
Knowledge and Attitudes on Community Participation in the
Management of Waste Bank in Bekasi City
Putri Nurul Hikmah Salsabila, Ony Linda and Elia Nur A’yunin
Public Health Study Program Faculty Of Health Sciences, Muhammadiyah University Prof. DR. Hamka,
Jl. Limau II, South Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Management of Waste Bank, Community Participation, Knowledge and Attitude.
Abstract: If not managed properly, waste will negatively impact public health and the environment. Waste management
in Indonesia is carried out by reducing and handling waste. This study aimed to explore the knowledge and
attitude of community participation in Waste Bank Management in Griya Persada Elok Housing, Bekasi City.
This was quantitative with a cross-sectional design. The research included 224 respondents who filled out
the online questionnaire. The results showed that participation was low (96.9%); 50.9% of respondents had
good knowledge; 50.9% of respondents had good attitudes, 84.4% of respondents had good education levels,
and 75,4% of community leaders participated in waste management. Increasing socialization and distribution
of the information about waste bank activities need it. Besides that, the participation of community leaders in
the waste bank as active customers need to be improved.
1 INTRODUCTION
The global environmental problem closest to human
life is the problem of waste, where waste problems
are often found in every Community. The issue of
waste is not only faced by developing countries, but
this waste problem has become a complex problem
faced by developed countries as well. Based on Law
Number 18 of 2008 concerning Waste Processing, it
is explained that waste is the result of daily activities
in solid form. In Indonesia, waste is a significant
problem that has a major impact on the environment.
In Indonesia, 240 cities still face waste management
problems (Kemenkes RI, 2013). Garbage problems
occur due to the number of humans, waste-producing
animals, high piles of garbage, and low public
awareness that is reluctant to dispose of waste in its
place (Lestari and Subhi 2018).
The waste problem is an important issue,
especially in urban areas. This happens because of the
amount of waste and the growth of the urban
population, which continues to increase yearly
(Wildawati 2020). All human activities cannot be
separated from what is called waste because the
impact of waste problems comes from humans, both
in the form of home activities and industrial activities.
As time goes on, the population will continue to grow,
and technology will become more sophisticated,
producing various waste in various types. The pattern
of waste management using the 'collect-transport-
dispose' system should begin to look for alternatives
to change it to more environmentally friendly
management. In principle, waste must be managed
directly at the place of origin because it is difficult to
obtain land that will be used as a landfill which will
have a more severe impact if the waste is not managed
properly (Suwerda, Sudibiyakto, and Kurniawan
2019).
In the waste management process, the important
things needed are residents' knowledge, attitudes, and
skills to manage the results of household waste and
the waste recycling process. Waste management
requires community participation in its
implementation. One form of community
participation in waste management activities in
Indonesia is the establishment of a Waste Bank
(Environmental Service, 2017). Minister of
Environment Regulation (PERMEN LH) No. 13 of
2012 states that community participation in the Waste
Bank program includes sorting, collecting, handing
over waste to the Waste Bank, and multiplying the
Waste Bank. The implementation of 3R activities is
still constrained due to low community participation
(Ministry of the Environment, 2012). Community
participation in waste management is still limited to
disposal (Haswindy and Yuliana, 2018)
Salsabila, P., Linda, O. and A’yunin, E.
Knowledge and Attitudes on Community Participation in the Management of Waste Bank in Bekasi City.
DOI: 10.5220/0011645700003608
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Social Determinants of Health (ICSDH 2022), pages 65-68
ISBN: 978-989-758-621-7; ISSN: 2975-8297
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
65
Community participation in the Waste Bank
program is to separate waste before saving it. The
Community must already know that the waste must
be grouped first before depositing it in the waste
bank. The garbage to be collected is grouped into five
types of classification, namely B3 waste (hazardous
and toxic materials), biodegradable waste, recyclable
waste, and waste, which can be reused, as well as
other waste. People selected to become customers
must be able to sort the garbage they want to deposit
in the waste bank, such as newspapers, plastic bottles,
used cardboard boxes, standard flowers, used iron,
and so on. Then after the waste is sorted, it is taken to
the waste bank, which will later be weighed and
recorded in a savings book.
Responding to these problems, the Bekasi City
government created a Waste Bank program described
in the Bekasi City Regulation No. 09 of 2017
concerning Waste Management to overcome the
increase in waste. The Waste Bank Program is a place
to build public awareness of sorting, recycling, and
reusing waste. Because if the waste is processed
properly, it will have a good selling value and will
become a new culture in Bekasi City.
In implementing the waste bank, community
participation has an essential role in the development
and sustainability of the waste bank (Ummah, N.,
Mahyudin, R. P., & Firmansyah, 2018). Lokita's
research (2012) explains that the success of the waste
bank program is influenced by the high community
participation (75%).
Based on a preliminary study that was carried out
on January 20, 2022, it was found that there are still
few people who want to participate in Waste
Management in the Waste Bank Program, which is
influenced by a lack of knowledge about Waste
Banks and how to manage them.
2 METHOD
The research was quantitative with a cross-sectional
design. This research was conducted in 2022 to
explore the description of knowledge and attitudes on
community participation in the management of the
Wijaya Kusuma waste bank, Griya Persada Elok
housing estate, Bekasi City, Indonesia. The research
included 224 respondents who filled out the online
questionnaire.
3 RESULT
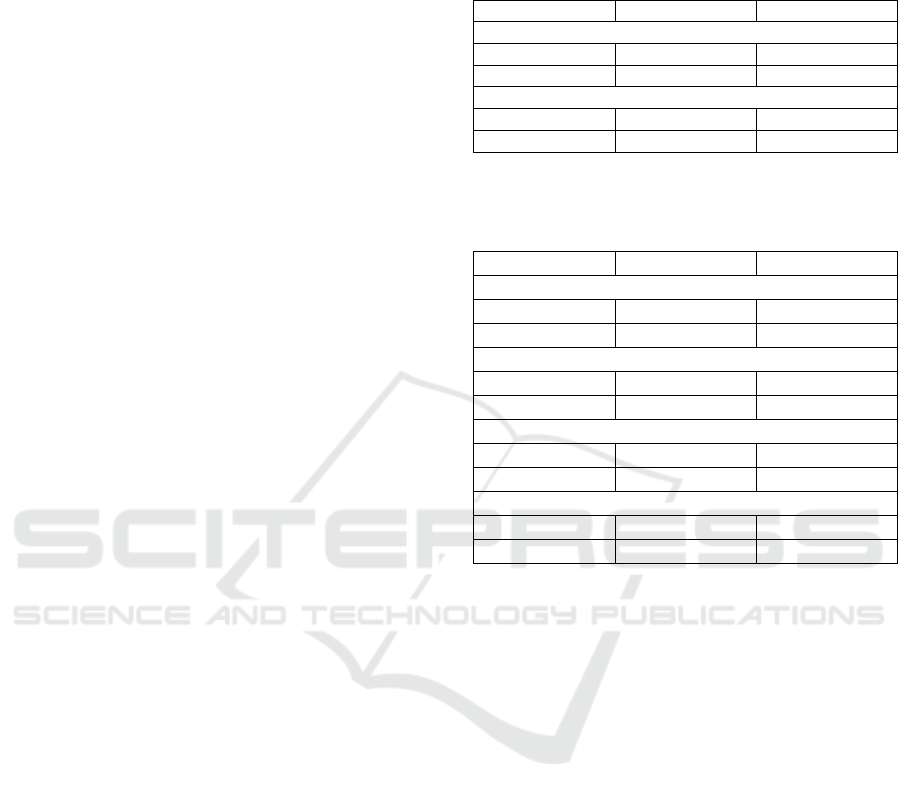
Table 1: Characteristics of Respondents.
Variable N (total = 224) %
Education level
Low 35 15.6
High 189 84.4
Status of Job
Working 71 31.7
Not workin
g
153 68.3
Table 2: Community Participation, Knowledge, Attitute,
and The Role Community Leader on Management Waste
Bank.
Variable N (total = 224) %
Community Participation
Low 217 96.9
Hi
g
h 7 3.1
Knowledge
Low 110 49.1
Hi
g
h 114 50.9
Attitude
Low 110 49.1
Hi
g
h 114 50.9
Roles of Communit
y
Leade
r
Low 169 75.4
Hi
g
h 55 24.6
This study sample had characteristics 84.4% have a
good education and 68.3% have a job (Table 1). The
result showed that the community participation in the
management of waste banks was low (96.9%). Of the
respondents' knowledge of management waste bank,
50.9% had a good understanding. Of respondents'
attitudes in waste bank management, 50.9% were
categorized as good. Besides that, the result also
showed the community leader had low participation
in the management waste bank (Table 2).
4 DISCUSSION
The Waste Bank program requires community
participation in its implementation. According to the
Regulation of the Minister of the Environment of the
Republic of Indonesia Number 13 of 2012 explains
that community participation in the Waste Bank
program includes activities of sorting waste,
collecting waste, submitting waste to the Waste Bank,
and multiplying the Waste Bank. The results of
research Based on these results, it can be seen that
there are more low forms of community participation
than high forms of community participation. So
ICSDH 2022 - The International Conference on Social Determinants of Health
66

community participation in this study is not seen well
because the results obtained are too low. This is
because community leaders do not play an active role
in providing examples, and there is still a lack of
socialization about waste banks, so residents are not
motivated to take an active part. On the other hand,
residents will be motivated when community leaders
carry out socialization related to the waste bank
program consistently to residents and provide direct
examples to be engaged in waste bank activities. They
will participate directly in waste bank activities.
The waste management process in its
implementation requires essential things such as
knowledge, attitudes, and skills of residents to
manage the results of household waste and the
recycling process. Knowledge also affects
participation because a person desires to participate
when he has extensive knowledge and knows the
impact of waste management. The results of the
univariate analysis test showed that 114 respondents
(50.9%) had good understanding, and more than 110
respondents (49.1%) had less knowledge. In this
study, it can be seen that respondents with good
knowledge will not necessarily have good community
participation, this happens because it is not followed
by actual involvement and there is still a lack of
socialization from community leaders regarding the
waste bank program to residents.
Attitudes influence the waste management
process because attitudes can determine a person in
deciding to act. So that someone's perspective will
also show how someone participates. The results of
the univariate analysis test showed that 114
respondents with good attitudes (50.9%) more than
110 with bad attitudes (49.1%). In this study, it can
be seen that the perspective of the respondents who
are already good does not necessarily make the
respondents also have high participation, this happens
because there is no desire from the respondents to
support and realize building a clean and healthy
environment.
The level of education influences the form of a
person's participation in the waste management
process. This study's results categorize the
respondents' education levels into two, namely low
education and higher education. Based on the
univariate analysis test results, it was found that as
many as 189 respondents with higher education
(84.4%) were more than 35 respondents with low
education (15.6%). The highest education level of
respondents is high school graduates (50%), college
graduates (34.4%), junior high school graduates
(14.7%), and elementary school graduates (0.9%).
Based on the univariate analysis test results, it
was found that as many as 153 respondents worked
more (68.3%) than 71 respondents who did not work
(31.7). This result is in line with the results of
knowledge (50.9%) and education level (84.4%),
which also get more results because when someone
has a high level of education, it will affect the level of
knowledge and work that the student will obtain. That
person. In this study, it can be seen that respondents
who work are not necessarily actively participating in
waste bank activities. This can happen because the
respondent will find it difficult to leave the job he has
for other activities outside of his job.
Community leaders influence someone's
participation because they have an important role in
socializing and providing information related to
Waste Banks. Community leaders also have an
important role as facilitators and motivators who will
directly assist the Community in Waste Bank
activities. The results of the univariate analysis test
showed that the role of community leaders in waste
bank management was still low (75.4%) more than
that of high community leaders (24.6%) in waste bank
management activities. In this study, it can be seen
that the role of community leaders is a supporting role
in waste management activities in waste banks. When
community leaders do not play an active role in
showing and inviting the Community to participate,
the results of community participation will also be
low because there is no encouragement from
community leaders to motivate the Community.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The result of this study indicated that it is necessary
to improve community behavior by making people
aware of the importance of handling waste starting
from the household itself and informing related
impacts that will be caused to families and the
environment. Residents who are already active
customers are expected to be able to invite and
provide support to other residents so that they want to
participate in waste management activities. A good
way of managing waste is to improve the knowledge
of residents who still have the idea that it is better for
garbage to be piled up and burned. and It is expected
to increase socialization regarding waste banks to
motivate the Community to attract people to
participate in waste management activities. Then it is
also expected that all community leaders can involve
themselves in participating in waste bank activities as
active customers. This aims to set an example to the
Community.
Knowledge and Attitudes on Community Participation in the Management of Waste Bank in Bekasi City
67

REFERENCES
Haswindy, Septu, and Fitriza Yuliana. 2018. “Partisipasi
Masyarakat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah Pemukiman
Pada Kecamatan Tungkil Ilir Kabupaten Tanjung
Jabung Barat.” Jurnal Ilmu Lingkungan 15(2):96. doi:
10.14710/jil.15.2.96-111.
Lestari, Nastiti Mugi, and Misbahul Subhi. 2018. Analisis
Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Perilaku
pengelolaan sampah rumah tangga di bank sampah
Kota Batu Analysis of Factors Related to the Behavior
of Domestic Waste Management in Batu City Garbage
Bank. 3(April):311–16.
Lokita, A. D. 2012. “Partisipasi Masyarakat Dalam
Program Kesehatan.” Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup Republik Indonesia. 2021.
Permen LHK RI No. 05 Tahun 2012, Tentang Jenis
Renc Usaha & Keg Wajib Memiliki Amdal.
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 6(11), 951–
952., 2013–15.
Nursalam. 2015. Metodologi Peneltian Ilmu Keperawatan:
Pendekatan Praktis. (P.P.Lestari, Ed) (4th Ed). 4th ed.
jakarta: salemba medika.
Pemerintah Kota Bekasi. 2017. Peraturan Daerah Kota
Bekasi No. 09 Tentang Perubahan Atas Peraturan
Daerah Nomor 15 Tahun 2011 Tentang Pengelolaan
Sampah. 1–7.
Suwerda, Bambang, Sudibiyakto Sudibiyakto, and Andri
Kurniawan. 2019. Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dan
Sikap Masyarakat Dalam Mengelola Sampah Berbasis
Bank Sampah Di Kabupaten Bantul. Jurnal Kesehatan
Lingkungan 9(3):100–104.
Ummah, N., Mahyudin, R. P., & Firmansyah, M. (2016).
2018. Kajian Faktor Pendorong Keaktifan Kinerja
Organisasi Dan Partisipasi Masyarakat Dalam
Pengelolaan Bank Sampah Kota Banjarbaru.
Banjarbaru: Universitas Lambung Mangkurat. 14(3):
245.
Wildawati, Despa. 2020. Faktor Yang Berhubungan
Dengan Pengelolaan Sampah Rumah Tangga Berbasis
Masyarakat Di Kawasan Bank Sampah Hanasty Kota
Solok. Human Care Journal 4(3):149. doi: 10.32
883/hcj.v4i3.503.
ICSDH 2022 - The International Conference on Social Determinants of Health
68
