Strategy Optimization and Simulation Analysis of Electricity-saling
Companies under Renewable Portfolio Standard
Weiqiang Huo
1 a
, Meiting Liu
1b
, Yang Tang
1 c
and Feng Zhou
2,* d
1
Hubei Power Exchange Center, HBPX, Wuhan, Hubei, China
2
School of Economics and Management, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
*
Corresponding author
Keywords: Renewable Energy Consumption Market System, Electricity Selling Company, Trading Strategy
Optimization, Simulation.
Abstract: In the context of energy supply constraint and ecological problems, governments have actively promoted the
development and utilization of renewable energy and released a series of incentive policies, one of which is
China's Renewable Energy Consumption Guarantee Scheme (RPS). Based on the RPS, this paper constructs
an optimization model for the annual portfolio purchase strategy of power sales companies with the objective
of studying how to optimize the portfolio purchase scheme and reduce the cost of power purchase. The
simulation results show that, as RPS keeps developing and maturing, the subjects who do not complete their
consumption responsibility will bear huge fines, so the optimal strategy is: when the price of renewable power
is lower than that of conventional power, the purchase of renewable power should be given priority; if the
consumption responsibility is still not fully satisfied at this time, the excess consumption of other subjects and
the lower price of green certificates should continue to be purchased until the consumption responsibility is
completed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since global industrialization , traditional fossil
energy sources have been heavily exploited and used,
leading to energy resource constraints and
environmental degradation. The key to addressing
these problems lies in adjusting the energy structure
and increasing the proportion of renewable energy
sources (RES). China is in a critical period of socio-
economic transformation and development, and
facing the dilemma of development and
environmental protection, the "decoupling" of
economic growth and environmental problems has
become a major issue in China's green development,
of which the key lies in how to achieve a sustainable
energy system transformation based on RES. At
present, China's energy system transformation has
indeed made substantial progress. In recent years,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7623-0350
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4417-9420
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5570-1451
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3646-2907
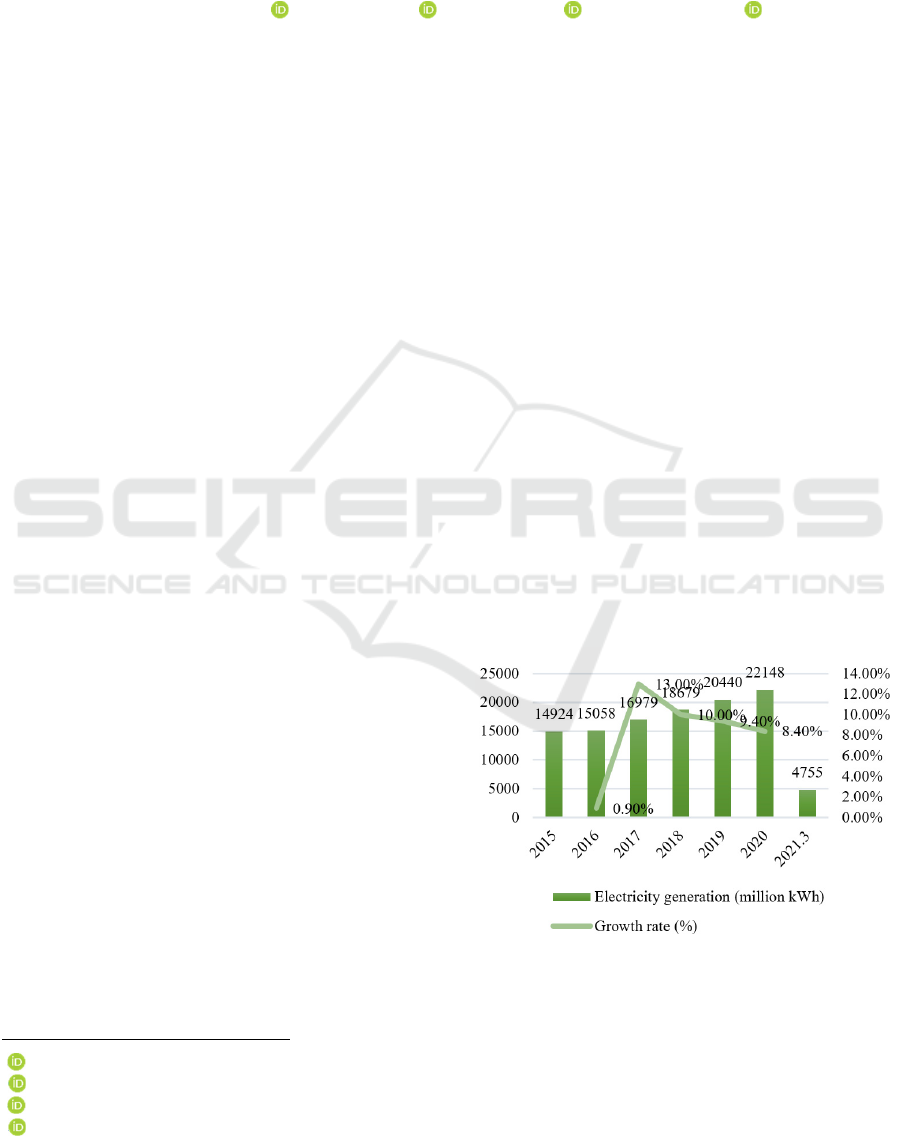
RES power generation and its installed capacity have
maintained a high level of growth (see Figure 1 and
Figure 2).
Figure 1: Renewable Energy Generation in China, 2015-
March.2021.
Huo, W., Liu, M., Tang, Y. and Zhou, F.
Strategy Optimization and Simulation Analysis of Electricity-saling Companies under Renewable Portfolio Standard.
DOI: 10.5220/0011260600003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 725-730
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
725
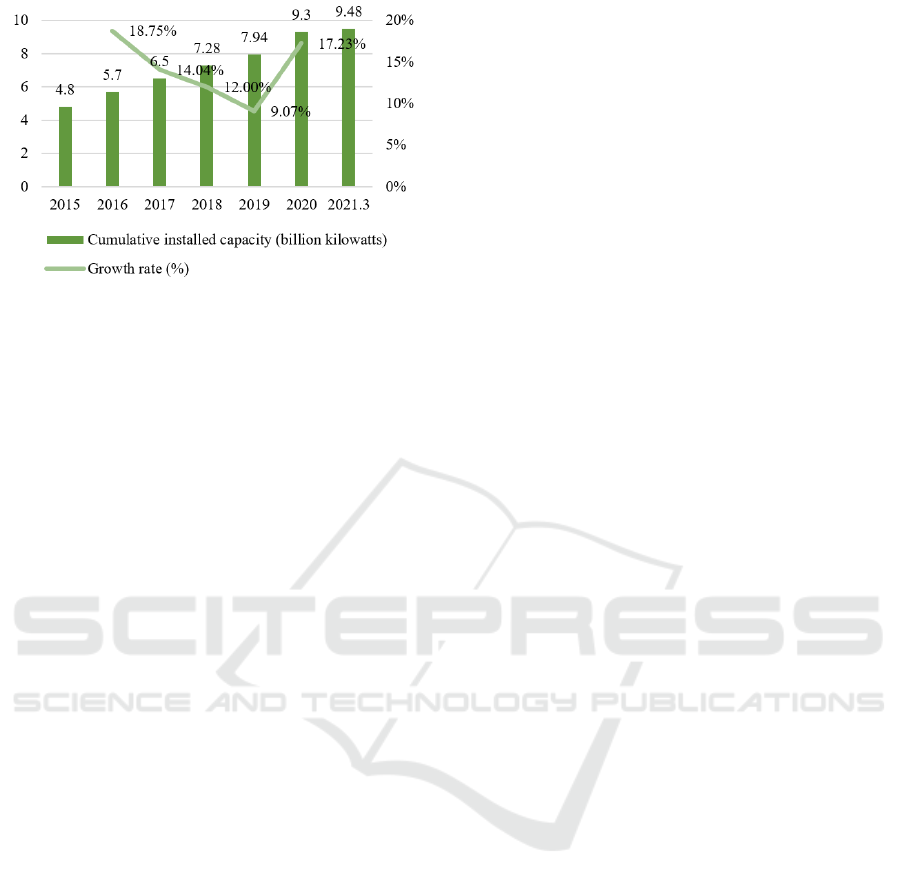
Figure 2: Cumulative Installed Capacity of Renewable
Energy Generation in China, 2015-March.2021.
However, with the gradual expansion of the scale
of RES, its consumption problem is increasingly
prominent. 2018 the amount of China's annual "three
abandoned" power was more than 100 billion
kilowatt hours, equivalent to the annual power
generation of the Three Gorges Power Station.
Therefore, in order to improve the RES consumption
rate and change the increasingly serious situation of
the new energy subsidy gap, the National
Development and Reform Commission and the
Energy Bureau jointly issued the Notice on
Establishing a Sound Renewable Energy Power
Consumption Guarantee Mechanism (hereinafter
referred to as "the Notice") on May 10, 2019, which
set the RES power consumption responsibility weight
for each provincial administrative region. In this
context, power sales companies have been able to
make a significant contribution to the development of
the renewable energy market. In this context, it is
important to study the trading strategy of power sales
companies as the first type of market players who
bear the responsibility of RES consumption.
2 REVIEW OF THE
LITERATURE
2.1 Review of Renewable Energy
Consumption Mechanism in China
Renewable energy power consumption guarantee
mechanism, also known as renewable energy quota
system (RPS), refers to a country or region mandatory
requirement that a certain percentage (i.e., quota
standard) of the power supplied by the power system
must be RES. foreign research on RPS started earlier,
the literature (
Helgese 2018
) established the electricity
market and green certificate trading market
equilibrium model, the study founds that the
implementation of RPS not only improves production
technology, but also can further improve social
welfare. The feasibility of implementing RPS in
China and its institutional design has been a research
hotspot for scholars in China for many years:
literature (
Feng 2017) selected indicators such as
obligation subject, operation mode, form of quota
target, and degree of incentive, summarized and
analyzed the practical experience of countries
currently implementing RPS on the electricity sales
side, and analyzed the feasibility of implementing
RPS on the electricity sales side in China with our
national conditions, and also designed the
implementation of quota system on the electricity
sales side in China The framework of RPS in China
is designed.
The RPS is the product of a series of policy
promotion. the Notice issued in May 2019 clearly
decomposes the required RES power consumption to
regional power sales companies and power
consumers and assesses their completion; the Notice
on the Preparation Outline of the Implementation
Plan for Provincial Renewable Energy Power
Consumption Guarantee (hereinafter referred to as
the Outline) issued in March 2020 further clarifies the
management mechanism and task division of labor
(
Zhang 2019) . The literature (Zhong 2020) argues that
the RPS jointly established by the Notice and the
Outline contains two main aspects.
1) The bearer of the consumption
responsibility: There are two types of market
participants, namely: ① grid enterprises,
independent power sales companies, and power sales
companies with the right to operate distribution grids,
which supply (sell) electricity directly to power
consumers; and ② power consumers and
enterprises with self-provided power plants, which
purchase electricity through the wholesale power
market. The quota is to be borne by the electricity
sales side rather than the generation side.
2) Market transaction mechanism for quota
assessment: The quota system is designed with two
sets of mechanisms to meet the weight of
consumption responsibility through market-based
transactions: (i) purchase the "excess" from market
players who have exceeded the annual consumption
volume, and both parties independently determine the
transfer (or transaction) price; (ii) voluntarily
subscribe to the "green certificate", and the RES
power corresponding to the green certificate is
recorded as the consumption volume.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
726
2.2 Review of the Trading Strategies of
Electricity-saling Companies
Foreign market-based reforms are earlier, and
literature (
Nojavan 2017
) combines multiple power
purchase paths such as RES and distributed power
sources to propose a variety of pricing schemes for
power sales companies for electricity contracts. In the
domestic literature (
Dai 2021
), in order to analyze the
impact of renewable energy consumption
responsibility assessment on power sales companies,
a power purchase portfolio investment model is
established; the penalty mechanism of consumption
responsibility assessment is introduced to realize the
evaluation of the role of assessment strength. The
literature (
Zhou 2020
) established a power purchase
portfolio investment model in order to analyze the
impact of renewable energy consumption
responsibility assessment on power sales companies.
3 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION AND
MODELING
3.1 Problem Description
1) Trading of Excess Consumption
After the electricity selling company and the
customer have completed the corresponding
consumption in the renewable energy trading market,
the consumption beyond the quota obligation can be
sold in the excess consumption trading market to gain
revenue, and the shortage can also be bought in the
market to realize the substitution of consumption
between responsible entities.
2) Trading of Green Certificates
Green certificates themselves do not have any
value, but under the quota system, their own price
reflects the environmental value of RES generation -
RES generators can sell their green certificate
holdings in the green certificate trading market and
receive additional green certificate proceeds, thus
compensating for the portion of RES generation costs
that exceed conventional energy generation,
effectively reducing the government's financial
burden.
3) Optimization problem of trading strategy for
Electricity-Saling companies
The power seller needs to make decisions in the
traditional spot market for electricity, the spot market
for renewable energy, the spot market for excess
capacity, and the spot market for green certificates, so
as to minimize the cost of power purchase under the
condition that the load demand and the minimum
consumption weight of renewable energy are met
(and bear the corresponding penalty when they are
not met).
In this paper, we take the optimal purchase
problem in the long-term phase (one year) as an
example, and study how the power seller allocates the
appropriate purchase ratio in the above markets to
meet the electric energy demand and renewable
energy quota requirements to maximize profit (with a
fixed sales tariff, the minimum cost of power
purchase can be used as an equivalent substitute for
the maximum profit).
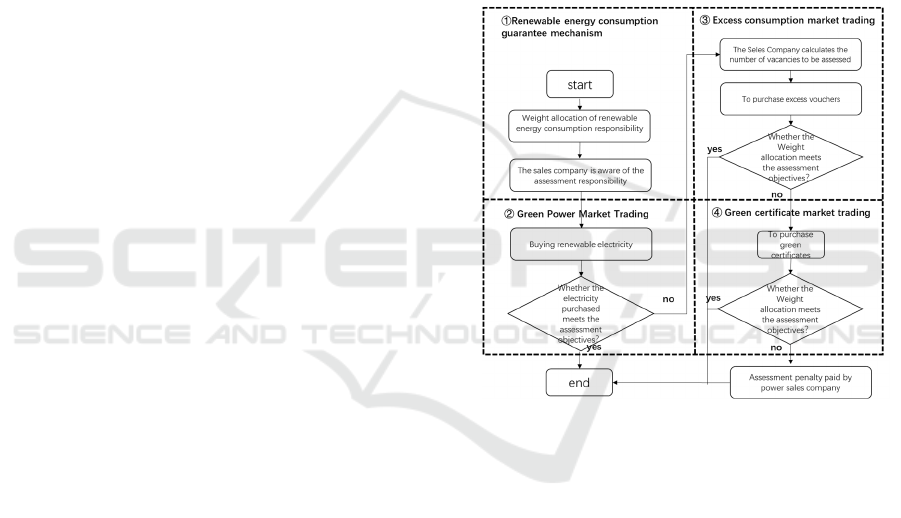
3.2 Problem Modelling
Figure 3: Renewable energy consumption market system
framework.
In the above process, because the power sales
company needs to ensure that the proportion of
purchased RES power is not less than k (consumption
weight), its transaction costs in carrying out power
trading business can be specifically divided into
power purchase costs and certificate costs: power
purchase costs include both traditional power and
green power, certificate costs include over-
consumption voucher expenses and green certificate
expenses (if the assessment target is not completed,
the shortage part pays the corresponding penalties ).
The mathematical expressions are as follows.
𝑚𝑖𝑛 𝐶
+𝐶
+
𝐶
+𝐶
+
𝑀⋅𝑚𝑎𝑥
𝑘𝑄 𝑄
𝑄
𝑄
,0
(1)
Strategy Optimization and Simulation Analysis of Electricity-saling Companies under Renewable Portfolio Standard
727
In the above equation, 𝐶
and 𝐶
denote the
power purchase cost for power sales companies to
purchase conventional power and renewable energy
power in the medium and long-term power market,
respectively, 𝐶
and 𝐶
denote the power
purchase cost for power sales companies to purchase
excess consumption vouchers and green certificates
in the excess consumption trading market and green
certificate trading market, respectively, and the last
term is the penalty cost, M is the penalty for the
assessed unit of electricity.
𝐶
=𝑝
⋅𝑄
(2)
𝐶
=𝑝
⋅𝑄
(3)
𝐶
=𝑝
⋅𝑄
(4)
𝐶
=𝑝
⋅𝑄
(5)
𝑄
、𝑄
、𝑄
、𝑄
indicate the purchase of
traditional power, renewable power, excess
consumption, and green certificates, respectively. In
the actual trading process of excess consumption and
green certificates, the subject of the transaction is the
voucher, but a voucher is equivalent to 1MWh of
renewable energy consumption, and in this paper, for
the purpose of unifying the quantum of a variable, all
of them are converted into units of electricity to
express.
𝑝
denotes the price of thermal power purchased
by the power selling company in the medium and
long-term power market. Thermal power is basically
stable in the current stage of the power market price,
so this price is set in this paper as a value that
fluctuates randomly within a small range, and
considering the environmental cost of its generation,
its price is bound to be higher than the market price
of renewable power 𝑝
; 𝑝
is the transaction price
of the power selling company in the RET market
transaction; 𝑝
and 𝑝
denote the license
purchase price of the power selling company in the
excess capacity market and the green license market,
respectively.
Constraints of power purchase and consumption
assessment for power sales companies:
𝑄=𝑄
+𝑄
(6)
𝑘⋅𝑄≤𝑄
+𝑄
+𝑄
≤𝑄
(7)
4 EXAMPLE ANALYSIS
Electricity price fluctuations and market demand
fluctuations are the risks that electricity sellers are
bound to face when participating in monthly and
annual centralized market bidding transactions.
Therefore, in the setting of the relevant parameter
values of this model, all kinds of electricity price
fluctuations and electricity consumption fluctuations
are considered, and the annual contracted electricity
and renewable energy consumption are decomposed
into each month, and the final combination forms an
annual optimal power purchase strategy.
4.1 Setting of Parameter Values
Consider the elimination weight k=0.3250 (constant)
and the unit penalty M=$10/unit (constant).
1
)
Fluctuations in electricity prices and electricity
market demand by category
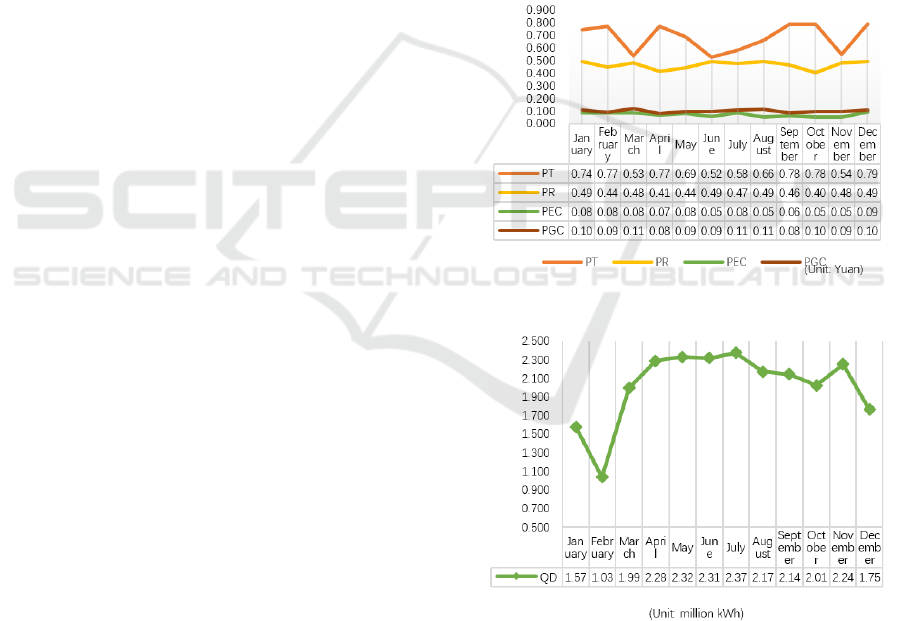
The fluctuation of various types of electricity
prices with the market over the 12-month period is
shown in Figure 4, and the QD (electricity market
demand) also fluctuates with the market conditions,
which is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4: Monthly average transaction price chart.
Figure 5: Electricity demand chart by month for power
sales companies.
2)Monthly QR, QEC Caps
There is almost no oversupply in the thermal
power market, so there is no cap constraint on QT
(purchased conventional power). However, the RES
market has lower prices due to the presence of
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
728
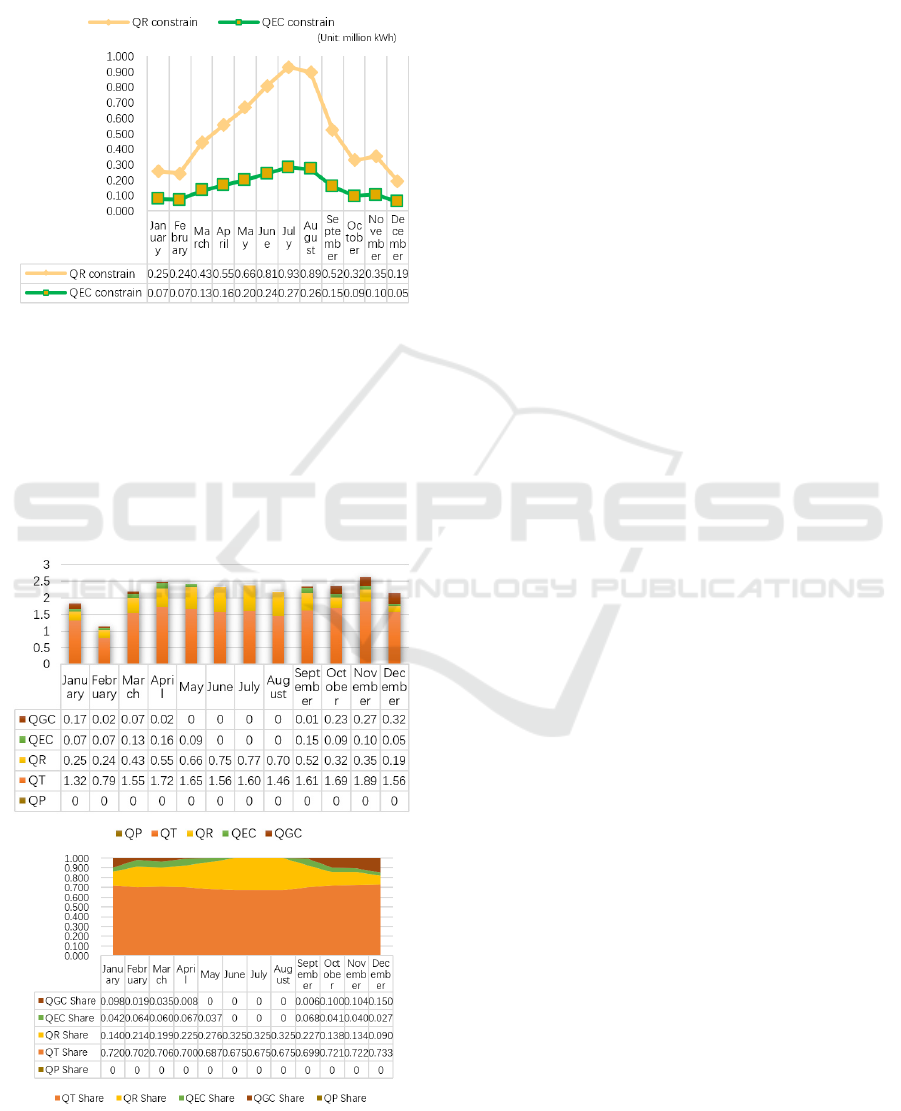
government subsidies and lower excess market prices
relative to green certificates, so there are constraints
on QR (purchased RES electricity power) and QEC
(purchased excess). Their limits that fluctuate with
the market are shown in Figure6.
Figure 6: QR and QEC constrains..
4.2 Simulation Analysis
Using matlab to simulate and analyze the case, we get
the purchase amount of each type of electricity and
the percentage of each type of electricity to the total
monthly electricity in 12 months under the optimal
decision as shown below, and the minimum total cost
under the optimal decision is RMB 15415676.76.
Figure 7: The chart of transaction results.
4.3 Analysis of Algorithm Results
1) Analysis of QP values
The annual QP is constantly 0. This is due to the
fact that with the implementation of the national
policy, the RPS is gradually maturing, so the penalty
for the responsible body to complete the consumption
volume is stronger, as shown by the unit penalty M of
10 yuan/unit - much higher than the unit price of other
types of electricity.
2) Analysis of QR values
Throughout the year, QR reached the upper limit
of the renewable energy limit constraint for
the month.
This is due to the existence of government financial
subsidies, resulting in much lower RES electricity
prices compared to conventional electricity prices,
rational power sellers will prefer RES electricity, so
in the premise that the demand for electricity on the
sales side of the market is greater than the supply of
RES electricity, RES electricity will be "snapped up".
3) Analysis of QEC values
From the simulation results, it can be seen that the
QEC reaches the upper limit of the excess constraint
for the month from January to April and from
September to December. This is due to the fact that
the price of "excess" is lower in this simulation
compared to "green certificates", so a rational
generator will give priority to purchasing excess to
fulfill the consumption responsibility if the market
demand is met and the consumption responsibility is
not met. In May, because the unfulfilled consumption
responsibility did not need to be satisfied by
purchasing all the "excess", and the price of "excess"
was still higher than that of "green certificates", only
"Since the RES consumption responsibility has been
fulfilled by QR from June to August, there is no
longer a need for the "excess" or "green certificates".
4) Typical Month Analysis
a) December: QT and QGC both takes the
largest share of electricity.
The QD (electricity market demand) in December
is small, but the QR cap is also small, so in order to
meet the QD, the remainder after all QRs are
purchased has to be provided by QT, which results in
the largest QT share in the 12 months; the small QR
cap also results in the QR alone not being able to meet
the consumption responsibility, so the excess or green
certificates have to be purchased; unfortunately, the
excess in December is exactly the smallest in the year,
and all the excess It is also impossible to meet the
remaining consumption responsibility. This results in
the remaining part of the surplus needing to rely on
"green certificates", and the remaining part is
Strategy Optimization and Simulation Analysis of Electricity-saling Companies under Renewable Portfolio Standard
729

relatively large, which explains why QGC accounts
for the largest percentage of the year.
b) February: When QD is minimal, purchase
decisions for all types of electricity are
considered.
February QD is the smallest of the year, when the
price of RES power is still lower than that of
conventional power, so priority is still given to
meeting market demand with all the RES power
available for purchase, and the remaining unsatisfied
portion is supplemented by conventional power.
However, the QR cap in February cannot meet the
consumption responsibility, so QEC and QGC still
need to be purchased; at this time, the price of
"excess" is still lower than that of "green certificates",
so priority is given to the purchase of "excess ".
However, the "Excess" cap in February is still unable
to meet the remaining consumption responsibility, so
finally, we still need to purchase 1.95% of the total
monthly power QGC.
c) July: When QD is at its maximum, purchase
decisions for all types of electricity are considered.
July QD is the largest of the year, and the RES
power available for purchase is also the largest of the
year, while the price of RES power is still lower than
that of conventional power, so priority is still given to
meeting the market demand with all the RES power
available for purchase, and the remaining unsatisfied
portion is supplemented by conventional power.
5 CONCLUSIONS
As the retail side of the grid continues to be
liberalized and the RPS continues to be improved, it
is critical that electricity sellers, as the obligated
bearers of consumption responsibility, adopt an
appropriate power purchase strategy to balance the
cost and risk of power purchase. In this paper, we
examine the combination of traditional, RES,
"overage" and "green certificates" strategies of
electricity sellers under the RPS on a monthly basis
with minimum annual purchase costs.
(1) Since the existence of government
subsidies keeps the price of renewable energy at a
lower level than the price of conventional energy,
electricity sellers should give priority to the purchase
of renewable electricity to meet their consumption
responsibilities.
(2) As the renewable energy quota system
continues to develop and mature, the ability of power
sales companies to meet their quotas will gradually
increase, and they will no longer have to rely on the
renewable energy contract market to meet their quota
needs, as they did in the early stages of development.
For fixed quota targets, purchases in the over-
consumption and green certificate spot markets will
also continue to increase as their prices fall.
(3) With the increase of renewable energy
quota target, the purchase volume of power sales
companies in renewable energy contract market,
excess consumption and green certificate spot market
will increase. The government can improve China's
power supply structure by increasing the quota target,
which will lead to a larger scale of renewable energy
consumption, but it cannot be increased indefinitely,
otherwise it will affect the operating efficiency of
power sales companies, and the quota target should
be reasonably set in accordance with the actual
situation of each region.
REFERENCES
Feng, QH Liu, Y Liu, S Wang. Exploring the Design of
Renewable Energy Quota System in China's Power
Sales Side (J). Automation of Electric Power System,
2017,41(24):137-141+158.
Helgesen, P.I. and A. Tomasgard, An equilibrium market
power model for power markets and tradable green
certificates, including Kirchhoff's Laws and Nash-
Cournot competition. Energy Economics, 2018. 70: p.
270-288.
Nojavan, S., K. Zare and B. Mohammadi-Ivatloo,
Application of fuel cell and electrolyzer as hydrogen
energy storage system in energy management of
electricity energy retailer in the presence of the
renewable energy sources and plug-in electric vehicles.
Energy Conversion and Management, 2017. 136: p.
404-417.
S Zhong, ZX Zhang, YH Guo, ZF Liang, L Ai, X Yan, Y
Li. Research on the pricing mechanism of renewable
energy power excess consumption transaction (J). Price
Theory and Practice, 2020(06):52-55+128.
SW Dai, L Zhang, NN Liu, M Yang, C Liu, SN Cao.
Analysis of Power Purchase Decisions of Electricity
Sales Companies Considering Renewable Energy
Consumption Responsibilities(J). Electric Power,
2021,54(09):156-164.
X Zhang, Z Chen, ZM Ma, Q Xia, XJ Dai, DX Lu, R Zhao.
Research on Electricity Market Trading System
Adapted to Renewable Energy Quota System (J).
Power Grid Technology, 2019,43(08):2682-2690.
XJ Zhou, Q Peng, R Yang, ZY Han, M Wang. Research on
E-commerce Bidding Strategies for Comprehensive
Energy Sale Considering the Impact of Transmission
Congestion under the Influence of Green Power
Certificate Transactions (J). Power Grid Technology,
2020,44(04):1317-1324.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
730
