
Knowledge Mapping Analysis of Research on Green Development
Haiyan Ye
1a*
and Yujie Huang
2b*
1
School of Economics and Management, West anhui university, Lu’an 237012, China
2
School of Humanities, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanchang 330013, China
Keywords: Green Development, Knowledge Mapping Analysis, Circular Economy, Low- Carbon Economy.
Abstract: As the ecological and environmental problems continue to worsen, China has also assumed more
responsibility for energy conservation and emission reduction. Green development is an inevitable way to
achieve "Carbon Neutrality". This paper used the software Citespace to obtain mapping, and analyzed the
relevant literature about green development from 2010 to 2020. Finally, the trend of the content was divided
into three stages. The first stage is from 2010 to 2013, focusing on the necessity and feasibility of achieving
green development in China. The second stage is from 2014 to 2017, focusing on the construction of green
development evaluation system. The third stage, from 2018 to 2020, studied in depth how to realize the green
development in each industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
Economic growth is not opposed to environmental
protection and resource conservation. The
development experience of some Nordic countries,
such as Denmark and Finland (Huang, 2015), shows
that there is a way to achieve production and
ecological win-win development. Based on green
development technologies, these countries promote
green development with green development systems
and laws as safeguards. At the APEC CEO Summit in
2013, Jinping Xi pointed out that growth based on
excessive resource consumption and environmental
pollution will not pay off, and called for innovative
development ideas and approaches to achieve Green
development. Green development stems from the idea
of green economy, and green economy came out in
the Blue Book of the Green Economy in 1989, written
by the British economist Pearce. Green economy
pursues the harmony between social development and
ecological environment, and advocates the
establishment of an environmental “Affordable
economy”. If a country only focuses on economic
development and ignores environment protection,
sustainable development will not be achieved, and
ecological crisis and resource depletion will threaten
the survival of mankind. Since the concept of green
development was put forward, the Central Committee
of the party has issued policies and taken measures to
promote green development. Green development has
been included in the “13th Five-Year Plan”. The
strategic position of green development in the overall
situation of China’s modernization construction was
emphasized again in the "Outline of the 14th Five-
Year Plan". In this period, Chinese scholars have also
carried out a large number of research on green
development, and has achieved fruitful results. This
study used the Knowledge Graph Analysis method to
analyse the literature in recent years, to understand
the overall picture of green development, to clarify
the evolution trend of the theme.
2 ANALYTICAL METHODS AND
DATA SOURCES
2.1 Analytical Methods
With problems of environmental pollution and
resource waste becoming more and more serious,
people have been exploring how to solve these
problems, and put forward the idea of green
development. Accordingly, China has formulated a
series of policies on green development, which has
also led scholars’ research on concept, realization
path and evaluation method of green development. In
order to clarify the trend of green development in
recent years, and to understand the current theoretical
Ye, H. and Huang, Y.
Knowledge Mapping Analysis of Research on Green Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0011735600003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 317-324
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
317
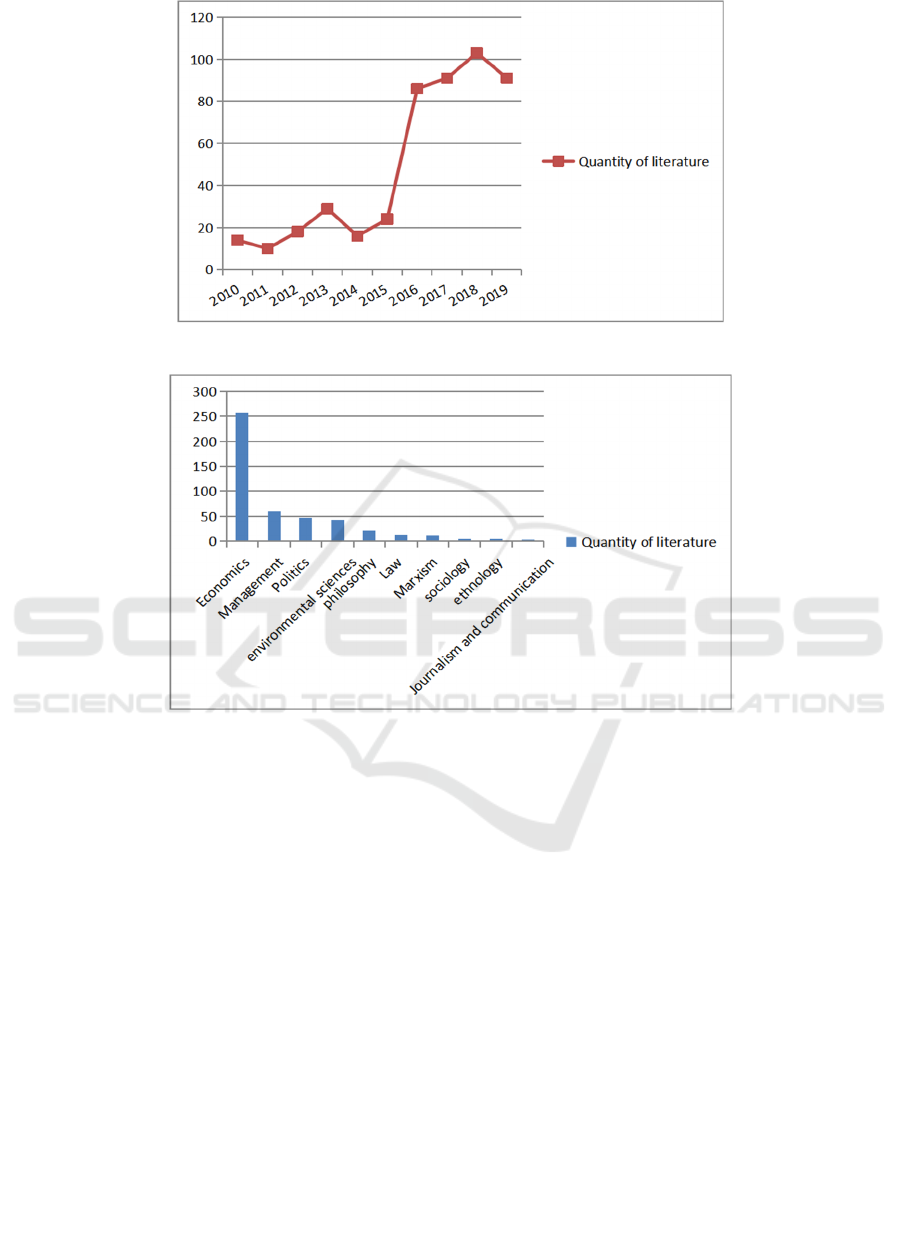
Figure 1: Statistics on the number of green development studies published in China from 2010 to 2019.
Figure 2: Statistical chart of the discipline distribution of green development research in China from 2010 to 2020.
frontiers, software Citespace was used to analyse the
recent literature on green development. Citespace is a
Java-based document visualization software
developed by Chinese American scholar Chaomei
Chen. The software integrates co-occurrence
analysis, cluster analysis and time series analysis,
aiming to reflect the overall situation of the literature.
2.2
Data Sources
The entire literature for this study was sourced from
the Chinese Social Science Citation Index (CSSCI).
This research searched the literature in recent years
(2010-2020) under the title of "Green Development",
and obtained 491 articles in total. Based on the
statistics, the quantity and the changing trend of the
literature related to green development research in
China from 2010 to 2019 were obtained. As can be
seen from Figure 1, the number of literature will be
relatively small, with about 20articals being
published each year. Since 2016, the number of
articles published has increased significantly, with
around 100 per year. The year 2016 marks the
beginning of the “13th Five-Year Plan”. As one of the
five development concepts, green development has
received more attention.
Research on green development in China involves
a wide range of disciplines. Among them, the number
of economic literature is the largest, 258, accounting
for 52.4% of the total. Figure 2 is the statistical chart
of the discipline distribution in China from 2010 to
2020. It can be seen, in addition to economics, other
disciplines covered by the literature include
management, political science, environmental
science, philosophy, law, Marxism, human and
economic geography, sociology.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
318

Table 1: Statistics on prolific author of green development research in China from 2010 to 2020.
Number Author Cited Times Number Author Cited Times
1 Chuanqing Wu 6 6 Zhibin Huang 4
2 Yaobin Liu 5 7 Huaxi Yuan 3
3 Fawen Yu 5 8 Aiping He 3
4 Lei Huang 4 9 Zhizhong Zhang 3
5 Chao Feng 4 10 Jianjun Zhao 3
Table 2: Statistics of highly-cited authors in China's green development research from 2010 to 2020(Top 10) .
Numbe
r
Autho
r
Cited Times Numbe
r
Autho
r
Cited Times
1 Angang Hu 64 6 Shujing Yue 17
2 Xiaoxi Li 39 7 Shi
y
i Chen 16
3 Bing Wang 38 8 Jianjun Zhao 14
4 Jianhuan Huan
g
19 9 Lin Li 13
5 Zhengge Tu 18 10 Jun Zhang 13
3 RESEARCH THREAD OF
GREEN DEVELOPMENT
3.1 Analysis of Highly Cited
Researchers
In recent years, there have been many high-yield
authors who have achieved fruitful results in green
development research. Table 1 lists the names of the
top ten authors in terms of the number of published
papers. They have studied green development from
multiple perspectives. For example, Chuanqing Wu
and Lei Huang from Wuhan University did a series of
studies on the green development in cities and
industries along the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
The research focused on the green development
efficiency and its synergy effect, the measurement of
the green development level and the promotion path.
Fawen Yu, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of
Social Sciences, pondered the motivation and path of
agricultural green development in the new era of
China under the background of the rural revitalization
strategy and the acceleration of agricultural and rural
modernization. Yaobin Liu, a professor at Nanchang
University, explored the impact of financial
deepening on China's green development process
from a financial perspective.
A large number of research results has provided
reference and research ideas for later scholars. Many
results have been cited many times for the field of
research to make a contribution. In order to identify
the core authors who currently make a significant
contribution to green development, the Citespace
software was used to generate a high-cited authors
statistical map, and the names of the top ten high-
cited authors and the numbers of citations were
reflected in Table 2.
As can be seen from Table 2, the papers of
researchers such as Angang Hu from School of Public
Administration of Tsinghua University, professor
Xiaoxi Li from Institute of Economics and Resource
Management of Beijing Normal University, professor
Bing Wang from Department of Economics of Jinan
University, Jianhuan Huang from Hunan University,
and Zhengge Tu from Central China Normal
University were cited frequently. Among them,
professor Angang Hu 's work was cited for 64 times,
ranking the first, followed by professor Xiaoxi Li and
professor Bing Wang, both of whom were cited more
than 30 times.
Figure 3: Statistics of highly-cited authors in green
development research in China.
Based on China’s national conditions and the
development concept in the "13th Five-Year Plan":
green development, Angang Hu, director of the
National Situation Center of Tsinghua University,
explained the goals, ideas and methods of green
development from the perspective of political
economy. Xiaoxi Li is devoted to the research on the
Knowledge Mapping Analysis of Research on Green Development
319

assessment of the level of green development, based
on the "human development index", and put forward
the "human green development index". Many foreign
economists have long proposed that if resource and
environmental factors are ignored in the study of
regional development efficiency and productivity, the
calculation results will be biased. Therefore, Bing
Wang considered resource and environmental factors,
put forward the concept of "green development
efficiency" to measure its efficiency level, and used
"green total factor productivity" to measure the level
of productivity growth. From the financial
perspective, Jianhuan Huang studied the impact of
financial development on green development and its
spatial spillover effect. Zhengge Tu studied how to
improve the efficiency of agricultural subsidies and
promote agricultural growth.
3.2 Analysis of Core Research
Institutions
Through the statistical analysis of green development
research institutions from 2010 to 2020, the results in
Figure 4 can be found that there are a number of
strong scientific research institutions in China
conducting green development-related research.
Among the institutions with the highest number of
papers are: Chinese Academy of Social Sciences,
Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural
Resources Research, Wuhan University, Central
South University of Forestry and Technology, Beijing
Normal University, Xi 'an Jiaotong University and so
on.
Figure 4: Statistics on core institutions of green
development research in China.
According to the statistical results, the core
research institutions were concentrated in China's
research institutes and universities, and Chinese
Academy of Social Sciences and universities in
central China have more achievements. The number
of papers published by the Chinese Academy of
Social Sciences is 19, while Wuhan University and
Central South University of Forestry and Technology
each published 8 posts. Most of the universities’
research results come from the School of Economics
and Management, and a few from the School of
Marxism. The total number of nodes is 227, the
number of Links is 29, and the Density is only 0.0009,
showing a scattered distribution basically. This
indicates a lack of connection and cooperation among
various research institutions.
Table 3: China's green development research institutions
and their number of published papers from 2010 to 2020
(Top 5).
Number Research Institution
Number of
Publishe
d
Pa
p
ers
1 Chinese Academy of
Social Sciences
19
2 Chinese Academy of
Sciences
8
3
Wuhan University 8
4
Central South
University of Forestry
an
d
Technolo
gy
8
5
Beijing Normal
Universit
y
7
3.3 Analysis of Core Journals
As can be seen from Figure 5, the most frequently
cited journals include: China's Population, Resources
and Environment, Economic Research, China's
Industrial Economics, and Management World.
These journals are the top journals in China's
management and economics disciplines, with
relatively high quality articles.
Figure 5: Statistics of highly-cited journals on green
development research in China.
Among these journals, "China's Population,
Resources and Environment" was cited the most, with
135 citations. It is headed by the Ministry of Science
and Technology, PRC and it is the journal of the
China Society for Sustainable Development. Its main
columns include sustainable development theory
research, sustainable industry. Green development
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
320

accords with the requirements for the inclusion of the
journal. The second most cited journal is Economic
Research, a national journal of comprehensive
economic theory, run by the Chinese Academy of
Social Sciences. Its columns involve circular
economy and ecological economy, so it also includes
some articles on green development.
Table 4: Statistics of China's green development research is
highly cited journal (Top 10).
Number Publication Name
Cited
Times
1 China's Population, Resources
and Environment
135
2 Economic Research 81
3 China's Industrial Economy 69
4 Management World 41
5 Economic Geography 40
6 Chinese Social Sciences 39
7 Energy Policy 36
8 Quantitative Economics and
Technical Economics Research
34
9 China Soft Science 31
10 Ecological Economics 31
4 THEORETICAL FRONTIER
ANALYSIS OF GREEN
DEVELOPMENT RESEARCH
4.1
Keyword Frequency Analysis
The key words of China’s green development
research from 2010 to 2020 were counted and the
high frequency keywords were obtained, as is shown
in Figure 6. The keywords include ecological
civilization, efficiency of green development,
sustainable development etc.
Figure 6: Statistic on high frequency keywords of green
development research in China.
The keywords reveal the research direction and
main ideas of the literature. At present, the research
on green development mainly focuses on the
following aspects: necessity and feasibility of
realizing green development in China, evaluation of
green development level and efficiency, green
development mode of each industry.
Table 5: Statistics on high frequency keywords of Green
development research in China.
Number Keywords Frequency
1 Green Development 307
2 Ecological Civilization 37
3 Concept Green of Development 33
4 Efficiency of green
Develo
p
ment
22
5
Yangtze River Economic Belt 17
6 Sustainable Development 12
7 Environmental Protection 11
8
Ecological Civilization
Construction
11
9
Green Econom
y
10
10
Environmental Re
g
ulation 10
4.2
Time Zone Distribution and Burst
Term Analysis of High Frequency
Keywords
Burst term is the term that appear or use more
frequently in a short period. The time zone map of
keyword can help us identify hotspots of research in
different periods.
Through the time zone distribution map of high-
frequency keywords, the trend of green development
research from 2010 to 2020 is divided into three
stages. The first stage is from 2010 to 2013, with the
most frequent keywords being: industrial structure,
climate change, sustainable development,
environmental protection, green economy. The
second stage is from 2014 to 2017, keywords are
circular economy, green development view,
Marxism, green development efficiency. The third
stage is from 2018 to 2020, keywords are
environmental regulation, high quality development,
green industrial development, green agricultural
development.
4.2.1 Main Research Contents in The First
Stage
In the first stage (2010-2013), the research on green
development mainly explored how to achieve
sustainable development.
Knowledge Mapping Analysis of Research on Green Development
321
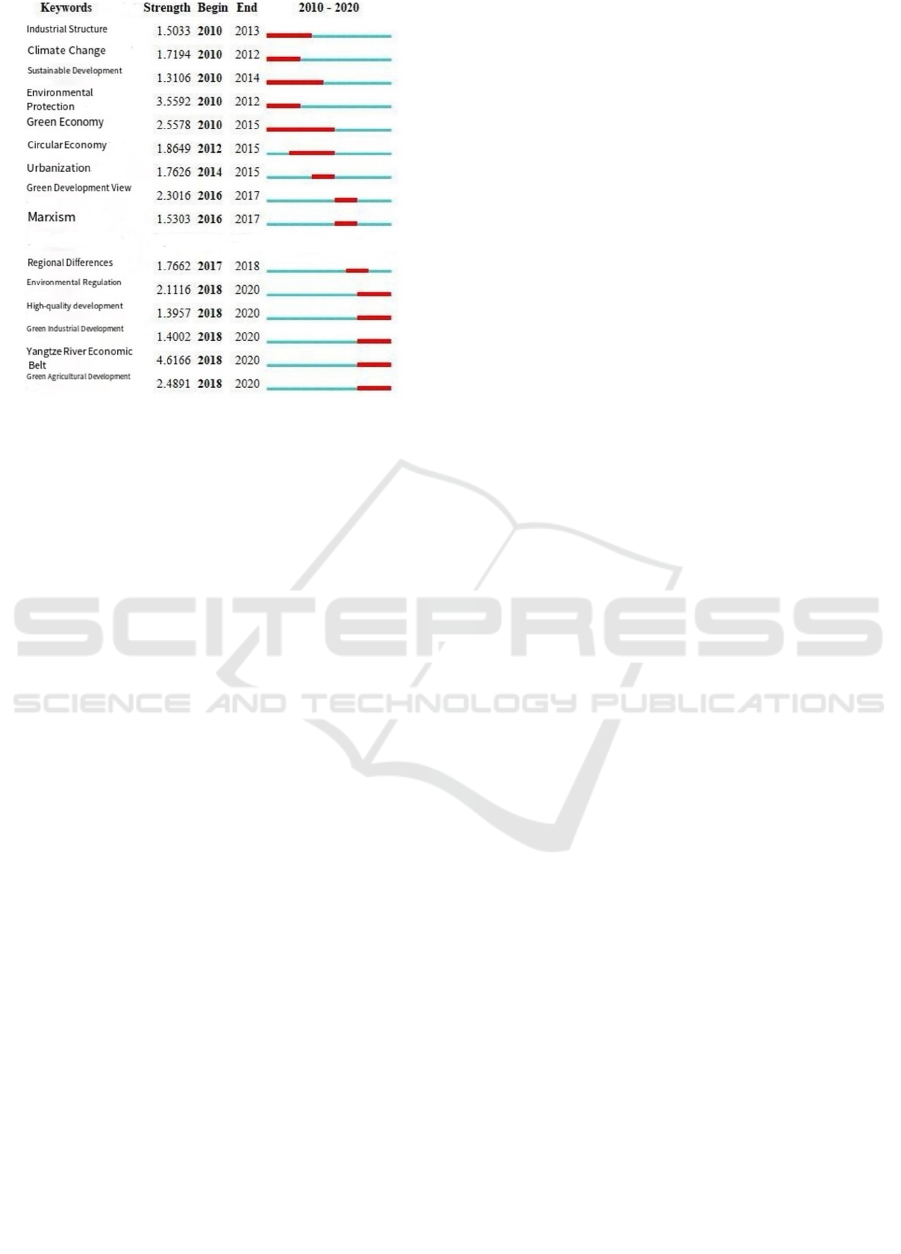
Figure 7: Statistics on burst term of high frequency
keywords in green development research in China.
Greenhouse gases emitted by human activities are
causing the temperature to rise. Global warming has
become a common problem for human survival. With
the rapid development of China's economy in recent
years, along with the energy consumption and
greenhouse gas emission, China has assumed
important responsibility of energy conservation and
emission reduction (Hu, 2010). We should achieve
economic development and growth, at the same time
we should also improve energy efficiency. Since the
concept of sustainable development was put forward
in 1987, the awareness of ecological and
environmental protection has been gradually
enhanced. To achieve green development, we need a
safer and cleaner development mode. Therefore,
extensive economic growth mode must be changed.
Forming green industrial system and developing low-
carbon economy and circular economy (Qiang, 2010)
are the keys.
"Decoupling" theory and Kuznets curve
hypothesis hold that economic development, resource
consumption and environmental pollution show an
inverted U trend. That is to say, with the development
of economy, resource consumption and
environmental pollution will increase and worsen
firstly, and then improve. These theories confirm the
possibility of low-carbon economic development. To
develop low-carbon economy, Zhijun Feng (2010)
believes that the following measures should be taken:
to adjust the industrial structure, develop low-carbon
technologies, use low-carbon energy, and expand the
potential of carbon sink (Feng, 2010). Based on the
development experience of developed countries,
compulsory transformation by administrative means
is not a long-term solution. Only by making use of
economic means and policies such as price and tax,
giving full play to the role of market mechanism can
arouse the initiative of enterprises in green
transformation (Huang, 2014).
Circular economy is based on the ecological laws.
The ecological damage and environmental pollution
caused by human economic activities should be
reduced through saving and recycling resource as far
as possible. Although the concepts of circular
economy and low carbon economy are different, their
intrinsic properties are the same as the connotation of
green economy (Liu, 2012).
4.2.2 Main Research Contents of The Second
Stage
The second stage (2014-2017) was based on Marxism
to construct China's green development view and
explore the harmonious development between man
and nature. In this stage, a lot of research has been
done on the evaluation of green development effects,
and the evaluation index system has been used to
measure the regional differences of green
development.
To make green development scientific and
sustainable, it is necessary to measure and evaluate its
effects. Foreign economists have recognized that
environmental factors should be taken into account
when measuring productivity. Currently, some
countries have already used green GDP as a method
to measure productivity. Many domestic scholars
have studied the assessment system which is suitable
for China's green development. For example, Bing
Wang (2014) combined the parameter Common
boundary model with Luenberger index to measure
the green development efficiency of 30 provinces and
cities in China from 2000 to 2010 (Wang, 2014)
by
putting CO
2
and SO
2
emissions into the framework of
total factor productivity analysis, and the regional
difference of green development level was compared.
Xiaoxi Li (2014) believes that green development is
to find a new way of economic growth, that "green"
and "development" should go hand in hand. On the
basis of human development index, resource and
environmental factors should be added to build a
human green development index system and measure
the green development index of different countries
(Li, 2014).
To achieve green development, the construction
of green cities and villages is the premise, and to
achieve the Green development of cities and villages,
the core is to realize the greening of industries (Wu,
2017). The green development level of urban
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
322

agglomeration plays an important role in promoting
the overall green development of China. Yue Huang
(2017) used projection pursuit model, Pearson
correlation, coefficient of variation and Theil index to
analyze the spatial characteristics (Huang, 2017)
comprehensively. The development of cities depends
on the concentration of industry into cities. Shujing
Yue (2015) calculated the green development
efficiency of 96 prefecture-level cities in China by
using SBM directional distance function in view of
the impact of industrial agglomeration on green
development of cities (Yue, 2015). The results
showed that an inverted U-shaped relationship was
presented between industrial agglomeration and
green development efficiency of cities. Since the 21st
century, the problem of ecological environmental
pollution in rural areas of China has become more and
more serious. Li Xie (2016) constructed an evaluation
index system of rural green development by
combining various DEA models with Gini criteria,
and its development performance is measured and
analyzed dynamically (Xie, 2016).
4.2.3 Main Research Contents in The Third
Stage
In the third stage, how to achieve green development
in various industries has been further studied, such as
agricultural green development, industrial green
development, etc.
Extensive manufacturing development mode has
caused industrial pollution and become one of the
main reasons of ecological pollution. In December
2018, the Central Economic Work Conference
proposed to "promote high-quality development in
the manufacturing sector". Green development
efficiency is an important indicator to measure
whether to achieve high-quality development level.
Under China's economic system, environmental
regulation is an important factor affecting the
efficiency of green development. Renfa Yang (2019)
analyzed the impact of environmental regulation on
China’s green industrial development. The results
showed that environmental regulation in eastern
China had a significant positive impact on green
industrial development, while the relationship
between environmental regulations and green
industrial development in central and western China
showed an inverted "U" shape (Yang, 2019). Aiping
He (2019) used SBM-DEA directional distance
function to calculate the green development
efficiency of China’s provincial regions, and also
proved that environmental regulation has a positive
on green development. However, the competition
between local governments will lead to the lack of
environmental regulation, so it is necessary to
improve the local assessment system (He, 2019).
Yongjun Tang (2019) measured the green
development level of enterprises and found that
gender, age and other characteristics of board
members play a moderating role between
environmental administrative supervision and green
development (Tang, 2019).
Since the 13th Five-Year Plan, China has issued
many guiding documents on green agricultural
development. In 2016, the "No.1 Document" of the
Central Government, proposed to "promote green
agricultural development". In September 2017, China
issued the Opinions on Promoting Green Agricultural
Development by Innovating Systems and
Mechanisms. To realize the green development in
agriculture, we must have a scientific understanding
of its connotation. Qianwen Gong (2020) pointed out
the connotation of green agricultural development
should be defined from three aspects: low carbon,
economy and security. The level of green agricultural
development should be evaluated from three
dimensions: low-carbon production, economic
growth and safety supply (Gong, 2020). Guided by
the conviction that "lucid waters and lush mountains
are invaluable assets", Weilin Sun (2019) constructed
an index system to measure the level of green
agricultural development (Sun, 2019). Agricultural
industrial agglomeration is an important way to
improve production efficiency. Therefore, some
scholars studied the relationship between agricultural
industrial agglomeration and green agricultural
development. For example, Lei Xue (2020) tested the
spatial spillover effect of agricultural industrial
agglomeration on the efficiency of green agricultural
development (Xue, 2020).
5 CONCLUSION
According to the statistical analysis of 492 papers
titled "green development" in CSSCI database,
Chinese scholars' research on this topic has been
increasing in recent years, especially after 2015.
"Green development" has been studied in many
disciplines, including economics, management,
political science and environmental science. Core
authors with a large number of posts are Chuanqing
Wu, Yaobin Liu, Fawen Yu, Lei Huang. Authors with
high citation frequency are Angang Hu, Xiaoxi Li,
Bing Wang, Jianhuan Huang. Core research
institutions include Chinese Academy of Social
Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan
Knowledge Mapping Analysis of Research on Green Development
323

University, Central South University of Forestry and
Technology. The core journals mainly include China's
population, Resources and Environment, Economic
Research, China's Industrial Economy, Management
World. High-frequency keywords include: green
development efficiency, sustainable development,
industrial structure, circular economy, environmental
regulation, industrial green development, agricultural
green development.
In this paper, the trend of research contents from
2010 to 2020 is divided into three stages. The first
stage, from 2010 to 2013, discussed the necessity and
feasibility of realizing green development in China
under the premise of global ecological environment
deterioration. In the second stage, from 2014 to 2017,
focused on building a green development level
evaluation system. The third stage, from 2018 to
2020, focused on how to achieve green development
in each industry. From the research results on green
development in recent years, we can see that
theoretical development is constantly meeting the
needs of social development. In 2021, the
government work report proposed "carbon peak" and
"carbon neutral". China has assumed the
responsibility of energy conservation and emission
reduction, and has pledged to achieve "carbon
neutral" by 2060. China shoulders the responsibility
of energy conservation and emission reduction. How
to achieve this goal through green development is an
important issue in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Fund project: Anhui Province Humanities and Social
Sciences Major Project (SK2019A0433), Anhui
Provincial Major Teaching Research Project in 2020
(2020jyxm2160). Outstanding Young Talents
Support Program for Universities in 2022
(gxyq2022061).
REFERENCES
Feng Zhijun, Zhou Rong. Low-carbon economy: the
fundamental approach to green development in China
[J]. China population, resources and environment, 2010,
20(04):1-7.
Gong Qianwen, Li Xuemin. Construction and measurement
of agricultural green development index: 2005-2018 [J].
Reform,2020(01):133-145.
Huang Juan, Wang Xingnan. The Practice and enlightenment
of green development in Northern European countries
[J]. Economic Review, 2015(07): 122-125.
Hu Angang. Global climate change and China's green
development [J]. Journal of the Party School of the CPC
Central Committee,2010,14(02):5-10.
Huang Qin, Yang Shuang. Accelerating the construction of
new urbanization through industrial transformation and
upgrading [J]. Economic Review,2014(01):44-47.
Huang Yue, Li Lin. Comprehensive measurement and
spatial-temporal evolution of green development level
of urban agglomerations in China [J]. Geographical
research, 2017, 36(07):1309-1322.
He Aiping, An Mengtian. Local government competition,
environmental regulation and green development
efficiency [J]. China population, resources and
environment, 2019, 29(03):21-30.
Liu Sihua, Fang Shijiao. Two engines of green
Development and Green Rise: On two basic forms of
ecological civilization innovation economy [J].
Economic Review,2012(07):38-43.
Li Xiaoxi, Liu Yimeng, Song Tao. The measurement of
human green development index[J]. Social Sciences in
China,2014(06):207-208.
Qiang Wei. Transform development mode Promote green
development [J]. Seek Truth,2010(01):31-33.
Sun Weilin, Wang Ruibo, Jiang Qian, Huang Shengnan.
Research on connotation and evaluation of agricultural
green development [J]. Chinese journal of agricultural
resources and regional planning,2019,40(04):14-21.
Tang Yongjun, Li Peng. Board characteristics,
environmental regulation and green development of
manufacturing enterprises: An empirical analysis based
on panel data of manufacturing enterprises from 2012
to 2016 [J]. Economic Survey, 2019, 36(03): 73-80.
Wang Bing, Huang Renjie. Regional green development
efficiency and green total factor productivity in China:
2000-2010 -- an empirical study based on the common
boundary of parameters [J]. Sankei review, 2014,
5(01):16-35.
Wu Xiaoxia, Zhang Shuangyue. The formation and future
trend of the concept of "green development". Economic
Issues, 2017(02):30-34.
Xue Lei, Shen Yun, Xu Chenghong. Agricultural industrial
agglomeration and agricultural green development:
efficiency measurement and influence effect [J].
Economic Survey,2020,37(03):45-53.
Xie Li, Wang Jinjin. Spatial differences of rural green
development performance in China [J]. China
population, resources and environment, 2016, 26(06):
20-26.
Yue Shujing, Zou Yulin, Hu Yaoyu. Impacts of industrial
agglomeration on green development efficiency of
Chinese cities [J]. Urban Issues,2015(10):49-54.
Yang Renfa, Li Nana. Environmental regulation and
China's industrial green development: theoretical
analysis and empirical evidence [J]. Journal of China
university of geosciences (social sciences edition),
2019, 19(05):79-91.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
324
