
Service Quality and Its Relation to Customer Trust and Loyalty
Lisa Binti Harun and Herlina
Business Administration, Politeknik Negeri Nunukan, Ujang Dewa, Nunukan, Indonesia
Keywords: Service, Service Quality, Customer Trust, Customer Loyalty.
Abstract: A consumer's perception of the quality of services offered is an essential aspect of consumer perception, which
influences consumer satisfaction.Services have a strong relation to quality. A better quality service will give
a better image in consumers' perception and improve their overall well-being. The improvement later would
lead to their trust and loyalty. The study aims to analyze the relationship between service quality and consumer
trust and loyalty in PT. Telkom Nunukan branch. The approach of the study uses a quantitative with an
explanatory survey method. It can be concluded that service quality positively and significantly impacts
customer trust and loyalty.
1 INTRODUCTION
Humans in their daily are inseparable from needs
towards goods and services.Those needs that can be
directly consumed or reprocessed. Thus, services
have evolved into an essential component of product
marketing activity. Services are a concrete activity
that one person provides to another, and the client is
more involved in the service-consuming process.
Services have a strong relations to quality. It
compares the anticipated service with the actual
service provided (Hidayat and Anasis, 2020). Service
quality is a crucial component in consumer
perception, which has an impact on consumer
satisfaction. A better quality of services provided will
give a better image in consumers’ perception.
Furthermore, there are five dimensions of service
quality known as SERVQUAL:(a)Reliability,
(b)Responsivenesss, (c) Assurance, (d) Empathy, and
(e) Tangible (Pakurár et al., 2019).
Some experts consider customer trust to be an
essential factor determining the success of
relationship marketing. This view is that customers
must have trust in the company, customers will feel
safe in conducting transactions with the company,
and transactions made will be guaranteed for
sure.Trust is the belief that a person will find what he
wants in others, not what he fears and later it become
an immediate effect on the decision that customers
must make, either to pursue or to end their
relationship with a firm (Nguyen et al., 2013). It can
reduce the risk of using services, because it can be
considered as a consequence of a positive evaluation
of service and customer loyalty (Putra et al., 2020).
Trust relies on someone or something that believes to
have consequences in the relationship between the
giver of trust and the one who is given the trust.
Reference (Erne, 2022) view the concept of trust as
the same as integrity, loyalty, concern, and keeping
promises. Trust is a critical element in meaningful
relationships; they build trust through networks of
friends and family.
There are three elements to create trust: shared
values, communication, and opportunistic behavior
(Morgan and Hunt, 1994). Moreover, three aspects
contribute to the formation of trust: ability, which
refers to the seller's or organization's skill and
qualities in influencing and authorizing a given field;
reputation; and legitimacy (Palilati, 2007). In this
case, the seller's ability to provide, serve, and secure
transactions from interference of other parties.
Additionally, there is benevolence, which is the
seller's willingness to create mutually beneficial
satisfaction for himself and the buyer. The seller can
minimize the profit obtained, but customer
satisfaction is also high. In addition, the final factor is
integrity, which relates to the seller's conduct or
business practices. Whether or not the information
given to consumers is accurate.
Long-term relationships with consumers in the
service and manufacturing industries hinge on
consumer confidence in the organization. Trust is the
essence of human connection complexity. This idea
is a future-oriented aspect of quality connections.
142
Harun, L. and Herlina, .
Service Quality and Its Relation to Customer Trust and Loyalty.
DOI: 10.5220/0011729500003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 142-147
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Appears to exist when consumers are willing to rely
completely on the company's future actions.
Reference (Ferinnadewi and Djati, 2004) provides
empirical evidence that consumer confidence in the
service sector created human dimensions such as
responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and reliability.
The impact on consumer loyalty is even more
significant when consumers who already have that
trust feel satisfied.Reference (Delgado‐Ballester et
al., 2001) proposes that the dimensions of trust are
divided into two parts, namely:
a. Brand can be Trusted (Brand Reliability)
Brands can help/satisfy consumer needs. Brands
influence individual beliefs to fulfill promises in
product operations.
b. Interest in the Brand(Brand Intentions)
Dimensions make individuals feel there is a guarantee
that the brand will be responsible and pay attention to
consumers.
Therefore, trust plays a vital role in the long-term
relationship between customers and the company,
mainly which includes customer confidence in the
quality, reliability, and integrity of the services
delivered by the company.
In the other hand, loyalty is an ancient term
traditionally used to describe loyalty and enthusiastic
devotion to a country, cause, or individual. In
contemporary business contexts, the term loyalty
describes the willingness of customers to continue to
subscribe to a company in the long term by buying
and using its goods and services repeatedly and
preferably exclusively and voluntarily recommending
the company's products to friends and colleagues
(Lovelock, 2007); (Putra et al., 2020). The
establishment of customer loyalty is not immediate,
but rather the result of a learning process and regular
service purchase over time. The greatest difficulty for
service marketers is to provide prospective
consumers with compelling reasons to do business
with them, maintain client loyalty, and increase
service usage. The effect of loyalty on the company
is that it gives a long-lasting source of income.
Customers will remain loyal only if they see that they
are receiving greater value (including superior
quality) than they would by moving to a different
service provider.
Loyal customers are those who have a positive
outlook on the firm, are devoted to repurchasing its
products or services, and recommend them to others.
It is a symptom that clients are reluctant to switch to
competitors due to their faith and reliance on the
quality of the service supplied (Elizar et al., 2020).
Customer loyalty occurs when repeated purchases by
the same customers and their willingness to
recommend products to other customers without
direct rewards. Ultimately, repeated use will impact
measurable financial results (Ramzi and Mohamed,
2010).
There are three dimensions to loyalty: behavioral,
attitude, and cognitive. Behavioral loyalty is assessed
by the frequency of purchases of the company's
products and services; attitudinal loyalty is measured
by client purchases; and cognitive loyalty is measured
by the customer's perceptions about the product.
Customer loyalty is the final effect of a purchase,
which expresses an attitude and intention to behave in
the future. It expresses a commitment to repurchase
the product needed by the company, a commitment to
recommend to others, an intention to increase the
amount of savings, an intention to or a desire to tell
positive things about the company, and a willingness
to pay a high price (Palilati, 2007); (Hidayat and
Anasis, 2020). From several opinions regarding
customer loyalty, the conclusion is that customer
loyalty is a positive attitude toward a service provider
by repurchasing products or services offered in the
long term and recommending the company to
colleagues and their families.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
1. Does the service quality has a significant effect
towards customer’s trust?
2. Does the service quality has a significant effect
towards customer’s loyalty?
3. Does the customer’s trust has a significant effect
towards customer’s loyalty?
4. Does the service quality has a significant
effecttowards customer’s trust and loyalty?
3 METHOD
3.1 Data Collection
The study is a quantitative study that involves
questionnaires and interviews as the method of
collecting data. Further, data were collected using the
probability sampling technique by distributing
questionnaires to 312 respondents.
It integrated the research variables: service
quality, customer trust, and loyalty. Furthermore,
each variable contains supporting indicators. The
indicators in service quality variables were tangible
(KP1), reliability (KP2), responsiveness (KP3),
assurance (KP4), and empathy (KP5). Meanwhile, for
Service Quality and Its Relation to Customer Trust and Loyalty
143
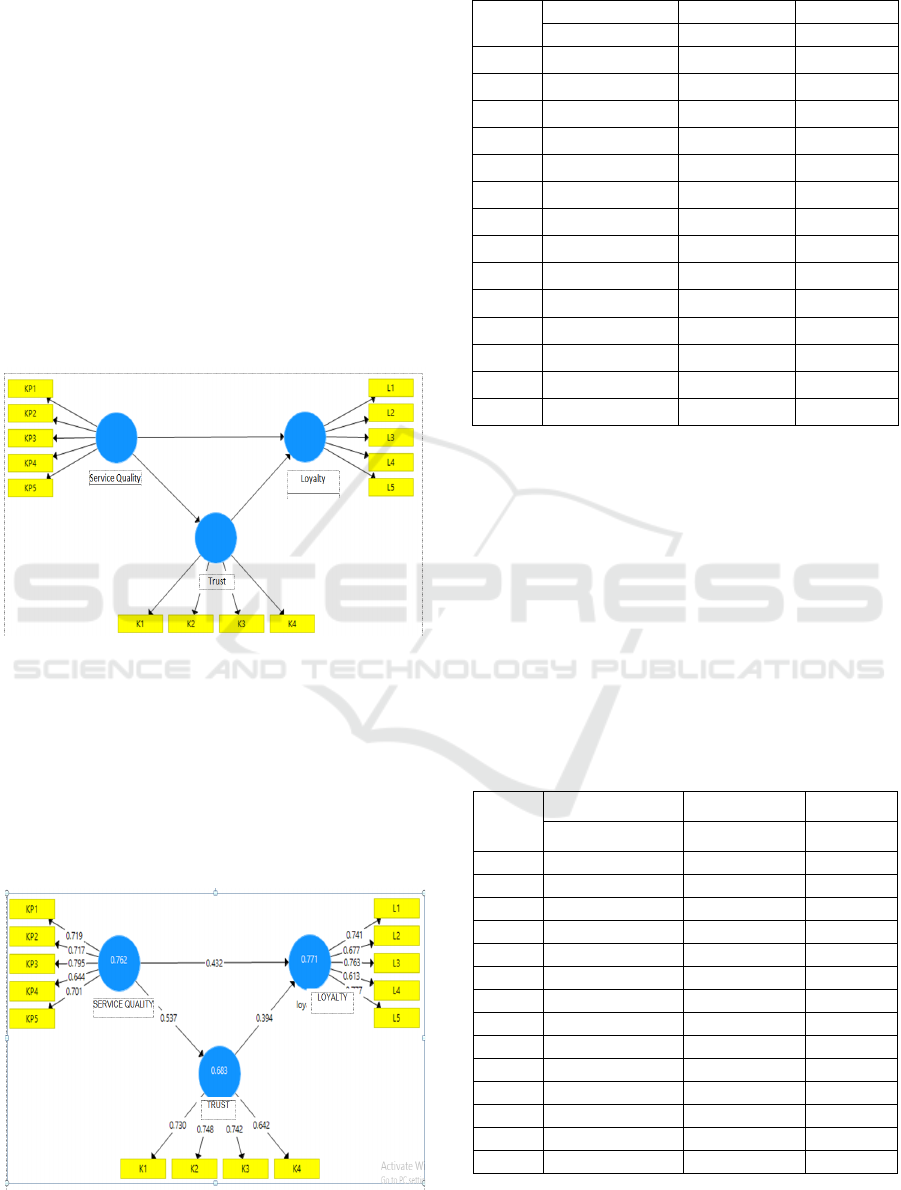
customer trust, the indicators were brand reliability
(K1&K2) and brand intentions (K3&K4). On the
other hand, the indicators of customer loyalty were
consistent buying (L1), recommending the products
to others (L2&L3), and consumers not moving to the
rival (L4&L5).
The next stage of the study was the validity and
reliability testing of the instrument using the SPSS 22
version to ensure the appropriateness of all items
from the questionnaire. The Path Analysis instrument
was used using the SmartPLS version 3.20. The steps
of the analysis were designing a structural model
(internal and external models), constructing a path
diagram, converting the Path diagram to regression,
parameterizing the hypothesis, and testing the
hypothesis. Source: SmartPLS ver.3 Output of
processed primary data.
Figure 1: Constructing Path Diagram.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Evaluation of Measurement Model
(Outter Model)
4.1.1 Convergent Validity Test
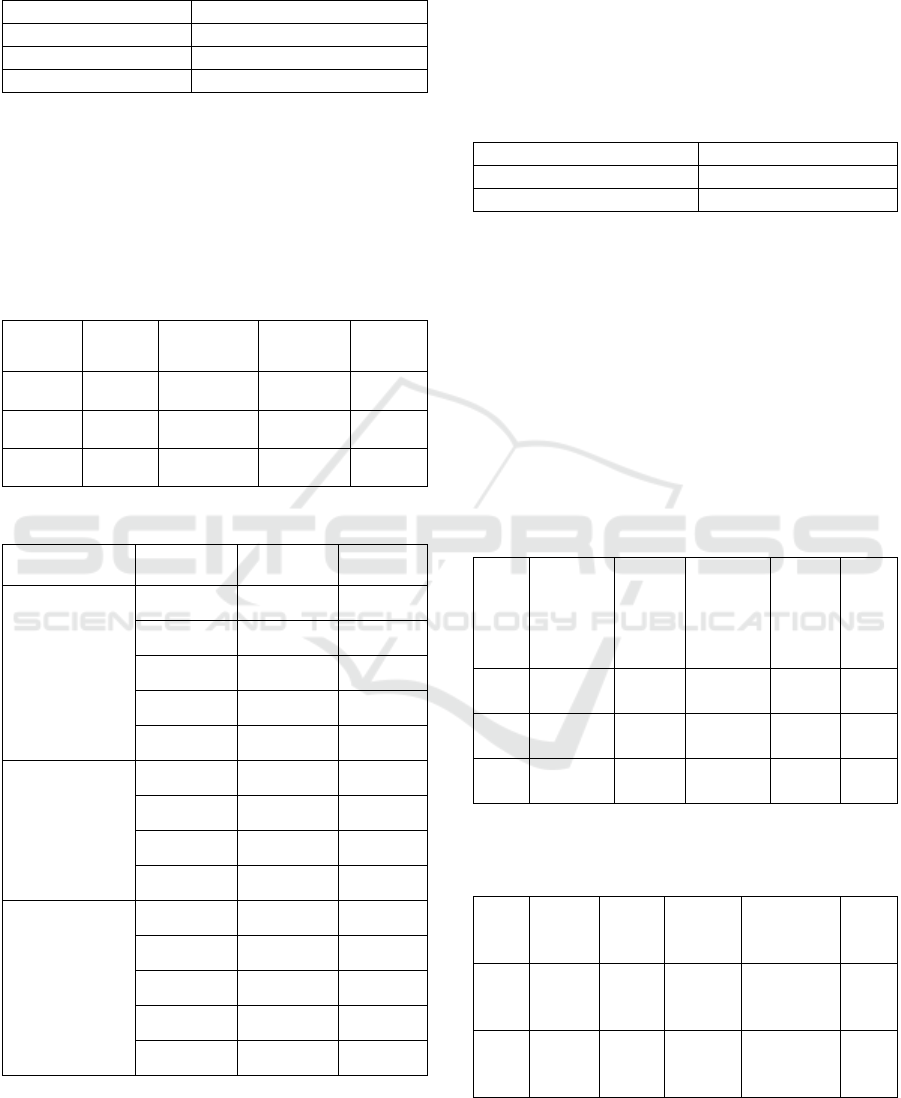
Figure 2: Output Loading Modelling Factor.
Table 1: Output Loading Modelling Factor.
Service Quality Trust Loyalty
X Y1 Y2
KP1 0,719
KP2 0,717
KP3 0,795
KP4 0,644
KP5 0,701
K1 0,730
K2 0,748
K3 0,742
K4 0,642
L1
0,741
L2
0,677
L3
0,763
L4
0,613
L5
0,777
The results in table 1 indicate that the loading factor
gives a value above the specified value, which is 0.5,
so the indicators used in this study have met and are
said to be valid.
4.1.2 Discriminant Validity Test
For reflective indicators, it is necessary to test
discriminant validity by comparing the values in the
cross-loading table. An indicator is declared valid if
it has the highest loading factor value for the intended
construct compared to the loading factor value for
other constructs.
Table 2: Output result for Cross Loading.
Service Quality Trust Loyalty
X Y1 Y2
KP1 0,719 0,419 0,248
KP2 0,717 0,349 0,282
KP3 0,795 0,419 0,259
KP4 0,644 0,353 0,387
KP5 0,701 0,377 0,356
K1 0,443 0,730 0,344
K2 0,418 0,748 0,394
K3 0,365 0,742 0,323
K4 0,301 0,642 0,405
L1 0,482 0,428 0,741
L2 0,326 0,401 0,677
L3 0,276 0,142 0,763
L4 0,302 0,193 0,613
L5 0,359 0,235 0,777
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
144
4.1.3 Average Variance Extracted (AVE)
Table 3: Output result of average variance extracted.
Variabel AVE
Service Quality 0,514
Trust 0,513
Loyalty 0,514
The results from table 3, the Average Variance
Extracted (AVE) calculation, indicate that all the
variables measured in this study have a variance value
of more than the index value of 0.5. So it can be said
that all the variance variables.
4.1.4 Reliability Test
Table 4: Reliability test results.
Variable Remark
Cronbach’s
Alpha
Composite
Reability
Remark
Service
Quality
(X) 0,762 0,840 Reliable
Trust (Y1) 0,683 0,808 Reliable
Loyalty (Y2) 0,771 0,840 Reliable
Table 5: Indicator reliability test results.
Variable Remark
Cronbach
Alpha
Remark
Service
Quality(X)
KP1 0,832 Reliable
KP2 0,832 Reliable
KP3 0,830 Reliable
KP4 0,832 Reliable
KP5 0,831 Reliable
Trust (Y1)
K1 0,830 Reliable
K2 0,830 Reliable
K3 0,832 Reliable
K4 0,832 Reliable
Loyalty(Y2)
L1 0,826 Reliable
L2 0,831 Reliable
L3 0,833 Reliable
L4 0,836 Reliable
L5 0,828 Reliable
Table 4 shows that all the variables measured in this
study have Cronbach's Alpha and Composite
Reliability values more than the index value of 0.6.
Therefore all variables are reliable.
4.2 Structural Evaluation
(Inner Model)
4.2.1 R
2
Testing
Table 6: Output calculation of R
2
.
R Square
Trust 0,286
Loyalty 0,292
The value of R-squared (R2) is used to measure how
much influence certain independent latent variables
have on the independent latent variables. The result
of R2 of > 0.67 indicates that the model is good, >
0.33 indicates a moderate model, > 0.19 indicates a
weak model, and> 0.17 indicates a weak model. Table
5.24 shows the R2 value of this study at 0.286 and
0.292, which means it has a weak model value.
4.2.2 Significance Test
a) Output Path Coefficient
Table 7: Output path coefficient.
Original
Sample
(O)
Sample
Mean
(M)
Standard
Error
(STERR)
T
Statisti
cs
(|O/ST
ERR|)
P
Valu
e
X -
>Y1
0,394 0,401 0,059 6,697 0,000
X-
>Y2
0,220 0,222 0,059 3,705 0,000
Y1-
>Y2
0,537 0,548 0,054 9,876 0,000
b) Output Indirect Effect
Table 8: Output indirect effect.
Original
Sample
(O)
Sample
Mean
(M)
Standard
Error
(STERR)
T Statistics
(|O/STERR|)
P
Value
X-
>Y1-
>Y2
0,211 0,216 0,039 5,449 0,000
X-
>Y1-
>Y2
0,211 0,216 0,039 5,449 0,000
Before testing the hypothesis, it is known that the T-
table value for the 95% confidence level (5% by
Service Quality and Its Relation to Customer Trust and Loyalty
145

testing two parties so that the alpha becomes 0.025)
and the degrees of freedom (df) = n-2 = 312-2 = 310
is 1.971. Hypothesis testing for each latent variable
relationship is shown as follows:
Table 9: Hypothesis testing.
No Results Examined Decision
1 T-test 0.394 H0 Rejected
H1 Accepted
SQ has
significant
effect on CT
2 T-test 0.220 H0 Rejected
H1 Accepted
SQ has
significant
effect on CL
3 T-test 0.537 H0 Rejected
H1 Accepted
CT has
significant
effect on CL
4 T-test 0.211 H0 Rejected
H1 Accepted
SQ has
significant
effect on CT and
CL
1. The influence of service quality on trust
The results suggested that the quality of service has a
major impact on consumer confidence in PT. Telkom
Nunukan Branch's telecommunications services. It
shows that the higher a company's service quality, the
more reasonable or strong consumer confidence will
be, and vice versa; if the company's service quality
declines, so will consumer confidence.
2. The influence of service quality on customer
loyalty
The results indicated that the quality of service has a
major impact on consumer loyalty to PT. Telkom
Nunukan Branch's telecommunications services. It
can be read that a company's customer loyalty will be
reasonable or high if its perceived service quality is
high, and vice versa; if the company's service quality
declines, consumer loyalty will also decline. Based on
this research, service quality plays a crucial part in
developing a general perception that affects customer
loyalty to a firm, demonstrating that good service
quality will lead to high customer courtesy, which can
improve customer loyalty.
3. The influence of customer trust on customer
loyalty
The results showed that consumer trust significantly
influences customer loyalty to telecommunication
services PT. Telkom Nunukan Branch. It can be
interpreted that the higher consumer trust in the
company, the consumer loyalty formed will also be
high, and vice versa; if consumer trust in the company
decreases, the formed consumer loyalty will
decrease.Based on this research, customer trust is
vital in forming a sense of security and trust in the
company, which will affect the level of loyalty itself.
4. The Influence of Service Quality on Customer
Trust and Loyalty
The results indicated that the quality of service
significantly influenced the trust and loyalty of
customers of telecommunications services PT.
Telkom Nunukan Branch. It can be interpreted that
the better the quality of service, the higher the
customer's trust in the company, and it will also
increase loyalty and vice versa. If the quality of
service is lacking, the customer's trust in the company
decreases, and the formed customer loyalty will
decrease. Customer loyalty is the final effect of a
purchase, defined as an attitude and intention to
behave in the future. It is expressed through a
commitment to re-purchase the product needed by the
company and a commitment to recommend it to other
people, the intention to increase the amount of
savings, the intention or desire to tell positive things
about the company, and the willingness to pay dearly.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the overall discussion, service quality has a
positive and significant impact on customer trust and
loyalty. Service quality has a significant effect on
customer trust, which directly and indirectly affects
customer loyalty.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Politeknik Negeri Nunukan financed/partially
supported this research. We appreciate the assistance
of our colleagues and the director of Politeknik
Manufaktur Bandung in completing this research. We
would also to show our gratitude to:
1. Arkas Viddy, Ph.D as Director of Politeknik
Negeri Nunukan who contributed in stimulated
this research.
2. Dr. Besse Asniwaty, SE, MSi, as Vice Director
1 of Politeknik Negeri Nunukan who
contributed in stimulated this research.
3. Dr. Rafiqoh, SE, MM as Vice Director 2 of
Politeknik Negeri Nunukan who allocated the
budget for this research.
We also immensely grateful to all reviewers of
ICAST especially for all of their insights.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
146

REFERENCES
Abdillah, W., & Hartono, J. (2015). Partial Least Square
(PLS): alternatif structural equation modeling (SEM)
dalam penelitian bisnis. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi, 22,
103-150.
Akbar, M. M., & Parvez, N. (2009). Impact of service
quality, trust, and customer satisfaction on customers
loyalty. ABAC journal, 29(1).
Ramzi, M., & Mohamed, B. (2010). Customer loyalty and
the impacts of service quality: The case of five star
hotels in Jordan. International Journal of Economics
and Management Engineering, 4(7), 1702-1708.
Arikunto, S. (2008). Prosedur Penelitian Bisnis. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Delgado‐Ballester, E., & Munuera‐Alemán, J. L. (2001).
Brand trust in the context of consumer loyalty.
European Journal of marketing.
Elizar, C., Indrawati, R., & Syah, T. Y. R. (2020). Service
Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Trust, and
Customer Loyalty in Service of Paediatric Polyclinic
Over Private H Hospital of East Jakarta, Indonesia.
Journal of Multidisciplinary Academic, 4(2), 105-111.
Ferinnadewi, Erna and Djati ,SP. (2004). Effort to Achieve
Consumer Loyalty Human Resources Perspective.
Journal of Managament and Enterpreneurship. Vol. 6,
No. 1, 15 – 26.
Hidayat, R., & Anasis, N. S. (2020, August). Analysis of E-
Service Quality on Website E-Commerce on E-
Customer Satisfaction. In First International
Conference on Applied Science and Technology (iCAST
2018) (pp. 90-94). Atlantis Press.
Erne, R. (2022). Lean Project Management-How to Apply
Lean Thinking to Project Management. Springer
Nature.
Lovelock, C. H., & Wright, L. K. (2007). Manajemen
pemasaran jasa. Jakarta: Indeks.
Morgan, R. M., & Hunt, S. D. (1994). The commitment-
trust theory of relationship marketing. Journal of
marketing, 58(3), 20-38.
Nguyen, N., Leclerc, A., & LeBlanc, G. (2013). The
mediating role of customer trust on customer loyalty.
Pakurár, M., Haddad, H., Nagy, J., Popp, J., & Oláh, J.
(2019). The service quality dimensions that affect
customer satisfaction in the Jordanian banking sector.
Sustainability, 11(4), 1113.
Palilati, A. (2007). Pengaruh nilai pelanggan kepuasan
terhadap loyalitas nasabah tabungan perbankan di
Sulawesi Selatan. Jurnal manajemen dan
kewirausahaan, 9(1), 73-81.
Pellokila, I. R., Bire, R. B., & Riwu, L. (2021, April).
Analysis of Service Quality with Dematel Model. In
International Conference on Applied Science and
Technology on Social Science (ICAST-SS 2020) (pp.
109-113). Atlantis Press.
Putra, I. P. K., Hudayah, S., & Achmad, G. N. (2020). The
Effect of Customer Value and Customer Trust on
Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty PT Samator Gas
Industri Samarinda Seberang. International Journal of
Economics, Business and Accounting Research
(IJEBAR), 4(02).
Service Quality and Its Relation to Customer Trust and Loyalty
147
