
Study on The Effect of Cause-Related Marketing Perception on
Customers' Out-of-Role Behavior Based on A Moderated Mediation
Model
Qing Zhou
*
School of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China
Keywords: Cause-Related Marketing Perception, Customers’ Out-of-Role Behavior, Brand Trust, Moral Identity.
Abstract:
Cause-related marketing, as a new marketing method, has attracted wide attention of scholars. A total of 156
Chinese adults were recruited in this study, and multiple regression equations were used to test the model.
Results suggested that cause-related marketing perception were related to customers’ out-of-role behavior.
Results also supported the mediating role of brand trust and the moderating role of moral identity. This study
reveals the significance of cause-related marketing for corporate.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cause-related marketing refers to the process in
which enterprises donate a certain amount of their
product sales revenue to specific nonprofit
organizations and use it to support related public
welfare undertakings. (Wang, 2019) Cause-related
marketing, as a type of corporate social responsibility,
has been widely concerned by the academic
community and the Chinese business community.
The customer's out-of-role behavior refers to the
enhancement behavior that is positive and beneficial
to the organization's role, and the behavior that is not
within the scope of responsibility but outside the
scope of work that is conducive to the development
of the organization, but it has a significant positive
impact on the organization. Customers’ out-of-role
behavior is of great significance to enterprises.
Previous studies (Zhao, 2007) have shown that
consumers, as the main body of modern marketing
concepts, influence how enterprises implement
cause-cause marketing and its effect. However, there
are few studies on how cause-related marketing
perception affects consumer behavior, especially
customer's out-of-role behavior. Therefore, we study
the relationship between enterprises’ perception of
good cause marketing and customers’ out-of-role
behavior, and clarify the relationship between the
two.
2 HYPOTHESIS
2.1 Cause-Related Marketing
Perception and Customers'
Out-of-Role Behavior
In the practice of cause-cause marketing, enterprises
can choose to donate a specific amount or a certain
proportion of their product sales revenue to public
welfare undertakings. Cause marketing in the form of
a percentage donation produces better results than in
the absolute form, because the abstract amount of
giving leads consumers to overestimate the level of
corporate giving. This study speculates that cause-
cause marketing can lead to a series of positive out-of-
role behaviors of customers.
Hypothesis 1: Cause-related marketing perception
has a significant positive impact on customers' out-of-
role behaviors.
2.2 Mediating Role of Brand Trust
Brand trust reveals consumers' evaluation of the
products provided by the enterprise. It is believed that
customers' trust in brands and enterprises promotes the
formation of value perception. Another view holds
that the higher consumers' perception of brand value,
the higher their trust in the brand will be. Brand trust
reflects a kind of reliability, which means that a brand
should have enough strength to influence consumer
demand. When analyzing the influence of customer's
Zhou, Q.
Study on The Effect of Cause-Related Marketing Perception on Customers’ Out-of-Role Behavior Based on A Moderated Mediation Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0011734200003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 251-256
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
251

perception of cause marketing on customer's out-of-
role behavior, taking brand trust as a mediating
variable can help us reveal the influence of cause
marketing on customer's out-of-role behavior more
accurately.
Hypothesis 2: Brand trust plays a mediating role
between cause-related marketing perception and
customer's out-of-role behavior.
2.3 The Moderating Effect of Moral
Identity
Moral identity refers to customers' perception of the
relationship between an enterprise and the public
welfare it supports in cause-cause marketing. Moral
identity is through a series of individual moral
qualities associated with moral behavior combining
self-concept, and under the constant collaboration
between social norms, and own a stable moral
qualities, its essence is a kind of self adjusting
mechanism, request individual behavior consistent
with the social moral quality, thus enabling individual
prosocial behavior. According to social cognitive
theory, moral identity is a key psychological
mechanism for transforming moral cognition into
moral behavior, which is activated by external
situational factors. Individuals with different moral
identities will have different degrees of activation,
which will affect other psychological factors of
individuals and show different individual behavioral
intentions. In conclusion, we predict that moral
identity positively moderates the relationship between
customer perception of cause-related marketing and
brand trust, and further influences customer's out-of-
role behavior through the mediating role of brand
trust.
Hypothesis 3: Moral identity plays a moderating
role between Cause-related marketing perception and
brand trust. The higher the moral identity is, the higher
the level of brand trust will be triggered by the
perceived cause-related marketing, which will have a
positive impact on the customers’ out-of-role
behavior.
Figure 1:Research Model.
3 METHOD
3.1 Participants
Based on the form of online questionnaires, 156
questionnaires were collected, and 140 valid
questionnaires were left after eliminating invalid
samples with many missing values and obvious
regularity, with an effective rate of 89.74%.
According to the characteristics of the sample, males
accounted for 28.6%, and the sample age was
concentrated between 18 and 29 years old, accounting
for 87.1%. In terms of education level, only 0.7% had
a junior high school degree or below, 2.9% had a
senior high school degree, 3.6% had a junior college
degree, 4.3% had a graduate degree or above, and
88.6% had a undergraduate degree. In terms of
monthly consumption expenditure, the proportion of
less than 1000 yuan is 8.6%, the proportion of 1000-
2000 yuan is 57.9%, the proportion of 2000-3000
yuan is 15.7%, the proportion of 3000-4000 yuan is
5.7%, and the proportion of above 4000 yuan is
12.1%.
3.2 Measures
The measurement of cause-related marketing
perception is measured by the scale developed in this
study, which is divided into two dimensions, namely,
self-interested perception and altruistic perception.
Each dimension has three items, and the total score is
obtained by the reverse scoring of self-interested
motivation and the average of altruistic motivation.
On a five-point Likert scale, "1" means "strongly
disagree" and "5" means "strongly agree." For the
self-interested subscale, items such as "I think the
enterprise carries out this activity solely for the
purpose of enhancing its brand image", and for the
altruistic subscale, items such as "I think the
enterprise carries out this activity for the sincere
purpose of promoting the development of social
public welfare undertakings". In this study, the
internal consistency coefficients of the egoistic and
altruistic subscales were 0.824 and 0.872,
respectively.
Brand trust is measured directly by the phrase
"more trust in the brand". The 5-point Likert scoring
method was used.
Customer's out-of-role behavior scale (Lv, 2012)
compiled by Lv Ying and Wei Haiying is used to
measure the customer's out-of-role behavior, which
contains 14 questions and is divided into three
dimensions: "customer voice behavior", "customer
recommendation" and "customer help". Items on the
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
252
customer behavior subscale are as follows: "I will
remind relevant personnel of some inappropriate
things in the store, such as out of stock"; items on the
customer recommendation subscale are as follows: "I
will recommend the store to my relatives and
friends"; and items on customer help are as follows:
"I will help customers in difficulty". In this study, the
internal consistency coefficients of the three
subscales were 0.858, 0.780 and 0.880, respectively,
indicating that the internal consistency of the
measurement tool was high.
The measurement of moral identity was adjusted
on the existing moral identity scale and reduced to 5
items. Some qualities is listed, items such as “it is
important to me to have these qualities”. The
reliability analysis shows that the internal consistency
coefficient of moral identity is 0.725, and the
reliability is good.
3.3 Data Collection and Processing
Data was collected online. The study followed the
principle of informed consent, and the concept and
explanation of "cause-related marketing" were given
at the top of the questionnaire. In this paper, SPSS
software was used to analyze the data characteristics,
multiple regression analysis method was used to
verify the relationship between variables proposed by
the hypothesis.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Common Method Deviation Test
The results may be affected by the common method
bias because the study variables were all self-reported
and filled out in a fixed period of time. Harman single
factor test is used to judge the common method bias
problem. The variance interpretation percentage of
the first common factor is 39.91%, less than 40%,
which can be considered that there is no serious
common method bias.
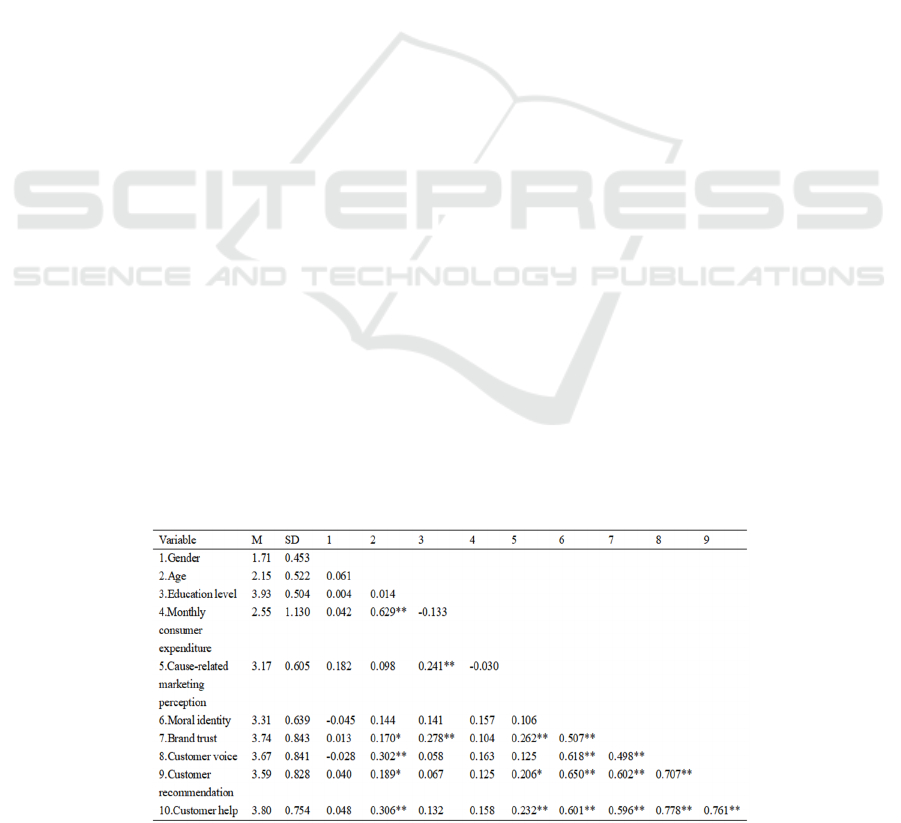
4.2 Correlation Analysis
The table shows the mean (M), standard deviation
(SD) and correlation coefficient of each variable.
According to the results in the table, cause-related
marketing perception is significantly positively
correlated with brand trust (r=0.262, p <0.01), but has
no significant correlation with customer voice (R
=0.125, p >0.05), while customer recommendation
and customer help are significantly positively
correlated (R =0.206, p <0.05; R =0.232, p <0.01);
Brand trust was positively correlated with customer
voice behavior, customer recommendation and
customer help (r=0.498, p <0.01; R = 0.602, p < 0.01;
R =0.596, p <0.01).
4.3 Hierarchical Regression Analysis
In this paper, hierarchical regression model is used to
test assumptions. Firstly, the mediating role of brand
trust is tested. M2 and M5 shows that cause-related
marketing perception had a significant impact on
brand trust (β=0.204, p <0.05) and customer voice
(β=0.137, p <0.05), while M6 showed that after brand
trust was included in M6, cause-related marketing
perception had a small impact on customer voice (β=-
0.0001, p >0.05), and the influence of brand trust on
customer voice was particularly significant (β=0.484,
p <0.01). Therefore, brand trust plays a full mediating
role between cause-related marketing perception and
customer voice. In addition, with the Bootstrap,
consistent results were obtained (95% confidence
interval [0.095, 0.401] of the mediating effect did not
include 0). Similarly, brand trust plays a full
Table 1: Mean, Standard Deviation and Correlation Coefficient of Variables.
Study on The Effect of Cause-Related Marketing Perception on Customers’ Out-of-Role Behavior Based on A Moderated Mediation Model
253
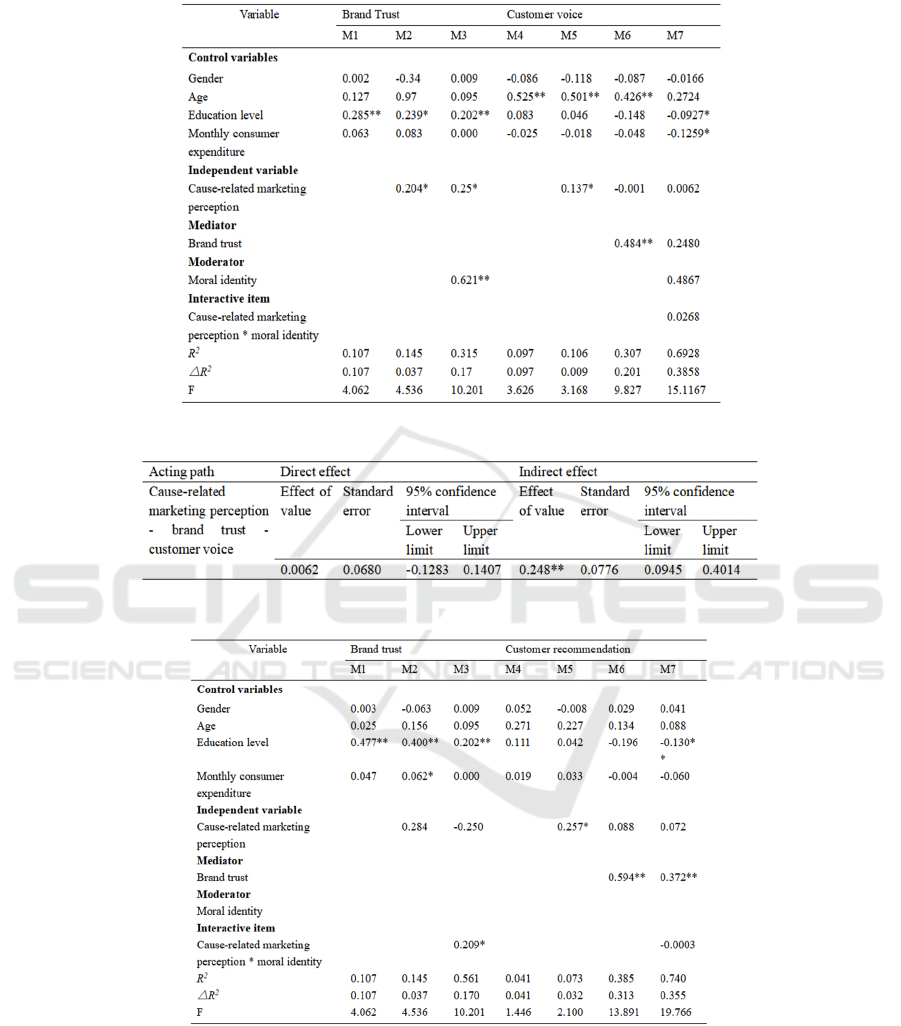
Table 2: Results of Regression Analysis 1.
Table 3: Results of Mediating Effect Analysis 1.
Table 4: Results of Regression Analysis 2.
mediating role between cause-related marketing
perception and customer recommendation, customer
help.
Secondly, the moderating effect of moral identity
is examined. As shown in Table 2, the product
coefficient (β=0.25, p <0.05) of cause-related
marketing perception and moral identity in M3 was
significant. In addition, as shown in Table 8, the
moderating effect was significant at both high and
low levels of moral identity (95% confidence interval
excluding 0).
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
254

Table 5: Results of Mediating Effect Analysis 2.
Table 6: Results of Regression Analysis 3.
Table 7: Results of Mediating Effect Analysis 3.
Table 8: Results of Regulatory Effect Analysis.
5 CONCLUSION AND
DISCUSSION
Based on the above data analysis, we find that cause-
related marketing perception can fully mediate the
role of brand trust in influencing customers' out-of-
role behaviors. Meanwhile, the impact of cause-
related marketing perception on brand trust is
moderated by customers' moral identity. In other
words, Moral identity moderates the first half of the
path of "cause-related marketing perception - brand
trust - customer's out-of-role behavior". Our
hypothesis test was validated.
5.1 Theoretical Significance
Cause-related marketing perception has a significant
positive impact on customers' out-of-role behaviors
through brand trust. As a new marketing method, the
Study on The Effect of Cause-Related Marketing Perception on Customers’ Out-of-Role Behavior Based on A Moderated Mediation Model
255

relationship between corporate cause-induced
marketing perception and customers' out-of-role
behaviors has not been paid much attention by
scholars. This study responds to the call to strengthen
the research on cause-related marketing perception
and customers' out-of-role behavior in the future.
5.2 Practical Significance
Study found that cause-related marketing perception
has a positive effect on customers’ out-of-role
behavior, so the enterprise should pay attention to
launch the marketing of the good karma, cooperate
with public welfare institutions to take more social
responsibility. It will not only improve the customers’
perception of enterprise, enhance the customers’ trust
and loyalty, it will also encourage the growth of
customers’ out-of role behavior, including customer
help to create a good marketing environment for
enterprises, customer voice for enterprises to provide
more constructive suggestions, customer
recommendation for enterprises to bring more
customers and thus bring higher profits. By revealing
the positive impact of cause-related marketing
perception on brand trust and customers’ out-of-role
behavior, this paper calls on enterprises to carry out
cause-related marketing, encourage more enterprises
to take social responsibility, and realize the
coordination and consistency of corporate goals and
social goals.
5.3 Limitations
Firstly, the number of questionnaires collected in this
study is small, the results are prone to deviation, and
the data is not representative. More samples can be
collected in future studies to continue to verify the
correctness of the conclusions in this paper. Secondly,
the research method adopted in this survey is
questionnaire, and the source of the survey design is
all self-assessment results, and it has strong relevance
to the context of the questionnaire items, which is
highly subjective. In addition, all the data are self-
reported and collected at the same time. Therefore,
common method differences may be a problem, and
causal inference is not guaranteed. In order to avoid
common method bias, future research should
consider using other people's data (e.g., family and
friends' evaluation of their customers' external
behavior, i.e. whether or not they recommend
companies that implement cause-cause marketing to
them) as external validation, rather than relying solely
on the sample's own self-assessment.
REFERENCES
Lv Ying, Wei Haiying. Journal of Beijing technology and
business university (social science edition), 2012,
27(02): 49-54.
Mora Elísabet, Vila Lopez Natalia, Küster Boluda Inés.
Segmenting the audience of a cause-related marketing
viral campaign[J]. International Journal of Information
Management,2021(prepublish):
Miranda Mafalda M., Silva Susana Costa e, Duarte Paulo,
GlaserSegura Daniel. Cause-Related Marketing: Do
Managers Understand and Use This Tool? [J].
Management & Marketing. Challenges for the
Knowledge Society,2020,15(4):
Shih Tsungjen, Wang Shaojung Sharon. Cause-Related
Marketing in the Telecom Sector: Understanding the
Dynamics among Environmental Values, Cause-Brand
Fit, and Product Type[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(9):
Thomas Sujo, Jadeja Ashwin. Psychological antecedents of
consumer trust in CRM campaigns and donation
intentions: The moderating role of creativity[J]. Journal
of Retailing and Consumer Services,2021,61:
Wang Jinpeng, Wang Junqing, Zhao Zhen, Shang Yanxu,
Wu Xiaojing. Journal of Marketing Research,
2019(34): 106-107.
Yucel-Aybat Ozge, Hsieh Meng-Hua. Consumer mindsets
matter: Benefit framing and firm–cause fit in the
persuasiveness of cause-related marketing campaigns
[J]. Journal of Business Research,2021,129:
Zhang Anran, Saleme Pamela, Pang Bo, Durl James, Xu
Zhengliang. A Systematic Review of Experimental
Studies Investigating the Effect of Cause-Related
Marketing on Consumer Purchase Intention[J].
Sustainability, 2020, 12(22)
Zhao Baochun, Tian Zhilong. Journal of Marketing
Economics, 2007, 021(002):70-73.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
256
