
Modeling the Results of Personnel Training for the Transport
Industry
V. S. Parshina
a
and T. B. Marushak
b
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: Modeling of educational processes, peculiarities of industry universities, Markov processes, evaluation of
learning results, management of learning processes, corrective action.
Abstract: The competencies acquired during the training are the basis for employers' assessment of the young specialists'
degree of readiness for specific activities. The purpose of the article is to develop a model of an internal
system for assessing the initial state of university applicants and the effectiveness of quantitative and
qualitative advancement of students in courses; and on their basis to determine the probability of their
successful graduation from the university. The data obtained is proposed to be used in the justification of
preventive measures to improve the quality of university graduates training. The results of the study are
presented, including the substantiation of methods for assessing the quality of training, the collection of
analytical data on quantitative and qualitative characteristics of discrete states of students for a specific
educational program. The modeling was carried out on the basis of stochastic Markov processes discrete in
time, describing the sequence of possible states of the objects of study with a certain probability. The results
obtained are of practical importance for the modernization of quantitative and qualitative results of students'
training based on their systematic assessment in the learning process.
1 INTRODUCTION
The task of increasing the level of human resource
development is determined by the economic and
social interests of society. It is implemented in the
form of competitiveness of educational institutions
graduates and personnel of organizations. Our
research on the formalization of the learning
management process at the university caused the need
to specify the target setting of the quality of training
specialists in accordance with the requirements of the
transport industry (Corporate Requirements for
Qualification of Russian Railways' Employees with
Higher and Secondary Professional Education). The
formulation of this task led to the development of a
model on the basis of which it is possible to carry out
operational and strategic management of qualitative
and quantitative components of the competitive
personnel training.
Currently, the complexity of assessing the level of
training of specialists for the industry is due to the
discrepancy between the requirements of the parties
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3932-776X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4978-7137
to the components of the quality of training, which
makes it difficult to model and interpret the
assessment. The results of the analysis are presented
in more detail in (Parshina, 2013). The basis for the
formation of the competence model of an employee
of the transport industry is the condition of
compliance with state and industry educational
standards (Fig. 1).
Figure 1: Competency model of an industry worker.
170
Parshina, V. and Marushak, T.
Modeling the Results of Personnel Training for the Transport Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0011581100003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 170-174
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Currently, work is underway to form the general
requirements of the parties to the quality of graduates.
After ensuring this compliance, it is possible to adjust
the evaluation criteria.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Emerging publications (with reference to employers)
about the incomplete compliance of the quality of
graduate training with the increased requirements of
the production and services sphere, put forward the
task of studying the causes of this phenomenon. At
the same time, there is a dropout of students during
training, which is reflected in the inefficient spending
of funds on training. Therefore, a comprehensive
study of the managerial impacts of the university on
the results of personnel training is relevant at the
present time. The analysis of theoretical sources
(Cripe, 2012; Mathis, 2012; Modern approaches to
knowledge management development. Collective
monograph, 2020; Bornmann, 2006; Black, 2009),
the review of modern practice in the field of education
(Sȧnchez, 2018; Alyahyan, 2020), the assessment of
the ratings of higher educational institutions and the
level of training in them by the eyes of employers
allowed us to identify problems of educational
activity that are insufficiently represented in the
literature and have specific character in this country.
Attention to the field of personnel training in the
world is initiated by the proclaimed general idea of
stable economic development. The formulated
national goals of educational processes are
complemented by intra-university systems for
monitoring and improving learning processes. The
review of modern literature demonstrates the
manifestation of the initiative of universities in
improving the quality of education. The experience of
the world's leading universities shows that the success
of an educational institution is determined by the
chosen strategy in the field of specialist’s training
quality (Care, 2018). One of the tasks is to develop
preventive measures to identify and work with
students at risk groups, which can significantly
increase the comprehensive effectiveness of training.
Such actions are conditioned by the desire to meet the
requirements of employers, students and their
parents. The effective and efficient application of
various methods of factual data analysis provides
solutions for determining the success factors of
university graduate. The study of the factors of
ensuring the quality of training, for example, in China
and Germany (Zhang, 2011), indicate the importance
of process management at various levels, including
the actions of the university.
The proposed research is aimed at developing a
methodology for analyzing the factual data of
educational processes to predict the effectiveness of
learning, keeping in mind the peculiarities of industry
education (Parshina, 2021; Parshina, 2019). With this
purpose, literature and modern information were
analyzed as part of the systematization of learning
processes. The analysis of the statistical methods used
to identify patterns, trends and probabilities using the
initial data is carried out. For data processing, the
Markov process method was chosen, which allows
predicting qualitative and quantitative indicators of
training specialists. The results obtained can be
converted into a compressed format and brought to
the involved university and corporation heads.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To predict the quantity and quality of graduates of the
transport university an analytical review of the
students' achievements depending on the admission
score was made. Bearing in mind that the formation
of competencies occurs in the process of mastering
specific disciplines, the analysis of students' progress
in them was carried out. The general basis for
assessing the quality of education serves the progress
in educational programs for the entire period of study.
The level of students' competence is considered on
the specific educational program "Management"
(period of study in the university in 5 years). The
training standard assumes mastering 22 general
cultural and 50 professional competences.
To get the necessary basis for assessing the level
of competence formation it is proposed to use: the
results of examinations and tests on academic
disciplines, coursework design, the results of all types
of practices and defense of the graduate qualification
work. In order to formalize the quality of the achieved
competences the criteria presented in table 1 were
developed.
Table 1: Сriteria of competences formation.
An interval of a
students, estimation
The level of
competence, %
4,5-5,0 > 90
4,0-4,5 80 – 90
3,5-4,9 70 – 80
3,0-3,4 60 – 70
3,0 < 60
Modeling the Results of Personnel Training for the Transport Industry
171
Then the average score of the students of the
academic group for each discipline and the average
score of the group for each cycle were calculated. The
results of calculations and an overall assessment of
the level of competence formation within a particular
cycle are presented in fragments in Table 2.
Table 2: Estimation of the level of students, competences
formation.
Training
cycles
The
average
students
scores
Codes of
formed
competences
The level
of
compe-
tence for-
mation,
%
Humanitarian
, social and
economic
4,15 14 general
cultural
com
p
etencies
80 - 90
Mathematical
and natural
science
3,80 4 general
cultural
competencies
70 - 80
Professional 4,22 3 general
cultural and
50
professional
competencies
80 - 90
Physical
Training
4,14 1 general
cultural
com
p
etence
80 - 90
Training and
industrial
practices
4,68 3 general
cultural and 3
professional
competencies
90 and
above
Final State
Attestation
4,24 2 general
cultural and
50
professional
com
p
etencies
80 - 90
As follows from the table, the actual level of
competence formation among students not less than
70%. All general cultural competencies were
mastered in the learning process. Among them, the
highest level of mastering the following
competencies (more than 90%): the desire for
personal and professional self-development; the
ability to critically assess personal strengths and
weaknesses; the ability to carry out business
communication: public speaking, negotiations,
meetings, business correspondence, electronic
communications; as well as the ability to take into
account the consequences of managerial decisions
and actions from a position of social responsibility.
To a lesser extent, they have mastered: possession of
a culture of thinking, the ability to perceive,
generalize and analyze information, setting goals and
choosing ways to achieve.
To manage the process of training competitive
graduates, their modeling based on Markov processes
was used. A homogeneous Markov chain is
constructed on the basis of the results of the Unified
State Exam obtained during the differentiated
analysis of applicants for admission, students'
academic progress during the entire period of study,
and the number of students who were expelled for
failure (Fig. 2). As a result of the calculation of the
chain, a conclusion was made regarding the
probability of obtaining the necessary training of
specialists, the total risk of student expulsions and
expulsions risks for groups of students with different
school preparation and academic performance at all
stages of training were calculated.
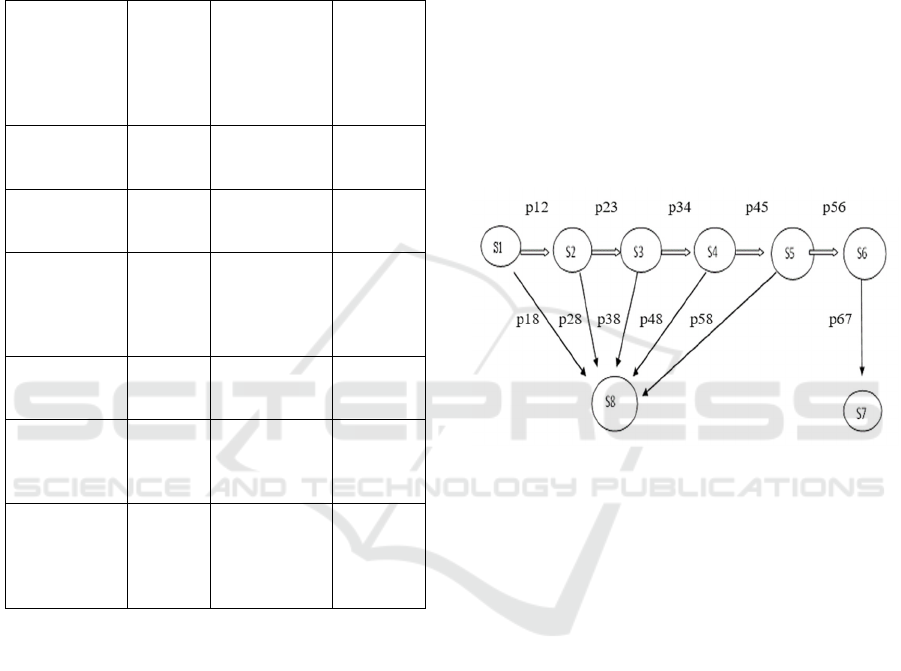
Figure 2: General view of the Markov chain to describe the
training of students of a particular direction of training.
Here: S1 – first year students;
S2 – second year students;
S3 – third year students;
S4 – forth year students;
S5 – fifth year students;
S6 – students who achieved the final state
certification;
S7 – professionals who graduated from the
university;
S8 – university students.
We use the basic concept in the theory of Markov
processes - the state to describe the object under
study, going through the stages from the applicant to
the graduate of the university. A graph of the states of
the Markov chain relative to the learning process at
the university is compiled in a general form and its
transition probabilities are marked up. The notation p
is used to describe the transition probability. So, to
change the state of S1 for a year, it is possible to
switch to the state of S2 with a probability of Р12, etc.
The academic performance of each student over the
entire period of study was analyzed. Further, based on
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
172
the calculations carried out, the probability with
which the student will move to the n-state next year
is determined; at the same time, he has improved or
worsened his condition. Low academic progress in
the initial period is determined by insufficient school
preparation of students. Basically, students who had
difficulties mastering the educational material in the
process of learning are expelled. Timely measures
taken (additional classes, assignment of a more
qualified teacher, involvement in the creative process,
etc.) will allow keeping the contingent of students.
Based on the data obtained, calculations were made
of the probability of first- and next-year students
moving up to the next level within the allocated point
ranges (Fig. 3).
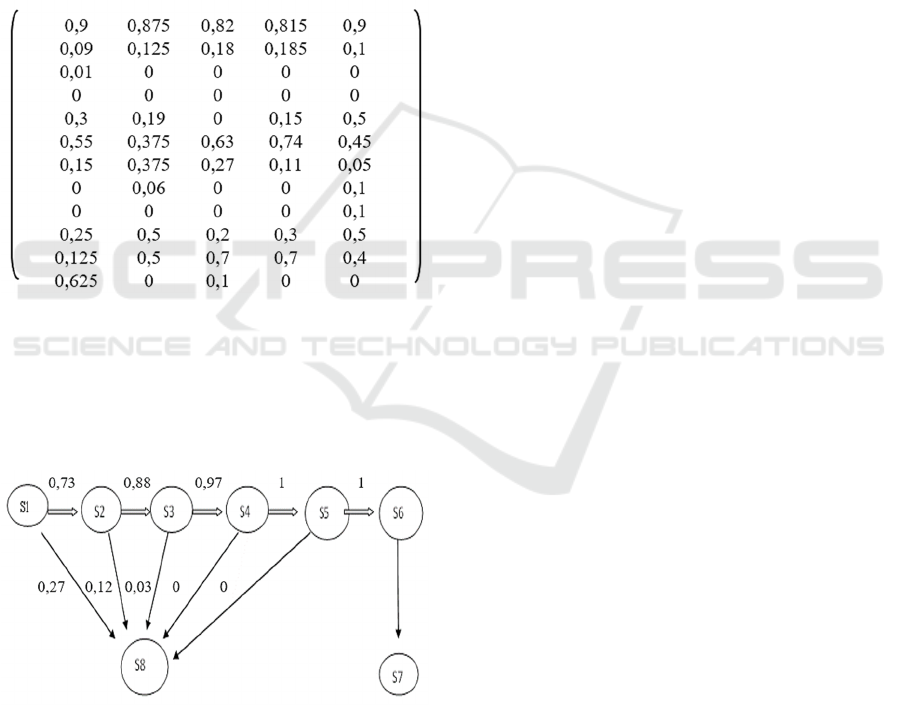
Figure 3: Matrix of probabilities of students’, transition to
the next course on groups in the distinguished intervals of
progress.
Next, the generalized values of the probability
matrix of students' advancement in a certain
educational program are calculated (Fig. 4).
Figure 4: Generalized values of the transition probability
matrix of students to the next course.
According to Figure 4, the probability of
transition of all students from the first year to the
second one is 0.73, from the second year to the third
one – 0.88, etc. There are practically no deductions in
the last year and all students defend their final
qualifying work. The analysis showed that first-year
students find themselves in a situation of the greatest
risk of expulsion. The probability of expulsion of a
fifth-year student is almost zero. Based on the logical
addition of risks, we calculate the overall degree of
risk of a student's expulsion in the learning process
(P):
Р = 0,27*0,88*0,97*1*1 + 0,12*0,73*0,97*1*1 +
0,03*0,73*0,88*1*1 + 0+ 0 = 0,32
The total risk of expulsion of a student for 5 years
of study is 0.32. Assistance to students in mastering
the educational program at any stage of preparation
will improve the quantitative and qualitative
effectiveness of the education process and increase
the efficiency of funds invested in training.
4 CONCLUSION
The process of preparing students at the university is
described in terms of the theory of Markov processes.
Modeling of learning processes and training results
with indication of stationary states and identification
of transition probabilities between them is carried out.
The data obtained is proposed to be used to manage
the quantitative and qualitative components of the
effectiveness of educational activities of the
university. The conclusions can be used by heads of
the University to implement timely and strategic
actions to optimize the level of development of
students’ competence mastering, reducing the
percentage of students’ expulsions, by students to
plan their own personal learning process and the
likelihood of graduation, and by heads of the transport
industry for the planning and selection of candidates
for training. The presented materials illustrate only a
part of the research carried out for the industry on the
improvement of the interaction of branch universities
and structural divisions of the corporation.
REFERENCES
Corporate Requirements for Qualification of Russian
Railways' Employees with Higher and Secondary
Professional Education. Approved 17.11.2009.
Parshina, V. S., Gusev, A. A., 2013. Theoretical,
methodological and organizational and
methodological aspects of training leaders based on a
preliminary assessment of their competencies in the
learning process. Yekaterinburg: UrGUPS, RF. p. 179.
Cripe, E., 2012. Competency development guide.
Workitect, Inc., p. 276.
Modeling the Results of Personnel Training for the Transport Industry
173

Mathis, R. L, Jackson, J. H., 2012. Human Resource
Management: Essential Perspectives. Cengage
Learning, p. 288.
2020. Modern approaches to knowledge management
development. Collective monograph. Ljubljana,
Slovenia ljubljana school of business. p. 542.
Bornmann, L., Mittag, S., Daniel, D., 2006. Quality
assurance in higher education – meta-evaluation of
multi-stage evaluation procedures in Germany. Higher
Education. 52. pp. 687–709.
Black, P., William, D., 2009. Developing a theory of
formative assessment. Education-al Assessment,
Evaluation and Accountability (formerly: Journal of
Personnel Evaluation in Education). 21(1), 5.
Sȧnchez, A., Paniagua, E., Simpson, O., 2018. Journal of
Interactive Media in Education. pр. 1-10.
Alyahyan, E., Düştegör, D., 2020. Predicting academic
achievement in higher education institutions: a
literature review and best practices. International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher
Education, 17, 3.
Care, E., Kim, H., Vista, A., Anderson, K., 2018.
Optimizing assessment for all. Education system
alignment for 21st century skills. Focus on assessment.
Brookings. USA. p. 41.
Zhang, F., Fang, W., Zhou, C., Liu, Z., 2011. A brief study
on teaching evaluation system based on fuzzy rule with
scientific teaching materials. In Advances in Computer
Science, Environment, Ecoinformatics and Education.
pp. 99-105.
Parshina, V. S., Gusev, A. A., Sizy, S. V., 2021. Сorporate
governance of industry-specific education. In the
collection: AIP conference proceedings. Scientific
conference on railway transport and engineering
(RTE). p. 100006.
Parshina, V. S., Kuznetsova, E. V., 2019. Interaction
between industry higher educational institutions and the
customer of educational services. In the collection: E3S
Web of Conferences. Innovative Technologies in
Environmental Science and Education (ITESE). p.
04001.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
174
