
The Pedagogical Aspect of Comparative Analysis of the Process
Duration Concept in English and Russian Languages
Gulnara Lutfullina
1a
, Yakha Bataeva
2b
and Luiza Sardalova
3c
1
Kazan State Power Engineering University, Kazan, Russia
2
Chechen State Pedagogical University, Grozny, Russia
3
Chechen State University, Grozny, Russia
Keywords: Duration, Substantive, Auxialiary Verbs, Temporality, Aspectuality.
Abstract: The purpose of this article is to identify the nouns representing aspectual meaning of duration in English and
Russian. The scientific novelty of the study is that temporal and aspectual duration are distinguished at
semantic level and at level of expression means. It was proved that in English and in Russian time meaning
of duration are represented by corresponding nouns and by nouns implying the time interval. Aspectual nouns
of duration indicate the action’s duration only if they are combined with verbal nouns or verbals. In English
the meaning of continuation not of duration is emphasized. In Russian the nouns of duration demonstrate
more significant activity compared to English.
1 INTRODUCTION
The relevance of the study is due to the need to
distinguish between the concepts of time and
aspectual duration, which are characterized by
morphological and lexical means of representation. It
is also of interest to consider the peculiarities of the
two languages in the representation of the category of
duration. The nouns of the aspectual meaning of
duration are difficult to analyze. On the one hand
there are deverbal nouns, on the other hand it is
necessary to recognize the possibility of expressing
duration by abstract nouns. Nouns are lexical means
of representing duration but morphological means
must also be taken into account. Traditionally time
and aspectual meaning of duration are distinguished
by Tenses.
To achieve the goal the following tasks were set
and solved:
1) to make a distinction between the concepts of
temporal and aspectual duration;
2) to analyze theoretically the quantitative
temporal-aspectual meaning of duration
realized by Tenses in English and Russian;
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1572-5314
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6695-9220
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5188-7199
3) to identify nouns with temporal meaning of
duration;
4) to make a comparative analysis of the nouns
with aspectual meaning of duration in two
languages.
The material of the study was the data of linguistic
corpus:
for English - British National Corpus (BNC),
for Russian - National Corpus of Russian
Language (RNC).
Comparative, structural, descriptive methods
were successfully applied. Qualitative and
quantitative analysis of linguistic corpus data
demonstrates the effectiveness of the use of digital
linguistics methods.
The practical significance of the study lies in the
fact that the analysis of English and Russian verbal
and non-verbal means of representing the duration in
makes possible to compare their features in order to
prevent linguistic interference. The obtained results
can enrich theoretical and practical grammar of the
English and Russian languages devoted to temporal
and aspectual problems.
32
Lutfullina, G., Bataeva, Y. and Sardalova, L.
The Pedagogical Aspect of Comparative Analysis of the Process Duration Concept in English and Russian Languages.
DOI: 10.5220/0011601000003577
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Actual Issues of Linguistics, Linguodidactics and Intercultural Communication (TLLIC 2022), pages 32-37
ISBN: 978-989-758-655-2
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 RESULTS AND DICUSSION
2.1 Different Approaches to Duration
Category
The theoretical basis of the study were researches in
the field of temporality and aspectuality (Kobozeva,
2000; Plungyan, 2011). The concept of temporal
meaning and temporal duration is described in
fundamental work of R. Deklerk "The Grammar of
the English Verb Phrase" (Declerck, 2006) and others
(Brinton, 2010). The situation interval / situation time
is the interval or duration of the actualization of the
predicative situation, expressed (Declerck, 2006). R.
Deklerk considers three means of expressing
temporal meanings:
1) verbal - Tenses;
2) non-verbal - nouns as parts of time
circumstances;
3) contextual means.
In Russian linguistics, the issues of temporality
and aspectuality are analyzed in the work “Time
reference in English” by M.Yu. Ryabova, where the
problems of chronological sequence and duration are
highlighted as a set of meanings for the categories of
time, type, taxis (Ryabova, 1993). According to A.
Mustajoki, the time phase can be expressed by variant
"continuation" not implying the Agent. He explores
two aspectual meanings – procedural and dynamic
(Mustajoki, 2006). The semantics of duration is
reflected in the works of A.V. Bondarko. The
following types of duration are distinguished: explicit
/ implicit, different degrees of duration, extended /
closed th, discontinuous / continuous (Bondarko,
2002).
2.1.1 A Distinction Between Time and
Aspectual Duration
The category of aspect is considered as a
representation of the internal development of an
action without reference to time axis. The category of
Time presupposes correlation with the time axis.
Often, aspectual and temporal meanings are
expressed jointly, they can be integrated into the
meaning of one Tense. It is necessary to distinguish
the qualitative characteristics of the action from the
quantitative characteristics.
Qualitative Time Meaning determines the
localization of the action in the past, present or future,
that is, determines its location on the time axis
(Lutfullina, 2016). In the representation of this
meaning, Tenses are involved as morphological
means of primary time localization. Nouns are
involved as lexical non-verbal means of secondary
time localization.
Qualitative Aspectual Meaning determines such
characteristics of an action as its repetition,
completeness, phase, that is the whole range of
possible features.
Duration is a quantitative characteristic of an
action, which can be both temporal and aspectual.
Quantitative time-aspect duration can be limited and
unlimited. Quantitative time meaning defines the
action localization on the time axis relative to two
points.
The nunc reference moment is the moment of
speech or the moment "now" from the Latin nunc.
A tunc reference moment is an arbitrarily chosen
moment "then" in the past or future from the Latin
tunc.
Quantitative aspectual meaning determines the
presence of an interval of action or the presence of
one of the limits.
Quantitative time meaning is a segment of the
localization of the action on the time axis, then the
quantitative aspectual meaning is the presence of an
interval or boundaries for the action itself.
2.1.2 Theoretical Analyses of Quantative
Time-Aspect Meaning of Duration
The morphological representation of the time-
aspectual meaning is realized by Tenses.
Present. English Present Continuous, Present
Simple Tenses and Russian Present Tense determine
the localization of the situation in present, that is nunc
simultaneity. The quantitative time meaning of
unlimited duration implies the absence of any limits
on the time axis, that is localization near “now”
moment. The quantitative aspectual meaning
coincides with it.
Past. In both languages past Tenses determine the
localization of the situation in the past until the
moment of speech, qualitative time meanings are the
following:
nunc anteriority meaning by English Past Simple,
Present Perfect,
tunc simultaneity meaning by English Past
Continuous, Russian Past Imperfect,
Tunc anteriority meaning by in English Past
Perfect and Russian Past Perfect.
The quantitative temporal meaning of duration is
one-side limited on the time axis by the moment
"now" for Past Tenses.
The quantitative aspectual meaning coincides
with the quantitative temporal meaning only for
The Pedagogical Aspect of Comparative Analysis of the Process Duration Concept in English and Russian Languages
33

English Past Simple, Present Perfect and Russian Past
Perfect.
For Past Perfect, the one-sided limitation of
duration shifts from the moment "now" to the moment
"then in the past", this is also noted in Russian Past
Perfect.
For English Past Continuous and Russian Past
Perfect Tenses the aspectual meaning of duration is
not limited.
English Past Perfect Continuous and Present
Perfect Continuous require a strict representation of
the process interval, they have a quantitative
aspectual meaning of limited duration.
Future. In both languages Future Tenses
determine the location of the situation in the future
after the moment of speech, the qualitative time
meanings are the following:
nunc posteriority for English Future Simple, for
Russian Future Tenses;
tunc simultaneity for Future Continuous;
tunc posteriority for English Future Perfect and
Russian future perfect. The quantitative time meaning
of duration is limited on the time axis by the moment
"now". The quantitative aspectual value coincides
with the quantitative temporal value only for English
Future Simple and for Russian Future Tenses. For
Future Perfect the one-side duration limit is shifted
and will not be after the moment “now”, but after the
moment “then in the future”, this is also noted in the
future perfect.
For English Future Continuous and for Russian
Future Imperfect the aspectual meaning of duration is
not limited. The quantitative temporal meaning of
duration is limited on the time axis by the moment
"now". The quantitative aspectual meaning coincides
with the quantitative temporal meaning only for
English Future Simple and for Russian Future Tenses.
For Future Perfect the one-sided duration limit is
shifted and will not be after the moment “now”, but
after the moment “then in the future”, this is also
noted in the future perfect. For English Future
Continuous forms and for Russian Future Imperfect,
the aspectual meaning of duration is not limited.
The quantitative time-aspectual meaning of Tense
implies the presence or absence of an action interval
and correlates with the meanings of non-verbal
means. Neutral adverbs are to biaxial or indifferent to
the time localization.
Time nouns of duration are nouns of quantitative
time meaning and deverbal nouns, which are
characterized by the presence of time limits. Nuclear
nouns with a denotative meaning of limited duration
in time: день / day, месяц / month, год / year, etc.
Peripheral nouns film, lecture imply the interval of
the process of realization - situations of viewing,
listening.
2.1.3 Aspectual Nouns of Duration in
English
Aspectual nouns of duration are an indicator of an
action duration only if they are combined with
deverbal nouns or verbals. Consider examples:
(1) …with the result that the duration of each
warrant would vary (BNC).
(2) Teachers' salaries are relatively low compared
with those for other professions requiring the
same duration of training (BNC).
(3) … ladder filter is rather a duration of the
signal being handled (BNC).
(4) Indeed, when the duration becomes infinite
(BNC).
The noun duration can be a subject and acts as an
abstract expression of duration without reference to a
process (4). Of the 50 analyzed examples only one
noun is combined with the V+ing form of the
deverbal noun duration of training (2). The most
common combinations with the nouns that imply a
time interval warrant, war, storm, lease, term,
conflict, election. It is logical to assume that subject
nouns cannot be combined with the concept of
duration. The possibilities of expressing the process,
the duration of which is emphasized, are extremely
diverse - from the deverbal noun warrant (1) to the
participial phrase the signal being handled (3).
(5) The lines of longitude are straight lines
converging on the north pole (BNC).
The noun longitude functions in only one
meaning, which is determined by its status as a
geographic term of longitude (5).
(6) … the audience spent the interval walking
about studying each others' clothes (BNC).
(7) … there is an interval during the performance
so that the sale of ice-cream, nuts and drinks
can take place (BNC).
(8) Treatment' interval was defined as the interval
between date of onset and the date therapy
(BNC).
(9) In a brief interval between merging The
European and the The Sunday Correspondent,
addressing sessions on global media the team
won (BNC).
The substantive interval in the given examples
(6), (7) is translated as an performance break, while
the content of the interval is revealed by actions
filling it: by verbals (6) and a subordinate clause (7).
The combination with the deverbal noun treatment'
interval can be similar to the combination with the
TLLIC 2022 - I INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE "ACTUAL ISSUES OF LINGUISTICS, LINGUODIDACTICS AND
INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION"
34
time nouns four week interval (8), since in both cases
an interval is implied. The noun interval is most often
combined with adjectives that define it a brief interval
(9). Sometimes the interval is represented by a pause
between actions.
(10) …ownership has been transferred without
continuity of management (BNC).
(11) Any strategy requires far more time and
continuity of action and work to bear fruit
(BNC).
(12) …which ensured continuity of the education
process throughout the years of compulsory
schooling… (BNC).
(13) … to emphasize the need for continuity in their
development through school life' (BNC).
(14) …which failed to achieve this continuity of
production (BNC).
Examples of correlation of an action with an
interval are marked by low frequency. Nouns of the
aspectual meaning of duration include:
1) deverbal nouns: to endure - duration, to
continue - continuity;
2) abstract nouns longitude and interval.
The noun continuity, as can be seen from the
analyzed examples (10) - (14) functions in different
meanings united by one content of the continuation of
the process. The meaning of duration is not
explicated, but only implied by the continuation
meaning. However, it should be noted its high
frequency of functioning with the deverbal nouns
production (14), development (13), education process
(12), continuity of management (10), action and work
(11).
In English, the emphasis is on continuation, not on
duration.
(15) Even going to the length of alleging in the
public press that it was the Board which was in
breach…(BNC).
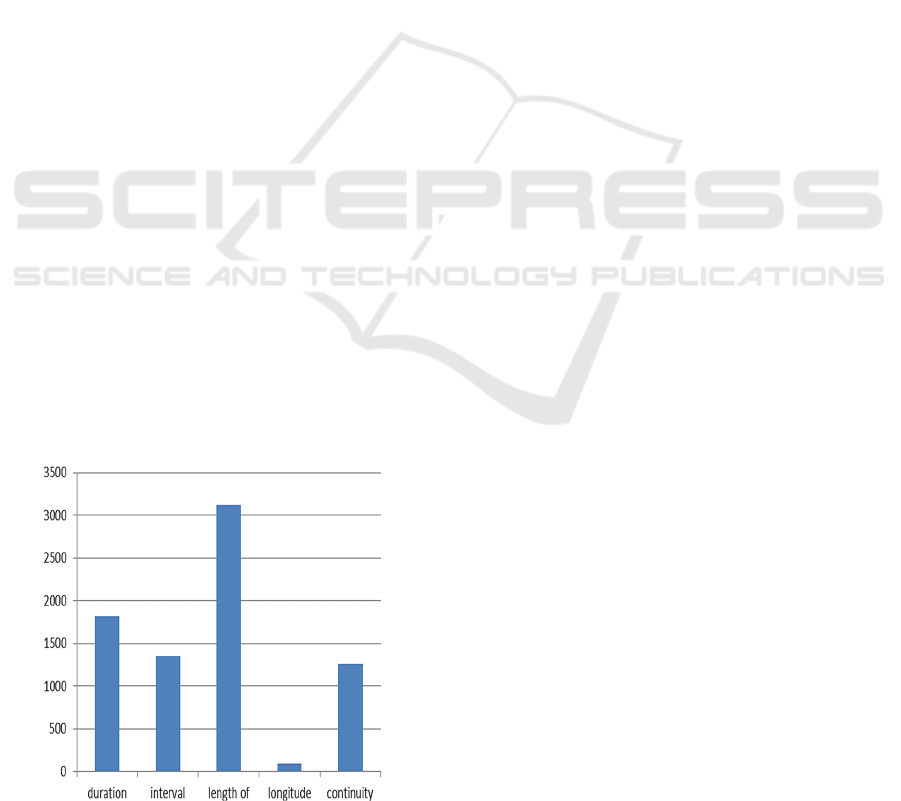
Figure 1: Frequency of English nouns.
The noun length of abstract meaning explicates
the length of time, expresses a time interval. This
noun is the most common (15). The abstract noun
incessancy means "the quality of something that goes
on without end or interruption." Its synonyms are
ceaselessness, continuousness, incessantness,
endlessness. These nouns express the property of
being (or appearing to be) infinite. However, no
examples of their combination with deverbal nouns or
verbals as an indicator of the duration of action have
been found. The distribution of frequency indicators
is shown in Figure 1.
2.1.4 Aspectual Nouns of Duration in
Russian
In Russian, the aspectual meaning of duration can be
expressed by nouns:
длительность,
продолжительность, интервал, долгота,
промежуток /
duration, duration, interval,
longitude, interval. Among them, deverbal
nouns can
be noted:
1) длительность / duration from the verb
длиться / to last,
2) продолжительность / duration from the
verb продолжаться / to continue.
We consider the following examples:
(16) В качестве таковой был принят
параметр длительности работы
в сфере ИТ / As such, the parameter of the
duration of work in the field of IT was taken
(RNC).
(17) Формально длительность обучения в
начальной школе не зависит от
возраста поступления ребёнка в школу
/Formally, the duration of education in
primary school does not depend on the child's
school entry age (RNC).
(18) Длительность видеосмотрения в
интернете растет с каждым годом / The
duration of video viewing on the Internet is
growing every year (RNC).
(19) Длительность первого в истории полёта
составила минуту,
скорость ― больше 40 километров в час /
The duration of the first flight in the history
was one minute, the speed was more than 40
kilometers per hour (RNC).
(20) Какова длительность передержки
растений в карантинном аквариуме для
достижения ими гарантированной
«чистоты»?… без химии / What is the
duration of overexposure of plants in a
quarantine aquarium in order to achieve
The Pedagogical Aspect of Comparative Analysis of the Process Duration Concept in English and Russian Languages
35

guaranteed "purity"? ... without chemistry ...
(RNC).
(21) На всех рынках происходит увеличение
средней длительности использования
интернета, в то время как длительность
потребления телевидения остается
стабильной / All markets are experiencing an
increase in the average duration of Internet use,
while the duration of television consumption
remains stable (RNC).
The substantive длительность / duration is
actively combined with deverbal nouns of various
morphemic forms (16) - (21).
(22) Продолжительность проживания
мигрантов превышает официально
разрешённый срок / The duration of residence
of migrants exceeds the officially permitted
period (RNC).
(23) Как изменится продолжительность
падения, если муравей во время падения
переползёт снизу вверх? / How will the
duration of the fall change if the ant crawls
from the bottom up during the fall? (RNC).
(24) Один параметр – продолжительность
нанесения краски / One parameter is the
duration of paint application (RNC).
(25) Продолжительность несения дежурства
стала единой / The duration of duty became
unified (RNC).
(26) Продолжительность обучения в
школе составляет 4 года / The duration of
schooling is 4 years (RNC).
(27) Продолжительность существования
Вселенной конечна / The duration of the
existence of the Universe is finite (RNC).
(28) Продолжительность расширения и
сжатия, разный объём при максимальном
расширении и т. п. / The duration of
expansion and contraction, different volumes at
maximum expansion, etc. (RNC).
(29) Both nouns продолжительность / duration
(22)-(28) and длительность / duration (16)-
(21) are more active in Russian than their
equivalents in English. The total sampling
method was used to analyze 30 examples with
the noun длительность / duration and the
same number with the substantive
родолжительность / duration. As a result,
examples of indicating the action duration were
identified: 6 examples with the first noun (16)-
(21) and 7 examples with the second (22)-(28).
It can be noted that these nouns are combined
with deverbal nouns expressing action,
regardless of their form, that is, with derivatives
on –ие (17), (18), (21)-(28), and on –a (16), (20).
Their functional equivalence is confirmed by
the possibility of combining
продолжительность / длительность
обучения / duration of training with the same
deverbal nouns. Based on the number of
identified and cited examples, it can be argued
that the noun продолжительность /duration
functions more often.
(29)
В продолжение прощания невесты с подру
гами звучали песни / In continuation of the
farewell of the bride with her friends, songs
sounded (RNC).
(30) … появился пресс-релиз, подтверждающий
продолжение его работы / ... there was a
press release confirming the continuation of his
work (RNC).
(31) …отмена выплат ―
"логическое продолжение начатой
работы/... cancellation of payments - "a
logical continuation of the begun work (RNC).
The frequency of functioning of the noun
продолжение / continuation is lower than that of
substantives explicating duration in 3 examples out of
30 analyzed (29)-(31).
(32) Интервал покупки не коррелирует
с численным составом семьи / The purchase
interval does not correlate with the size of the
family (RNC).
(33) Анализа охватывает временной интервал
процесса деятельности / The analysis
covers the time interval of the process of
activity (RNC).
(34) Интервал движения во время Олимпиады
составит 10 минут / The interval of movement
during the Olympiad will be 10 minutes (RNC).
The frequency of combinations of the noun
интервал / interval with deverbal nouns to
represent the action duration is also 3 examples (32)-
(34) out of 30 analyzed. Quantitatively dominates the
expression интервал времени / time interval: 47
tokens out of 555 detected.
(35) Каждый промежуток молчания
обливал его ужасом… / Each interval of
silence doused him with horror ... (RNC,
https://ruscorpora.ru/new).
The functioning of the noun промежуток /
time gap with deverbal nouns to represent the
duration of the action is the least frequent - only 1
example out of 30 (35).
The vast majority of combinations were found
with the word врем/ time, about 3 examples with the
meaning of a spatial interval.
TLLIC 2022 - I INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE "ACTUAL ISSUES OF LINGUISTICS, LINGUODIDACTICS AND
INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION"
36
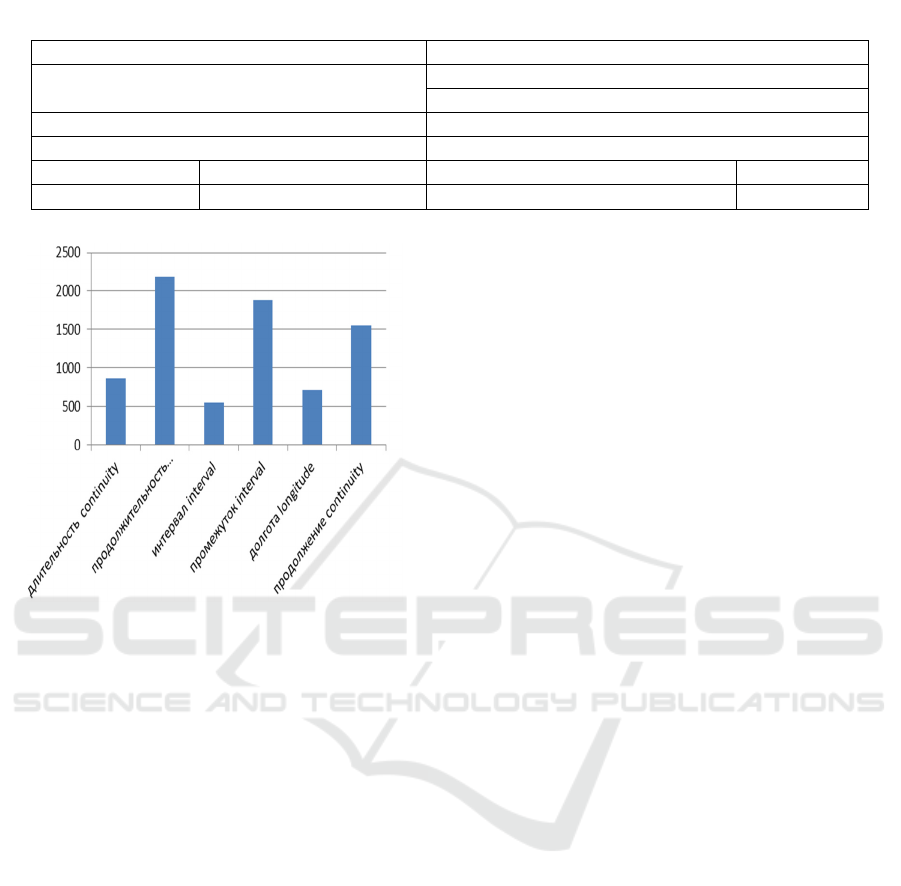
Figure 2: Frequency of substantives of the Russian
language.
The frequency of functioning of nouns is
presented in Table 1 in accordance with the
equivalence values in the two languages. One noun
duration in English corresponds to 2 substantives in
Russian длительность, продолжительность.
/ duration. The distribution of frequency indicators is
shown in Figure 2.
3 СONCLUSIONS
Thus, as a result of the analysis, we came to the
following conclusions:
1. Time duration means an interval of time,
aspectual duration implies its being filled with action.
The quantitative time-aspectual meaning of the
duration of Tenses makes it possible to determine
both the localization of the action on the time axis and
the presence of its limits.
2. The nouns of time meaning of duration are time
nouns and nouns implying the presence of an interval.
Aspect nouns of duration are an indicator of the action
duration only if they are combined with deverbal
nouns or verbals. We have discovered the following
nouns of duration
duration, longitude, interval,
length, continuity, длительность,
продолжительность, промежуток,
долгота, интервал, продолжение
which
aspectual meaning of duration actively implements
continuity, while the frequency of the rest is very low:
duration, interval. In English the emphasis is on
continuation, not duration. In Russian these nouns
demonstrate significant activity compared to English
длительность, продолжительность /
duration. The frequency of functioning of the rest is
distributed in descending order as follows: interval,
gap, continuation.
The prospect of further study of this problem may be
to identify the conditions for the functioning of the
substantives of aspectual semantics.
REFERENCES
Kobozeva, I. M., 2000. Linguistic semantics.
Plungyan, V. A., 2011. Introduction to grammatical
semantics: grammatical meanings and grammatical
systems of the languages of the world.
Brinton, L. J., Brinton, D. J. 2010. The linguistic structure
of modern English.
Declerck, R. 2006. The Grammar of the English Verb
Phrase. 1: The Grammar of the English Tense System.
A Comprehensive Analysis.
Ryabova, M. Yu., 1993. Temporal reference in English.
Mustajoki, A., 2006. Theory of functional syntax: from
semantic structures to linguistic means.
Bondarko, A. V., 2002. Theory of meaning in the system of
functional grammar: on the material of the Russian
language.
Lutfullina, G. F., 2016. Representation of particular
aspectual meanings of repetition and familiarity by
verb-infinitive analytical structures in French and Tatar
languages. Philology and man. 1. pp. 107-114.
BNC - British National Corpus. https://www.english-
corpora.org/bnc/.
RNC - National Corpus of Russian Language.
https://ruscorpora.ru/new.
Table 1: Frequency of functioning nouns in English and Russian.
En
g
lish lan
g
ua
g
e Russia Lan
g
ua
g
e
duration 1818 duration 863
len
g
th 2187
interval 1355 interval 555
len
g
th of 3121
g
ap1875
lon
g
itude 93 len
g
th 717
continuit
y
1257 continuit
y
1551
The Pedagogical Aspect of Comparative Analysis of the Process Duration Concept in English and Russian Languages
37
