
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
Yibing Tang
School of Public Administration and Media, Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Algorithm, Chinese Youth Group, Privacy Management, The Theory of Planned Behavior.
Abstract: In the age of algorithm, people can receive the information they are interested in more and more quickly.
Although algorithm recommendation brings convenience to people and reduces time cost, some platforms
collect users' personal information without the users realizing it. The purpose of these platforms to collect
user information is to more directly and accurately understand the user's content preferences. However, this
approach brings a great threat to users' privacy and security. In this case, people pay more and more attention
to privacy management. This paper is based on the above background and the Chinese youth’s privacy
management in the age of algorithms. The author conducted a quantitative study through a questionnaire
survey combining online and offline form in order to explore the influencing factors of privacy protection
attitude of Chinese youth groups. This study takes the Theory of Planned Behavior as the core and mainly in
discuss the attitude towards the behavior. The final conclusion is as follows: demographic variables and
privacy ownership affect the behavior beliefs; demographic variables, the knowledge of the result of privacy
invasion and no inconvenience has been caused by privacy management influence the outcome evaluations
together. Because behavior beliefs and outcome evaluations are two factors that affect the attitude towards
the behavior, the author conclude that privacy ownership, demographic variables, the knowledge of the result
of privacy invasion and no inconvenience has been caused by privacy management influence the attitude
together.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recommendation Algorithm is a double-edged sword,
it generally brings convenience for people, in the
meantime it makes many people fall into an
ambivalence which means that it will bring some
privacy problems. At this point, some people started
to protect their privacy by some defensive ways with
the purpose of “gaming the algos” or “confuse
algorithms” (Head, 2020), such as, giving the social
media some wrong answer or creating more than one
accounts on the same platform.
Many studies have been discussed how algorithm
impact people’s daily life and their reading behavior
from the perspective of elite and technical
determinism. The author focuses on the privacy
management in people's lives, and tries to figure out
how they deal with these privacy issues.
This article mainly discusses the attitude and
behavior towards algorithm privacy acquisition from
Chinese youth group and want to show the readers
how the new Chinese youth group fight against
algorithm and the “tipping point” (Gladwell, 2006) for
protecting their privacy by the defensive way. The
research method used in this article is questionnaire
survey and the questions based on the Theory of
Planned Behavior. Also, this study depicted the whole
picture of the new generation how they treat the
privacy acquisition in the age of algorithms and why
they protect their privacy by some defensive ways.
2 DEFINITION OF RELATED
CONCEPTS
2.1 “Youth”
There are four types of division criteria in the
definition of age including calendar age, physiological
age, psychological age and social age (Li, 2009),
which are respectively applicable to different fields
and situations.
In 1968, the United Nations Educational,
Scientific and Cultural Organization made three
definitions of youth in its report on youth. The first
point is the age group between 15 and 24 years old,
152
Tang, Y.
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0011732000003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 152-162
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
the second point is focus on the special educational,
social and family situations, those who did not start
school, did not start work or set up a family were
defined as youth. Third, youth is defined by their state
of mind. They are imaginative, courageous rather than
cowardly, adventurous rather than pleasure-seeking
(Uneso, 1968). Social age is not mentioned in this
report, which is an age standard based on the maturity
of social behavior.
In the social environment of China, physiological
age and psychological age more used for academic
research. And Social age is more used for the
formulation of laws and regulations. Therefore, the
calendar age which defines the lower limit and upper
limit of the age of youth is easier to distinguish and
common in use.
Considering that the sample of this study is
Chinese youth, the author decided to adopt the most
common definition of youth age range in China-15
~34 years old for the calendar age.
2.2 Personal Privacy
Warren et al. put forward the concept of personal
privacy for the first time and published in 1890
(Warren, 1890). Personal privacy is a unique right that
should be protected. In many years of academic
research on privacy, the definition of privacy is mainly
divided into two categories: one is based on value and
regards privacy as a commodity (Bennett, 1995); the
other is based on homology and regards privacy as a
state (including anonymity, concealment, reservation
and secrecy) or a control (Westin, 1968).
2.3 Algorithm and Privacy Disclosure
There are most platform will allow users to set some
permissions, such as microphone, location and so
forth, before using the algorithm platform. Therefore,
in this case, the legitimate privacy acquisition
confirmed by users is recognized, which does not
belong to the definition of privacy disclosure in this
study; while obtaining privacy without giving a
prompt belongs to the definition of privacy disclosure
in this study. Taking algorithms and privacy leaks as
an example, when a conversation is “listened” by a
mobile phone, then there is an advertisement for items
related to the conversation content in the shopping
software.
2.4 Theoretical Framework and
Hypothesis
• Theory of Planned Behavior
American psychologists M. Fishbein and I. Ajzen put
forward the Theory of Reasoned Action, in which
subjective norms and attitudes play a leading role in
the behavioral intention.
Later, Ajzen found that people's behavior is not
entirely voluntary, but under some kind of control.
Therefore, he expanded Theory of Reasoned Action
and added a new concept of "perceived behavior
control" to develop into a new model called Theory of
Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991).
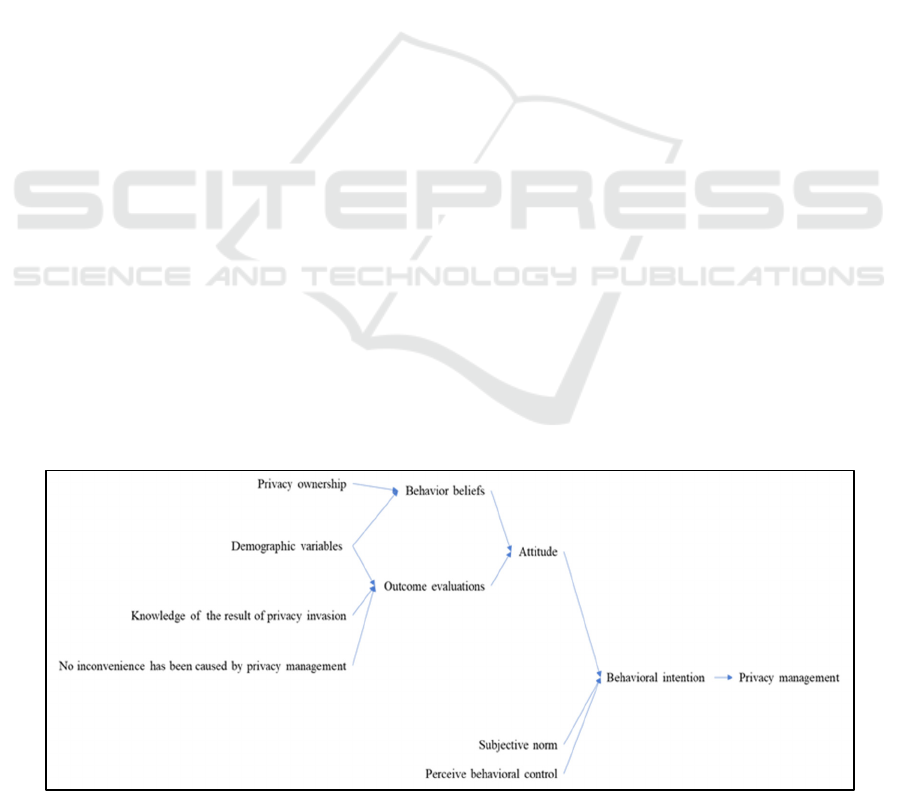
According to Theory of Planned Behavior (as
shown in figure 1), behavior intention is the
antecedent of actual usage. Moreover, attitude,
subjective norm and perceived behavioral control are
the three main variables that determine behavioral
intention. The more positive attitude, the greater
support from salient groups, the stronger perceived
behavioral control, the behavioral intention will be
greater. The detailed explanation of the three main
variables of the Theory of Planned Behavior is
following.
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework-Theory of Planned Behavior.
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
153

• Attitude toward The Behavior
Attitude is the core concept of the Theory of Planned
Behavior, and the attitude toward behavior is the
evaluation of the degree to which an individual likes
or dislikes to perform a specific behavior. Behavior
attitude includes two parts: one is behavior beliefs, the
other is outcome evaluation. The author infers that
demographic variables and privacy ownership affect
the behavior beliefs; demographic variables, the
knowledge of the result of privacy invasion and no
inconvenience has been caused by privacy
management influence the outcome evaluations
together. Because behavior beliefs and outcome
evaluations are two factors that affect the attitude
towards the behavior. So, the author thinks that
privacy ownership, demographic variables (include
age, gender, education and major), the knowledge of
the result of privacy invasion and no inconvenience
has been caused by privacy management influence the
attitude together. Therefore, the author makes the
following hypothesis:
H1. Demographic variables affect the attitude
toward privacy control.
H2. Privacy ownership affects the attitude toward
privacy control.
H3. The knowledge of the result of privacy
invasion affects the attitude toward privacy control.
H4. No inconvenience has been caused by privacy
management affects the attitude toward privacy
control.
2.4.1 Subject Norm
Subjective norm refers to the social pressure that
individuals feel about whether or not to carry out a
certain behavior. It reflects the influence of salient
individuals or groups on individual behavior decision.
Subjective norms are influenced by normative belief
and motivation to comply. "Normative belief" refers
to an individual's imagination of whether the salient
individuals or groups should perform a specific
behavior; “motivation to comply” is an individual's
intention to comply with the expectation of the salient
individuals or groups (Fishbein, 1977).
2.4.2 Perceived Behavior Control
Perceived behavioral control refers to a hinder from
individual's past experience and expectation, which
reflects an individual's perception of the factors that
promote or hinder executive behavior. When
individuals think that the more resources and
opportunities they have, the less obstacles they expect,
the stronger their perceptual behavior control over
their behavior. There are two ways of influencing
perceptual behavior control: one is that it has
motivational implications for behavior intention; the
other is that it can directly predict behavior.
3 METHODOLOGY
The research objects are the Chinese youth who had
used algorithm platform from 15 to 34 years old. This
study adopts the survey method of combining paper
questionnaire and network questionnaire in order to
obtain the real and effective opinions of the public.
Paper questionnaire is used for pilot study and
semi-structured interview before the formal
questionnaire, the pilot study sample is 20 randomly
selected friends around the author. After collecting the
paper questionnaire, the author interviewed them
about the difficulty of filling in the questionnaire, the
time spent and the suggestions of questionnaire
design. Then, the author uses SPSS to analyze the
reliability and validity of this study. A small number
of items affecting the reliability and validity of
variables were deleted, and finally a formal
questionnaire was formed.
Formal questionnaire survey was conducted
online, which is distributed and collected through
WeChat, Douban, Weibo and other forms by using the
Questionnaire Star online survey platform. It mainly
conducted from March 10, 2021 to March 15, 2021,
and a total of 107 questionnaires were collected. After
screening, a total of 94 valid questionnaires were
obtained, and the qualified rate was 87.9%.
The main screening methods are as follows. First,
the answer from the respondents who are not in the
sample spacing are deleted. Secondly, the filling time
is too short or too long was eliminated. Thirdly, the
author added the verification question in the
questionnaire design (for example,” Please choose the
second option”), and eliminated the questionnaires
with incorrect answers.
3.1 Measure
On the basis of the previous maturity scale and
research content, this study combined with the
situation of Chinese youth to make corresponding
modifications and form a questionnaire. (as shown in
Table 1).
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
154
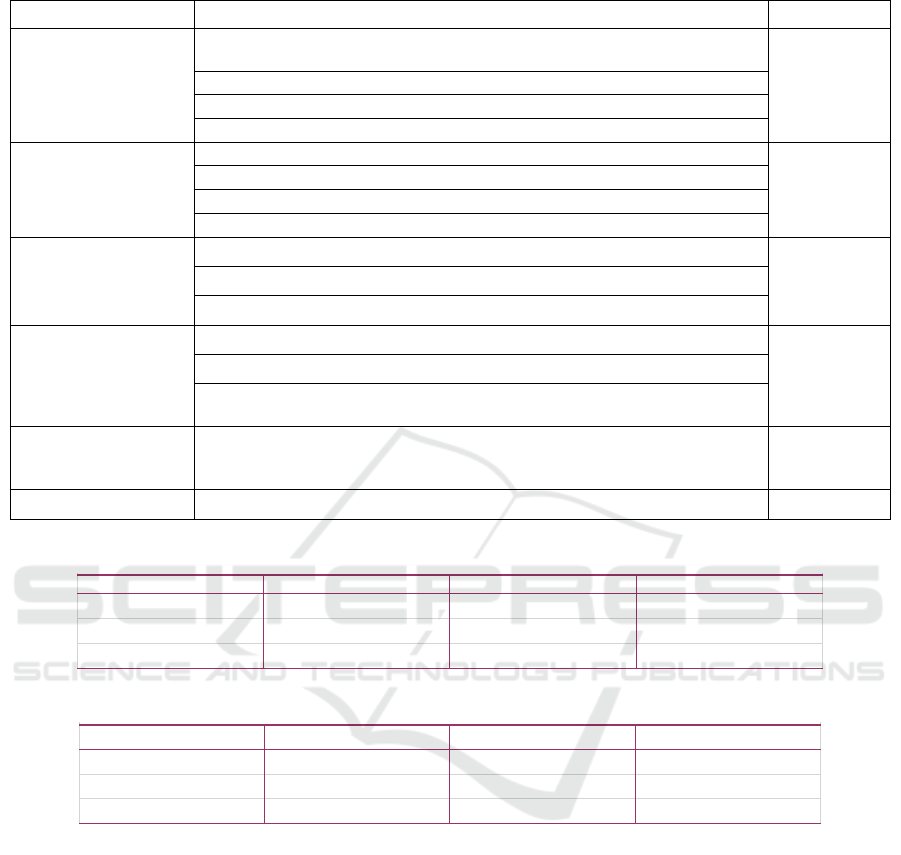
Table 1: The Variable and Indexes.
Variable Indexes References
Attitude I'm very sensitive when someone or an organization asks me to provide
p
ersonal information.
(Bansal, 2008)
I'm worry about the privacy leakage in the process of using the Internet.
I'm worry that using algorithmic recommendation will reveal my privacy.
I'm puzzle by I can't control how the software uses my information.
Demographic
variables
Age
Gender
Education
Major
Privacy ownership I always pay attention to the request permission when installing the platform.
I think I need privacy protection.
I pay more attention to privacy protection than most people.
Knowledge of the
result of privacy
invasion
I've experienced personal information being leaked. (Smith, 1996;
Smith, 2011)
I often hear some personal privacy has been leaked from the media reports.
There are relatives or friends who have been divulged of their personal
p
rivac
y
, resultin
g
in the disru
p
tion of their normal life.
No inconvenience has
been caused by
p
rivacy management
I've protected my privacy in some defensive ways.
Privacy protection in the platform hasn't caused inconvenience for me.
Table 2: Questionnaire results-"I'm worry about the privacy leakage in the process of using the Internet."
Table 3: Questionnaire results- "I'm worry that using algorithmic recommendation will reveal my privacy."
4 DATA ANALYSIS
4.1 Attitude
There are 96.8% of the research objects worry about
privacy leakage in the process of using the Internet
((as shown in Table 2), while the research objects who
worry about privacy leakage in the process of using
the recommendation algorithm are slightly less than
the former, but still as high as 92.6% ((as shown in
Table 3). And 72.3% of the respondents were worried
that they could not control how the algorithm platform
used their information (as shown in Table 4).
When some individuals or groups try to obtain
their personal information, 92.6% of the research
objects are sensitive to it and worry about their
privacy. Nevertheless, 7.4% of the people don't care
about it (as shown in Table 5).
According to the questionnaire answers of the
attitude part, the vast majority of people are worried
about privacy leakage (including online platform
access and offline access), but a few people are not
aware of the privacy problems that algorithms may
bring.
R
ate
P
ercentage
C
umu
l
at
i
ve percentage
YES 91 96.8 96.8
NO 3 3.2 100.0
Total 94 100.0
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
YES 87 92.6 92.6
NO 7 7.4 100.0
Total 94 100.0
o . wo y t at us g a go t c eco e dat o w evea y p vacy.
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
155

Table 4: Questionnaire results- "I'm puzzle by I can't control how the software uses my information."
Table 5: Questionnaire results- "I'm very sensitive when someone or an organization asks me to provide personal information."
Table 6: Questionnaire results-Age.
4.2 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Age
The age distribution of all the research object is shown
in Table 6, and the age of the subjects is widely
concentrated in 19-23 years old. In the study of the
relationship between the attitude towards privacy
management behavior and age, the author adopts the
linear regression method. The analysis results show
that in the table ANOVAa (as shown in Table 7), Sig
is 0.192b, which is much higher than 0.05 (in statistics,
SIG < 0.05 is generally considered as significant
coefficient test) In the Model summary (as shown in
Table 8), R is the coefficient of determination. The
result shows that the R of age and attitude is + 0.136a,
so the relationship between them is weak and positive.
In other words, the higher age of the research object,
the more obvious the attitude and attention of the
algorithm platform to obtain privacy information.
4.3 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Gender
The gender distribution of all the respondents is shown
in Table 9, of which 23.4% are male and 76.6% are
female. In the study of the relationship between the
attitude towards privacy management behavior and
gender, the author adopts the method of linear
regression. The analysis results show that in the table
ANOVAa (as shown in Table 10), Significance is
0.740b, which is much higher than 0.05. The result
shows that the correlation coefficient of gender and
attitude is + 0.035a (as shown in Table 11), so there is
almost no relationship between them.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
156
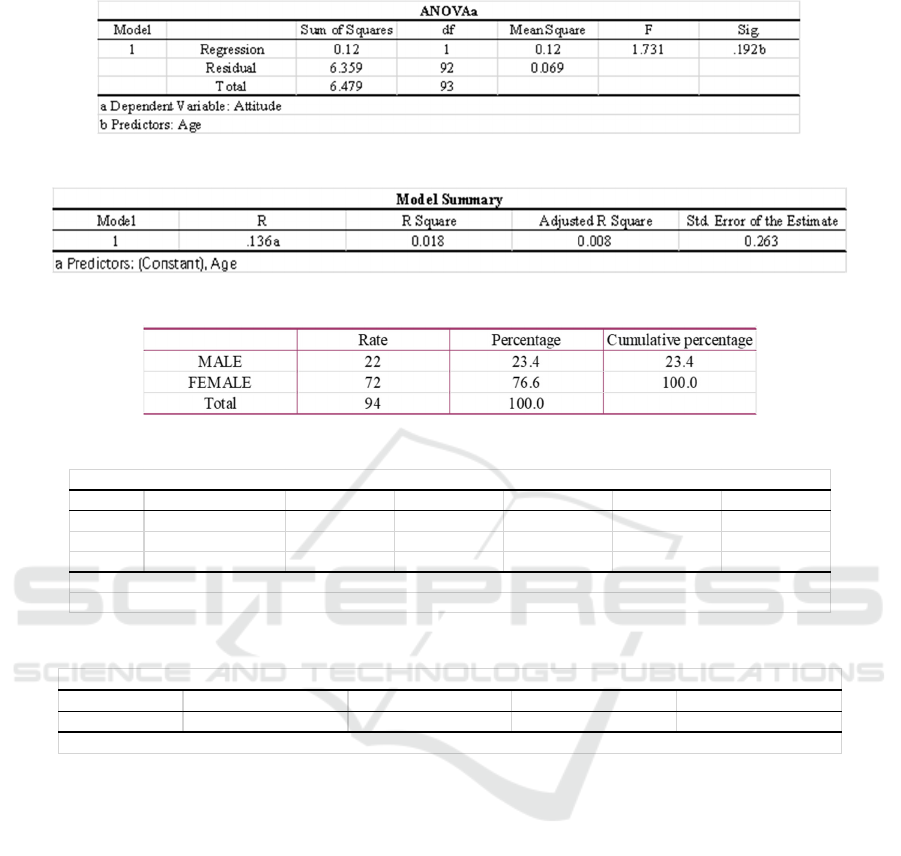
Table 7: Statistical Data- ANOVAa between attitude and age.
Table 8: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and age.
Table 9: Questionnaire results-Gender.
Table 10: Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and gender.
Table 11: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and gender.
4.4 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Education
The education of all respondents is shown in Table 12,
most of which are undergraduate degrees. In the study
of the relationship between the attitude towards
privacy management behavior and education, the
author adopts the method of linear regression. The
analysis results show that in the ANOVAa (as shown
in Table 13), Sig is 0.210, which is much higher than
0.05. In the model summary, the correlation
coefficient of education and attitude is + 0.131a (as
shown in Table 14), so the relationship between them
is weak and positive. That is to say, the higher
education degree of the research object, the more
obvious the attitude and attention of the algorithm
platform to obtain privacy information.
4.5 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Major
The majors of all the respondents are shown in Table
15, among which management, mathematics and
literature account for the highest proportion. In the
study of the relationship between the attitude towards
privacy management behavior and majors, the author
divides the 13 kinds of majors commonly used in
Chinese universities into two groups base on the level
of logicality, and adopts the linear regression method.
The analysis results show that in ANOVAa (as shown
in Table 16), Sig is 0.62b, which is higher than 0.05.
In the model summary, R of the major and attitude is
+ 0.193a (as shown in Table 17), so the relationship
between them is weak and positive. That is to say, the
higher logicality major they study, the more obvious
the attitude and attention of the algorithm platform to
obtain privacy information.
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.008 1 0.008 0.11 .740b
Residual 6.471 92 0.07
Total 6.479 93
b Predictors: (Constant), Gender
ANOVAa
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate
1 .035a 0.001 -0.01 0.265
Model Summary
a Predictors: (Constant), Gender
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
157
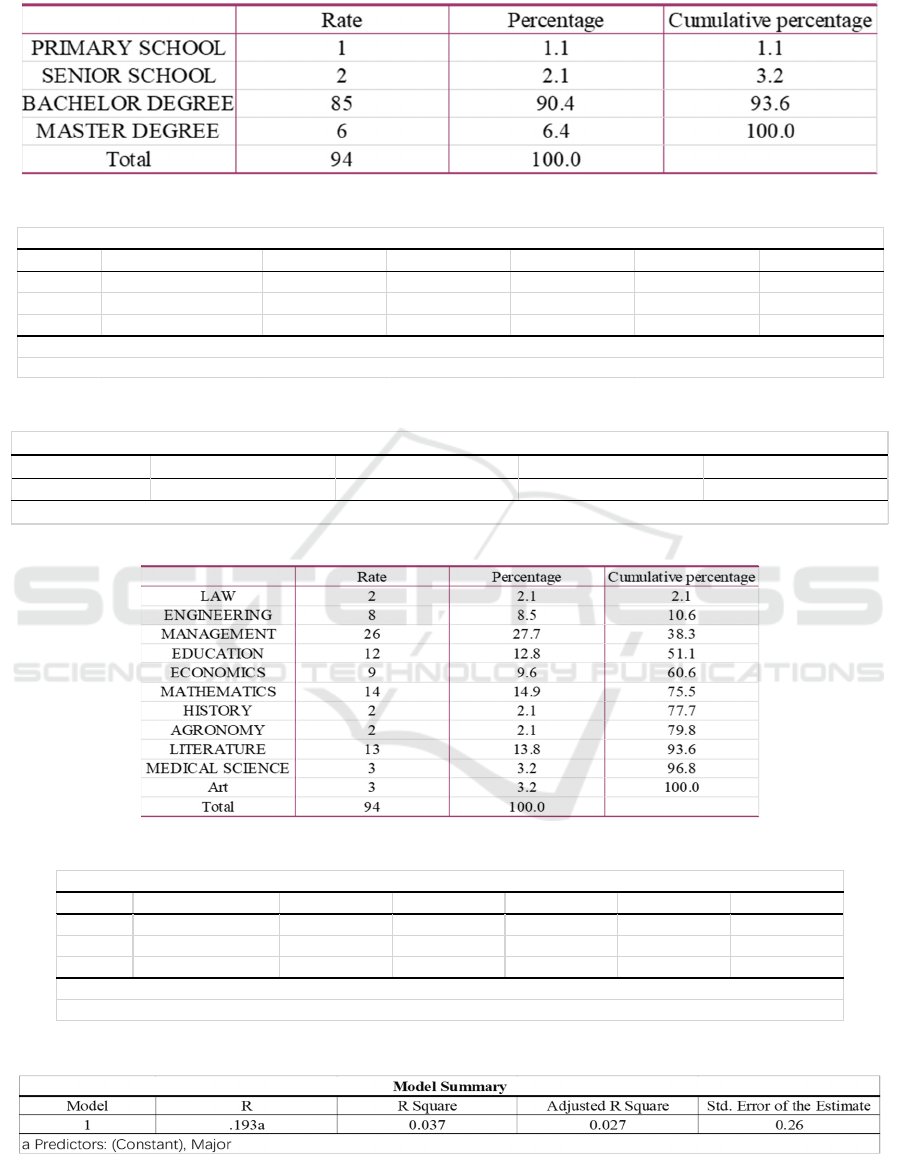
Table 12: Questionnaire results-Education.
Table 13: Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and education.
Table 14: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and education.
Table 15: Questionnaire results-Major.
Table 16: Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and major.
Table 17: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and major.
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.11 1 0.11 1.595 .210b
Residual 6.368 92 0.069
Total 6.479 93
b Predictors: (Constant), Education
ANOVAa
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate
1 .131a 0.017 0.006 0.263
Model Summary
a Predictors: (Constant), Education
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.242 1 0.242 3.572 .062b
Residual 6.237 92 0.068
Total 6.479 93
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
b Predictors: (Constant), Major
ANOVAa
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
158
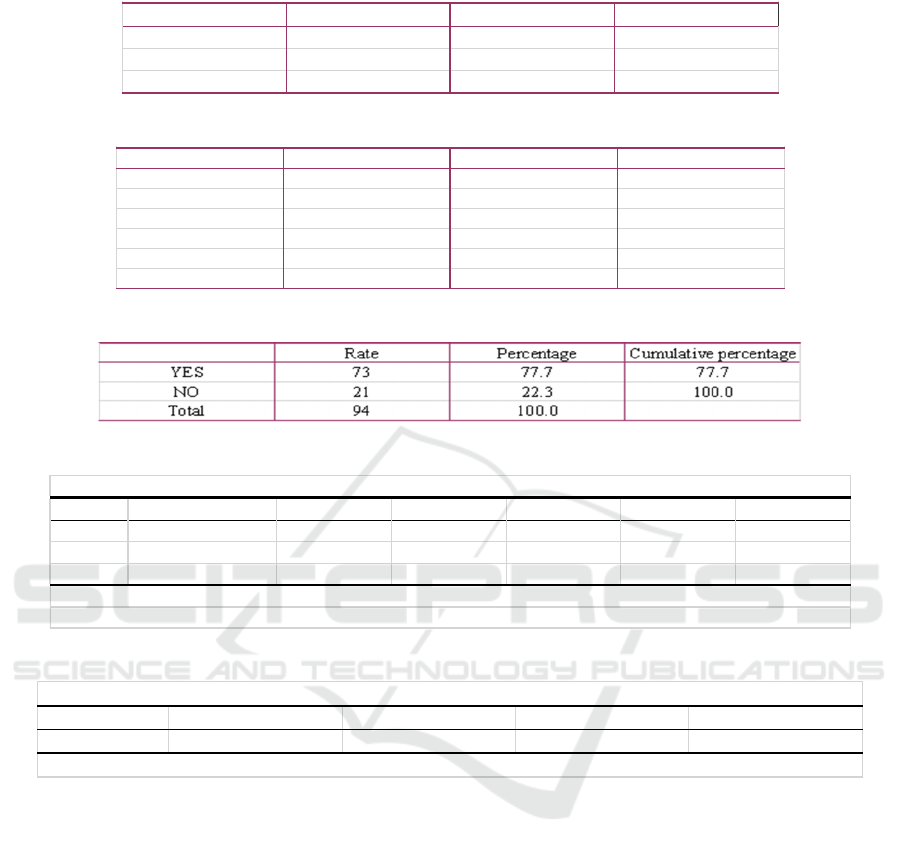
Table 18: Questionnaire results- "I always pay attention to the request permission when installing the platform."
Table 19: Questionnaire results- "I think I need privacy protection."
Table 20: Questionnaire results- "I pay more attention to privacy protection than most people."
Table 21: Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and privacy ownership.
Table 22: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and privacy ownership.
4.6 Privacy Ownership
According to the survey results of the privacy
ownership, 95.7% of the respondents think they need
privacy protection (as shown in Table 19), and far
more than half of the respondents think they pay more
attention to privacy protection (as shown in Table 20)
than others which means that they agree with their
right of privacy. At the same time, 92.6% of the
subjects had pay attention to the setting of platform
permissions (as shown in Table 18), which means that
the agreement of their right to control privacy.
The above research results show that most people
recognize their privacy ownership when using the
algorithm platform, but a large number of people think
that they pay more attention to privacy protection than
others, which means that they are ambitious about
their privacy management behavior, and their
understanding is not comprehensive enough.
4.7 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Privacy Ownership
In the study of the relationship between the attitude
toward privacy management and privacy ownership,
the author uses linear regression method to analyze.
The results showed that in the analysis of variance (as
shown in Table 21), SIG was 0.00b, lower than 0.05.
In Model Summary, the R value of privacy and
attitude is + 0.370a (as shown in Table 22), and the
relationship between them is positive. In other words,
the more Chinese youth have the right to privacy, the
more obvious the attitude of the algorithm platform to
obtain private information.
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
YES 87 92.6 92.6
NO 7 7.4 100.0
Total 94 100.0
Form9.
ypy q p g p
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
VERY DISAGREE 0 0.0 0.0
DISAGREE 1 1.1 1.1
NO NECESSARILY 3 3.2 4.3
AGREE 25 26.6 30.9
VERY AGREE 65 69.1 100.0
Total 94 100.0
pyp
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.887 1 0.887 14.597 .000b
Residual 5.592 92 0.061
Total 6.479 93
ANOVAa
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
b Predictors: (Constant), Privacy ownership
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate
1 .370a 0.137 0.128 0.247
Model Summary
a Predictors: (Constant), Privacy ownership
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
159
4.8 Knowledge of The Result of
Privacy Invasion
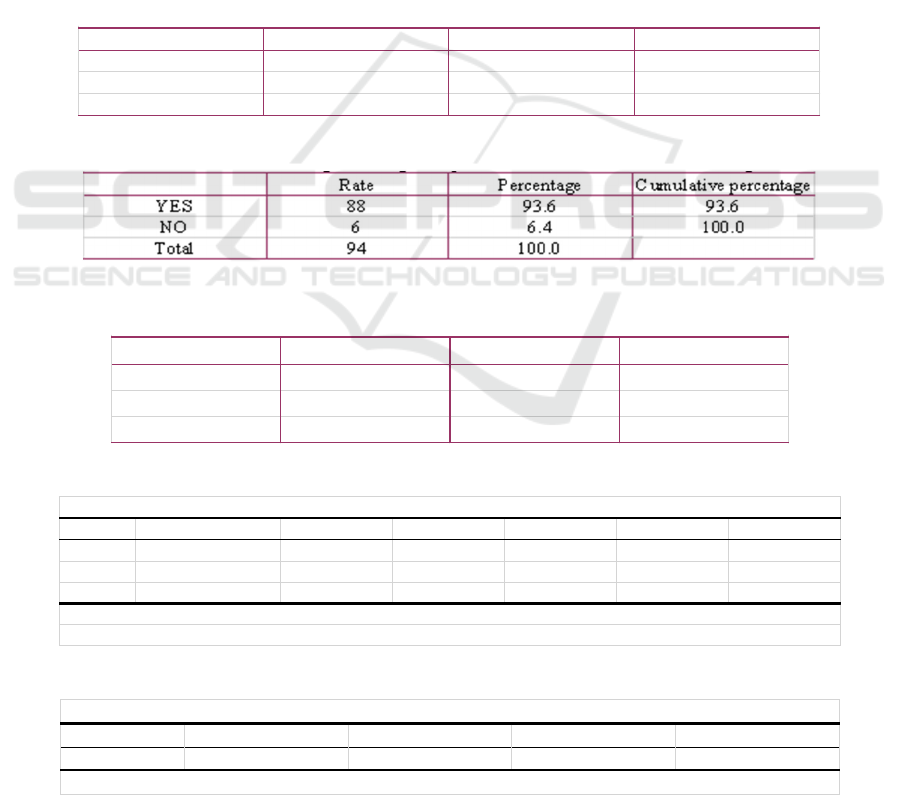
This part mainly focuses on the source and
understanding of privacy disclosure. There are more
than 70% of the subjects who have been experienced
the privacy invasion (as shown in Table 23). At the
same time, there are only 39.4% of them heard about
the situation and consequences of privacy leakage
from their relatives or friends (as shown in Table 25).
Combined with the results of Table 23, it can be
inferred that the topic of privacy leakage is rarely
mentioned among relatives or friends. In addition,
93.6% of the subjects often hear or see the news about
personal privacy disclosure in the media (as shown in
Table 24), which brings great convenience to the
dissemination of knowledge about privacy disclosure.
4.9 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Knowledge of The Result of
Privacy Invasion
In the study of the relationship between attitude and
the knowledge of the result of privacy invasion, the
author uses linear regression method to analyze. The
results show that sig is 0.379b (as shown in Table 26),
which is much higher than 0.05b. In the model
summary, the R value of privacy and attitude is +
0.092a (as shown in Table 27), and the relationship
between them is weakly positive. In other words, the
more Chinese youth have knowledge of the result of
privacy invasion, the more obvious their attitude
towards the algorithm platform to obtain private
information.
Table 23: Questionnaire results- "I've experienced personal information being leaked."
Table 24: Questionnaire results- "I often hear some personal privacy has been leaked from the media reports."
Table 25: Questionnaire results- "There are relatives or friends who have been divulged of their personal privacy, resulting in
the disruption of their normal life."
Table 26: Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and Knowledge of the result of privacy invasion.
Table 27: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and Knowledge of the result of privacy invasion.
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
YES 66 70.2 70.2
NO 28 29.8 100.0
Total 94 100.0
pp g
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
YES 37 39.4 39.4
NO 57 60.6 100.0
Total 94 100.0
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.054 1 0.054 0.78 .379b
Residual 6.424 92 0.07
Total 6.479 93
ANOVAa
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
b Predictors: (Constant), Knowledge of the result of privacy invasion
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate
1 .092a 0.008 -0.002 0.264
Model Summary
a Predictors: (Constant), Knowledge of the result of privacy invasion
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
160
4.10 No Inconvenience Has Been Caused
by Privacy Management
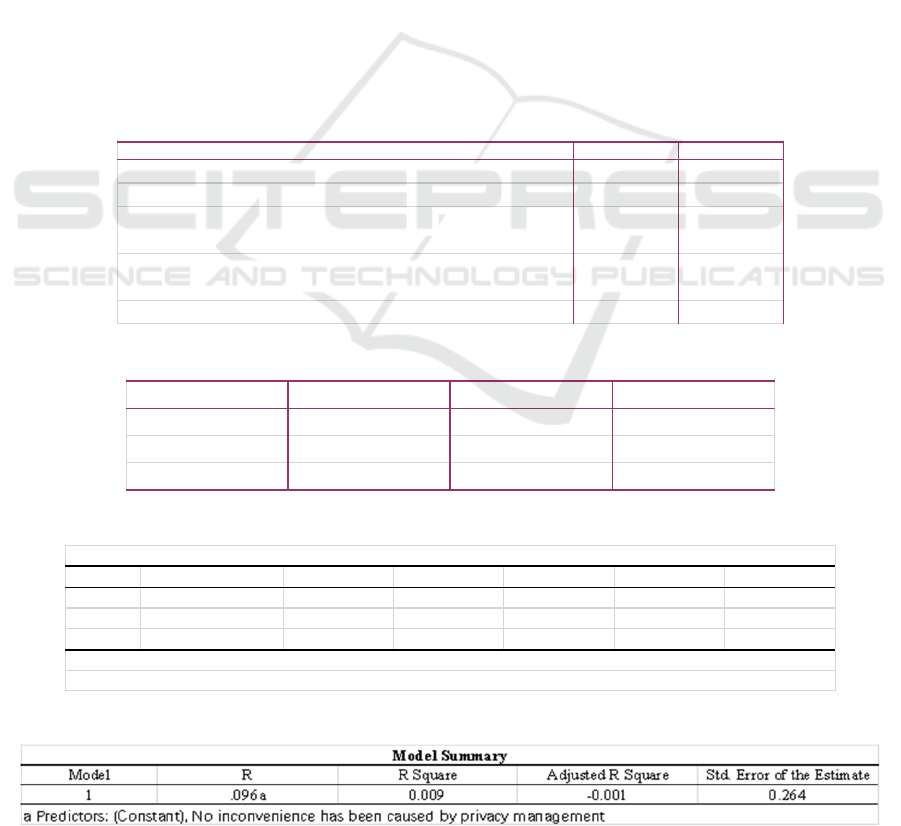
In all the questionnaire results, 72.3% people think
that privacy management does not bring the
inconvenience (as shown in Table 29). In the specific
implementation process (as shown in Table 28),
85.1% of the research objects will protect their privacy
in the algorithm platform by turning off the
permission of microphone, location, etc., in addition,
79.8% of the research objects will also protect their
privacy through clean the Relevant software search or
viewing records regularly and open the traceless
browsing settings or use some special search tools.
Because this is a semi open question, which allows the
subjects to supplement the ways to protect privacy.
They also cover the camera with objects and use
different avatars and nicknames on different platform
to do their privacy management.
According to the above data, although 72.3% of
the people think that privacy management does not
bring inconvenience to themselves. In fact, even
though privacy management will bring some troubles
to the use of the platform, some of the research objects
will still do privacy management on the algorithm
platform.
4.11 The Relationship Between Attitude
and Inconvenience Has Been
Caused by Privacy Management
In the study of the relationship between attitude and
inconvenience has been caused by privacy
management, the author uses linear regression method
to analyze. The results show that sig is 0.355b (as
shown in Table 30), which is much higher than 0.05b.
In the model summary, the R value of privacy and
attitude is + 0.096a (as shown in Table 31), and the
relationship between them is weakly positive. That is
to say, the more Chinese young people think that
privacy management on the algorithm platform will
not bring inconvenience to them, the more obvious
their attitude towards obtaining privacy information
on the algorithm platform.
Table 28: Questionnaire results- "The defensive practices I have done for protected my privacy. "
Table 29: Questionnaire results-"Privacy protection in the platform hasn't caused inconvenience for me."
Table 30 Statistical Data-ANOVAa between attitude and inconvenience has been caused by privacy management.
Table 31: Statistical Data-Model Summary between attitude and inconvenience has been caused by privacy management.
R
ate
P
ercentage
Turn off the permission of microphone, location, etc. 80 85.1
Clean the relevant software search or viewing records regularly. 75 79.8
Open the traceless browsing settings or use some special search
tools.
75 79.8
Register more than one account on the same platform to avoid
binding all activities to a single identity.
24 25.5
The others 5 5.3
ppypy
Rate Percentage Cumulative percentage
YES 68 72.3 72.3
NO 26 27.7 100.0
Total 94 100.0
yp p
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 0.06 1 0.06 0.862 .355b
Residual 6.419 92 0.07
Total 6.479 93
ANOVAa
a Dependent Variable: Attitude
b Predictors: (Constant), No inconvenience has been caused by privacy management
Privacy Management of Chinese Youth in the Age of Algorithms
161

5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSION
The vast majority of Chinese youth are worried about
privacy leakage, but a few people are not aware of the
privacy problems that algorithms may bring.
Demographic variables affect the attitude toward
privacy control. The relationship between attitude and
age, attitude and education, attitude and major are
weak and positive. However, there is almost no
relationship between attitude and gender (It is
reasonable to think that the behavioral differences
brought by gender are mostly based on the differences
in education, social discipline and resources, rather
than physiological differences. Nowadays, because of
the increasingly equal gender, the impact of gender on
behavior is gradually weakening.)
Privacy ownership affects the attitude toward
privacy control. Most youth can recognize and use
their privacy ownership in the age of algorithms, but
they think their privacy management behavior
ambitiously and don’t understand enough.
The knowledge of the result of privacy invasion
affects the attitude toward privacy control. Most of the
young people have experienced privacy leakage. Most
of their knowledge about privacy leakage comes from
the media, but they seldom discuss this topic with their
relatives and friends.
No inconvenience has been caused by privacy
management affects the attitude toward privacy
control. Some youth think that the policy management
is inconvenience, but most of them still do the privacy
management on the algorithm platform.
For this study, the author think that there are
mainly the following limitations. First, the author did
not carry out the quota, the proportion of gender and
age is not consistent with the real proportion, resulting
in the relationship between them and attitude is not
obvious. Secondly, the author thinks that the influence
of education on the attitude towards privacy
management is false, and the essence of it is the
influence the combination of age and practical
experience. In the future research, the author hopes to
conduct a more specific and extensive qualitative
research on people's specific behavior of privacy
protection through interviews.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Thanks for the inspiration and help of Mr. Wei FANG
from the Communication Department of Beijing
Information Science and Technology University.
REFERENCES
A. J. Head, B. Fister, and M. MacMillan. Information
Literacy in the Age of Algorithms: Student Experiences
with News and Information, and the Need for Change.
Project Information Literacy, 2020.
A. F. Westin. Privacy and Freedom, New York: Atheneum,
1968.
B. Li, N. Li and J Li. Soul Medicine, 2009, pp.15-17.
C.J. Bennett. The political economy of privacy: A review
of the literature. Hackensack, NJ: Center for Social and
Legal Research, 1995.
G. Bansal, & F. Zahedi. The moderating influence of
privacy concern on the efficacy of privacy assurance
mechanisms for building trust: A multiple-context
investigation. ICIS 2008 Proceedings, 7.
H.J. Smith, S.J. Milberg, & S.J. Burke. Information
privacy: Measuring individuals' concerns about
organizational practices. MIS quarterly, 1996, 167-196.
H.J. Smith, T. Dinev, & H. Xu. Information privacy
research: an interdisciplinary review. MIS quarterly,
2011, 989-1015.
I, Ajzen. The theory of planned behavior. Organizational
Behavior and Human Decision Processes, vol. 50,
1991, pp. 179–211.
M. Fishbein and I. Ajzen. Belief, attitude, intention, and
behavior: An introduction to theory and research, 1977.
M. Gladwell. The tipping point: How little things can make
a big difference. Little, Brown, 2006, pp. 304.
S.D. Warren, L.D. Brandeis. The right to privacy. Harvard
Law Review, vol.4, 1890, pp. 193-220.
Uneso. Report on Youth. UNESCO 15C/65 rev, General
Conference. Paris. 1968, pp.3.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
162
