
Knowledge of History Contributes to the Emergence of Innovations:
An Anthropological Approach in the Humanitarian Block of
Transport Education
Zlata Anatolyevna Shmidt
1,2
and Nadezhda Semyonovna Sidorenko
2
1
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
2
South Ural State Humanitarian Pedagogical University, Chelyabinsk, Russian Federation
Keywords: Transport education, historical knowledge, anthropological approach, educational technologies, history of
rail transport, railway transport engineers.
Abstract: The article deals with the issues of the content of transport education, the place and role of the humanitarian
block in it. The disciplines of the social and humanitarian block have significant resources for the formation
of general cultural competencies and professional moral qualities, such as responsibility, initiative,
determination, and others arising from the worldview, moral and other attitudes formed by these disciplines.
The question of the significance of history as a factor in the emergence of innovations has been updated.
Aspects of the significance of the anthropological approach in the teaching of historical disciplines of the
humanitarian block of transport education are revealed. It has been established that this approach focuses on
the reconstruction of the deep program of all types of human activity, embedded in the cultural tradition of
the social universe, including activities in the field of railway transport, allows you to focus on the
humanistic side of history. This approach actualizes a personal approach to history, including the history of
railway transport, the study of the role of its outstanding representatives – railway transport engineers,
which has a direct impact on the comprehensive training of a specialist, as well as on the formation of
motivation for his future professional activity. The article analyzes the practice of using the anthropological
approach in teaching historical disciplines in the process of training railway transport specialists at the
Chelyabinsk Institute of Communications - a branch of the «Ural State University of Railway Transport».
An opinion was expressed about the effectiveness of using the project activity method in order to make the
most of this approach. Scientific novelty lies both in the very formulation of the problem, and in the
identification and systematization of empirical material on the topic of research and its introduction into
scientific circulation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern requirements for the organization and
content of transport education are defined as the
main components – the formation of professionalism
and competence of managers and specialists;
responsibility for prepared and adopted decisions,
proper performance of their official duties, which
follows from the established basic principles of
professional service in the federal railway transport,
enshrined in the regulations of the Ministry of
Railways of Russia (Charter of Railway Transport of
the Russian Federation, 2002).
The solution of this problem by the higher
educational institutions of the country in this area,
whose competence includes the training of railway
transport engineers, is based on determining the
appropriate content of theoretical and practical
training of specialists. National practice, historically
established and conditioned by accumulated
practical experience, includes, along with general
technical and special disciplines, also humanitarian
disciplines. The share of the humanitarian block
occupies an insignificant part, which does not
detract from its importance in the professional
training of specialists. The inclusion of this element
in the educational program is determined by the
need to form a number of necessary personal
qualities that an engineer must possess. The
disciplines of the humanitarian block contain ample
opportunities for the formation of a responsible
Shmidt, Z. and Sidorenko, N.
Knowledge of History Contributes to the Emergence of Innovations: An Anthropological Approach in the Humanitarian Block of Transport Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0011580200003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 129-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
129

approach to the performance of duties, creative
thinking, and the desire for self-development among
students. A special place among them belongs to
historical disciplines, which have not only cognitive,
but also educational potential.
Pedagogical science and practice have developed
a number of effective methods and techniques for
using historical material in the process of preparing
and educating students. One of them is the
anthropological approach, which focuses on the
personal factor in the historical process, in the
development of science and technology.
The use of this approach in the system of modern
transport education is extremely important. Deep
geopolitical transformations that pose new
challenges to the Russian economy initiate the
search for effective ways to solve them, including
from the side of railway transport. Under these
conditions, the importance of the personal
participation of each in solving the tasks set
increases. An appeal to the history of the country,
the history of the country's railway transport and its
prominent figures can have a significant impact on
the formation of the necessary competencies of
modern engineers and other railway transport
specialists.
The purpose of this article is to identify the place
and role of the humanitarian block in transport
education and the possibility of strengthening its
cognitive and educational potential based on the use
of the anthropological approach.
Achieving this goal involves solving the
following tasks:
1. Determine the role of the humanitarian block
in transport education and the place of historical
disciplines in it.
2. To reveal the educational possibilities of the
anthropological approach in teaching history using
project technologies in the system of transport
education.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Methodologically important for this study are the
ideas of I. Beckman and his followers (I. G. M.
Poppe, E. Hartig), associated with the idea of private
and general technology as a correlation of actions
and knowledge for the development of production,
the need to develop the widest possible approach to
definition of the concept of technology as a
methodology for any human activity (
Beckmann,
1806). The relevance of developing a general theory
of activity was shared by the Russian scientist P.K.
Engelmeyer (Engelmeyer, 1917). In the modern
philosophy of technology in the interpretation of the
concept of technology, special attention is paid to
the field of social engineering and related social
technology, due to the need to assess the
consequences of scientific and technological
developments, the role of the individual in the
development of the technical sphere of society.
(
Ropohl, 1979). A. Grunvald raises the question of the
need to consider technical activity as a collective
one, which implies its critical reflection, that is, its
study in a historical aspect (Grunwald, A., 2002).
The modern understanding of technology as an
objective activity is increasingly realized in the
context of the embodiment of technical artifacts in
economic and social structures. This understanding
of technology as social engineering actualizes the
anthropological approach to its study (Gorokhov,
2011).
The issues of the content of modern engineering
education in the field of transport are reflected in the
publications of leading scientists and teachers of the
country's transport universities. The issues of the
correlation of general technical and humanitarian
sciences in the system of training specialists in the
field of transport were raised by Professor of the
Moscow State University of Railway Transport E.S.
Spiridonov (
Spiridonov, 2016), candidates of technical
sciences – I.G. Ovchinnikov (Ovchinnikov, 2016)
and I.I. Ovchinnikov (
Ovchinnikov, 2010) and other
specialists. The authors are critical of the
relationship between the humanitarian and technical
blocks in transport education.
Representatives of the Siberian State Transport
University - Yu.D. Mishin, S.M. Churikov ( Mishin,
2019), N.A. Olshannikova (Olshannikova, N., A.,
2018.] and others, on the contrary, actualize the
importance of the humanitarian block within the
framework of the problem of modernizing domestic
engineering education. They raised questions of the
formation of modern value orientations in technical
education based on the humanities.
The presence of debatable aspects on this issue
actualizes the statement of the stated scientific
problem.
The direction of anthropology originates from
philosophical science in the 1920s in the ideas of A.
Gehlen (Gelen, 2007), M. Scheler (Scheler, 1993),
G. Plesner (Plesner, 2004), as a comprehensive
science about man, about the problem of personality.
In the 1960s and 70s. the anthropological turn is
manifested in historical science as a shift in the
interests of social historians from the study of
objective structures and processes to the study of the
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
130

past in its anthropological interpretation. The subject
of research is the comprehension of the subjective
mental worlds of representatives of certain social
groups and the elucidation of the system of ideas and
concepts underlying any human action (Repina,
2006). The anthropological approach expands the
use of information retrieval methods at the expense
of those used by anthropology – methods of the
history of life and activities of an individual or social
group, analysis of an episode, events, and others that
focus on the humanistic side of history.
Thus, the use of the anthropological approach,
along with others, in the study of history in transport
education is determined, first of all, by the fact that
this approach focuses on the reconstruction of the
deep program of all types of human activity,
embedded in the cultural tradition of the social
universe, including activities in the field of railway
transport.
3 BODY: PLACE AND ROLE OF
THE HUMANITARIAN BLOCK
IN TRANSPORT EDUCATION
The inclusion of humanitarian disciplines in the
training program for engineering and technical
personnel was laid down from the very beginning of
the birth and development of engineering education
in Russia – the creation in 1896 of the Imperial
Moscow Engineering School of the Department of
Railways, which in 1913 was called the Moscow
Institute of Railway Engineers. The need to form the
general cultural competencies of future engineers is
due to the fact that his professional activity is
connected with the management of both technical
objects and social groups and individuals.
Modern processes of development of scientific
and technical, technical and technological and socio-
cultural phenomena, due to changes in the
geopolitical situation, increasing social tension,
significantly increase the importance of the
humanitarian component in the technical education
of a modern specialist. A modern engineer needs to
understand technology as an objective activity in the
context of the implementation of its results in
economic and social structures, which means
understanding technology as a social engineering,
closely related to posing the problem of social
technology of consent, identifying consequences and
influencing society.
The period of study at the university is of
fundamental importance in the process of becoming
a student's personality. Its content is a kind of
transition of a young person (a team of students),
who has mainly the qualities of an object of
influence, into a new quality - the subject of activity.
This is largely facilitated by the fact that along with
the development of their future profession, students
are involved in various types of social activities that
require competencies of interpersonal interaction.
The content of the disciplines of the humanitarian
block is largely focused on their formation.
Assimilation by students of the basics of the
humanities contributes to the formation of a broad
approach to understanding the essence of socio-
economic relations, the development of personal
goals and values. We share the opinion of A.N.
Popov and O.Yu. Malakhova that the study of the
disciplines of the social and humanitarian cycle
allows students to realize the «humanistic
dimension» of their future profession, to overcome
the technocratic orientation of thinking, which often
accompanies the professional training of an engineer
(Popov, 2020).
In this regard, the importance of forming, along
with technical, also general cultural competencies of
the future railway engineer, increases. The
disciplines of the humanitarian block - philosophy,
history, sociology, political science, cultural studies,
ecology and a number of others - are oriented
towards achieving this task. Their role in the system
of general training of the future specialist is, first of
all, in the formation of the ability to logically
correctly, reasonably and clearly express their
thoughts, defend their point of view without
destroying relationships; treat historical heritage and
cultural traditions with respect and care, be able to
analyze and evaluate historical events and processes;
to promote the development of theoretical, logical
thinking, a creative approach to solving social and
professional problems and tasks, the desire for
constant self-education and self-improvement, the
ability to realize the social significance of one's
future profession, to have a high motivation to
perform professional activities (Egorova, 2019).
Insufficient attention to the social and
humanitarian block of disciplines can seriously
affect the formation of professional and universal
competencies of future specialists, in the
performance of their duties. Researchers state the
existence of this problem - graduates of railway
universities, building their work, often do not take
into account the «human dimension» of their field of
activity, and also often have a very narrow technical
thinking, act «according to a clear algorithm»
(Ezhova, 2019).
Knowledge of History Contributes to the Emergence of Innovations: An Anthropological Approach in the Humanitarian Block of Transport
Education
131

The performance of professional activities within
the framework of modern engineering activities, in
addition to designing complex systems and
performing technical calculations, requires the
engineer to participate in the process of discussion
and adoption of socio-cultural and managerial
decisions. At the same time, he must be guided not
only by technical calculations, but by all means take
into account the anthropological factor: this is what
determines the effectiveness of engineering activities
in many respects.
The disciplines of the social and humanitarian
block have significant resources for the formation of
professional moral qualities, such as responsibility,
initiative, determination, and others arising from the
worldview, moral and other attitudes formed by
these disciplines.
Systematic, creative approaches in teaching the
disciplines of the social and humanitarian block are
focused on the formation of a modern engineer who
focuses on innovation in his work. We are close to
the definition of the concept of «innovation in
engineering activity», proposed by Yu.D. Mishin
and S.M. Churikova, as an activity (including an
advanced and creative approach) aimed at creating
and developing new technologies and equipment
that have a high economic effect, demand and
competitiveness and are presented in the form of
marketable products (Mishin, 2019).
4 THE PRACTICE OF USING
THE ANTHROPOLOGICAL
APPROACH IN THE PROCESS
OF TRAINING RAILWAY
TRANSPORT SPECIALISTS AT
THE CHELYABINSK
INSTITUTE OF RAILWAYS - A
BRANCH OF THE «URAL
STATE UNIVERSITY OF
RAILWAY TRANSPORT»
The use of the anthropological approach in teaching
historical disciplines is due to the cognitive potential
contained in it - the reconstruction of the socio-
cultural program of activities in the field of railway
transport, embedded in the cultural tradition of
Russia in the past and present.
Strengthen the value of this method allows the
application in practice of relevant forms, techniques,
technologies and methods of the educational process
in the presentation of historical material. Among
them, the most relevant for the realization of the
possibilities of the anthropological approach
contains, in our opinion, the project technology,
which includes micro and macro projects. This
allows the inclusion of elements of research
activities designed to integrate historical and
technical knowledge. The result of the project is the
proposal of a real practical result, designed in the
form of a specific product of the student's activity.
The purpose of the project is to deepen and expand
the student's knowledge of the discipline being
studied, the ability to apply the acquired
competencies to solve professional problems.
Mostly students who successfully master the
educational material are involved in the
implementation of projects.
The technology of the project method is an
expedient activity of the student on an active basis.
The relevance of project activity is expressed in the
ability to form the student's personal qualities, which
develop only in activity and cannot be learned
verbally. Such personal qualities are: the ability to
work in a team, take responsibility for a decision,
share responsibility and analyze the results of
activities. The technology of the project method
makes it possible to form such a field of the
educational process in which students are its active
participants, and not passive extras, students develop
their own analytical view of information, freedom in
choosing methods and types of activities to achieve
the goal (Stolyarenko, 2014).
Projects can be experimental or theoretical. In
the course of teaching historical disciplines, the
second type dominates. The form of its presentation
can be an abstract, scientific article, oral
presentation. The defense of the project can take
place both during training sessions and be taken out
at educational and practical conferences with the
presentation of reports on the results of the project.
In order to enhance students' interest in this type of
activity, one should carefully consider the topics of
project assignments. It should be relevant, connected
with the history of the railway industry, with its
regional aspect, which allows you to bring the
studied material closer to the location of the
educational institution, enhancing its emotional
perception. Examples of some project assignments
used in teaching students at the Chelyabinsk Institute
of Railways - a branch of the «Ural State University
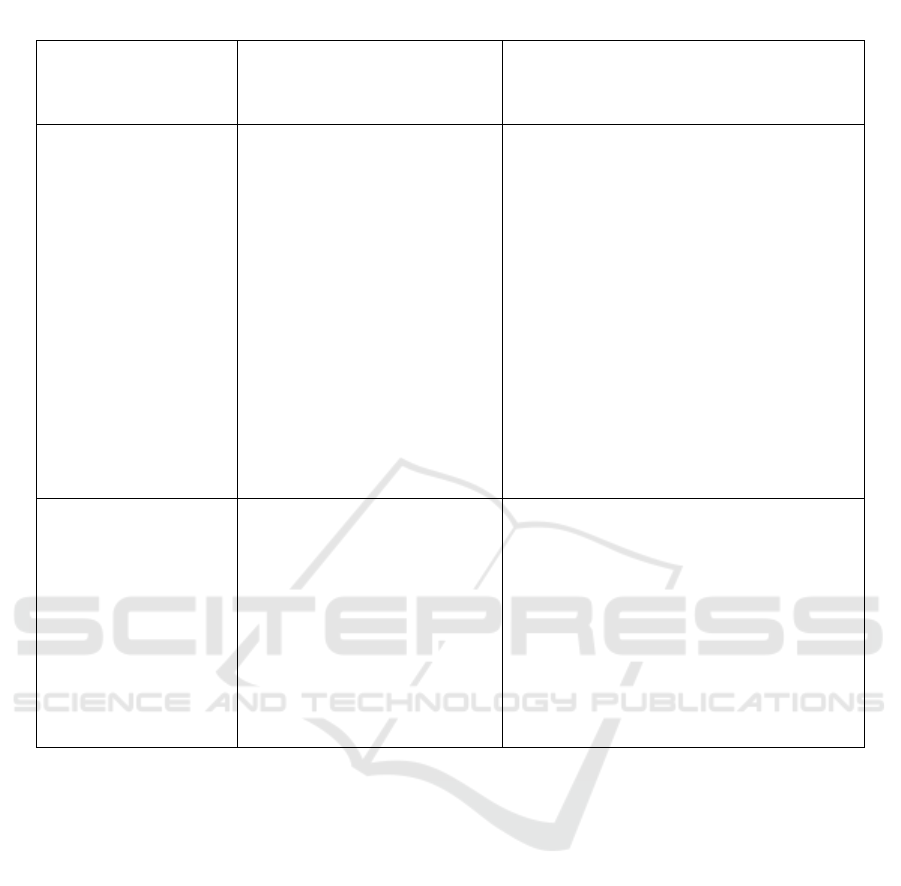
of Railway Transport» are shown in Table 1.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
132
The technology of project activity implies a high
degree of student interest. To do this, such
formulations of tasks can be used that cannot leave
them indifferent. For example, you can invite
students to interpret the following statement by N.G.
Garin-Mikhailovsky about the labor feat of
engineers in the construction of railways in the
Urals: «Eight percent of the prospectors left the
stage forever, mainly from nervous breakdown and
suicide. This is the percentage of the war. More
conscientiousness, energy, enterprise - and these
seemingly terrible mountains will part and reveal
their secret, invisible to anyone, not marked on any
maps, passages and passages, using which you can
reduce the cost and significantly shorten the line»
(Nikulkov, 1989).
Such a formulation of the project activity will
guide the student not only to the study of specific
historical material on the development of the road
network in the region, but also to the study of the
motivational side of the activities of railway
engineers, the study of biographical material.
Learning in this case acquires an emotional coloring,
initiating the search for something new. At the stage
of introspection and reflection, the student forms the
basis for an adequate assessment of the significance
of the work of railway engineers and awareness of
personal responsibility for professional
competencies and future professional activities.
The project of studying architectural artifacts
related to the history of railway construction and
road formation seems to be effective. In our practice,
we used such an object as the building of the former
Chelyabinsk two-class men's railway school, located
in the immediate vicinity of the institute. The
implementation of this project, in addition to the
content side, revealing the history and practice of
training technicians for the railway service – drivers,
assistant drivers, road foremen and others in the
South Urals, brings students to another problem – a
Table 1: Approximate topics of project research for students of transport education in the course of history.
Theme of the historical
discipline of the
humanitarian block of
transport education
Pages of the history of railway
transport with the inclusion of
a regional component
Topics of project assignments
Economic development
of Russia in the second
half of the 19th - early
20th centuries
development of the railway
network in the Urals in the
second half of the 19th - early
20th centuries
technical progress in railway
construction in the Urals in the
second half of the 19th - early
20th centuries
micro projects:
– photo-history of the Great Siberian Route
(Photo by Prokudin-Gorsky, William Henry
Jackson about the survey and construction
work on the construction of the railway);
– outstanding engineer N.G. Garin-
Mikhailovsky in the history of railway
construction in the Southern Urals;
– compiling a biographical map «Engineers of
Railways of the Urals»;
– a creative project using photographic
materials of the regional railway construction
of the early twentieth century S.M. Prokudin-
Gorsky, William Henry Jackson;
macro projects:
– features of railway construction in the Urals
in the second half of the XIX century.
(preparation of scientific report)
Culture of Russia in the
second half of the 19th -
early 20th centuries
emergence in Russia of the
profession of a railway engineer
development of transport
education and special educational
institutions in the country and in
the Urals
micro projects:
– which officers for the first time in the
Russian army appeared Asterisks on shoulder
straps (the specifics of the training of railway
engineers in higher educational institutions of
Russia);
– architectural artifact of Chelyabinsk (city of
Chelyabinsk, Svobody street, 175): what is its
connection with the history of railway
transport in the Urals (the former building of
the male school of the station Chelyabinsk,
Orenbur
g
p
rovince
)
Knowledge of History Contributes to the Emergence of Innovations: An Anthropological Approach in the Humanitarian Block of Transport
Education
133

practical one – the preservation of this architectural
artifact as historically valuable for the region.
Determining the topics of research projects, one
should also use such potential as «upbringing by the
walls» – through the traditions of honest service of
graduates and teachers of the institute, using the
materials of the museum complex.
In general, the examples of using the technology
of project activity proposed in the article increase
educational motivation, cognitive and personality-
oriented activities of students.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
At present, the world's leading universities show a
trend of transformational processes aimed at
overcoming contradictions and improving the
quality of training of engineering personnel. The
principles of humanization stand out as the main
value orientations of engineering education at the
present stage. In order to overcome the crisis in the
system of engineering education, the personal and
multilateral education of a specialist is increasingly
being developed, along with the pragmatic approach
of the cult of «technical sciences» as the main
criterion for competitiveness. The quality of
engineering personnel is recognized at the state level
as one of the key factors in the development of the
country's economy, as well as the basis of its
technological and economic independence. The
purpose of this process is the formation of a cultured
person, developed intellectually, spiritually, morally,
aesthetically and physically, possessing dialogue and
creative thinking, able to improve himself, build
harmonious relations with the surrounding nature
and society, able to participate in the humanization
of social reality by his actions and deeds
(Gabysheva, 2018).
The implementation of the humanization of
educational activities in the technical profile of the
specialty is carried out systematically, methodically
organized, positively supplementing the educational
program in order to form the versatile competencies
of future railway transport specialists. Humanitarian
disciplines have a historical and cultural,
multifactorial saturation, which allows the student to
explore the development of technical sciences in the
conditions of a certain historical era, mentality.
On the example of the Chelyabinsk Institute of
Railways, a branch of the «Ural State University of
Railway Transport», a positive experience in the
formation of professional competencies of technical
students in the process of teaching history based on
an anthropological approach using project
technologies was revealed.
6 CONCLUSION
Based on the analysis of scientific literature and
practical experience in training railway transport
specialists at the Chelyabinsk Institute of Railway
Transport, a branch of the «Ural State University of
Railway Transport», it can be said that the study of
the disciplines of the humanitarian block allows you
to activate the cognitive interest of students in the
learning process, helps to expand their horizons. A
special place among them is occupied by historical
disciplines containing rich concrete historical
material that substantiates the significant role of
transport engineers in the development of the
country's and region's railway transport in a
historical aspect. The use of an anthropological
approach to historical material makes it possible to
enhance its cognitive and educational potential,
focusing on the reconstruction of the motivational
basis of activity inherent in the cultural tradition of
the social universe, the comprehension of historical
experience as a factor in the emergence of
innovations. The use of the anthropological
approach in the approach to historical material
actualizes the introduction of the project method into
the practice of teaching as one of the modern
innovative teaching methods that contribute to the
active involvement of students in the learning
process.
The practical experience of using project
technologies in the process of teaching history
confirms their cognitive and educational potential.
The use of project technologies contributes to the
formation of research competencies necessary for
the professional training of a specialist, and is
oriented towards the search for innovations. Design
technologies, creating an active field of student
activity, contribute to the formation of his personal
qualities, corporate culture of involvement in the
rich and heroic history of the country and its railway
transport, outstanding railway transport engineers.
REFERENCES
Beckmann, J., 1806. Design of General Technology. –
Stock of small notes on machinerey learned subjects.
Goettingen.
Gabysheva, L. K., 2018. Transformation of the model of
education in the context of the humanization of
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
134

engineering training. Humanitarianization of
engineering education: methodological foundations
and practice: materials of the international scientific
and methodological conference. p. 864.
Gelen, A., 2007. The image of man in the light of modern
anthropology. Personality. Culture. Society 3 (37), pp.
37 – 51.
Gorokhov, V. G., 2011. The concept of «technology» in
the philosophy of technology and the peculiarity of
social and humanitarian technologies. Epistemology
and Philosophy of Science 28, 2, pp. 110-123.
Grunwald, A., 2002. The technical and the non-technical.
A fundamental distinction and its cultural significance.
Technology images and technology concepts in
transition-a technology-philosophical and general
technical analysis. Scientific Reports FZKA 6697. pp.
37-39.
Egorova, Yu. N., Sinkina, E. V., Zotova, T. A., Genvareva
Yu. A., 2019. Formation of General Cultural
Competences of the Future Railway Engineer in the
Study of General Educational Disciplines. World of
science, culture, education 1 (74), pp. 32-34.
Ezhova, T. V., Malakhova, A. V., 2019. Problems of
formation of technical intelligentsia: competence-
based approach. Youth science in the 21st century:
traditions, innovations, vectors of development, pp.
182-185.
Mishin, Yu. D., Churikova, S. M., 2019. Modernization of
domestic engineering education: a change in the vector
of improvement. Bulletin of the Siberian State
University of Communications: Humanitarian
Research, 1(5), pp. 84-91.
Nikulkov, A. V., 1989 Contemporary from the last
century: Essay on the life of N.G. Garin-Mikhailovsky,
pp. 68-75.
Ovchinnikov, I. I., Ovchinnikov, I. G., 2016. On the
problems of training engineers of communications.
Internet magazine «Transport facilities» 3, 2, http://t-
s.today/PDF/01TS216.pdf.
Ovchinnikov, I. G., Ovchinnikov, I. I., 2010. Training of
specialists in the field of transport construction:
application of information technologies. Red line.
Roads. Innovations in road construction 47, pp. 26-27.
Olshannikova, N. A., 2018. Formation of modern value
orientations in education. Bulletin of the Siberian State
University of Communications: Humanitarian
Research 2(4), pp. 54-60.
Plesner, H., 2004. Stages of the Organic and Man: An
Introduction to Philosophical Anthropology, p. 368.
Popov, A., N., Malakhova, O., Yu., 2020. The potential of
social and humanitarian knowledge in the professional
training of a railway engineer. Bulletin of the Siberian
State University of Communications: Humanitarian
Research 1(7), pp. 24-29.
Repina, L. I., Zvereva, V. V., Paramonova, M. Yu., 2006.
History of historical knowledge, p. 288.
Ropohl, G., 1979. A systems theory of technology. Laying
the foundations of general technology, p. 360.
Spiridonov, E. S., 2016. Some aspects of the training of
railway engineers. Transport systems: development
trends. Collection of proceedings of the international
scientific-practical conference. Under the general
editorship of B.A. Levin, pp. 502-505.
Stolyarenko, L. D., 2014. Psychology and Pedagogy of
Higher School, p. 620.
Charter of Railway Transport of the Russian Federation
(as amended on July 2, 2021) Adopted by the State
Duma on December 24, 2002 Approved by the
Federation Council on December 27, 2002 –
https://docs.cntd.ru/document/901838121. On the
basics of professional service in the federal railway
transport. Instruction of the Ministry of Railways of
Russia dated December 29, 1995 No. 144u.
https://tkrfkod.ru/zakonodatelstvo/ukazanie-mps-rf-ot-
29121995-n-144u/.
Scheler, M., 1993. Man and history. THESIS: Theory and
history of economic and social institutions and systems
1, 3, pp. 132-154.
Engelmeyer, P. K., 1917. Evrology or the General Theory
of Creativity. Questions of theory and psychology of
creativity 7, pp. 76-108.
Knowledge of History Contributes to the Emergence of Innovations: An Anthropological Approach in the Humanitarian Block of Transport
Education
135
