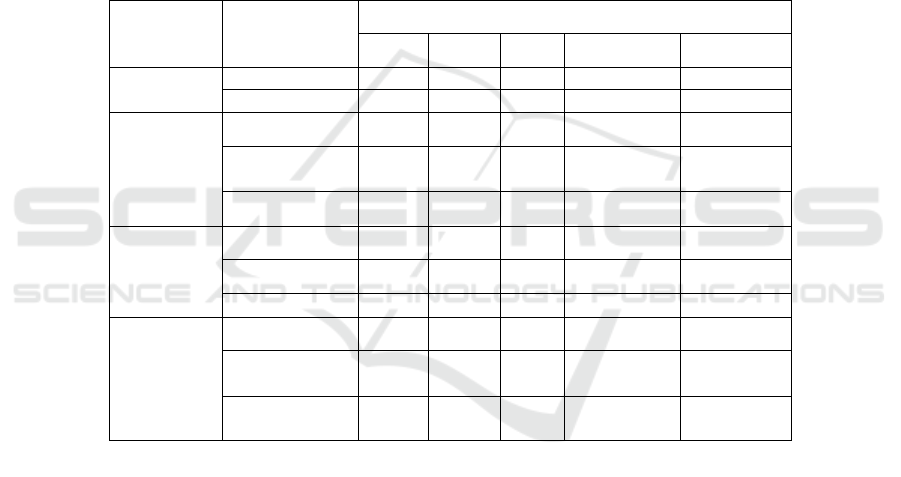
Table 3: Company A's 2015 metric affiliation matrix.
Tier 1
Indicators
Secondary
indicators
Two-level fuzzy judgment matrix
Very
safe
Safer Fair Dangerous Very dangerous
Debt Service
Risk
Current ratio 0.94 0.02
Gearing ratio 1
Operational
Risk
Total assets
turnover
0.23 0.77
Accounts receivable
turnover ratio
1
Inventory turnover
rate
0.36 0.64
Earnings Risk
Operating profit
mar
g
in
0.50 0.50
Return on total
assets
0.18 0.82
Return on net assets 1
Development
Risk
Operating growth
rate
1
Operating profit
growth rate
0.63 0.37
Total assets growth
rate
0.11 0.89
The first-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of
the company's financial risk: according to the above
calculation, it is known that the relative importance
weight vector of each secondary index of company A
about debt service risk: Q1=(03333,0.6667), using
the fuzzy synthetic operation formula A=Qi*Ri, the
first-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation matrix of
the company about debt service risk is obtained:
A1=(0.6667,0.3266, 0.0067, 0, 0); the relative
importance weight vector of each secondary indicator
of operational risk: Q2=(0.6480, 0.2298, 0.1222), and
the first-level fuzzy integrated evaluation matrix of
operational risk: A2=(0.2738, 0.2272, 0.4990, 0,0);
the relative importance weight vector of each
secondary indicator of profitability risk: Q3=(0.6480,
0.2298, 0.1222). vector: Q3= (0.7380,0.0944,
0.1676), the first-level fuzzy integrated evaluation
matrix of the company on profitability risk:
A3=(0.1846,0.4464,0.3690,0,0); the weight vector of
the relative importance of the second-level indicators
on development risk: Q4=(0.66702222,01111), the
first-level fuzzy integrated evaluation matrix of the
company on development risk:
A3=(0.1846,0.4464,0.3690,0,0); the weight vector of
the second-level indicators on development risk:
Q4=(0.66702222,01111), the first-level fuzzy
integrated evaluation matrix of the company on
development risk The first-level fuzzy integrated
evaluation matrix of the company about development
risk: A4=(0.6667,0.1400.0944,0.0989,0). It can be
seen that the solvency, operating capacity,
Early Warning Analysis of Company’s Financial Risk based on Fuzzy Evaluation Method
673

profitability and development capacity of Great Wall
Company are within the safe range in 2016.
Secondary fuzzy comprehensive evaluation:
according to the fuzzy synthesis operation
formula:C=Q*A, the relative importance weight
vector Q=(0.0448,0.2674,0.4627,0.2251) for each
level of indicators of Company A, the secondary
fuzzy comprehensive evaluation result was obtained
as C= (0.3386, 0.3134,0.3257,0.0223,0) after fuzzy
synthesis operation. The comprehensive evaluation
score is calculated by the formula Z=C*V, where
V=(100,80,60,40,20) to get Z=79.4, which shows that
the financial situation of Company A in 2016 is in the
range of mild risk and is a normal operating
enterprise, which is better than the financial situation
in 2015. Among them, solvency and development
capacity reach excellent indicators with minimal
financial risk, but operating capacity and profitability
still have some risk and a few indicators are not good
enough.
5 EARLY WARNING ANALYSIS
OF FINANCIAL RISK OF
COMPANY A
In this paper, the improved fuzzy comprehensive
evaluation method is used to construct a financial risk
early warning model for Company A. The financial
statements and related data from 2012-2016 are used
to study the financial risk early warning analysis of
Company A. The financial risk early warning model
is established and empirical analysis is conducted.
The study has certain contribution to the subsequent
research in this field. Although some conclusions
were obtained and some results were achieved in the
research process of this paper, there are still
shortcomings and we hope to explore them more
deeply in the future research process.
REFERENCES
Hou X. H. Research on the construction and application of
financial risk early warning indicators of Internet
insurance companies. Hunan Forum,2019,32(03):89-
101.
Hou XH, Peng JJ. Research on financial risk early warning
of Internet insurance companies based on entropy value
method and efficacy coefficient method. Financial
Theory and Practice,2019,40(05):40-46.
Hou XH. Research on early warning of financial risk of
Internet insurance companies based on fuzzy
comprehensive evaluation method. Hunan social
science,2019(04):88-99.
Huang J,Li LQ.Study on the application and optimization
of financial risk early warning system of KY company.
Friends of Accounting, 2018(11):150-153.
Xiong Y,Zhang Yutang. Research on early warning of
financial risks of listed companies based on F-score.
Management Modernization,2019,39 (01):111-115.
Yan Chun,Wang Zeyi. Research on early warning model of
financial risk of life insurance companies based on Pls-
Logit model. Technology and Innovation
Management,2018, 39(01):102-110.
Zhang JG,Chen F,Wang B. Research on financial risk early
warning of manufacturing companies based on PSO
optimization SVM . Friends of Accounting,
2017(14):52-56.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
674
