
Establishment of a Dual SYBR Green I Fluorescence PCR Assay for
African Swine Fever Virus and Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
Xinyou Yu
1
, Tong Li
2
, Tianzhi Li
1
, Lin Dong
3
, Jinliang Wang
4,*
and Zhiqiang Shen
1
,
†
1
Shandong Lvdu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Binzhou, Shandong 256600, China
2
College of Veterinary Medicine, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao, Shandong 266109, China
3
Postdoctoral Research Station of Shandong Lvdu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Binzhou, Shandong 256600, China
4
Shandong Binzhou Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine Academy, Binzhou, Shandong 256600, China
Keywords: African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV), Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV), SYBR Green Ⅰ,
Fluorescence PCR.
Abstract: The present study envisaged the development of a fluorescence PCR test for the simultaneous detection of
the African swine fever virus (ASFV) and the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) by designing specific
primers based on the sequences of the p72 gene of ASFV and the N gene of PEDV in GenBank. Subsequently,
the sample loading system and the PCR program was optimized to establish a dual SYBR Green I fluorescence
PCR assay for ASFV and PEDV. Furthermore, the specificity, sensitivity and repeatability of the established
assay were evaluated. Finally, the established PCR assay was tested using clinical samples. The results
demonstrated that the optimal loading amount of each primer in a 20 µL reaction system was: F1 0.5 µL, R1
0.8 µL, F2 1.5 µL and R2 1.2 µL; the optimal PCR program was: reverse transcription at 42 ℃ for 5 min;
pre-denaturation at 95°C for 2 min; and 40 cycles of (denaturation at 94°C for 5 s followed by annealing at
53°C for 25 s, where the fluorescence was collected). The established assay exhibited a good specificity and
did not cross-react with other common swine viruses. The sensitivity of detecting the ASFV and PEDV was
8.8 copies/µL and 3.7 copies/µL, respectively, and the within-run and between-run coefficients of variation
of T
m
values were not more than 1.0%. The test results of 162 clinical samples using the established PCR
assay were consistent with the reference methods. The dual SYBR Green I fluorescence PCR assay
established in this study for detecting ASFV and PEDV showed high sensitivity and good specificity, and it
can be used for the rapid detection of these two clinical diseases.
1 INTRODUCTION
African swine fever virus (ASFV) can cause African
swine fever (ASF), a severe and highly contagious
infectious disease in swine (Yu and Li, 2018). The
clinical signs include high fever, vomiting,
petechiation of the skin, and bloody diarrhea in pigs
(Jin et al., 2020). Extensive hemorrhage of the various
internal organs was observed in the swine autopsy
(Zhang et al., 2019). ASFV was first detected in a pig
farm in Shenyang, China in August 2018 (Chen et al.,
2018), and it has been prevalent in pig farms in China
for more than 3 years till now. As the clinical variants
emerged, the virulence of the virus diminished, and
the pig farm epidemic eased. The mortality rate of the
infected swine was low in some pig farms (Zhang et
al., 2021). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus 2 (PEDV)
is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus in the
family Coronaviridae (Dong et al., 2021). It can
cause porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) in swine and
is widespread in pig herds worldwide. The clinical
signs include vomiting, watery diarrhea, and
dehydration. The disease has an acute onset, rapid
spread, and a high mortality rate. It can occur
throughout the year, but occurs more often in the
winter and spring (Geng et al., 2021).
Although there are kits for detection of single
pathogen, the operations are cumbersome, and the
cost is high. There is an urgent need to develop a rapid
on-site screening kit for simultaneous detection of
both ASFV and PEDV. Fluorescence polymerase
chain reaction (PCR) has been widely used as a fast,
sensitive and cheap detection method. Compared to
traditional PCR, it has a higher sensitivity and does
not require detection of PCR products by
electrophoresis, reducing the risk of aerosol
Yu, X., Li, T., Li, T., Dong, L., Wang, J. and Shen, Z.
Establishment of a Dual SYBR Green I Fluorescence PCR Assay for African Swine Fever Virus and Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus.
DOI: 10.5220/0011594000003430
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences (ABS 2022), pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-607-1; ISSN: 2795-5893
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5
contamination in the laboratory. To date, there have
been no reports on the dual SYBR Green I
fluorescence PCR method for the simultaneous
detection of ASFV and PEDV. In this pursuit, the
present study aimed to establish a dual SYBR Green
I fluorescence PCR assay to improve the detection
efficiency of ASFV and PEDV.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Plasmids, Strains, and Field
Samples
The plasmids pMD-p72 and pMD-N containing the
ASFV and PEDV-specific gene fragments,
respectively, were synthesized by General
Biosystems (Anhui) Co., Ltd. The Classical swine
fever virus (CSFV), Porcine reproductive and
respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), Porcine
circovirus type 2 (PCV2), Porcine transmissible
gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), Porcine rotavirus (RV),
Porcine pseudorabies virus (PRV) and Porcine
deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) were employed from our
laboratory in the study. A total of 162 pig nasal swab
samples were collected from the pig farms in northern
Shandong from January 2021 to December 2021.
2.2 Primers, Reagents, and
Recombinant Standard Plasmid
Construction
The sequences of the ASFV p72 gene and PEDV
nucleocapsid (N) gene were downloaded from the
GenBank. Specific primers were designed based on
the conserved parts, and further synthesized by
General Biosystems (Anhui) Co., Ltd. The primers
are shown in Table 1. The One-Step TB Green
PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit (Cat. No: RR096A) was
purchased from Takara Bio Inc. (Dalian). The
plasmid miniprep kit was procured from BioTeke
Corporation Co. Ltd. The MyGo Pro quantitative
fluorescence PCR instrument was procured from
Qingdao Buffett Biological Company. The full length
of p72 gene (1941 base pairs) of ASFV (Accession no.
MK554698.1) and N gene (1326 base pairs) of PEDV
(Accession no. MW122505.1) were synthetized and
cloned into the pMD18 vector by Sangon (Shanghai,
China), respectively. The concentration of these
recombinant standard plasmids was determined by
NanoDrop One (ThermoFisher Scientific). The copy
numbers of pMD-p72 and pMD-N plasmids were
2.9×10 9 copies/μL and 1.5×10 9 copies/μL,
respectively. All these plasmids were stored in −20°C
before use.
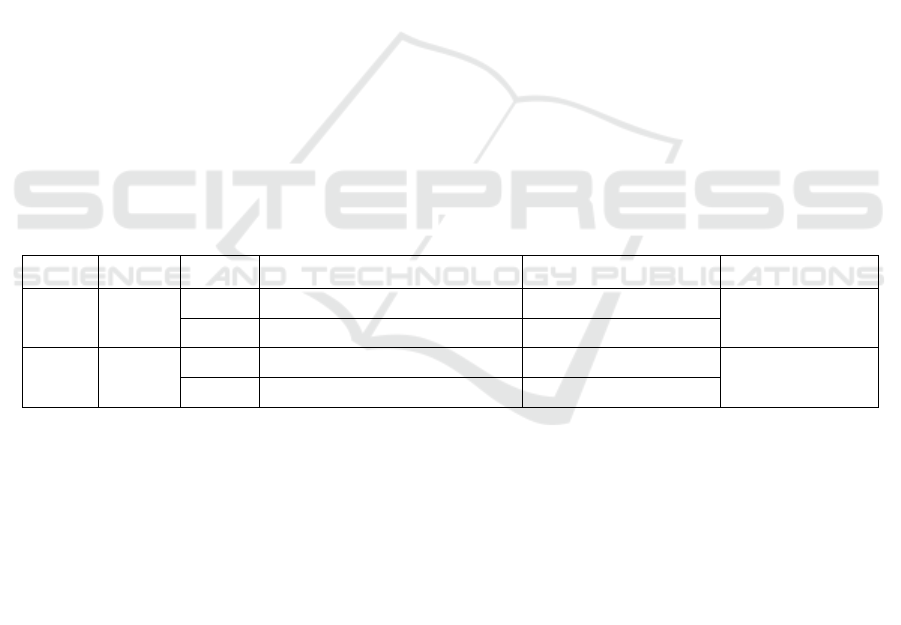
Table 1: Primers used in the duplex SYBR Green Ⅰ Fluorescence PCR assay.
Virus Gene Name
Primer Sequence (5’→3’)
Position GenBank No.
ASFV p72
F1 CATGGGCAGCTTCAAACGT 391-409
MK554698.1
R1 CAATGGGTCTTCCAAAAG 479-496
PEDV N
F2 TAAGGACCAGCAAATTGGA 135-153
MW122505.1
R2 GTTGTTGCCATTACCACGA 453-471
2.3 Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction
Viral nucleic acid was extracted from each sample
using Simply P Virus RNA/DNA Extraction Kit
(Cat.No:BSC67M1; Hangzhou Bori Technology Co.,
Ltd) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The viral DNA/cDNA were stored at − 20 °C for
further study.
2.4 Establishment and Optimization of
Dual Fluorescence PCR Assay
The lyophilized primers F1 and R1 of ASFV, and F2
and R2 of PEDV, respectively, were prepared to
reach a concentration of 15 µmol/L using ultrapure
sterile water. The reaction system was prepared
according to the instructions of the One-Step TB
Green PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit. A total volume of 20
µL was employed for the analysis. This included 10
µL of 2× One-Step TB Green RT-PCR Buffer III, 0.5
µL of PrimeScript RT Enzyme Mix II, and 0.5 µL of
Ex Taq HS, 1 µL of plasmid template pMD-p72, 1 µL
of plasmid template pMD-N, adjusted amounts of
primers for optimization, and adjusted amount of
ultrapure sterile water to make a final volume of 20
µL. The negative control was set up using ultrapure
water to replace the template. After thorough mixing,
the reaction systems were placed in the MyGo Pro
quantitative fluorescence PCR instrument. The PCR
program was set and conducted using various
annealing temperatures such as 51°C, 52°C, 53°C,
54°C, 55°C, 56°C, 57°C, and 58°C.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
6
2.5 Evaluation of Specificity,
Specificity and Repeatability
To evaluate the specificity of the primer and probe
sets, the synthesized plasmids pMD-p72 and pMD-N
were diluted 10-fold serially, added to the
fluorescence PCR reaction system as templates, and
amplified using the established dual fluorescence
PCR method. For the sensitivity evaluation, the
nucleic acids of CSFV, PPRSV, PPrV, PCV2, TGEV,
PRV, and PDCoV were used as templates to test the
specificity of the established dual fluorescence PCR
assay.
For the evaluation of the repeatability of this
method, the plasmids pMD-p72 and pMD-N samples
of three selected dilution gradients from section 1.6
were used as templates, with three replicates for each
dilution, to perform dual fluorescence PCR. The T
m
values of the melting curves were analyzed to
calculate the within-run and between-run coefficients
of variation (CV).
2.6 Detection of Clinical Samples
The test samples were collected from various pig
farms in northern Shandong from January 2021 to
December 2021, including healthy hogs and diseased
hogs. In the operation of pig nasal swab collection, a
sterile cotton swab was inserted into the pig’s nasal
cavity and rotated. Then, the swab was withdrawn
from the nostril and placed in a sterilized centrifuge
tube containing 2 mL of normal saline. The tube was
securely closed, put in an ice incubator, and
transported to the laboratory within 24 hours. The
samples were tested using the established ASFV and
PEDV dual SYBR Green I fluorescence PCR. At the
same time, they were tested using the ASFV
fluorescence PCR assay following the national
standard GB/T 18648-2020 and the PEDV
fluorescence PCR assay following the local standard
DB33/T 2254-2020. The test results from our
established PCR were compared to those obtained
from the standard PCR.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Establishment and Optimization of
the Dual Fluorescence PCR Assay
The established optimal loading amounts of primers
were: F1 0.5 µL, R1 0.8 µL, F2 1.5 µL and R2 1.2 µL
in the 20 µL reaction system. The optimal annealing
temperature was 53 °C. The optimal established
fluorescence PCR reaction program was found to be:
reverse transcription at 42 °C for 5 min, pre-
denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min; a total of 40 cycles
of denaturation at 94 °C for 5 s and annealing at 53 °C
for 25 s (where the fluorescence was collected). After
the amplification, the melting curves were drawn and
analyzed, with the increase in temperature to 97 °C at
a rate of 0.1 °C/s and the fluorescence was measured
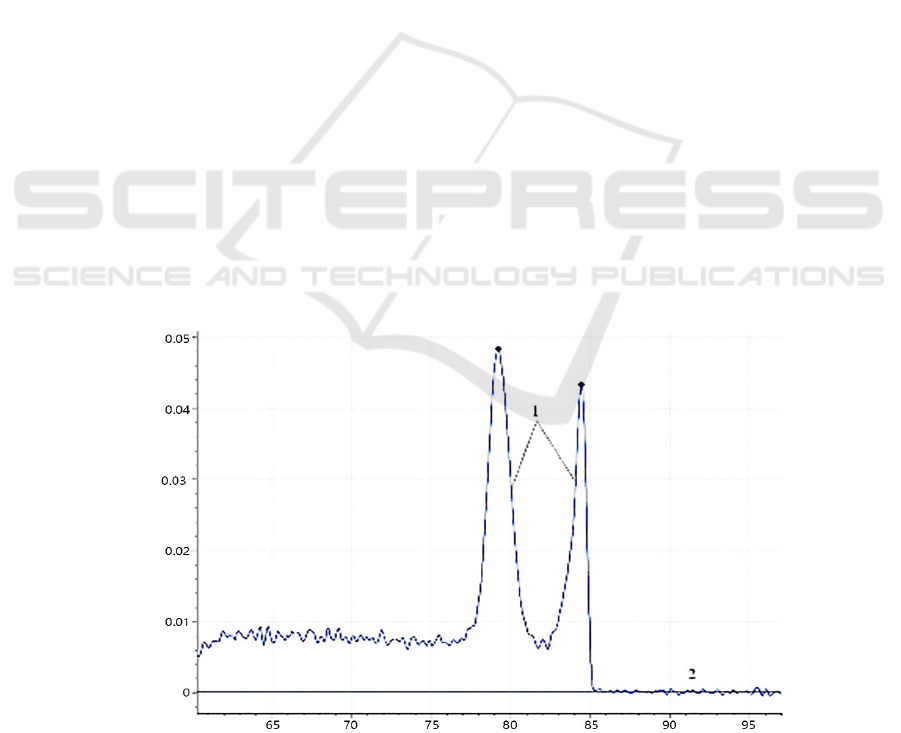
(Figure 1).
Notes: 1. Plasmid standard template, 2. Negative control.
Figure 1: Melting curves of the dual fluorescent PCR.
Establishment of a Dual SYBR Green I Fluorescence PCR Assay for African Swine Fever Virus and Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
7
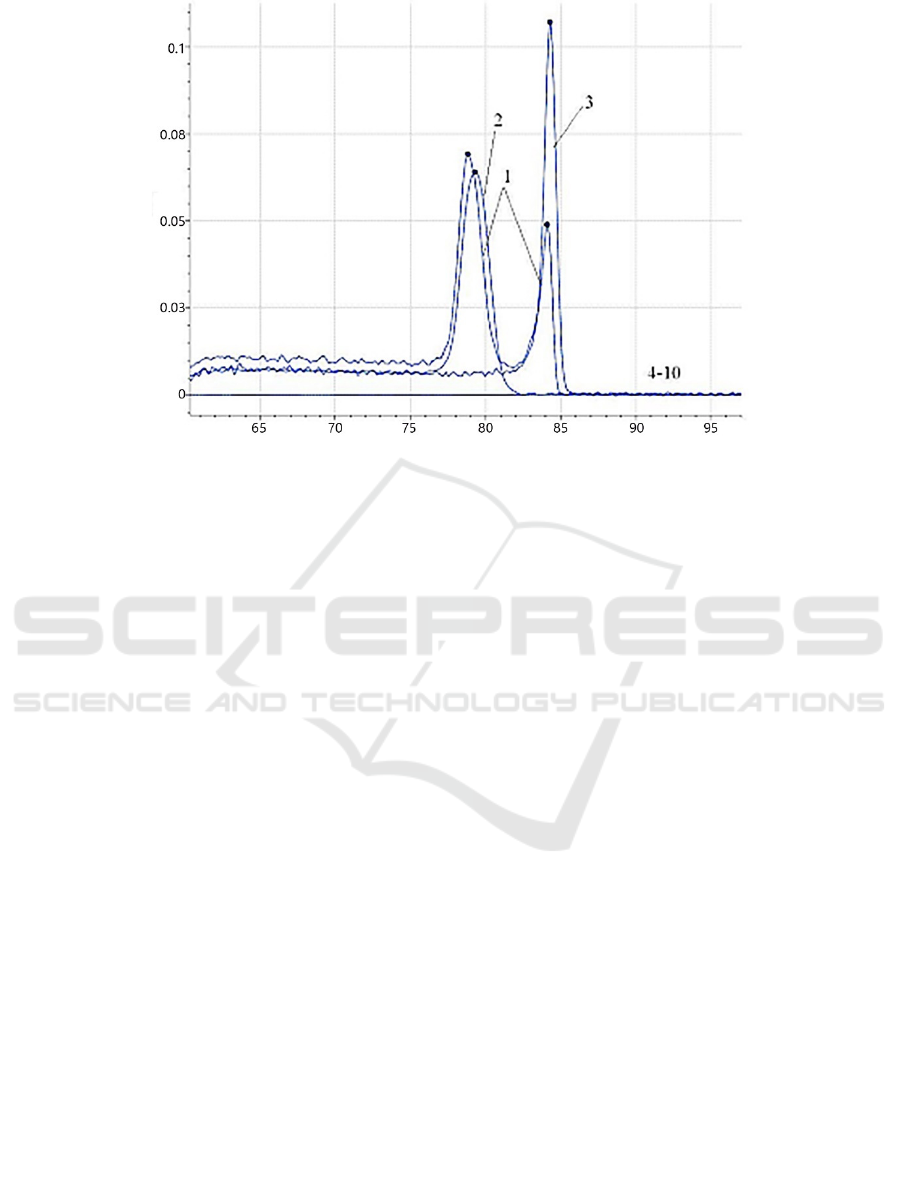
Notes: 1. Plasmid pMD-p72/ORF1, 2. Plasmid pMD-p72, 3. Plasmid pMD-ORF1, 4~10. SFV, PPRSV, PPrV, PCV2, PTGEV,
PRV, and PDCoV.
Figure 2: Amplification specificity of the dual fluorescent PCR assay.
3.2 Evaluation of Sensitivity
The concentration of the plasmid pMD-p72 was
determined to be 8.8×10
9
copies/µL. The
fluorescence PCR using 10-fold gradient diluted
plasmid showed that the detection limit of plasmid
pMD-p72 was 8.8 copies/µL. The concentration of
plasmid pMD-N was determined to be 3.7×10
9
copies/µL, and the fluorescence PCR using 10-fold
gradient diluted plasmid showed that the detection
limit of plasmid pMD-N was 3.7 copies/µL.
3.3 Evaluation of Specificity
The established dual SYBR Green I fluorescence
PCR was subjected to the specificity test. The results
showed that the plasmid pMD-p72 had a specific
peak with a T
m
value of (79.21 ± 0.5) ℃, the plasmid
pMD-N had a specific peak with a T
m
value of (84.11
± 0.5) ℃, the plasmid pMD-p72/N had double peaks
with T
m
values of (79.21 ± 0.5) ℃ and (84.11 ±
0.5) ℃. While the other tested pathogens, SFV,
PPRSV, PPrV, PCV2, PTGEV, PRV, and PDCoV, did
not demonstrate specific T
m
values at (79.21 ± 0.5) ℃
or (84.11 ± 0.5) ℃ (Figure 2). The results indicated
that the established method offered a good specificity
and no cross-amplification reactions with other
pathogenic genes.
3.4 Evaluation of Repeatability
Three different concentrations of 8.8×10
5
, 8.8×10
3
,
and 8.8×10
1
copies/µL of the plasmid pMD-p72 were
selected from the serial dilution, with three repeats at
each concentration, were subjected to the dual
fluorescence PCR. Similarly, three concentrations of
3.7×10
5
, 3.7×10
3
, and 3.7×10
1
copies/µL of plasmid
pMD-N were selected with three repeats for each
concentration, were subjected to the dual
fluorescence PCR. The T
m
values of the tested
samples were recorded, and the within-run and
between-run coefficients of variation were calculated,
respectively. The results showed that the within-run
and between-run coefficients of variation of the two
plasmids were not more than 1%, indicating a good
repeatability of the proposed assay (Table 2).
3.5 Diagnostic Performance
The results of the ASFV and PEDV dual SYBR Green
I fluorescence PCR on162 pig nasal swab samples
revealed 0 ASFV positive and 18 PEDV positive,
with no cases of dual infections. Single fluorescence
PCR for the ASFV and PEDV following related
standards, demonstrated consistent results with the
developed dual SYBR Green I fluorescence PCR
assay.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
8
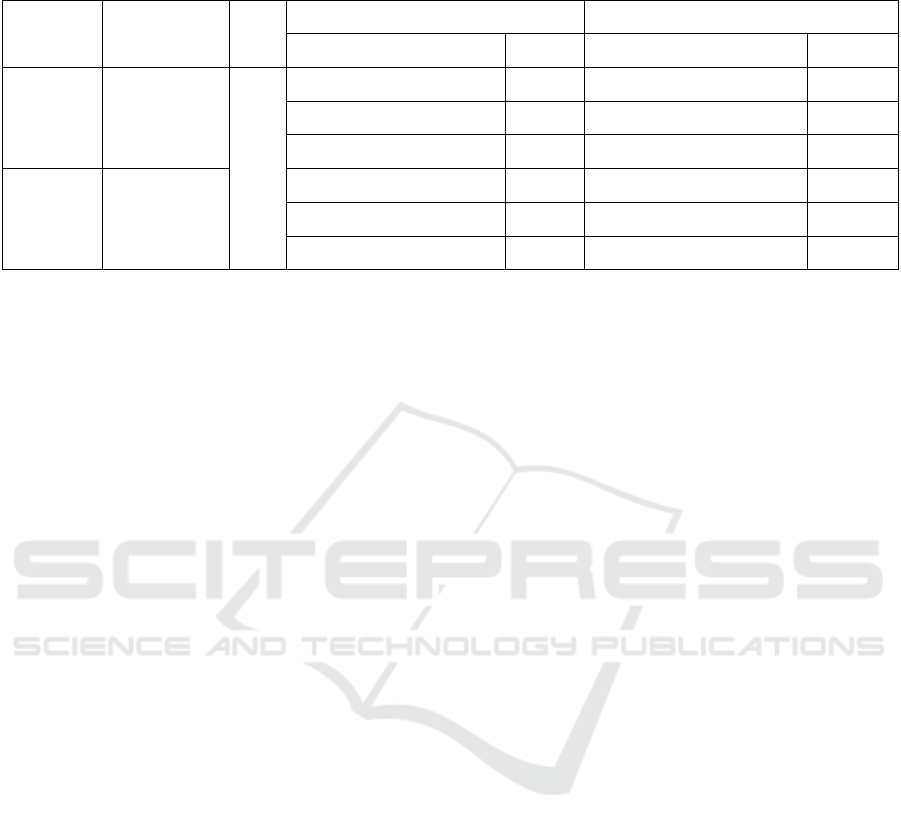
Table 2: Within-run and between-run repeatability test results of dual fluorescence PCR.
Virus Plasmid
Concentration
N Within-run CV Between-run CV
Mean ± standard deviation CV/% Mean ± standard deviation CV/%
ASFV 8.8×10
4
8.8×10
3
8.8×10
2
3
3
3
3
3
3
79.150±0.254 0.321 78.880±0.165 0.209
79.520±0.148 0.186 79.220±0.425 0.536
78.920±0.632 0.801 79.320±0.612 0.772
PEDV 3.7×10
4
3.7×10
3
3.7×10
2
84.110±0.280 0.333 83.960±0.341 0.406
84.220±0.172 0.204 84.130±0.655 0.779
83.870±0.625 0.745 84.350±0.351 0.416
4 DISCUSSION
China has a huge market for the pork production and
consumption, and the outbreak of ASF and PED have
dealt a severe blow to the swine industry in China.
The accurate and rapid diagnosis of ASF and PED is
an important step in the control and prevention of
these diseases. The fluorescence PCR method has the
advantages of being rapid, high sensitivity and ease
of operation, and it has been widely applied in the
detection of various pathogens. Fluorescence PCR
methods can be divided into two classes: dye-based
and probe-based. Compared with the probe-based
fluorescence PCR, the dye-based assays do not
require the synthesis of expensive probes, thereby
reducing the cost in research and development.
However, the dye-based assays have a higher
requirement for primers, especially for dual PCR
assay, which is the key in the assay establishment.
Another difference from the probe-based method is,
the dye-based fluorescence PCR has an extra step of
melting curve analysis after amplification. With the
increase in the temperature, the melting temperature
at which half of the amplified products dissociate is
the T
m
peak. Each peak represents a specific product.
By analyzing the difference in T
m
peaks, multi-
pathogen detection can be realized. Additionally, it
has no special requirements for fluorescent PCR
instruments, and a good versatility. At present, there
is no dual SYBR Green I fluorescence PCR assay
available for detecting ASFV and PEDV.
The ASFV genome consists of a double-
stranded DNA sized 170-190 kb. The p72 gene is
highly conserved, and often serves as a target gene for
the detection of ASFV (Jia et al., 2020). The
nucleocapsid (N) gene encodes the PEDV
nucleocapsid protein, and it is highly conserved and
often used as a target gene for the detection of PEDV
(Pan et al., 2019). The dual SYBR Green I
fluorescence PCR assay proposed in this study for the
simultaneous detection of ASFV and PEDV can
screen the two pathogens rapidly in just 50 minutes.
The key to the successful establishment of the dual
fluorescence PCR assay is the design of primers. In
this study, four primers were found after the screening
of a large number of primers. They exhibited close
annealing temperatures, but did not interfere with
each other. We further optimized the loading amount
of each primer in the reaction system.
The proposed method can reduce costs and
simplify the tedious sample loading steps. The
specific T
m
peaks of ASFV and PEDV were found to
be at (79.21 ± 0.5) ℃ and (84.11 ± 0.5) ℃,
respectively. Our assay exhibited a good specificity
and did not cross-react with common porcine
pathogens. The limits for detecting ASFV and PEDV
were found to be 8.8 copies/µL and 3.7 copies/µL,
respectively. Tests on different concentrations of
ASFV and PEDV plasmid samples exhibited good
repeatability of the established assay. Neither of the
within-run CV nor between-run CV of T
m
of the two
plasmids was greater than 1%. Furthermore, among
the clinically obtained 162 pig nasal swabs tested
with the dual fluorescence PCR assay, 0 positive
ASFV cases and 18 positive PEDV cases were found,
and no dual infection cases were found. The 162
samples were subjected to single-plex ASFV and
PEDV PCR assays following related standard and the
results were consistent with the dual SYBR Green I
fluorescence PCR assay. In this study, the T
m
values
of the two viruses were obtained using the existing
kits and instruments, but the difference between the
two T
m
values remained unchanged. Although the T
m
values of the two target products fluctuated, the
amplitudes were not more than 1 °C. In conclusion, a
Establishment of a Dual SYBR Green I Fluorescence PCR Assay for African Swine Fever Virus and Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
9

dual SYBR Green Ⅰ fluorescence PCR assay was
established in the present study, which was found to
be time-saving with high sensitivity, high efficiency,
and good repeat-ability. The results indicate that the
proposed assay has an excellent potential to become
a useful laboratory diagnostic tool in the detection of
ASFV and PEDV in clinical samples.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This study was financially supported by Shandong
Major Science and Technology Innovation Project
(No. 2019JZZY020606).
REFERENCES
Chen, T., Zhang, S. F., and Zhou, X. T., et al. (2018).
Discovery and epidemiological analysis of the first
African swine fever epidemic in China. Chinese
Journal of Veterinary Science, 38(9): 1831-1832.
Dong, S. J., Xie C. F., and Si, S. F., et al. (2021).
Development of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus
vaccine. Chinese Journal of Biological Engineering,
37(08): 2603-2613.
Geng, C., Lu, H. Y., and Liang, W., et al. (2021). Isolation,
identification and pathogenicity of porcine epidemic
diarrhea virus HB2018. Chinese Journal of Veterinary
Science, 41(09): 1704-1709.
Jia, Y. F., Zhao, F. J., and Zhu, J. J., et al. (2020)
Establishment of a real-time quantitative SYBR Green
I fluorescence PCR assay for African swine fever virus.
Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 54(1): 69-
73.
Jin, Z. B., Li, M. G., and Luo, X. F., et al. (2020). Research
progress on genomics and diagnostic technology of
African swine fever virus. Heilongjiang Animal Science
and Veterinary Medicine, 2020(23): 52-54.
Pan, X. C., Shen, X. H., and Zhao, R. H. et al. (2019).
Cloning and expression of the N gene of the Anhui
strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Journal of
Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 47(17): 91-93.
Yu, X. Y., and Li, T. Z. (2018). Advances in the etiology,
epidemiology, diagnosis and control of African swine
fever. Feed Review, 2018(10): 39-41.
Zhang, C. H., Yang, J. H., and Lin, Y. X., et al. (2019).
Establishment of a nucleic acid extraction-free
quantitative fluorescence PCR assay for African swine
fever virus. China Veterinary Science, 49(10): 1216-
1221.
Zhang, Y. Y., Zhang, J. Y., and Yang, J. J., et al. (2021)
Identification of a natural variant of African swine fever
virus. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 41(2):
199-207.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
10
