
Evaluation of Method of Visual Gene Chip Detection for Four
Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquatic Products
Lin Lu
National Institute of Metrology, China, Beijing 100029, China
Keywords: Aquatic Products, Pathogenic Bacteria, Visual Detection, Gene Chip, Evaluation.
Abstract: In this manuscript, the author developed a gene chip detection method that combined tyramine signal
amplification technology and nanogold-labeled silver staining technology. Four pathogenic bacteria (Listeria
monocytogenes, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, V. cholera, and Staphylococcus aureus) in aquatic products were
used as targets to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity and repeatability of this method. The detection sensitivity
of this method can reach 103CFU/mL, and it is no different from the specificity of fluorescence detection.
The coefficient of variation CV value of the hybridization repeatability results of different points on the same
chip and different batches of chips were also less than 15%. The sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility
of the four visual gene chip detection methods for pathogenic bacteria in aquatic products all show good
performance, which has practical promotion significance in the detection of pathogenic bacteria in aquatic
products.
1 INTRODUCTION
Food safety has become a widespread and far-
reaching social issue. With the development of
society and people’s concerns regarding health, the
safety and health of aquatic products is receiving
increasing attention. Consumers and government
authorities are paying more and more attention to the
quality and safety of aquatic products, and the safety
and quality management of aquatic products has
become an important factor in ensuring food quality
and promoting social stability (Gao et al., 2007).
China is one of the largest producers of aquatic
products in the world. Over the past 20 years, total
aquatic production has continuously grown, and
China’s aquatic production reached about 49 million
tonnes in 2011, accounting for 35% of the world’s
aquatic production, ranking it first in the world. In
particular, aquaculture production accounted for
more than 70% of the world total (Weng et al., 20211,
Shuai et al., 2011). However, the detection rate of
Listeria monocytogenes in salmon in China was 5–
7%, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in elephant mussels
was 9–10%, and of V. parahaemolyticus in jumbo
crab was 7–8%. Vibrio cholerae, a national Class I
controlled infectious disease, had a detection rate of
about 3%, and pathogenic Escherichia coli and
Salmonella were also detected at high rates (Wang
and Tao, 2009, Wang et al., 2008, Jin et al., 2008).
Internationally, the European Union, the United
States, Japan, and others have strengthened their
health and safety testing measures for imported
aquatic products or increased their detection
programs. For example, the European Union
stipulates that the four pathogenic Vibrio species with
the highest risk - V. parahaemolyticus, V.
alginolyticus, V. cholerae and V. vulnificus – should
not be detected in shrimp and fish products, and other
aquatic products also have similar requirements for
corresponding Vibrio species. Because the quality of
China’s exports of aquatic products often varies and
can exceed the required acceptable pathogen levels of
importing countries, products are often rejected,
creating a series of “green barriers”. Such measures
result in greater challenges to China’s aquatic
products export trade (Bobrow et al., 1989).
Because chilled and fresh aquatic products are
not easy to preserve, a rapid and sensitive detection
method is urgently needed to protect the interests of
businesses and the health of consumers. The existing
methods of detecting pathogenic bacteria in aquatic
products in China, whether for import or export
industry standards, or national standards, take a long
time. Negative results need at least 3–4 days, and
positive results need 5–10 days. Existing detection
50
Lu, L.
Evaluation of Method of Visual Gene Chip Detection for Four Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquatic Products.
DOI: 10.5220/0011595700003430
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences (ABS 2022), pages 50-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-607-1; ISSN: 2795-5893
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

methods such as immunochromatography, ELISA,
and PCR can only detect one kind of foodborne
pathogenic bacteria at a time. Many experiments are
needed to identify or investigate a suspicious sample,
and the operation is cumbersome and time-
consuming, and cannot meet the needs of multiple
detection (Meany et al., 2011, Deng et al., 2011, Qi et
al., 2010). To address this need, the author has
combined tyramine signal amplification technology
and nanogold-labeled silver staining technology. A
visualized gene chip detection method was
established for simultaneous detection of four
pathogenic bacteria in aquatic products: L.
monocytogenes, V. parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae,
and Staphylococcus aureus.
2 MATERIALS & METHODS
Strains: The standard strains used in this experiment
were selected by the Academy of Military Medical
Sciences: L. monocytogenes, V. parahaemolyticus,
V. cholerae, and S. aureus. The strain names and
standard strain numbers are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Experimental standard strains and their numbers.
Strain Bacteria numbe
r
Listeria monocytogenes
54003, 54005, 54006,
54007, 7644
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
20502, 20506, 20507,
20511
Vibrio cholerae O139 M045
Staphylococcus aureus
26001, 26111, 26113,
13565, 27661
Clinical samples: The 10 positive reference
strains used in our laboratory were positive strains of
imported aquatic products. They were identified as
pathogenic bacteria of L. monocytogenes, V.
parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae and S. aureus by
conventional culture methods. The samples were
cultured in enrichment solution for 3 h before use.
Instruments and reagents: The instruments used
included an iCycler PCR instrument (Bio-Rad Co.),
GenePix 4000B scanner (Axon Co.), PixSys 5000
spotter (Cartesian Co.), and Model 8909 DNA
synthesizer (ABI Co.). The PCR-related reagents
were purchased from Bao Biological (Dalian) Co.
Ltd., gene chip substrate from CEL Associates Co.,
Cy3 fluorescent dye from Amersham Co., tyramine
signal amplification-Cy3 reagent from PE Co., and
streptavidin–HRP and coupling buffer from Sigma
Co.
Evaluation of gene biochip specificity: The
standard strains of the target pathogenic bacteria and
the standard strains of related proximate and distant
genera were selected and amplified by multiplex PCR
with universal primers. They were then hybridized
with a variety of pathogenic detection probes
obtained by screening, and the specificity of each
probe on the gene chip was systematically evaluated.
Evaluation of gene chip sensitivity: The
sensitivity standards of various pathogenic bacteria
were provided by the China Institute of Drug and
Biological Product Identification and the Institute of
Microbiology and Epidemiology of the Academy of
Military Medical Sciences. The standards were
diluted with saline in a 10-fold gradient, and the DNA
processed with reference to the genomic DNA
extraction procedure.
Evaluation of gene chip repeatability: Three
batches of L. monocytogenes were randomly selected
from different batches of biochips for repeatability
tests. Then three chips were randomly selected from
three different batches of chips, and the detection
results obtained by multiplex PCR amplification and
gene chip hybridization were statistically analyzed to
evaluate the repeatability of the chips.
Preparation of fresh shrimp liquid contaminated
with L. monocytogenes: Fresh shrimp detected by
conventional culture methods in our laboratory were
pulped by apparatus, and 1 mL of serially diluted L.
monocytogenes DNA diluent (10
1
–10
6
CFU/mL) was
added to each 0.1 g of fresh shrimp pulp to make a
final concentration of 10
1
–10
6
CFU/mL/0.1 g
suspension of fresh shrimp pulp. Then 9 mL of 75%
ethanol was added, mixed, and centrifuged at 100×g
for 1 min to remove large particles. The supernatant
was transferred to a new centrifuge tube and
centrifuged at 10,000×g for 10 min. Then the
supernatant was carefully aspirated, sterilized saline
was added for one washing, and DNA extract added
to the final precipitate, boiled for 10 min, and
centrifuged. Of the supernatant, 8 μL was used for
PCR detection. Preparation of sensitivity simulation
samples of V. parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae, and S.
aureus: V. parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae, S. aureus
sensitivity simulation samples were prepared
referring to the previous section.
Evaluation of Method of Visual Gene Chip Detection for Four Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquatic Products
51
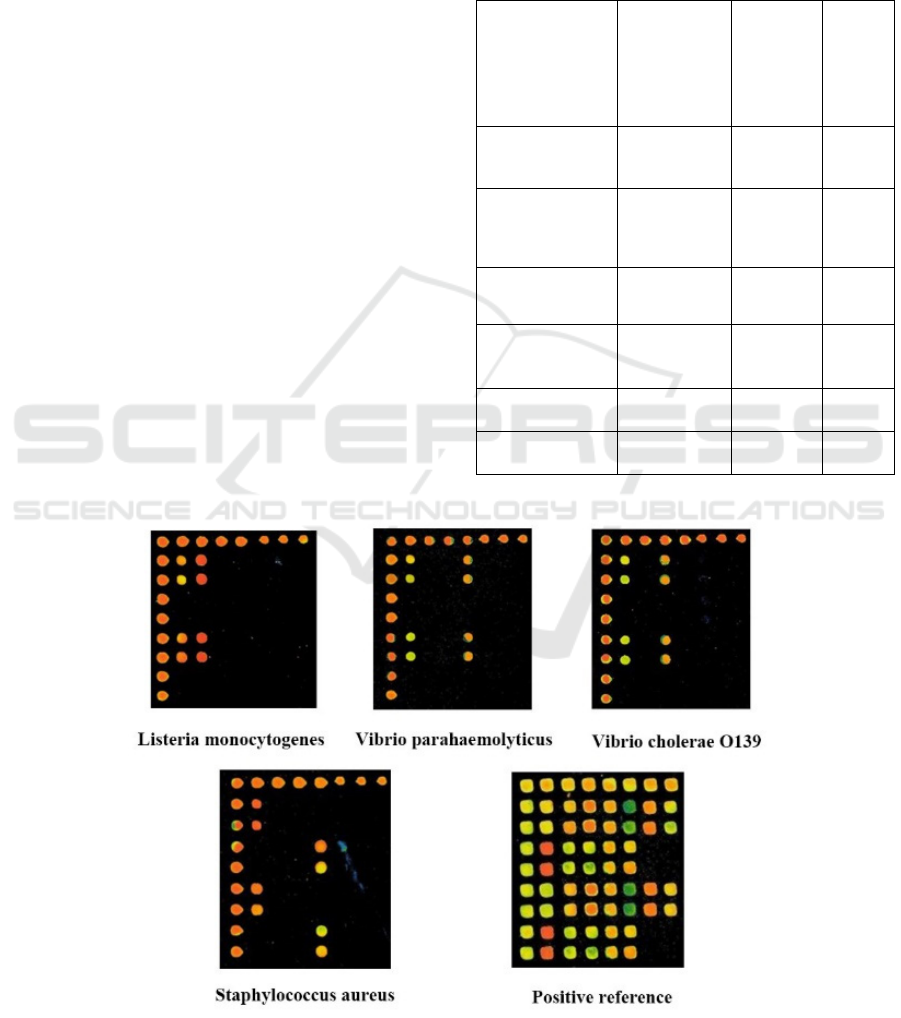
3 RESULTS
3.1 Specificity of Gene Biochip
Detection
To examine the specificity of the method for the
detection of the four pathogenic bacteria, the positive
and negative references provided in Table 1 and from
the Academy of Military Medical Sciences were
compared. The results of gene biochip hybridization
showed that the probes for the four pathogenic
bacteria were highly specific under the above
optimized reaction system (Figure 1). For the other
non-target pathogenic bacteria, no fluorescent signal
appeared at any probe position except for the positive
signal of the internal control probe, while no
fluorescent signal appeared for the negative probe or
the blank control (Azizipour et al., 2020).
3.2 Determination of Cutoff Value
Cutoff value is the criterion to determine whether the
fluorescence signal value of a gene chip is positive or
not. In this experiment, the cutoff value of the probes
was calculated and determined based on the
specificity evaluation. For each probe, a positive
strain, a negative strain, and a blank were selected for
gene chip hybridization. The hybridization
fluorescence signal value of the positive strain was
much higher than the background value of the
negative strain and the blank control hybridization
(Figure 1). Through repeated experiments, we
determined the background statistical average of the
negative strain and the blank control + 2 standard
deviations as the cutoff value of each probe (Table 2).
Table 2: Cutoff values of four aquatic product pathogenic
bacteria probes.
Bacterial name
Fluorescenc
e mean of
negative
bacteria and
blank
control
Standard
deviation
Cutoff
value
Listeria
monocytogenes
485.25 24.89 535.03
Vibrio
parahaemolytic
us
586.75 34.13 655.01
Staphylococcus
aureus
696.27 52.60 801.47
Vibrio cholerae
O139
467.6 36.15 539.9
Vibrio cholerae
non-O139
278.625 30.28
339.18
5
Internal control 221.16 22.90 266.96
Figure 1: Specificity detection results.
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
52
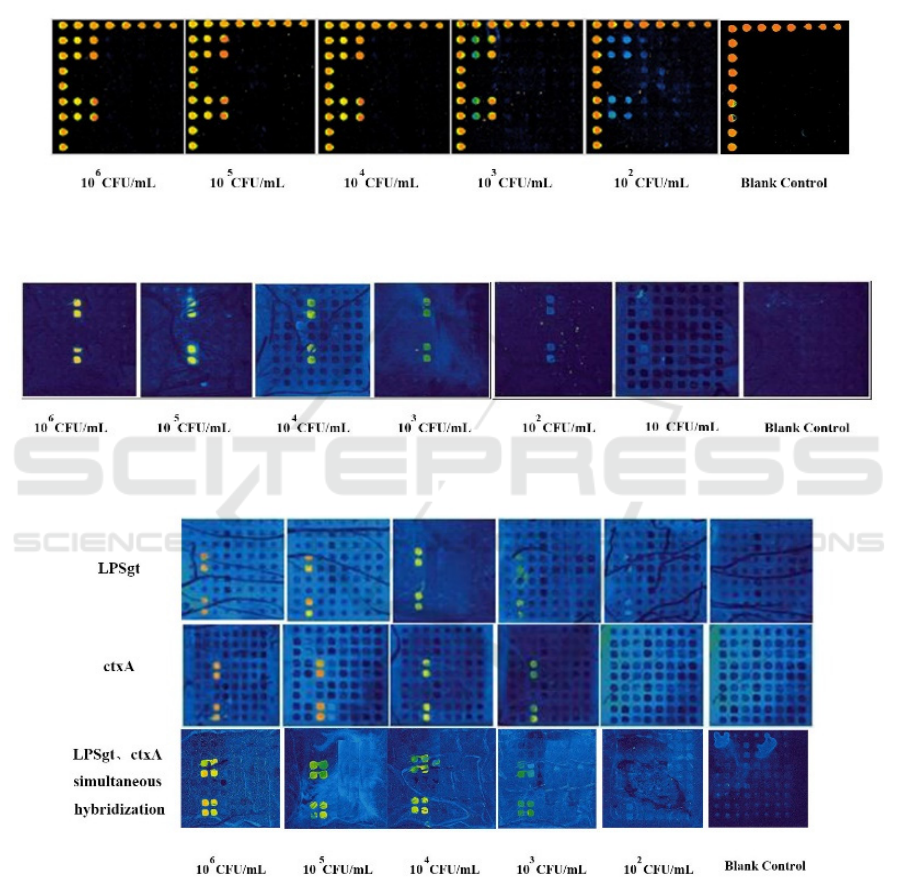
3.3 Sensitivity of Pure Culture
Pathogenic Bacteria
In this experiment, the sensitivity of pure cultures of
L. monocytogenes, V. parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae,
and S. aureus were evaluated separately. The
sensitivity of the detection was determined according
to the cutoff values of the probes (Table 2) after the
initial concentrations of the above target bacteria
were diluted with saline in a 10-fold gradient, directly
boiled and lyse, PCR amplified, and hybridized. The
results are shown in Figures. 2–5 (Park et al., 2018,
Bunin et al., 2020).
Figure 2: Sensitivity of detection of Listeria monocytogenes.
Figure 3: Sensitivity of detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Figure 4: Sensitivity of detection of Vibrio cholera.
Evaluation of Method of Visual Gene Chip Detection for Four Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquatic Products
53
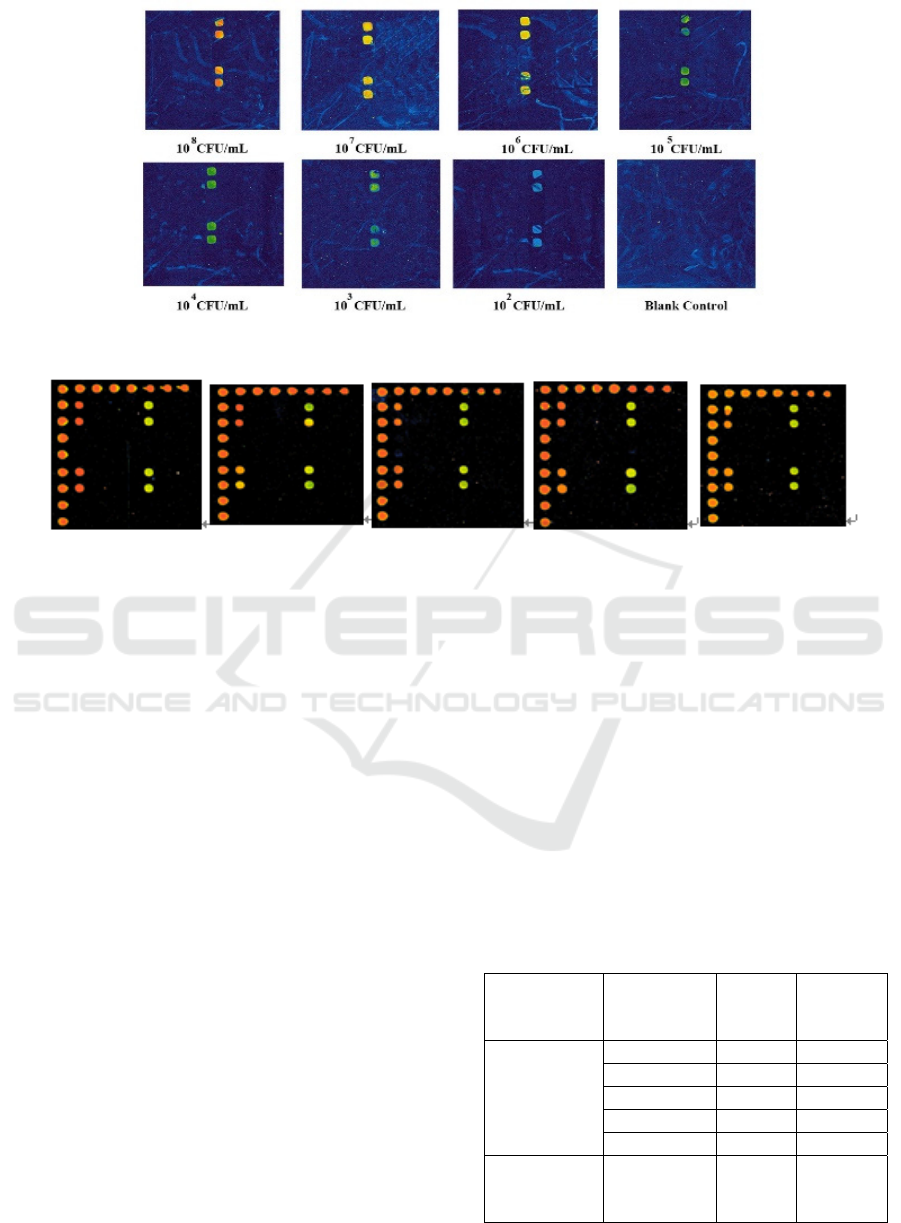
Figure 5: Sensitivity of detection of Staphylococcus aureus.
Figure 6: Gene biochip repeatability evaluation.
The sensitivity of all four pathogenic bacteria
reached 10
3
CFU/mL (Figures 2–5), while L.
monocytogenes and S. aureus corresponding to 10
2
CFU/mL showed fluorescent signals in the
hybridization plot, but the signal value was lower than
the cutoff value of the probe of the bacteria, so it
could not be taken as a positive result. Meanwhile, we
observed from Figure 4 of hybridization of LPSgt and
ctxA genes of V. cholerae O139 that when
hybridizing one gene alone, the fluorescence signal
value of each gradient was higher than the value of
simultaneous hybridization. Apparently two genes
hybridized at the same time affected each other,
probably because the annealed PCR products
hybridized with each other, reducing the amount of
hybridization with the corresponding probe, but the
statistical analysis of simultaneous hybridization
showed that sensitivity reached 10
3
CFU/mL (Dou et
al., 2019).
3.4 Repeatability of Gene Biochip
Detection
Listeria monocytogenes was selected to evaluate the
repeatability of the gene biochip. The PCR
amplification and gene biochip hybridization were
performed with 10
6
CFU/mL of the pathogenic
bacteria, and a negative control without a template
was set up. The experiment was repeated five times
and intra- and inter-slice repeatability were
calculated, thus assessing the repeatability of this
method of detection. The results of the experiments
are shown in Figure 6, and the statistical analysis
results are shown in Table 3. For the single-amplified
L. monocytogenes probe, the coefficients of variation
(CV) of the repeatability of different spots on the
same chip were less than 15%, and the CVs of the
hybridization repeatability results of different batches
of spot systems of the chip were also less than 15%,
indicating that repeatability of detection was good
(Park et al., 2018).
Table 3: Statistical results of gene biochip repeatability
evaluation.
Repeatability
Number of
experiments
Internal
control
probe 1
Listeria
monocyt
ogenes 1
Intra-Slice
repeatability
V (%)
1 8.31 6.38
2 7.23 9.46
3 5.29 8.33
4 9.33 8.74
5 7.45 9.12
Inter-slice
repeatability
CV (%)
7.82 8.65
ABS 2022 - The International Conference on Agricultural and Biological Sciences
54

4 DISCUSSION
Cutoff value is a criterion to determine whether a
hybridization fluorescence signal is positive or not. In
this experiment, the background values of positive
fluorescence signal value, negative fluorescence
signal value, and blank control were statistically
analyzed through multiple repetitions, and the
corresponding cutoff value determined for each probe
(Table 2). The cutoff value is not only used to judge
the hybridization results, but also provides a reliable
basis for the evaluation of sensitivity. The sensitivity
of this experiment was respectively evaluated for L.
monocytogenes, V. parahaemolyticus, V. cholerae,
and S. aureus, and the sensitivity reached 10
3
CFU/mL. This experiment evaluated the
reproducibility with L. monocytogenes and showed
that the CV of inter- and intra-slice reproducibility of
this gene chip was less than 15%, indicating that the
method was accurate, reliable, and repeatable.
Therefore, the results of this method for the
evaluation of gene chip detection for the visualization
of the four aquatic pathogenic bacteria showed the
high specificity of each probe, the intra- and inter-
slice CV was less than 15%, the repeatability was
good, and the sensitivity of the four pathogenic
bacteria reached 10
3
CFU/mL. Therefore, the
detection method can be used for sensitive and high-
throughput detection of four kinds of aquatic products
pathogens, which provides fast and accurate detection
technology for improving the pathogenic bacteria of
imported and exported aquatic products, and is of
great significance for ensuring the quality and safety
of imported and exported aquatic products.
REFERENCES
Azizipour, N., Avazpour, R., Rosenzweig, D. H., et al
(2020). Evolution of biochip technology: A review
from lab-on-a-chip to organ-on-a-chip. Micromachines,
11(6): 599.
Bobrow, M. N., Harris, T. D., Shaughnessy, K. J., et al
(1989). A novel method of signal amplification.
Journal of Immunology Methods, 125(2):279–85.
Bunin, E., Khatisashvili, G., Varazi, T., et al (2020). Study
of arsenic-contaminated soil bacterial community using
biochip technology. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution,
231(5): 1-12.
Deng, Z., Ge, Y., Cao, Q., et al (2011). The detection of a
transgenic soybean biochip using gold label silver stain
technology. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
Letters, 21(22):6905–8.
Dou, M., Macias, N., Shen, F., et al (2019). Rapid and
accurate diagnosis of the respiratory disease pertussis
on a point-of-care biochip. EClinicalMedicine, 8: 72-
77.
Gao, S., Xie, M. and Jin, D., et al (2007). Study on the
establishment of a method for the detection of common
pathogenic microorganisms in aquatic foods using gene
chip technology. Biotechnology Communication,
18(1):72–6.
Jin, D., Qi, H., Chen, S., et al (2008). Simultaneous
detection of six human diarrheal pathogens by using
DNA biochip combined with tyramide signal
amplification. Journal of Microbiology Methods,
75(2):365–8
Meany, D. L., Hackler, L. Jr., Zhang, H., et al (2011).
Tyramide signal amplification for antibody-overlay
lectin biochip: a strategy to improve the sensitivity of
targeted glycan profiling. Journal of Proteome
Research, 10(3):1425–31.
Park, M., Kang, B. H., Jeong, K. H. (2018). Based biochip
assays and recent developments: A review. BioChip
Journal, 12(1): 1-10.
Qi, H. J., Chen, S. H., Zhang, M. L., et al (2010). DNA
biochips for visual detection of human pathogenic
microorganisms based on tyramine signal amplification
coupled with gold label silver stain. Analytical And
Bioanalytical Chemistry, 398(6):2745–50.
Shuai, J., Fu, L., Zhang X., et al (2011). Rapid detection of
major pathogenic Vibrio spp. in aquatic products by
dual-channel fluorescent PCR. Chinese Journal of
Food, 11(5):151–7.
Wang, N. and Tao, Y. (2009). Establishment of a multiplex
PCR method for the detection of three pathogenic
bacteria in aquatic products. Journal of Food
Biotechnology, 28(3): 397–402.
Wang, Y., Long, L., Cai, X., et al (2008). Isolation and
serological identification of Salmonella in aquatic
products. Inspection and Quarantine Science, 18:42–
44.
Weng, S., Zhu, J., and Li, J. (2011). Establishment and
evaluation of a multiplex PCR method for the detection
of four common pathogenic bacteria in aquatic
products. Journal of Aquaculture, 35(2):305–14.
Evaluation of Method of Visual Gene Chip Detection for Four Pathogenic Bacteria in Aquatic Products
55
