
Staff Turnover as a Problem of HR Risk
Tatiana Pavlovna Volkova
Ural State University of Railway Transport, Yekaterinburg, Russia
Keywords: Staff turnover, organization management, HR risks, railway industry.
Abstract: This article discusses the turnover of personnel of the organization as a problem of HR risk. Special attention
is paid to the theory of the issue and methods of staff turnover management in various sectors of the national
economy. The article analyzes alternative approaches to this phenomenon. Staff turnover is presented as a
problem of HR risk in the organization, affecting the safety of management of socio-economic systems. Based
on the study of various points of view of domestic and foreign researchers, it has been established that the
economic issues of the designated phenomenon have been studied to a greater extent, and to a lesser extent
the organizational, managerial and psychological reasons for the dismissal of employees. As a result of
increased staff turnover, the costs of attracting new employees and their adaptation are increasing, and HR
risks arise in the organization. The author proposed additions to the Target programs: the program of effective
induction into office, the program "for linking and retaining employees", the program of social protection of
personnel, structural and organizational generation of the personnel reserve. The results can be used by the
heads of the railway industry of specific departments and services in connection with a deeper analysis of the
issues of staff turnover in the studied industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to experts, high staff turnover is a rather
acute problem of large Russian companies. Russian
Railways JSC, the Sverdlovsk Railway, is no
exception. The natural turnover rate is considered to
be 3-5%. An increased indicator is usually called a
figure above this mark, up to 20%. The purpose of our
study is to study the high turnover of personnel in
individual divisions of Russian Railways JSC,
especially among such a social group as young people
who enter and leave before they have worked for a
year in the organization, including low-skilled
employees of leading professions, to identify the
causes of this process, as well as management and
regulation of this process in unstable economic
conditions, the definition of HR risks of the
organization.
As modern scientists note, high staff turnover
cannot be approached one-sidedly. This should be
understood and analyzed from at least three points of
view: based on the economy of the industry, the
enterprise and a specific person.
It is impossible to consider high staff turnover as
a continuous negative, questions of information
ownership about potential turnover allow you to
predict the activities of the organization for the long
term.
It should be noted that an in-depth approach to the
study of the reasons for the dismissal of personnel in
various sectors of the national economy affects and
determines not only the economic side, but also the
organizational and managerial, as well as extremely
important psychological aspects of personnel
management, which is not always present in socio-
economic consideration.
Along with domestic researchers, these issues
were studied by foreign authors. Names such as
A.Fayol, R.Bennett, W.Harrison, Farrell, Rasbalt,
Lee, Fireman, etc. should be mentioned.
For example, Professor R. Bennett of the
University of London proposed the following
interpretation of a retiring employee, who can be
controlled by registration, having information that a
new employee will be hired in place of the dismissed
one. R. Bennett made calculations of the labor
turnover index; characterized the level of turnover in
individual departments and groups of employees
(Bennett, 2020).
Henri Fayol, a classic of the school of
administrative management, wrote that increased
286
Volkova, T.
Staff Turnover as a Problem of HR Risk.
DOI: 10.5220/0011583900003527
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific and Practical Conference on Transport: Logistics, Construction, Maintenance, Management (TLC2M 2022), pages 286-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-606-4
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

staff turnover is the result of poor management, and
low turnover can lead to depression, stagnation.
Another idea of the view on staff turnover was
reflected by Harrison (Harrison, 1996). He argued
that this is not an event that takes place at any point
in time, but a process that takes place over time and
contains changes between the employee and the
organization (Dickter, 1996).
Rassbult and Farrell (Rassbult, 1981; Farrell,
1983) believed that a low level of loyalty to work is
the cause of increased staff turnover.
Such scientists as Lee (Lee, 1994), Fireman
(Fireman, 1996) justified their own conceptual theory
of staff turnover, where, in our opinion, most of all
the employee evaluates his psychological feelings
that allow him to leave the organization or stay (Lee,
1996).
The problem of staff turnover was dealt with by
many domestic scientists: Odegov Yu.G., Kibanov
A.Ya., Shchekin G.V., Zhuravleva P.V., Kartashova
L.V., Kozina I.M., Grigorieva I., Filippov A.V.,
Kondakova A.A., Volkova I.A., Notchenko V.V.,
Zhukova M.V., Boikova M.A., Bulgakova M.A.,
Gagarinskaya G.P., et al, the published works
summarized the essential causes of staff turnover and
the features of overcoming them (Volkova, 2018;
Notchenko, 2013; Boikova, 2017; Bulgakova, 2017;
Gagarinskaya, 2017).
So, Yu.G. Odegov noticed that the essence of
the category "increased staff turnover" may be due
to: the specifics of the industry (in the field of trade,
hotel service staff turnover is higher); the status of
personnel (administrative and managerial personnel
has a lower turnover than linear); the location of the
company geographically (in companies located in
small cities, staff turnover is lower than in large
cities); employees are more likely to be dismissed
with low unemployment. Unstable employment of
young people in modern conditions was also noted
(Odegov, 2018).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Quantitative indicators are put forward as one of the
methods of analyzing staff turnover in our study. We
have analyzed these data on the whole for Russian
Railways JSC for the last five years, and specifically
for one of the divisions – the Tyumen Center for the
Organization of the work of railway stations for 2018-
2020. We especially note that we are considering not
only quantitative data. We also emphasize that staff
turnover is rarely considered in relation to HR risks.
HR risks in modern conditions are becoming one of
the objects of research in the digital economy
(Personnel management in the digital environment: a
monograph, 2021). Moreover, staff turnover acts as
one of the factors of HR risk, where the main role is
played by low wages, work schedule, unsatisfactory
working conditions, psychological atmosphere in the
team (Sahakyan, 2016).
Staff turnover is included by some authors in the
personnel security of the enterprise, information
threats (Kuznetsova, 2019; Boydalo, 2017; Korolev,
2019; Fursov, 2020).
Turning to statistics, let's consider the percentage
of staff turnover of Russian Railways JSC over the
past few years. According to the annual reports of
Russian Railways JSC in 2020, 723.5 thousand
people worked, in 2017 - 755.0 thousand people. The
reduction in the number of personnel occurred by
4.2% compared to 2017. The turnover rate has
decreased slightly over the past 5 years (See Table 1).
Table 1: Indicators of staff turnover of Russian Railways
JSC for 2016-2020, in %.
Rates
of staff
turnove
r
2016
year
2017
year
2018
year
2019
year
2020
year
As % 7,5 6,7 6,4 6,7 6,2
Compiled by the author: according to Reports on the
activities of Russian Railways JSC in the field of
sustainable development.2019 p.137; 2020 p.171
Table 2: Indicators of staff turnover, including by position Central Suburban Passenger Company JSC
for 2018-2020, in %.
Rates
2018 2019 2020
Total turnover percentage, %
15,2 16,2 11,4
% turnover by position "Cashier-controller"
19,6 20,4 18,9
% turnover by position "Electric locomotive driver"
1,3 1,6 1,9
% turnover by position "Electric locomotive driver's assistant"
3,1 5,6 8,0
Compiled by the author: according to the Annual Report of Central Suburban Passenger Company JSC according to the
results of work for 2020. p.27.
Staff Turnover as a Problem of HR Risk
287
The threshold value of staff turnover in
accordance with the internal calculation methodology
of Russian Railways JSC is set at 8%. Today, this
indicator is steadily kept below the threshold. But if
we take specific railway divisions, branches,
individual professions, regions, the statistics are very
different. Thus, in recent years, the turnover of
personnel on the Sverdlovsk Railway was 10.1%. In
Central Suburban Passenger Company JSC of the
Central Federal District, the statistics are as follows:
The turnover threshold is not a static indicator.
Thresholds vary by industry and category of
personnel. Based on practice, we note that the
turnover of unskilled employees (movers, cleaners)
can reach 50%.
Staff turnover is influenced by many factors:
employee qualifications, education, age, and much
more.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Among the most significant, in our opinion, and not
always systematically studied, are psychological
factors. As a rule, they rarely come to the attention of
managers. Therefore, firstly, it is necessary to identify
important socio-psychological reasons for staff
turnover at the enterprise, determining what kind of
character they have: objective or subjective.
Secondly, as possible reasons for dismissal from the
organization, to study and present the methodology
for the diagnosis of individual characteristics of the
employee. This is carried out at the selection stage:
professional tests, personal questionnaire,
motivational questionnaire of RZD, SHL test of RZD.
In other words, the dismissal of an employee is
determined by the unsuitability of the employee's
personal qualities to the nature and content of
professional occupations, and this leads to increased
personnel turnover.
Turning to the practice of individual railway
transport units on the issue of interest to us, and
performing an analysis of the movement of personnel
and staff turnover in the Tyumen Center for the
organization of work of railway stations, a structural
subdivision of the Sverdlovsk Directorate of Traffic
Management, a branch of Russian Railways JSC for
2018-2020, we observe a staff turnover of 14.58% in
2020 (See. Table 3)
The age group of those who quit voluntarily are
young people aged 20 to 30 years who have worked
in the organization for about a year (See Table 4.5).
63.89% leave the organization before they have
worked for a year; 66.7% are young people aged 20
to 30 years. These statistics are also relevant for other
departments of the studied industry.
What is being done to consolidate the personnel
in Russian Railways JSC:
− A detailed analysis of the reasons for the outflow
of staff in the first year of work is being
conducted.
− Analyzes the statistics of retiring personnel by
category, especially by age category — up to 35
years.
− On the basis of questionnaires filled out by
dismissed employees, statistics are generated for
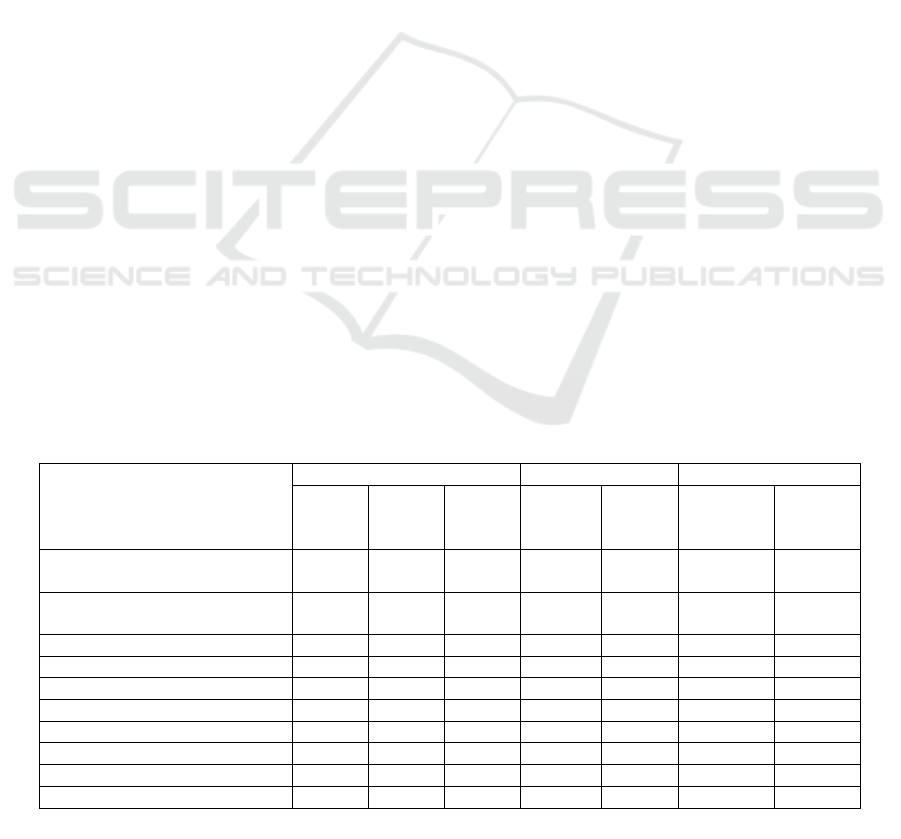
Table 3: Calculation of staff turnover coefficients in the Tyumen Center for the organization of work of railway
stations for 2018-2020.
Key indicators
Years Absolute deviation Growth rate, %
2018 2019 2020
2019/
2018
2020/
2019
2019/
2018
2020/
2019
Staff, average number of
em
p
lo
y
ees,
p
eo
p
le.
590 573 569 -17 -4 -2,88 -0,70
Total turnover of the workforce,
p
eo
p
le.
179 222 159 43 -63 24,02 -28,38
Acce
p
ted,
pp
l. 82 95 76 13 -19 15,85 -20
Dismissed,
pp
l. 97 127 83 30 -44 30,93 -34,65
including:
voluntaril
y
47 108 34 61 -74 129,79 -68,52
retirement 45 19 48 -26 29 -57,78 152,63
violation of labor disci
p
line 2 0 0 -2 0 Х Х
service in the Armed Forces 3 0 1 -3 1 Х Х
Staff turnover rate, % 16,45 22,18 14,58 5,73 -7,61 34,86 -34,29
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
288
reasons of outflow, Roadmaps and Programs for
securing personnel are developed.
In our opinion, Targeted programs related to
reducing staff turnover should be supplemented with
the following issues:
− carry out a more objective final control by the
mentor on the problem of the appointment of
an accepted employee; to monitor on an
ongoing basis in order to study the potential
turnover of personnel in the organization; to
perform promotion to the personnel reserve
after three years of work in the company; to
staff the personnel reserve not only for key
specialists, but also for lower-level managers;
to reduce staff turnover among employees
enrolled in the personnel reserve.
4 CONCLUSION
The conclusions that we came to in the course of our
study of the problem.
− When characterizing the turnover of personnel
by the personnel management department,
calculate the turnover intensity coefficient on
an ongoing basis, which allows you to track
stabilization issues in individual divisions and
structures of the enterprise.
− Strengthen the study of socio-psychological
aspects of staff turnover, using the latest
techniques and technologies to analyze these
processes of a particular enterprise
− Carry out constant monitoring in the
departments of the studied industry, where
there is a high turnover of personnel among
various categories of personnel.
− Analyze and identify HR risks arising from the
dismissal of employees using digital
technologies in this activity, paying attention to
the information component, material costs
provided by the organization.
REFERENCES
Bennett, R., 2020. Coefficients of calculation of staff
turnover. HR-maximum: information portal.
http://www.hrmaximum.ru/articles/management/430.
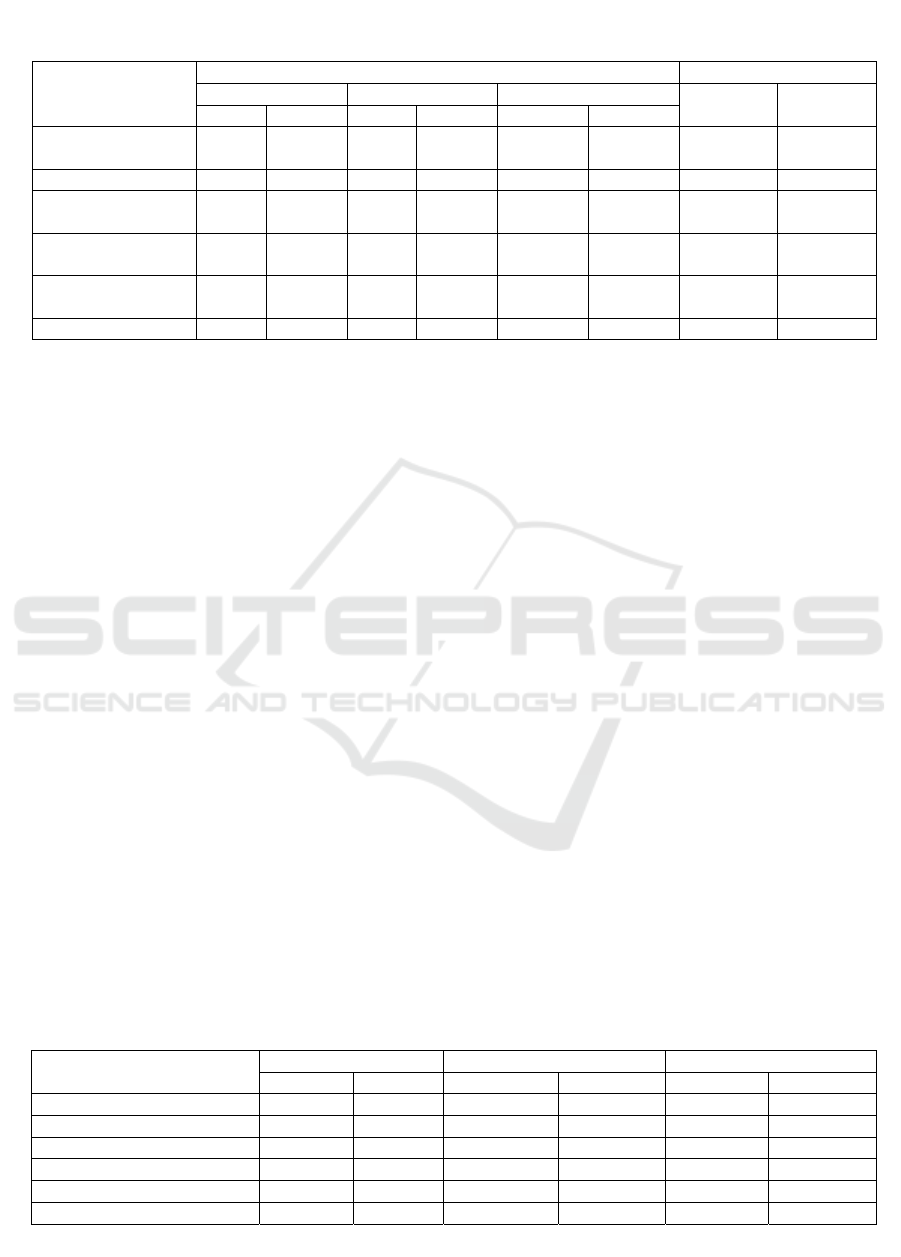
Table 4: Number of employees by age, who left voluntarily in the Tyumen Center for the organization of work of
railway stations for 2018-2020.
Indicator
Absolute deviation
2018 2019 2020
2019/
2018
2020/
2019
p
erson %
p
erson %
p
erson %
Dismissed at his
own request
47 100,00 108 100,00 34 100,00 61 -74
includin
g
:
age from 20 to 30
years
28
59,57
72
66,67
18 52,94
44
-54
age from 30 to 40
y
ears
12
25,53
34
31,48
13 38,24
22
-21
age from 40 to 50
y
ears
6
12,77
2
1,85
38,82
-4
1
over 50
y
ears 1 2,13 0 0,00 0 0,00 -1 0
Table 5: Number of employees of the Tyumen Center for the organization of work of railway stations by work
experience, dismissed at their own request in 2018-2020.
Dismissed employees with
work experience
2018 2019 2020
p
erson %
p
erson %
p
erson %
up to 1 yea
r
28 59,57 69 63,89 23 67,65
from 1 to 5 years 8 17,02 17 15,74 3 8,82
from 5 to 10
y
ears 7 14,89 4 3,70 2 5,88
from 10 to 15
y
ears 2 4,26 9 8,33 4 11,76
over 15
y
ears 2 4,26 1 0,93 2 5,88
Total 47 100 108 100 34 100
Staff Turnover as a Problem of HR Risk
289

Dickter, D. N., Roznowski, M., Harrison, D. A., 1996.
Temporal tempering: An event history analysis of the
process of voluntary turnover. Journal of Applied
Psychology. 81. pp.705-716.
Lee, T. W., Mitchell, T. R., Wise, L., Fireman, S., 1996. An
Unfolding Model of Voluntary. Staff turnover.
Academy of Management Journal. 39 (1). pp. 5-36.
Volkova, I., Kondakova, A., 2018. Formation of the process
of personnel turnover management of the organization.
Bulletin of the Belgorod University of Cooperation,
Economics and Law. 5. pp. 141-152.
Notchenko, V., Zhukova, M., 2013. Investigation of the
problem of high staff turnover in industrial
enterprises. Bulletin of Pskov State University. Series:
Economy. Right. Management. 2. pp. 111-120.
Boikova, M. A., 2017. Personnel training system as a tool
to reduce staff turnover. Collection of scientific articles
of the II International Scientific and Practical
Conference. "Modern studies of human resources
management problems". pp. 67-73.
Bulgakova, E. N., Sevostyanov, D. A., 2017. The concept
and essence of staff turnover. Proceedings of the
scientific and practical conference "Socio-economic
problems of improving management activities: theory
and experience". pp. 33-35.
Gagarinskaya, G. P., Schmidt, A. V., Gagarinsky, A. V.,
2017. Problems of formation of the process of selection,
recruitment and hiring of employees to regulate the
turnover of personnel of the organization. Journal
Economics and Entrepreneurship. 8-1 (85-1). pp. 505-
510.
Odegov, Yu. G., Babynina, L. S., 2018. Non-standard
employment as a possible factor in using the potential
of the youth workforce in Russia. Journal Monitoring
Public Opinion: Economic and Social Changes. 4. pp.
386-409.
Personnel management in the digital environment: a
monograph. 2021. p. 122.
Sahakyan, M. K., Matveev, E. V., Skvortsov, E. A., 2016.
Types of HR risks in personnel management. Journal
Agrarian Education and Science. 2. pp. 44-51.
Kuznetsova, N. V., 2019. Personnel security of the
organization: the essence and mechanism of ensuring.
p. 286.
Boydalo, M. K., Zhigulin, G. P., 2017. Methodology and
model for assessing professional compliance of
personnel in matters of information security. Scientific
and Technical Bulletin of the Volga region. 3. pp. 86-
91.
Korolev, M. I., 2019. The problem of security in the theory
of the firm. Development and contradictions. Bulletin
of Volgograd State University. 1(20). pp. 53-58.
Fursov, V. A., Lazareva, N. V., Kushch, E. N., Avetova, K.
G., 2020. Personnel security of the enterprise:
approaches, diagnostics, directions of improvement.
Bulletin of the Altai Academy of Economics and Law. 4
(2). pp. 270-276.
TLC2M 2022 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC AND PRACTICAL CONFERENCE TLC2M TRANSPORT: LOGISTICS,
CONSTRUCTION, MAINTENANCE, MANAGEMENT
290
