
Research on Optimization Technology of Cost Management and
Control of Power Grid Enterprises under the Background of Smart
Grid Application
Jing Yu and Yaru Han
Power Economic Technology Research Institute of State Grid Fujian Electric Power Co., Ltd., Fujian, Fuzhou, 350012,
China
Keywords: Factor Analysis, Photovoltaic Energy, Listed Companies, Financial Analysis.
Abstract: With the continuous advancement of power science and technology, strengthening the intelligent
construction of power grids has become one of the key development strategies of power grid enterprises.
The invoice terminal in the business hall of a power grid enterprise is an important link between the power
grid and power customers, and it is also an important indicator of the intelligent level of the power grid. For
this reason, the grid enterprise has invested a lot of money in the investment and construction of the invoice
terminal and technology upgrade. However, the lack of in-depth cost-effective analysis of the input of the
invoice terminal by the power grid enterprises has caused problems of low capital input efficiency of the
invoice terminal from time to time. Therefore, this paper selects F provincial-level grid enterprise business
hall invoice terminal as the research object, combines the DEA theory to carry out the input cost
effectiveness evaluation, and analyzes the main factors affecting the output effect of the invoice terminal, in
order to further promote the intelligent development of the power grid. Provide reference and reference for
the effect of enterprise capital input and output.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, as social and economic development
enters a new normal, external supervision and
inspection have become stricter, electricity prices and
the complexity of the operating environment have
increased, and the implementation of the deepening
of the strategic system of power grid companies and
the continuous improvement of high-quality
development requirements. In this context, power
grid companies must attach great importance to cost
input and output effects and improve cost
management efficiency.
Literature (
Jin, 2021) analyzed the current status
and problems of cost accounting management of
power grid companies, and based on the perspective
of comprehensive budget management, proposed a
cost accounting optimization strategy for power grid
companies. Literature (
Wang, 2020) starts from the
situation faced by power grid enterprises and the
status quo of cost management, and proposes
measures to strengthen lean cost management of
enterprises, which provides a reference for
enterprises to improve their cost management level.
From the perspective of supply chain, the literature
(
Wu, 2021) takes T Grid Company as the specific
research object, conducts in-depth research on T Grid
Company’s infrastructure projects, finds the
shortcomings of T Grid Company’s cost
management, and proposes corresponding
optimization suggestions. Literature (
Xu, Ling, Cheng,
Wang, 2019
) analyzed the impact path of the power
transmission and distribution price reform on the cost
management, fixed asset management, investment
management and budget management of power grid
enterprises, and proposed a "one foundation, three
grasps" financial management strategy. Literature
(
Zou, Zhang, Wu, Chen, 2020) based on the traditional
weighted average cost of capital calculation method,
introduced the risk adjustment coefficient of power
grid projects, proposed a weighted cost of capital
(WACC) model suitable for power grid companies’
overseas investments, and obtained key international
regions through empirical analysis. Based on the
WACC calculation results, a regression fitting
analysis was carried out through WACC and credit
risk rating quantitative indicators, and a credit rating
risk adjustment model was proposed.
Yu, J. and Han, Y.
Research on Optimization Technology of Cost Management and Control of Power Grid Enterprises under the Background of Smart Grid Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0011360200003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 967-972
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
967

It can be seen from the above that the relevant
research on the cost input-output effect of power grid
enterprises is still blank. Therefore, it is necessary for
this article to select the typical business types of
power grid companies to carry out cost input
effectiveness analysis and research.
2 INVOICE TERMINAL
BUSINESS INTRODUCTION
2.1 Business Background
With the popularization of the mobile Internet, the
public has put forward higher requirements for
service quality while the demand for electricity
continues to increase. On this basis, the invoice
terminal has gradually become an important part of
the business hall of the power grid company. From
the experience point of view, high-quality service
means friendliness and convenience, which is
conducive to improving the business environment.
Relying on technical advantages and understanding
of customers' own needs, the invoice self-service
terminal provides customers with a strategy of
efficient experience. Adding self-service can
alleviate the problem of excessive traffic in
traditional business halls, make up for the lack of
original business hours, and provide customers with
better service. Come for easy, convenient and
considerate service. As an extension and supplement
of
the service of the business hall, the self-service
Figure 1: Wall-mounted multi-function self-service
terminal.
Figure 2: Through-the-wall multi-function self-service
terminal.
invoice terminal has gradually become an
indispensable strategic means and tool.
2.2 Necessity Analysis
As a self-service payment channel for customers, the
invoice terminal can effectively divert the payment
business in the physical business hall, shorten the
time for customers to pay in the business hall, and
reduce the overall service and marketing costs of the
enterprise. It is an effective part of the physical
business hall. Compared with the traditional service
mode, self-service terminals have obvious
advantages: First, self-service terminals adopt
human-computer interaction, which avoids problems
such as customer dissatisfaction caused by service
attitude and service quality. Second, labor costs are
getting higher and higher, and the advantages of self-
service terminals in saving labor and reducing
operating costs will become increasingly prominent.
The third is that the self-service terminals put in
place extend the service hours of the business halls,
provide customers with more convenient services,
and improve the cost-effectiveness of business
outlets. Fourth, self-service terminals, as modern and
automated advanced equipment, have established a
good public image for power grid companies.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
968
2.3 Service Objects and Objectives
Service object: electricity customers with various
needs such as business application, list printing,
invoice printing, scanning code payment, etc.
Invoice terminal
service content
Electricity business
application
List printing
Invoice printing
......
Scan code to pay
Figure 3: Invoice terminal service content.
Service objectives: First, to effectively relieve the
pressure of queuing in the business hall and improve
the efficiency of business settlement. The second is
to save human resources, reduce labor costs and the
total operating costs of business halls. The third is to
improve the work efficiency and quality of the staff
in the business hall, and reduce the workload of the
staff.
Function
Relieve business
pressure
Save human
resources
Reduce labor costs
Reduce employee
workload
Improve employee
productivity
Figure 4:Invoice terminal function.
3 RESEARCH ON THE
EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS
SYSTEM OF INVOICE
TERMINAL COST INPUT
BASED ON DEA THEORY
3.1 Basic Ale of DEA Theory
There are many types of DEA models, among which
the theory of the
RC
2
model is relatively complete.
Competing power companies are the decision-
making units. There are a total of
n
power
companies. Each power company has
m
types of
input (X) and
s
types of output (Y),
j
DWU
's input
and output
12
(, ,..., )
T
jjjmj
xxx x=
,
12
( , ,..., )
T
jjjsj
yyy y=
,
nLj ,,2,1=
.
0
0
max
.. 1
0, 0
T
T
T
j
T
j
uy
vx
uy
st
vx
uv
≤
≥≥
(1)
Among them,
12
(, , , )
T
m
vvv v=
and
12
(, , , )
T
s
uuu u=
respectively represent the
weight coefficients of
m
types of input and
s
types
of output. The Charnes-Cooper transformation of the
above formula can be transformed into an equivalent
linear programming model:
0
1
0
1
1
min
..
0, 1, 2, ,
n
j
j
n
jj
j
j
st x x
yv
jnE
θ
λθ
λ
λθ
=
=
+
≤
≥
≥= ∈
(2)
The model after being processed by non-
Archimedes infinitesimal (
ε
):
Research on Optimization Technology of Cost Management and Control of Power Grid Enterprises under the Background of Smart Grid
Application
969
0
1
0
1
1
min[ ]
..
0, 1, 2, , , 0
TT
n
j
j
n
jj
j
j
SS
st x S x
ySy
jnES
ee
θ
λθ
λ
λθ
∧∧
−+
−
=
+
=
+−
−+
+=
−=
≥= ∈ ≥
(3)
Among them,
TT
Le )1,,1,1(
ˆ
= , if 1
0
=
θ
,
0=
−
S
,
0=
+
S
are satisfied, then
0j
DWU
is
called DEA.
Suppose the optimal solution of the model is
0
θ
,
0
λ
,
−0
S
,
+0
S
, if
1
0
=
θ
, and
0
0
=
−
S
,
0
0
=
+
S
, then DMU is called DEA
effective; if
1
0
=
θ
, and
0
0
≠
−
S
,
0
0
≠
+
S
,
then DMU is called weak DEA effective; if
1
0
<
θ
,
the DMU is said to be non-DEA valid.
Its economic significance is: if a decision-making
unit is DEA effective, from the perspective of the
production function, it is both technically effective
and scale-effective, that is to say, for these decision-
making units, the input
X
and the output obtained
Y has reached the optimum.
3.2 Construction of Cost-effectiveness
Analysis Index System
Based on the invoice terminal cost input
characteristics and output effect, the analysis index
system is shown in the table below:
Table 1. Cost benefit analysis index system.
Investment index
Number of invoice
terminal configuration
Number of employees
Investment costs
Effectiveness and output
effect index
Frequency of bill
printing
4 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
This paper takes the cost input of F provincial power
grid enterprise Z and N as the cost effectiveness
analysis.
4.1 Analysis of the Cost and Input
Situation
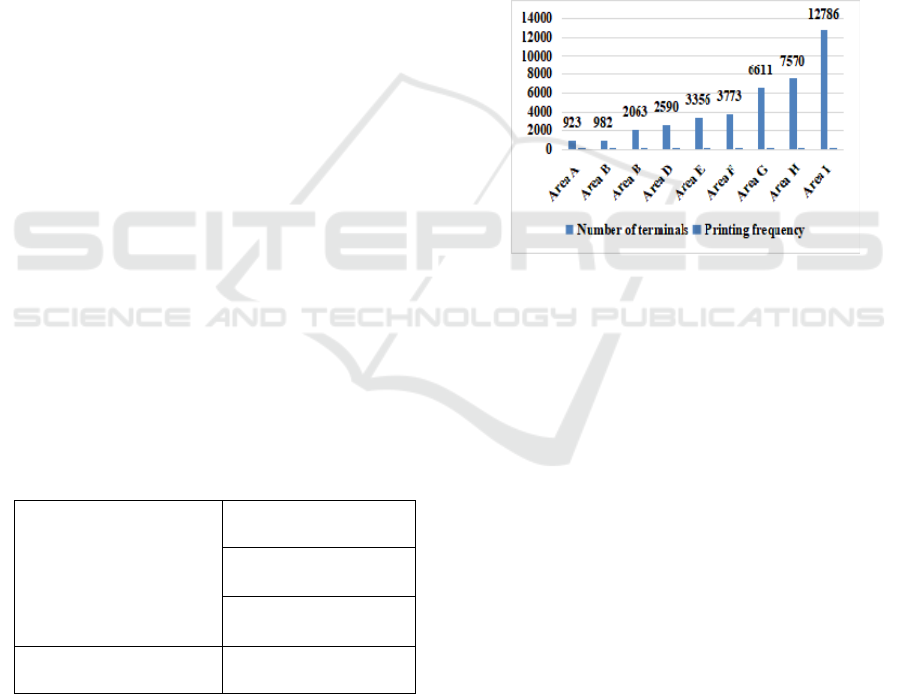
Z company invested a total of 80 invoice terminals,
with a total cost of 2,178,400 yuan. Among them: 26
receipt printing terminals were funded by the
provincial company, and M company leased in by
means of financial leasing, with a total cost of
278,200 yuan. 54 units were funded by M company,
of which 14 QR code scanners were purchased
through low-value consumables at a total cost of
70,000 yuan, and 40 integrated business handling
terminals were leased in the form of operating leases,
with a total cost of 1,830,200 yuan. The usage of
invoice terminals in 9 regions of Z company is
shown in the figure below:
Figure 5: Comparison of invoice terminals in different
regions of Z company.
It can be seen from the above figure that the use
frequency of invoice terminals in Z company is
uneven, with great differences.
N Company N’s 90 invoice terminals, with a
total cost of 2,610,200 yuan, were all purchased by
Ningde Company. Among them: 28 three-in-one
smart self-service payment terminals and 9 QR code
scanning printers were rented in operating leases at a
cost of 1,995,600 yuan; 14 self-service invoice
printers were rented in by financial leasing at a cost
of 447 million yuan; 39 Two QR code scanners were
purchased as low-value consumables at a cost of
167,600 yuan and a total cost of 2,610,200 yuan.
The usage of invoice terminals in 7 regions of
company n is shown in the figure below:
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
970
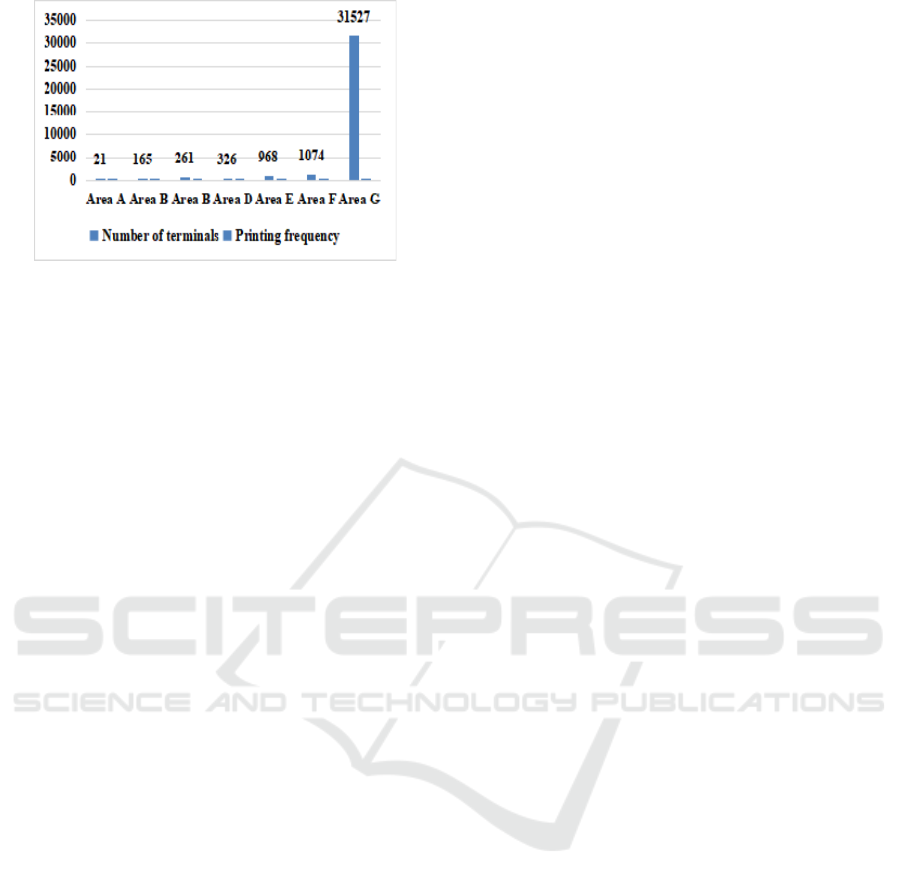
Figure 6: Comparison of invoice terminals in different
regions of N company.
It can be seen from Figure 6 that the use
efficiency of invoice terminal of company n is much
lower than that of company Z.
4.2 Conclusion of Cost-effectiveness
Analysis based on DEA Theory
Combined with the DEA analysis and conclusions,
combined with the actual use of the invoice terminal,
the problems with the cost input of the invoice
terminal of the F provincial grid enterprise are as
follows:
1) Lack of standards for terminal launch At
present, there is no unified standard for terminal
release. Terminal release control is extensive.
Business halls declare purchases according to their
needs, and then allocate them to business halls
according to business volume and passenger flow.
There is a large discretionary power and no unified
release standard has been formed. Unified
management and control.
2) The terminal utilization rate is uneven Z
company and N company's invoice terminal use
frequency is uneven, there is a large deviation in
input-output effect, it is necessary to
comprehensively consider factors such as regional
economy, business hall traffic, business volume and
other factors to rationally optimize the number of
terminal inputs.
4.3 Improvement Suggestions
First, the unified and clear terminal delivery
standards. Formulate scientific and reasonable
terminal delivery standards, standardize the source
of funds, conduct unified control over the terminal
demand declaration, and then give delivery after
professional examination and approval, strengthen
lean control, to provide institutional guarantee for
the standardized operation of the terminal.
Second, to establish a terminal regular analysis
mechanism. Strengthen data acquisition, timely and
accurately obtain various business data of terminal
operation through application platform, improve
analysis efficiency, conduct multi-dimensional
comparative analysis of the terminal use efficiency
by collecting data, strengthen closed-loop control,
trace the root cause according to analysis results, and
reasonably allocate idle resources in the region to
ensure the overall use efficiency of the terminal.
Third, optimize the allocation of resources and
utilization efficiency. Comprehensive control the
demand of terminal use, and study measures
according to local conditions to improve the
efficiency of terminal use. Based on the problem of
low use efficiency of terminals in individual
business halls, consider the overall coordination,
allocation and revitalization within the region, so as
to improve the penetration rate and utilization rate of
terminals in the whole region. At the same time, the
promotion of online electronic invoice may bring
negative impact to the business hall terminal,
including whether terminal purchase scientific, cost
economy, reasonable additional input, use
efficiency, etc., it is necessary to analyze the
terminal utilization efficiency, the overall control
around the use of the terminal, provide support for
subsequent decisions.
The fourth is to strengthen the depth of
feasibility study and quality control. Further improve
the depth and quality of the feasibility study. In
response to the insufficient depth of the project
application materials, it is required to analyze and
evaluate the customer groups, main service targets,
type and scale of enterprises, business hall traffic,
business volume and other subdivisions during the
application, and fully demonstrate them. The
necessity, rationality and economy of the terminal
placement plan to avoid over-configuration,
advanced configuration and capital waste.
4.4 Factor Naming
Table 3 shows the factor load matrix after rotation,
the first common factor has a greater load on variable
quick ratio, current ratio, cash ratio, total asset
growth rate, asset liability rate, cost and expense
utilization rate, this shows that these six variables are
highly correlated and fall into one category, which is
called the solvency factor, and the second public
factor, which has a greater load on the Yield valve
and operating profit margin, puts the two variables
Research on Optimization Technology of Cost Management and Control of Power Grid Enterprises under the Background of Smart Grid
Application
971

into the same category, the third public factor has a
greater load on the turnover rate of accounts
receivable and the growth rate of net profit, and is
named as the development capacity factor, it’s called
the operational capability factor.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The investment in the construction of the invoice
terminal in the business hall of the power grid
enterprise has not only improved the intelligent
application level of the power grid, but also improved
the customer's intelligent power consumption
perception level. This article takes the business hall
invoice terminal, one of the smart grid application
technologies, as the research object, with the goal of
improving its input and output effects, and builds a
DEA theory-based business hall invoice terminal cost
effectiveness evaluation technology, which
effectively guides the funds of power grid enterprises
Invest in the improvement of lean management level
to help the continuous improvement of the intelligent
level of the power grid.
REFERENCES
Jin Wenai. Analysis on Cost Accounting Management of
Power Grid Enterprises from the Comprehensive
Budget [J]. Finance and accounting study, 2021 (23):
108-110.
Wang Qiong. Analysis of Cost Management and Lean
Management Measures [J]. Western Accounting, 2020
(11): 40-42.
Wu heying. Power Enterprise Cost Management Research
from the Supply Chain perspective —— takes T
Power Grid as an example [J].Business, 2021 (07):
110-111.
Xu Nan, Ling Yunpeng, Cheng Jialu, Wang Yongli.
Influence of power transmission and distribution price
reform on Financial Management of Power Grid
Enterprises [J]. Price Theory and Practice, 2019 (09):
38-41.
Zou Guilin, Zhang Jigang, Wu Liangzheng, Chen Wen.
Study on weighted average capital cost of overseas
investment of power grid enterprises [J]. Management
of China Electric Power Enterprises, 2020 (33): 76-78
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
972
