
Space Geeks: A Proposed Serious Game to Teach Array Concept for
Novice Programming Students
Abdelbaset Jamal Assaf
a
, Mohammed Eshtay
b
and Lana Issa
c
Abdul Aziz Al Ghurair School of Advanced Computing, Luminus Technical University College, Amman, Jordan
Keywords:
Serious Games, Computer Programming, Game-based Learning, Education, Arrays, 3D Games.
Abstract:
The failure rates in introductory programming courses still shows that there is a continuous need in research
to investigate and propose new methods and techniques of teaching introductory to programming courses to
attract more people to the information technology field and build more skilled programmers from their first
course. This study investigates students levels in multiple topics in introduction to programming, then, pro-
poses a new science fiction themed game called Space Geeks. The game is initially designed to target arrays,
and is extendable to cover more programming concepts. The design of this games helps students enhance
their coding skills, gives motivation using game features, and helps them understand the arrays concept by
visualisation and graphics. This work will open more insights to focus on further introductory topics such
as arrays since that there has been other work to focus on other topics such as variables, input/output, and
problem solving.
1 INTRODUCTION
The information technology sector is attracting a lot
of students around the world according to the National
Centre for Education Statistics, there is an increase of
11.7% in Information technology studies around the
world. Many people have understood the need for
information technology specialisations, after seeing
that it is involved in many fields in the daily human
lives, such as education, healthcare, engineering, and
business. This led to innovating many specific ma-
jors in higher education related to computer science
and information technology, with the different spe-
cialisations offered by many higher education insti-
tutions around the world. They all need introductory
and beginner courses in the first year of any program,
to prepare students for any computer science related
major. Teaching introductory courses is considered
challenging. It shapes the basic idea about computer
science for students, it allows them to understand how
to think like programmers, and builds their problem-
solving skills. Many students do not know how to
handle introductory courses, because they’re still new
to IT-related studies, new to higher education tech-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3468-1388
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5325-5304
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9440-3366
niques. Where the student is more responsible for
their education, and also some have weak computer
skills, thus, the failure rates are sometimes high in
some introductory courses (Cheah, 2020). Many re-
searchers have studied and analysed this problem over
the years (Luxton-Reilly et al., 2018). On the other
hand, many researchers suggested methods for im-
proving teaching introduction to programming, such
as gamification, blended learning, rewards, etc. one
of the suggested approaches is using serious games
in teaching programming (Lamb et al., 2017). Seri-
ous Games were used as learning activity in classes
to increase the quality of learning (Lamb et al., 2017)
and enhance the academic achievements of students in
multiple topics such as programming and mathemat-
ics (Alonso-Fern
´
andez et al., 2019; Fokides, 2018;
Giannakoulas and Xinogalos, 2018).
(Bergeron, 2006) defined serious games as “in-
teractive computer application, with or without sig-
nificant hardware component, that has a challenging
goal, is fun to play and engaging, incorporates some
scoring mechanism, and supplies the user with skills,
knowledge, or attitudes useful in reality”. Further,
the study by (Laamarti and El Saddik, 2014) defined
serious games as “an application with three compo-
nents: experience, entertainment, and multimedia”.
The different definitions of serious games highlight
the importance of different characteristics that must
Assaf, A., Eshtay, M. and Issa, L.
Space Geeks: A Proposed Serious Game to Teach Array Concept for Novice Programming Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0011589200003318
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2022), pages 431-438
ISBN: 978-989-758-613-2; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
431

be present in the serious games to engage, motivate
and immerse the users such as entertainment and en-
joyment. If a serious game doesn’t engage or moti-
vate the user in an interactive and entertaining way as
a video game does, the user will not be immersed and
focused while using the serious game. Thus, the se-
rious game will fail to deliver its educational content
to the user or the benefits of playing the game will be
minimised.
(Dale, 2006) conducted a survey on teachers of
CS1 courses and stated that the lack of practice is
the reason behind the difficulties the students face
in learning computer programming. Furthermore,
(Gomes and Mendes, 2007) have highlighted the need
for an increased amount of practice time and students’
engagement. Therefore, serious games can be used to
motivate and engage students, which can lead to an
increase of practice time.
The next section will explore the previous work
that have been conducted to enhance students’ under-
standing in introductory courses. In Data collection
section, the failure rates in programming courses are
investigated and data is collected and analysed to val-
idate the previous findings. Further, analysis of a sur-
vey to identify the difficult concepts of computer pro-
gramming is presented. The proposed game section
highlights the developed game and finally the conclu-
sion section that presents a summary for the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Many interesting teaching techniques and tools were
introduced in recent years, that include moving
towards increased student engagement, interactive
learning, adaptive tutoring, augmented reality, and
more (Hantoobi et al., 2021). Serious games have
been used by many people to create a more interactive
and entertaining learning environment that increases
the learner’s attention and supports them in their
academic achievements during programming courses
(Daoudi, 2022; Zhao et al., 2021). Serious games
were found to have a positive effect on the learner’s
journey during programming courses, it was proven
to support the learning activity of students, increase
their motivation, help with better academic achieve-
ment and knowledge acquisition (Kasenides, 2021;
Lamb et al., 2018; Hainey et al., 2016).
Focusing on programming, especially in intro-
ductory courses, many students struggle with shap-
ing their mental models for understanding the basics
of programming, some struggle with the syntax, the
problem solving, coding skills, or data structures. A
lot of studies were made in this area to test methods
that improve the student’s learning and understand-
ing of certain topics (Ramabu et al., 2021; Luxton-
Reilly et al., 2018; Sorva, 2013; Sorva, 2008). One
of the suggested techniques was the use of visuali-
sation in various programming conceptions such as
variables, recursion, and sorting algorithms (AlZoubi
et al., 2015; Tuparov et al., 2014; Badri et al., 2011;
Sorva, 2008).
One of the important topics that was discussed in
previous research work is teaching arrays. Many tech-
niques were introduced and tested to ease the process
of understanding and dealing with arrays in program-
ming courses. (Hilton and Janzen, 2012) proposed us-
ing test-driven development as a main focus to guide
the process of teaching arrays. On the other hand,
(R.Z. Ramli and Osman, 2015) suggested focusing on
visualisation to teach arrays. Also, (Figueiredo and
Garc
´
ıa-Pe
˜
nalvo, 2021) proposed a predictive machine
learning model based on student behaviour in course
to assist with teaching arrays. Serious games were ap-
plied in different ways, in many studies that focused
on arrays (Baker et al., 2012). Wu’s castle was one of
the early examples to be introduced to literature, that
teaches arrays and loops (Eagle and Barnes, 2008).
In general, many serious games were used to
teaching computer programming concepts such as Al-
ice, which is well-known serious game that is an in-
novative block-based programming environment, it’s
an open-source game written in Java. It is a 3D in-
teractive environment that has visual and narrative as-
pects (Aktunc, 2013). Moreover, one of the vastly
used serious games is Scratch which is a multime-
dia environment developed by the media lab at the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Users can de-
velop programs by fitting fragments of computer pro-
grams together. The game allows the users to drag
and drop blocks to teach them about programming
topics such as variables, conditions, loops and ob-
jects (Bittencourt et al., 2015; Mishra et al., 2014).
Another famous games that was used in previous lit-
erature to teach programming is Robocode. It was
applied in different approaches to teaching many pro-
gramming concepts (Liu, 2008; Long, 2007; Bierre
et al., 2006). Catacombs (Barnes et al., 2007), Saving
Serra (Barnes et al., 2007), Elemental (Chaffin et al.,
2009) and Prog & Play (Muratet et al., 2011) are other
examples of games that are specifically developed to
teach about programming. More details are shown in
the comparison table 1, that summarises the features
in every game from previous work in research, based
on style of programming, the main concepts that are
covered in the game. Also, the game’s approach of
program construction, using typing or assembling vi-
sual objects.
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
432
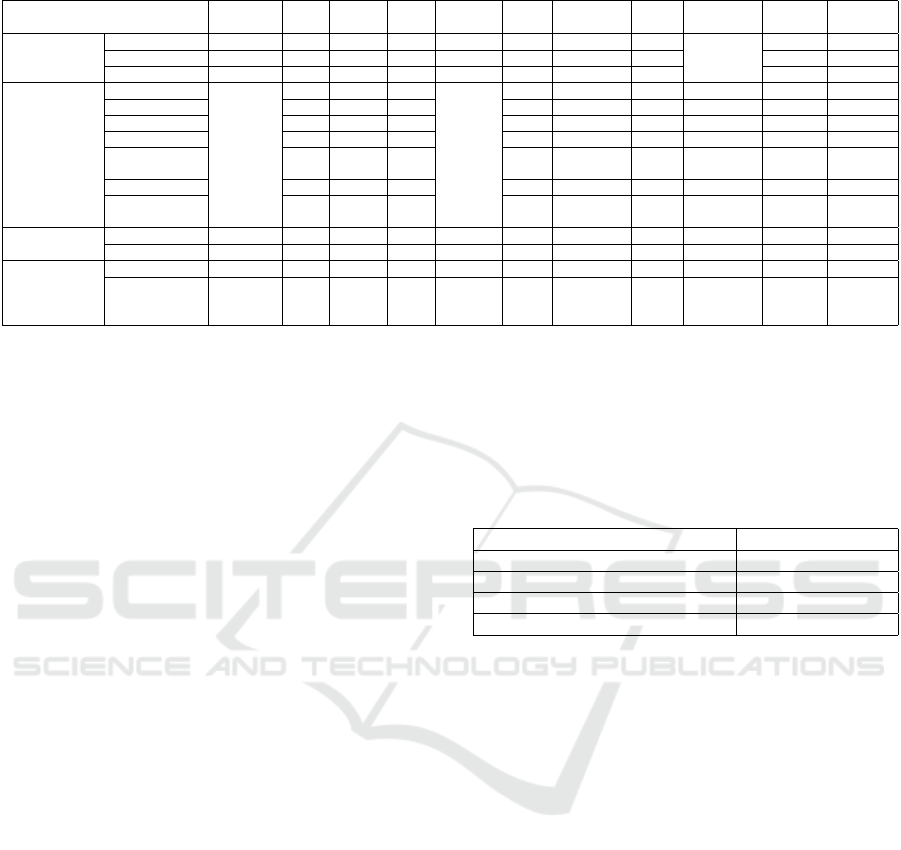
Table 1: Games comparison.
Comparison Criteria / Game Robocode Alice Scratch Jeroo
Bomber-
man
Turtle
logo
Catacombs
Wu’s
Castle
Prog&Play Lightbot
PlayLogo
3D
Style of
programming
Procedural X X
Multiple
X X
Object-based X X
Object-oriented X X X X
Covered
concepts
Variables
Java
language
X X X
C
language
X X X X
Conditions X X X X X X X
Loops X X X X X X X
Methods X X X X X X X
User-defined
data types
Recursion X
Collections/
arrays
X X X
Code
representations
Text X X X X X X X X X X
Pictures X
Program
construction
Typing code X X X X X X X X
Assembling
graphical
objects
X X X
3 DATA COLLECTION
Previous research found that the failure rates in pro-
gramming courses are high. Moreover, the literature
showed that some programming concepts are more
difficult than others. In order to validate the previ-
ous findings and to highlight the most difficult pro-
gramming concepts for novice students. Data were
collected and analysed as shown in the following sub-
sections.
3.1 Exploring Failure Rates in
Programming Courses
In many universities around the world, Students con-
tinue to withdraw or fail introductory programming
courses at rates over 30% (Bennedsen and Caspersen,
2019; Bennedsen and Caspersen, 2007). (Simon
et al., 2019) ”found that pass rates in introductory
programming courses appear to average about 75%;
that there is some evidence that they sit at the low
end of the range of pass rates in introductory STEM
courses.”. This brought to our attention that we need
to understand which topics are more difficult for stu-
dents than others, so we wanted get insights on how
students’ level varies from one topic to another. First,
we analysed the grades of three introductory courses
that discusses topics that are related to programming,
which are: Introduction to programming using Java,
Introduction in information technology, and Maths
for computing. Then, we did further analysis to
understand how students respond to different topics
in introductory courses, that they take in their first
semester.
We analysed 2213 records of first year British
diploma students, in four different majors, Software
Engineering, Cyber Security, Artificial Intelligence,
and Cloud Computing, in Amman, Jordan. Table 2
shows the number of students in each major. Our find-
ings about pass/fail rates are shown in Table 3.
Table 2: Students majors.
Major Number of students
Diploma in Software Engineering 1281
Diploma in Cyber Security 674
Diploma in Artificial Intelligence 221
Diploma in Cloud Computing 36
We can see that the percentage of students
who failed introduction to programming is higher
than 30% as mentioned before by (Bennedsen
and Caspersen, 2019), where the percentage is
33.5%. Unlike Introduction in Information Technol-
ogy, where the students pass rates are very high since
that it does not include actual coding only simple al-
gorithms design using flowcharts, also learning about
computer software and hardware, logical gates, and
other IT related topics such as databases, networking,
and software engineering. We notice that the Maths
for Computing course has also normal fail rate but the
percentage of students grades between 50 and 70 is
41.77% out of all passing students, which is consid-
ered a little high, but not as introduction to program-
ming, since that it also does not require coding, but
just maths concepts related to programming, like sets,
graphs, prime numbers, probabilities, etc. The rea-
son why introduction to programming has the highest
failing rate is because it contains coding and problem
solving, with focus on problems that contains loops,
nested loops, and arrays.
Several studies have demonstrated that novice
programmers have difficulties in learning Object Ori-
ented Programming concepts (Kunkle and Allen,
Space Geeks: A Proposed Serious Game to Teach Array Concept for Novice Programming Students
433
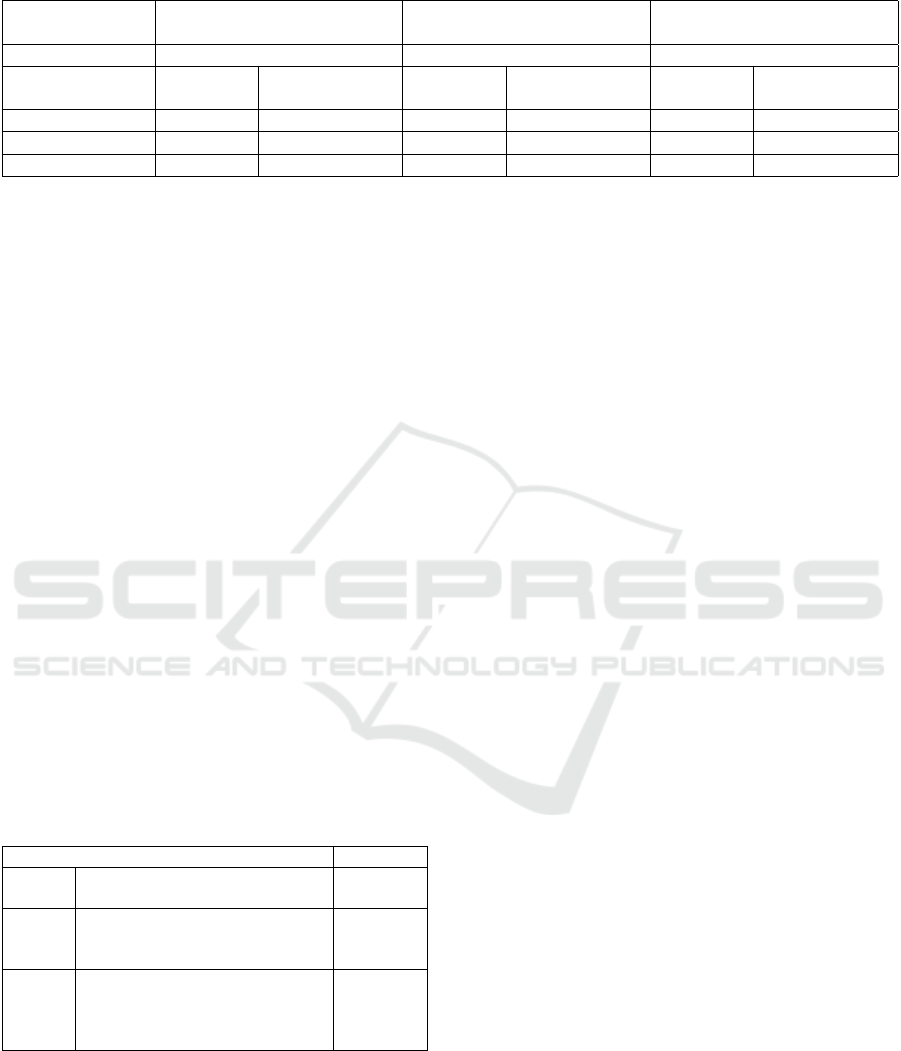
Table 3: Students marks in the introductory courses.
Course
Introduction to
Programming
Math for
Computing
Introduction in
Information Technology
Records analysed 800 records 706 records 706 records
Number of
students
Percentage from
total
Number of
students
Percentage from
total
Number of
students
Percentage from
total
Passed 532 66.50% 644 91.20% 553 78.33%
Failed 268 33.50% 62 8.78% 153 21.67%
Grade 50-70 346 65.04% 358 55.59% 231 41.77%
2016; Bennedsen and Caspersen, 2007; Goosen and
Pieterse, 2005; Kelleher and Pausch, 2005; Ragonis
and Ben-Ari, 2005). For example, students face sev-
eral problems understanding classes, objects, recur-
sion and inheritance (Yan, 2009). There are issues
that emerge when teaching programming at an early
stage, where students struggle with analysing and de-
signing of the code (Papadopoulos and Tegos, 2012;
Lopez et al., 2008; Cooper et al., 2000). Further, stu-
dents face difficulties because of the rigid program-
ming syntax and the large amount of time required to
assemble a simple output (Sloan and Troy, 2008).
3.2 Programming Concepts Survey
In order to investigate the reasons behind the high fail-
ure rate in the Introduction to Programming course in
our school and to study students’ levels in multiple
programming concepts. We distributed an online sur-
vey to over 100 students in the computer science de-
partment. The aim was to analyse and get feedback
on the reason why the failing rate is 33.5% and the
percentage of students who got a grade between 50
and 70, is 65% out of all passing students. We re-
ceived 97 responses, Table 4 shows the demographic
description.
Table 4: Demographic description of the surveyed students.
Demographic Description Frequency
Gender
Male
Female
56
41
Age
18
19
20 or over
60
25
12
Major
Diploma in Software Engineering
Diploma in Cyber Security
Diploma in Artificial Intelligence
Diploma in Cloud Computing
33
24
29
11
In the survey, we asked students some background
questions to get insights about their behaviour in pro-
gramming courses. Students were asked to evaluate
the difficulty of the concepts included in introduction
to programming course, which are variables, condi-
tions, input and output, loops and arrays. The results
are shown in Figure 1
We notice that the hardest concept for students
was arrays, where 53% of the students’ rated arrays as
a hard topic. Arrays are considered one of the essen-
tial topics in introductory programming courses, in
order to form a good basis to learning more about pro-
gramming such as problem solving, data structures
and algorithms, and advanced programming skills.
Teaching arrays could be challenging especially for
novice students (Rigby et al., 2020), which motivates
us to find a solution to improve the students’ un-
derstanding of the arrays concept and helps students
achieve better in this topic. We have also asked the
if they were interested in learning introduction to pro-
gramming concepts using serious games. 79 out of 97
students answered that they are very interested.
It is worth noting that the games that focused on
arrays are limited, but there has been a decent amount
of work targeting loops, conditions, variables, and
methods. Hence, we propose new game that offers
a road map for learners in programming courses to
learn arrays in particular. The road map contains mul-
tiple tasks for the student to complete, focused on ar-
rays, with animation and visualisation for the written
solutions. In the next section, an explanation about
the game and the game-play is provided.
4 PROPOSED GAME
Space Geek is a third-person camera view, which sup-
ports interactive camera. It was designed with the
aim to enable introductory programming students to
practice and implement their knowledge in Java ar-
rays. This means that it should be used in parallel
with classroom or online education and not as a stand-
alone tool for teaching arrays. The game is developed
using Unity3D game engine and it is connected to an
external API which serves as a Java compiler.
Space Geeks is a science fiction themed game,
in which the goal is to help the character to move
through the rooms by writing code to answer several
questions to reach the end of the alien building so the
character can reach outer space. Figure 2 shows a
screenshot of the character in game.
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
434

Figure 1: Programming concepts evaluation.
Figure 2: The character in the game.
In each room there is a computer, in which the
character can interact with. Once the character inter-
acts with the computer a screen appears with a ques-
tion. The screen contains source editor to write code
to answer the question. The player should answer the
question by writing Java code to solve the problem.
After the code is written the player can submit the
code. The external API will compile it and return the
result to the user as seen in Figure 3. If the question is
answered correctly, then an animation will be played
to visualise the answer. The animation can vary from
constructing an array of objects to reordering a pile
of objects. The animation was added to visualise the
process since several studies associated all the chal-
lenges in teaching computer programming to the lack
of visualisation (Derus and Ali, 2012; Rosenberg and
K
¨
olling, 1997).
Figure 3: Java code compilation.
The questions are represented by levels, where
each level is a room. The player cannot get out of the
room unless the question is answered. Once the ques-
tion is answered correctly, then the room’s door will
be unlocked and the character can move to the next
room. The current prototype of the game consists of 9
questions embodied by 9 rooms. It starts with a sim-
ple question which is declaring an array and as you
move through the rooms, the questions become more
complex.
A noteworthy effort has been made by (Calder
´
on
and Ruiz, 2015). They explored the literature and
summarised the quality characteristics that have been
used to evaluate serious games into 18 characteristics,
which are game design, user’s satisfaction, usability,
users experience, understandability, enjoyment, mo-
tivation, user interface, playability, pedagogical as-
Space Geeks: A Proposed Serious Game to Teach Array Concept for Novice Programming Students
435

pects, performance, learning outcomes, engagement,
usefulness, cognitive behaviour, social impact, accep-
tance and efficacy. (Abdellatif et al., 2018a) grouped
the quality characteristics based on their importance
into two groups, which are primary and secondary.
The game was designed taking into considera-
tion the primary quality characteristics of serious
games which are usability, motivation, engagement,
user’s experience and understandability that were
highlighted by (Abdellatif et al., 2018b) with empha-
sis on understandability and usability quality char-
acteristics among other quality characteristics due to
their superior importance.
The game is expandable, since more questions can
be added or even a new topic can be introduced such
as conditions, loops, data structures and algorithms.
This version of the game supports only Java. How-
ever, it can be extended to other programming lan-
guages by simply using other compilers APIs.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Many students continue to fail introductory to pro-
gramming courses. Failure rates are still above 30%
as mentioned in previous research work, and as we
prove in this research. The studies must continue on
finding and improving innovative techniques of teach-
ing introductory programming topics, because of the
great need in the world for more people working in
the information technology field. In this research, we
analysed students records to get accurate insights on
students levels in multiple introductory courses, we
investigated the failure rates and the overall average.
Our findings show that there was 33% failure rate in
introduction to programming. Then, we studied stu-
dents responses to evaluate their knowledge in many
introduction to programming topics, and we found
that many students face problems with understand-
ing arrays. This study proposed a new game; Space
Geeks, that targets arrays as the main concept, its a
science fiction themed game that includes visualisa-
tion, graphics and animation, and it is consisted of
multiple levels that adds motivating features for stu-
dents. This game also encourages students to apply
their coding skills and motivates them to do coding
exercise at every room in the game to finish more
steps in the game road map, since that many students
have lack of practice and need motivation to enhance
their coding skills. For future work, several tests must
be applied to Space Geeks, starting from assessing the
quality of the game for the purpose of highlighting
the game strengths and weaknesses in order to im-
prove them. Moreover, a suitability test must take
place such as the work suggested by (El Borji and
Khaldi, 2014) to check if the game is applicable on a
certain audience. Finally, Space Geeks must be tested
in an educational environment by designing an exper-
iment to measure the effectiveness of using it on stu-
dents, if any. This test will be used to measure two of
the most important quality characteristics of a serious
game which are learning outcomes and pedagogical
aspects. As they form the difference between video
games and serious game in which their occurrence
make games have educational content and purpose.
REFERENCES
Abdellatif, A. J., McCollum, B., and McMullan, P. (2018a).
Serious games: Quality characteristics evaluation
framework and case study. In 2018 IEEE Integrated
STEM Education Conference (ISEC), pages 112–119.
Abdellatif, A. J., McCollum, B., and McMullan, P. (2018b).
Serious games quality characteristics evaluation: The
case study of optimizing robocode. In 2018 Interna-
tional Symposium on Computers in Education (SIIE),
pages 1–4.
Aktunc, O. (2013). A teaching methodology for introduc-
tory programming courses using alice. International
Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER), 3.
Alonso-Fern
´
andez, C., Calvo-Morata, A., Freire, M.,
Mart
´
ınez-Ortiz, I., and Fern
´
andez-Manj
´
on, B. (2019).
Applications of data science to game learning analyt-
ics data: A systematic literature review. Computers &
Education, 141:103612.
AlZoubi, O., Fossati, D., Di Eugenio, B., Green, N., Al-
izadeh, M., and Harsley, R. (2015). A hybrid model
for teaching recursion.
Badri, S., Denholm-Price, J., and Orwell, J. (2011). Lay-
out for learning - designing an interface for students
learning to program. volume 1, pages 324–332.
Baker, A., Zhang, J., and Caldwell, E. R. (2012). Rein-
forcing array and loop concepts through a game-like
module. In 2012 17th International Conference on
Computer Games (CGAMES), pages 175–179.
Barnes, T., Richter Lipford, H., Powell, E., Chaffin, A., and
Godwin, A. (2007). Game2learn: building cs1 learn-
ing games for retention. volume 39, pages 121–125.
Bennedsen, J. and Caspersen, M. (2007). Failure rates in
introductory programming. SIGCSE Bulletin, 39:32–
36.
Bennedsen, J. and Caspersen, M. E. (2019). Failure rates
in introductory programming: 12 years later. ACM
Inroads, 10(2):30–36.
Bergeron, B. P. (2006). Developing Serious Games”.
Charles River Media. Charles River Media.
Bierre, K., Ventura, P., Phelps, A., and Egert, C. (2006).
Motivating oop by blowing things up: An exercise in
cooperation and competition in an introductory java
programming course. In Proceedings of the 37th
SIGCSE Technical Symposium on Computer Science
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
436

Education, SIGCSE ’06, page 354–358, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Bittencourt, R. A., dos Santos, D. M. B., Rodrigues, C. A.,
Batista, W. P., and Chalegre, H. S. (2015). Learning
programming with peer support, games, challenges
and scratch. 2015 IEEE Frontiers in Education Con-
ference (FIE), pages 1–9.
Calder
´
on, A. and Ruiz, M. (2015). A systematic literature
review on serious games evaluation: An application to
software project management. Computers & Educa-
tion, 87:396–422.
Chaffin, A., Doran, K., Hicks, D., and Barnes, T. (2009).
Experimental evaluation of teaching recursion in a
video game. Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIG-
GRAPH Symposium on Video Games, Sandbox ’09.
Cheah, C.-S. (2020). factors-contributing-to-the-
difficulties-in-teaching-and-learning-of-computer-
programming-a-literature-review. Contemporary
Educational Technology, 12:ep272.
Cooper, S., Dann, W., and Pausch, R. (2000). Alice: A 3-d
tool for introductory programming concepts. Journal
of Computing Sciences in Colleges, 15(5):107–116.
Dale, N. B. (2006). Most difficult topics in cs1: Re-
sults of an online survey of educators. SIGCSE Bull.,
38(2):49–53.
Daoudi, I. (2022). Learning analytics for enhancing the us-
ability of serious games in formal education: A sys-
tematic literature review and research agenda. Educa-
tion and Information Technologies.
Derus, S. and Ali, A. (2012). Difficulties in learning pro-
gramming: views of students. In 1st International
Conference on Current Issues in Education, volume
134 of ICCIE 2012.
Eagle, M. and Barnes, T. (2008). Wu’s castle: Teach-
ing arrays and loops in a game. SIGCSE Bull.,
40(3):245–249.
El Borji, Y. and Khaldi, M. (2014). Comparative study to
develop a tool for the quality assessment of serious
games intended to be used in education. International
Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET),
9(9):pp. 50–55.
Figueiredo, J. and Garc
´
ıa-Pe
˜
nalvo, F. (2021). Teaching and
learning tools for introductory programming in uni-
versity courses. In 2021 International Symposium on
Computers in Education (SIIE), pages 1–6.
Fokides, E. (2018). Digital educational games and math-
ematics. results of a case study in primary school
settings. Education and Information Technologies,
23:851–867.
Giannakoulas, A. and Xinogalos, S. (2018). A pilot study
on the effectiveness and acceptance of an educational
game for teaching programming concepts to primary
school students. Education and Information Technolo-
gies, 23:1–24.
Goosen, L. and Pieterse, V. (2005). Roller coaster riding:
highs and lows of understanding oo. In Proceedings
of the 35th Conference of SACLA, pages 109–114.
Hainey, T., Connolly, T. M., Boyle, E. A., Wilson, A., and
Razak, A. (2016). A systematic literature review of
games-based learning empirical evidence in primary
education. Computers & Education, 102:202–223.
Hantoobi, S., Wahdan, A., Al-Emran, M., and Shaalan, K.
(2021). A Review of Learning Analytics Studies, pages
119–134.
Hilton, M. and Janzen, D. (2012). On teaching arrays with
test-driven learning in webide. Annual Conference on
Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Ed-
ucation, ITiCSE.
Kasenides, N. . P. N. (2021). amazechallenge: An interac-
tive multiplayer game for learning to code. In 29TH
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INFORMA-
TION SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT, ISD2021.
Kelleher, C. and Pausch, R. (2005). “lowering the barriers
to programming: A taxonomy of programming envi-
ronment and languages for novice programmers. In
ACM Computing Surveys,, volume 37, pages 83–137.
Kunkle, W. M. and Allen, R. B. (2016). The impact of dif-
ferent teaching approaches and languages on student
learning of introductory programming concepts. ACM
Trans. Comput. Educ., 16(1).
Laamarti, F., E. M. and El Saddik, A. (2014). An overview
of serious games. International Journal of Computer
Games Technology.
Lamb, R., Annetta, L., and Firestone, J. (2017). A meta-
analysis with examination of moderators of student
cognition, affect, and learning outcomes while using
serious educational games, serious games, and simu-
lations. Computers in Human Behavior, 80.
Lamb, R. L., Annetta, L., Firestone, J., and Etopio, E.
(2018). A meta-analysis with examination of mod-
erators of student cognition, affect, and learning out-
comes while using serious educational games, serious
games, and simulations. Computers in Human Behav-
ior, 80:158–167.
Liu, P. L. (2008). Using open-source robocode as a java pro-
gramming assignment. SIGCSE Bull., 40(4):63–67.
Long, J. (2007). Just for fun: Using programming games
in software programming training and education – a
field study of ibm robocode. 2015 IEEE Frontiers in
Education Conference (FIE), 6:279–290.
Lopez, M., Whalley, J., Robbins, P., and Lister, R. (2008).
Relationships between reading, tracing and writing
skills in introductory programming. In Proceedings
of the Fourth International Workshop on Computing
Education Research, ICER ’08, page 101–112, New
York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
Luxton-Reilly, A., Becker, B., Ott, L., Simon, Giannakos,
M., Paterson, J., Albluwi, I., Kumar, A., Scott, M.,
Sheard, J., and Szabo, C. (2018). Introductory pro-
gramming: a systematic literature review. In Rossling,
G. and Scharlau, B., editors, ITiCSE 2018 Companion
- Proceedings Companion of the 23rd Annual ACM
Conference on Innovation and Technology in Com-
puter Science Education, pages 55–106. Association
for Computing Machinery (ACM).
Mishra, S., Balan, S., Iyer, S., and Murthy, S. (2014). Ef-
fect of a 2-week scratch intervention in cs1 on learn-
ers with varying prior knowledge. In Proceedings of
Space Geeks: A Proposed Serious Game to Teach Array Concept for Novice Programming Students
437

the 2014 Conference on Innovation & Technol-
ogy in Computer Science Education, ITiCSE ’14, page
45–50, New York, NY, USA. Association for Comput-
ing Machinery.
Muratet, M., Torguet, P., Viallet, F., and Jessel, J. (2011).
Experimental feedback on prog&play: A serious
game for programming practice. Computer Graphics
Forum, 30(1):61–73.
Papadopoulos, Y. G. S. and Tegos, S. (2012). Using mi-
croworlds to introduce programming to novices. 2012
16th Panhellenic Conference on Informatics, pages
180–185.
Ragonis, N. and Ben-Ari, M. (2005). A long-term investiga-
tion of the comprehension of oop concepts by novices.
Computer Science Education, 15(3):203–221.
Ramabu, T. J., Sanders, I., and Schoeman, M. (2021).
Teaching and learning cs1 with an assist of manipu-
latives. In 2021 IST-Africa Conference (IST-Africa),
pages 1–8.
Rigby, L., Denny, P., and Luxton-Reilly, A. (2020). A miss
is as good as a mile: Off-by-one errors and arrays in
an introductory programming course. New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Rosenberg, J. and K
¨
olling, M. (1997). Testing object-
oriented programs: Making it simple. volume 29,
pages 77–81.
R.Z. Ramli, A. K. and Osman, N. (2015). Visualization
makes array easy. In In Proceedings of the 2015 In-
ternational Conference on Testing and Measurement:
Techniques and Applications, TMTA ’15, pages 381–
384.
Simon, Luxton-Reilly, A., Ajanovski, V. V., Fouh, E., Gon-
salvez, C., Leinonen, J., Parkinson, J., Poole, M., and
Thota, N. (2019). Pass rates in introductory program-
ming and in other stem disciplines. New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Sloan, R. H. and Troy, P. (2008). Cs 0.5: a better ap-
proach to introductory computer science for majors.
In SIGCSE ’08.
Sorva, J. (2008). The same but different students’ under-
standings of primitive and object variables. New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Sorva, J. (2013). Notional machines and introductory pro-
gramming education. 13(2).
Tuparov, G., Tuparova, D., and Jordanov, V. (2014).
Teaching sorting and searching algorithms through
simulation-based learning objects in an introductory
programming course. Procedia - Social and Behav-
ioral Sciences, 116.
Yan, L. (2009). Teaching object-oriented programming with
games. Procs 6th Int Conf on Information Technology:
New Generations,, 2009:969–974.
Zhao, D., Muntean, C. H., Chis, A. E., and Muntean, G.-
M. (2021). Learner attitude, educational background,
and gender influence on knowledge gain in a serious
games-enhanced programming course. IEEE Trans-
actions on Education, 64(3):308–316.
WEBIST 2022 - 18th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
438
