
Organizational Green Climate and Employee Green Behavior: A
Moderated Mediation Model
Xuedong Liang
1
, Biaoshuai Li
1
, Qunxi Gong
1, 2
, Sipan Li
1
and Gengxuan Guo
1*
1
Business School, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
2
Sichuan Haina Rendong Science and Technology Co. Ltd, Chengdu, China
Keywords:
Green Climate, Employee Green Behavior, Green HRM, Autonomous Motivation.
Abstract:
As the sustainable development of the environment continues to deepen and refine today, the green behavior
of employees is increasingly being paid attention to. In order to clarify the relationship between organizational
green climate and employee green behavior, we construct a theoretical model, using green climate as the
antecedent variable, green HRM as the moderating variable, and employee autonomy as the mediating
variable, then validates the model by empirical analysis. We obtained conclusion that 1) green climate is
positively related to firm employee green behavior; 2) green climate is positively related to employees’
autonomy motivation; 3) employees’ autonomy motivation mediates the relationship between green climate
and employee green behavior; 4) green HRM positively moderates the effect of green climate on autonomy
motivation and the mediating role of autonomy motivation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, building an environmental and
sustainable society has turn into the main trend, the
green behaviors of organizations and individuals has
gradually become the focus of society. Employees, as
participants and implementers of the enterprises’
production and related pro-environmental policies
(Peng, 2019), their workplace green behaviors have
the significance of interacting with the organization
to improve the company’s environmental
performance from the perspective of organizational
management; and it also has the effect of constructing
environmentally friendly values at the individual
level from the perspective of environmental
psychology.
Given the important value of employee green
behavior, scholars have explored the factors that
influence employee green behavior. The existing
literature has explored the influence of personal
factors (personality traits, emotions, etc.) and
leadership style, such as the role of responsibility
(Kim, 2017) and green transformational leadership
(Graves, 2013). However, the literature on effect of
green climate is still to be improved.
About green climate, existing research has
focused on its normative role, considering it influence
employees by forming a descriptive norm or
examining its impact on task-oriented green
behaviors (Norton, 2014). Few research discussed
about the role of autonomy in this context. In
addition, research on the effect mechanism between
green climate and green behavior of employees is
relatively scarce, so exploring the mediating role of
autonomous motivation between them is required
now.
Therefore, this study proposes a theoretical model
to describe the relation between green climate, and
green behavior, as well as the role of autonomous
motivation and green HRM. Through this study, we
hope to enrich the theoretical research in the field
related to employee green behavior and provide
insight into the practice of green management in
enterprises.
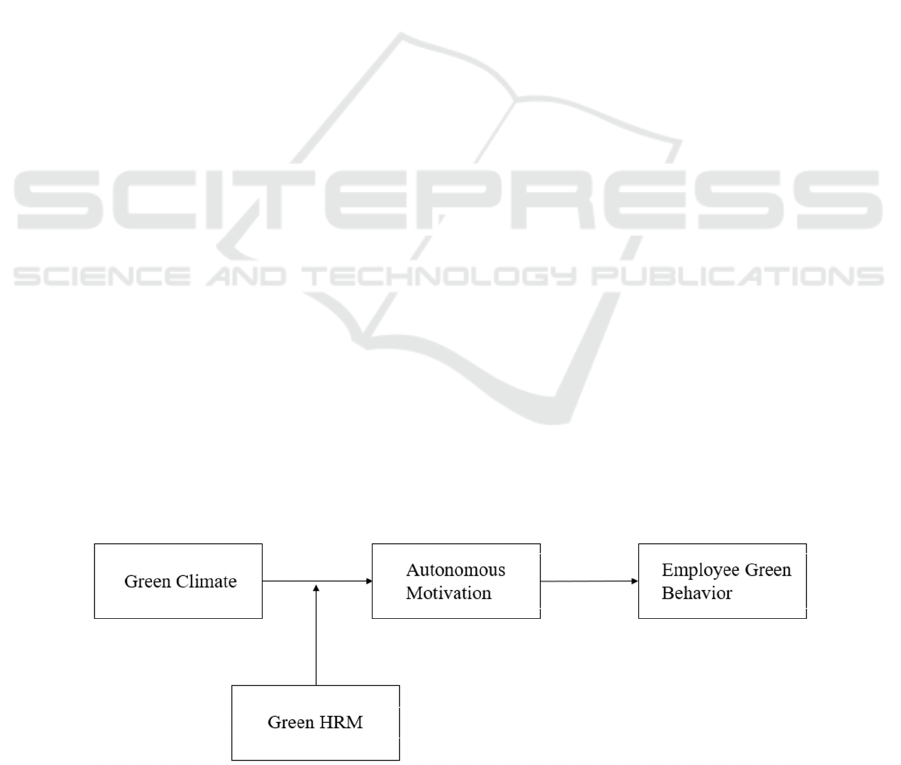
2 THEORY AND HYPOTHESIS
2.1 Impact of Green Climate on
Employee Green Behavior
Green climate refers to the organizational climate
created by a series of sustainability policies. Studies
have shown that work climate has a strong link to
280
Liang, X., Li, B., Gong, Q., Li, S. and Guo, G.
Organizational Green Climate and Employee Green Behavior: A Moderated Mediation Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0011734900003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 280-284
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
employees’ attitudes and behaviors. In this regard, the
presence of environmental protection factors in a
organization’s work climate is likely to impact
employees’ perceptions and behaviors of
environment protection. The green climate in the
workplace consists of two aspects: one is pro-
environmental values from organization, and the
other is from colleagues. Employees in a green
workplace are likely to perceive and accept green
ideas from their organization and colleagues, and
agree on the value of green behaviors, and thus are
more probably to adopt environmental behaviors in
their daily work. Therefore, we propose the following
hypothesis:
H1: Green climate positively influences employee
green behavior.
2.2
The Mediating Role of Autonomy
Motivation
Motivation drives employee behavior. According to
self-determination theory, autonomous motivation
drives individuals to engage in activities that are
consistent with their potential selves. Autonomous
motivation t includes identity motivation and internal
motivation. Identity motivation can drive employees
to engage in green behaviors by the consistent
concept and goals of environmental sustainability,
while internal motivation drives employees to engage
in green behaviors by stimulating their interests and
satisfying their emotional needs. Therefore,
employees with higher levels of autonomy motivation
are more likely to participate in pro-environmental
activities or generate related behaviors actively,
consistently, and effectively.
As we mentioned above, organization’s green
climate can convey and emphasize green values to
employees through the culture of organization and
attitudes of colleagues. The stronger the green
climate, the more frequently and clearly employees
are likely to perceive the green values. The more
employees internalize the values, the more
meaningful they will perceive environmental
activities to be, and the more they may generate the
idea of participating in environmental protection.
Happiness will be brought by the behavior that is
consistent with their values, so they will be more
active in the pro-environmental activities. Therefore,
we propose the following hypotheses:
H2: Autonomy motivation positively influences
employee green behavior.
H3: Green climate positively influences
autonomy motivation.
H4: Autonomy motivation mediates between
green climate and employee green behavior.
2.3
The Moderating Role of Green
HRM
Green HRM is business organizations use their HRM
departments to effectively implement environmental
sustainability policies. Organizations that implement
a higher degree of green HRM are able to make it
easier for employees to feel and integrate into the
organizational green climate, thus stimulating
employees’ environmental awareness and triggering
their autonomous motivation so that they will
perceive green behaviors as valuable and meaningful,
proactive, and self-determined behaviors. In addition,
the organization’s implementation of green HRM
puts forward a series of environmental protection
measures in action and also clarifies its environmental
attitudes in thought, which will have a subtle
influence on employees’ green-related attitudes and
behaviors. Therefore, we propose the following
hypotheses:
H5: Green HRM positively moderates the
relationship between green climate and autonomous
motivation.
H6: The green HRM positively moderates the
indirect effect of green climate on employee green
behavior through autonomous motivation.
Figure 1: Theoretical framework.
Organizational Green Climate and Employee Green Behavior: A Moderated Mediation Model
281

3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
3.1 Sample and Procedure
This study used a questionnaire survey to collect data
from employees of an enterprise in Chengdu, China.
We contacted the HRM department of the company
and distributed and collected the questionnaire with
their cooperation. To minimize the negative impact on
the environment, an online questionnaire was used as
the main method. The average length of time to fill
out the questionnaire was 5 minutes. After screening
out the questionnaires that took less than 2 minutes to
answer and contained a large number of consecutive
identical options, 349 valid questionnaires were
obtained for data analysis.
3.2 Measures
The measurement scales used in this study are all
derived from the maturity scales in the past literature.
The scale items are all on a 5-point Likert scale,
measuring the following variables:
Green climate: we used the scale developed by
Norton et al. (Norton, 2014), including 8 items such
as "Our company is concerned with becoming more
environmentally friendly", Cronbach’s α coefficient
is 0.91.
Autonomy motivation: the scale developed by
Graves et al. (Graves, 2013). was used, including " I
would engage in green behaviors at work because it
allows me to achieve goals I consider important" and
six other questions, Cronbach’s α coefficient is 0.94.
Employee green behavior: the scale developed by
Kim et al. (Kim, 2017) was used, which is close to the
actual office workplace and includes six items such as
"avoiding unnecessary printing to save papers", with
a Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.82.
Green HRM: The scale used by Dumont et al.
(Dumont, 2017) was adopted, including 6 questions
such as "My company provides employees with green
training to promote green values". The Cronbach’s α
coefficient is 0.79.
4 HYPOTHESIS TESTING
In order to test the effect of green climate on
employee green behavior, the mediating role of
autonomy motivation, and the mediating role of green
HRM, we used SPSS 24.0 to perform a stepwise
regression analysis on the collected data. During the
testing process, the Process macro plug-in developed
by Hayes et al. (Hayes, 2013) was used for Bootstrap
robustness test.
First, the main effect test, i.e., the effect of green
climate on employee green behavior. Model 4 is a
regression model of the control variables (gender,
age, and education) on employee green behavio.
Model 5 is a regression model of employee green
behavior after adding the independent variable (green
climate). In model 5, green climate has a significant
positive effect on employee green behavior (β=0.33,
p<0.01), so hypothesis 1 is supported.
Second, the mediating effect test, i.e., the
mediating effect of green HRM between green
climate and employee green behavior. In model 2,
green climate has a significant positive effect on
employee autonomy motivation (β=0.571, p<0.01),
Table 1: Regression test of Autonomy motivation and Employee Green Behavior (N=349).
Variables
Autonomy motivation Employee green behavior
Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5 Model 6 Model 7
Gender 0.191** 0.139** 0.138** -0.084 -0.115* -0.145** -0.14**
Age 0.039 0.083 0.082 -0.065 -0.038 -0.077 -0.054
Education 0.268** 0.161** 0.143** 0.036 -0.026 -0.051 -0.923
Green climate 0.571** 0.595** 0.33**
0.224**
Autonomy motivation 0.054** 0.186**
GHRM 0.012
Green climate*GHRM 0.104*
R
2
0.087 0.394 0.403 0.015 0.117 0.107 0.138
∆R
2
0.079 0.387 0.393 0.006 0.107 0.096 0.125
F 10.955** 55.81** 38.549** 1.713 11.327** 10.206** 10.892**
Note: * indicates significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-tailed).
** indicates significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-tailed)
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
282

Table 2: Tests of mediating effects with moderation (N=349).
Degree of adjustment
variable
Conditional Indirect Effect Moderated Mediator
Estimate Boot SE BC 95% CI INDEX S.E. BC 95% CI
Low GHRM 0.1011 0.0428 0.0186 0.1881
0.0137 0.096 0.0001 0.0362
Medium GHRM 0.1102 0.0462 0.02004 0.2035
High GHRM 0.1236 0.0523 0.0203 0.2298
Note: This study uses bootstrap for random sampling 5000 times.
so hypothesis 3 is supported; in model 6, employee
autonomy motivation has a significant positive effect
on employee green behavior (β=0.054, p<0.01), so
hypothesis 2 is supported; after adding the mediating
variable (autonomy motivation), the effect of green
climate on employee green behavior (β=0.224,
p<0.01) in model 7 remains significant, and
employee autonomy motivation also has a significant
positive effect on employee green behavior (β=0.186,
p<0.01). Therefore, hypothesis 4 was supported.
Third, the moderating effect test, i.e., the
moderating effect of green HRM between green
climate and employee autonomy motivation. In
Model 3, after adding the moderating variable (green
HRM), green climate still has a significant positive
effect on employee autonomy motivation (β=0.595,
p<0.01). Also, after the interaction of green climate
and green HRM, it shows a significant positive effect
on employee autonomy motivation (β=0.104,
p<0.05), so hypothesis 5 is supported.
Also, the point estimate of the mediating effect
with moderation is 0.0137 and a 95% confidence
interval of [0.0001, 0.0362], excluding zero. That
means, as the value of green HRM changes from one
standard deviation below the mean to one standard
deviation above the mean of the rubric, the mediating
role of employee autonomy motivation increases
significantly, thus hypothesis 6 is supported.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Theoretical Implications
The study improves the influence mechanisms
affecting employee green behavior and provides an
empirical evidence of self-determination theory in
employee psychology and behavior research.
Besides, by exploring the moderating role of green
HRM, it provides a theoretical basis for how green
policies can guide and promote employee green
behaviors, and provides new perspectives for
exploring environmentally sustainable development
strategies at the micro level.
5.2 Practical Implications
Since green climate can have a positive impact on
employee green behavior, companies could
participate in building an pro-environmental culture
and team climate, so that employees can be
influenced in daily work. In addition, as the
moderating effects of green HRM are verified,
companies could adopt appropriate recruitment
strategies to attract employees who share the same
environmental values as the organization.
5.3 Limitations and Future Research
Due to reality factors, this study still has some
limitations. Firstly, this study only used employees’
self-assessment. Self-evaluation from a single source
may affect the authenticity and accuracy of the data.
Future research can use multi-source data, such as
evaluation of leaders and colleagues.
Secondly, Autonomous motivation is not the only
path for employees to produce green behavior, the
motivation that drives employees to show
environmental behaviors in the workplace may also
include factors such as employees’ impression
management motivation, which can be explored in
future studies.
6 CONCLUSION
This study obtained the following conclusions: first,
green climate can positively influence employee
green behavior; second, autonomy motivation can
positively influence employee green behavior; third,
autonomy motivation shows a mediating role in the
influence of green climate on employee green
behavior; fourth, green HRM can positively
moderate the influence of green behavior and
enhance the mediating role of autonomy motivation.
Therefore, we suggest that organizations could work
on the development of an environmentally friendly
society by building the green climate, and suggest
that future research could explore other mechanisms
Organizational Green Climate and Employee Green Behavior: A Moderated Mediation Model
283

that affect employee green behavior.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (Grant No.71902128)
and the Department of Science and Technology of
Sichuan Province Fund (Grant No.2021JDRC0002).
REFERENCES
Dumont, J., Shen, J., & Deng, X. (2017). Effects of green
HRM practices on employee workplace green
behavior: The role of psychological green climate and
employee green values. Human Resource Management,
56: 613-627.
Graves, L. M., Sarkis, J., & Zhu, Q. (2013). How
transformational leadership and employee motivation
combine to predict employee proenvironmental
behaviors in China. Journal of Environmental
Psychology, 35: 81-91.
Hayes, A. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation,
and conditional process analysis. Journal of
Educational Measurement, 51: 335-337.
Kim, A., Kim, Y., Han, K., Jackson, S. E., & Ployhart, R.
E. (2017). Multilevel influences on voluntary
workplace green behavior: individual differences,
leader behavior, and coworker advocacy. Journal of
Management, 43: 1335-1358.
Norton, T. A., Zacher, H., & Ashkanasy, N. M. (2014).
Organisational sustainability policies and employee
green behaviour: The mediating role of work climate
perceptions. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 38:
49-54.
Peng, J., Hou, N., & Pang, Y. (2019). Employees' green
behavior: Summarizing the concept and the theoretical
explanation. Advances in Psychological Science, 27:
1297-1306
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
284
