Multi-Agent Cooperation Mechanism of Hydropower Plants in
Central China Based on Raiffa Solution
Man Jiang
1
, Shunming Bai
1
, Kun Xiao
2
and Debin Fang
2
1
State Grid Huazhong Branch, Wuhan 430077, Hubei, China
2
School of Economics and Management, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, Hubei, China
Keywords:
Carbon Emission Reduction, Clean Energy, Cooperative Game, Hydropower Cooperative Alliance, Raiffa
Solution Algorithm.
Abstract:
“Carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality” have been national development strategies in China. The power
industry is crucial for achieving the carbon reduction targets. However, the dysfunctional competition of
hydropower plants in Central China leads to massively inefficient utilization of clean hydropower, which also
has an adverse impact on the consumption of wind power and photovoltaic energy. To solve this problem, this
paper proposes the regional hydropower alliance mechanism based on the cooperative game model. By using
the Raiffa solution algorithm, the models are performed based on the technical and economic parameters of
typical provinces and river basins in Central China. The results demonstrate that the benefit from the
hydropower cooperation alliances across river basins and the same river basins in Central China can be
feasibly distributed. What’s more, the research has vital guiding significance on building an efficient regional
power market order in Central China and promoting carbon emission reduction in power generation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions
has been a key issue concerning the destiny of
mankind and sustainable development. In 2020,
Chinese President Xi Jinping clearly stated that
carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China would
have been respectively reached by 2030 and 2060
(Wu, 2021). However, the problem of carbon
emissions in China is very serious. According to
statistics from the U.S. Energy Administration, as the
world’s largest carbon emitter, China emits more than
10 billion tons of greenhouse gases each year, of
which nearly 40% comes from its power generation
industry. Therefore, reducing carbon emission in
power generation is a key way to speed up the
realization of the “dual carbon” strategy in China.
Nowadays, in China, the problems of carbon
emissions in power generation mainly come from its
reliance upon fossil fuels, and coal power still
occupies the main position of the power generation
structure (Xiao, 2020). Therefore, it is an important
measure to promote carbon emission reduction in
China’s power generation by replacing thermal power
with clean hydropower, wind power, photovoltaic
and other forms. In this context, hydropower and
clean energy power generation in Central China have
developed rapidly, and the proportion of installed
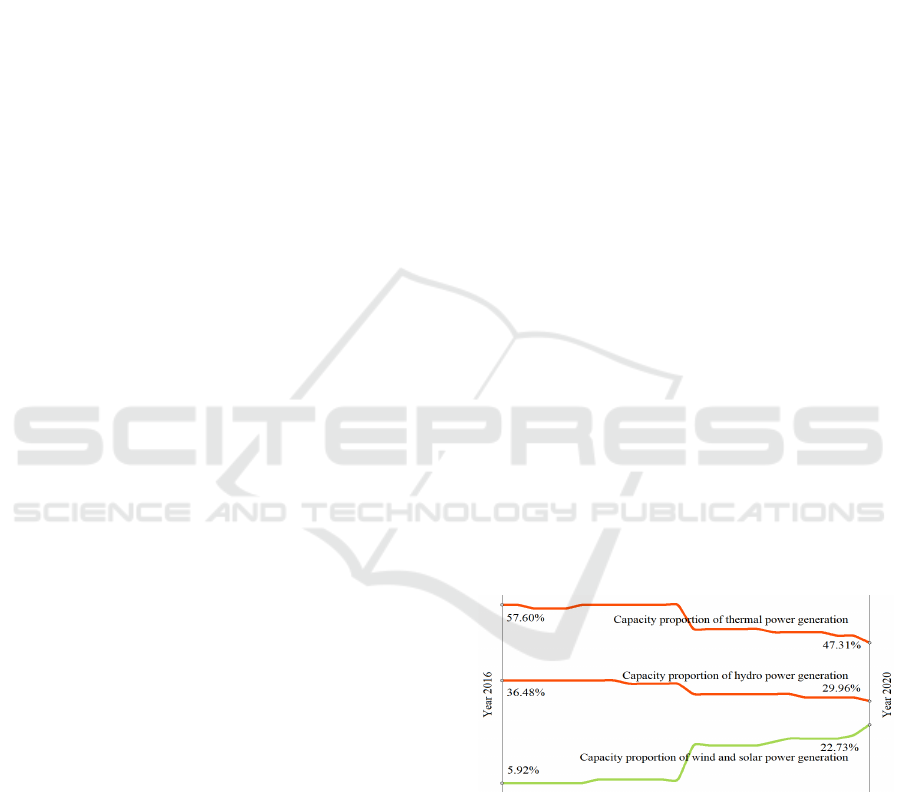
capacity has increased significantly. Figure 1 shows
the development trend of the power generation
installation structure in Central China.
Figure 1: Development trends of power generation
installation types in Central China.
Although hydropower, wind power, and
photovoltaic power generation in Central China have
developed rapidly, the problem that clean energy
power generation in Central China is not fully utilized
has also been prominent. For example, in 2020, the
underutilized hydropower, wind power, and
photovoltaic power generation in Central China were
469 million kWh, 292 million kWh, and 2.55 million
Jiang, M., Bai, S., Xiao, K. and Fang, D.
Multi-Agent Cooperation Mechanism of Hydropower Plants in Central China Based on Raiffa Solution.
DOI: 10.5220/0011736100003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 325-330
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
325

kWh, respectively. The power generation space
corresponding to these underutilized clean energy
resources is actually filled by coal-fired thermal
power, which is detrimental to the realization of
carbon emission reduction in power generation and
China’s “dual carbon” strategic goal.
It is found through field survey that although there
are many rivers in Central China, and hydropower has
been fully developed, the interest conflicts between
power generation and water use still occur along
upstream and downstream for many hydropower
plants in the same river basin. Meanwhile, the
contradiction that hydropower plants across river
basins seize market share also appears. What is
worse, water conflicts lead to malicious release or
closure of power plants in the same river basin,
resulting in deficient utilization of water energy and
hindering the maximization of power generation
efficiency. At the same time, in the cross-basin
competition, the rush to generate hydropower in each
river basin directly squeezes the grid-connected space
of wind power and photovoltaic power generation.
What is more, the hydropower game due to
competition not only damages the full utilization of
water energy in the river basin, but also harms the
consumption of wind power and photovoltaic power
generation. This game model is not conducive to
establishing an orderly and efficient power market
and dispatching order in Central China at the micro-
level, and also hinders the achievement of carbon
emission reduction in power generation and the
realization of the “dual carbon” goal at the macro
level. Therefore, it is imminent to change the
situation of bad hydropower competition in Central
China. Based on the cooperative game model, this
study builds a hydropower distribution mechanism in
Central China to explore the role of this mechanism
on promoting carbon emission reduction of power
generation in Central China.
2 COOPERATION GAME
MODEL CONSTRUCTION OF
HYDROPOWER PLANTS IN
THE BASIN OF CENTRAL
CHINA
For each hydropower plant in the same watershed, the
expectation of cooperation rather than malicious
competition is that cooperation can make the
individual obtain more benefits than the competition
(Ambec, 2008). However, the basis of cooperation
lies in the reasonable distribution of cooperation
income, otherwise, the collapse of the cooperative
alliance will damage the income of the alliance, and
the relationship that individual returns to competitive
will also hurt the income of the individual.
2.1 Construction of Game Model for
Hydropower Cooperation in the
Same Basin of Central China
It is assumed that there are
i
n
hydropower plants on
each river.
I
refers to the collection of river basins
in Central China, and
i
is a natural number, which
represents the serial number of the river (
iI⊂
). For
watershed
i
,
N
={1,2, , n }
ii
represents the set
of game players of all hydropower plants in
watershed
i
, and
,
iii
SNS∀⊆ ≠∅
is called a
cooperative alliance, whose characteristic function is
:2
i
n
ii
vR→
, and
() 0
i
v
φ
=
.
i
R
is the set of real
numbers. Moreover,
()
ii
vS
indicates the
maximum benefit that each participant in the
cooperative alliance
i
S
obtains under the condition
forming the alliance, and then
{
}
iii
TNv= ,
denotes the game alliance on
i
N
.
For a single watershed
i
and the cooperative
game
{
}
iii
TNv= ,
of hydropower plants on the
watershed, if there is a real array
,,
()
i
ij iIjS
x
∈∈
,
then:
,
,
()
i
ij i i
iIjS
x
vS
∈∈
=
(1)
,,
()
i
ij iIjS
x
∈∈
can be called the feasible payment
vector of
i
S
, and the economic meaning of
,,
()
i
ij iIjS
x
∈∈
denotes the share of each individual
j
allocated from the total income
()
ii
vS
. When
ii
SN=
, namely when all individuals participate in
the cooperative alliance, if
,,
()
i
ij iIjS
x
∈∈
, then:
,
,
1
({ }),( ),( [1, ])
()
i
ij i i
n
ij i i
j
x
viIjn
xvN
=
≥∈∈
=
(2)
,,
()
i
ij iIjS
x
∈∈
will be called a feasible profit
distribution solution of the cooperative game. For
alliance game
i
T
, if the set of all individual
allocations of hydropower plants in basin
i
of
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
326

Hunan Province is recorded as
()
ii
E
v
, then:
,,
() { | ,() ( )}
i
N
ii ij i ij i i i i
Ev x R x vxn vN=∈ ≥ =
(3)
Equation (3) is the rational condition for
individual
j
in each hydropower plant. What is
more, for the game subject
j
, if the income gained
by joining the single-watershed cooperative game
alliance is less than the income gained when
j
leaves the cooperative alliance and acts alone,
j
will withdraw from the alliance. Therefore, the
collective rationality condition of all hydropower
plants in a single basin is based on the super-
additivity of Equation (3), which can be derived as
follows:
,
1
()
i
n
ij i i
j
x
vN
=
≥
(4)
At the same time, considering that the total
allocated amount of all hydropower plants in a single
basin
i
cannot exceed the total income of the basin,
we have:
,
1
()
i
n
ij i i
j
x
vN
=
≤
(5)
According to Equations (4) and (5), it can be
known that if the Equation (3) can be satisfied,
namely when the individual rationality and collective
rationality conditions of a single-basin hydropower
cooperative game are met at the same time, it means
that all hydropower plants in basin
i
will
completely distribute all the benefits. The remaining
question below is what the allocation of each
hydropower plant is to achieve
,
1
()
i
n
ij i i
j
x
vN
=
=
.
Assuming that the profit of all individuals in the
Central China basin
i
is recorded as
i
B
, the profit
of the remaining
1
i
n −
parties when no individual
j
participates is recorded as
(\ ) , [1, ]
ij i
vj biIj n=∈∈,
, while
,1 , 2 ,
[, ,, ]
iii in
bbb b=
. In addition, the distribution of
all cooperation among the parties is marked as
,1 ,2 ,
[, ,, ]
i
iii in
x
xx x= .
2.2 Construction of Game Model for
Inter-basin Hydropower
Cooperation in Central China
As is shown in Section 2.1, I is used to denote the
collection of river basins in Central China. It is
assumed that these rivers cooperate in a unified cross-
basin optimal dispatch. At this time, the individual
participating in the cooperation is basin
i
. Suppose
its cooperative alliance is denoted as
TS
, and the
distribution of cooperative income by each individual
is denoted as vector
12
[, , , ]
n
yyy y=
(
n
is the
number of rivers in set I).
The basis of cross-basin hydropower cooperation
is that the benefits obtained by basin i when
participating in the cooperation are at least not lower
than the benefits when it leaves the cooperative
alliance, and the excess profits obtained from the
cooperation need to be distributed to each individual
participating in the cooperation with a reasonable
manner. Besides, hydropower cross-basin
cooperative game distribution is the most important
concept of cooperative game. To obtain an executable
distribution, the distribution formed is classified,
forming the core concept, which can be defined as
follows:
(,) ()
i
iI
eTS y vTS y
∈
=−
(6)
In Equation (6),
(,)eTS y
reflects the
satisfaction of the Hunan Inter-basin Hydropower
Cooperation Alliance (denoted as
TS
) with the
allocation plan
y
. When
(,)eTS y
is larger, it
means that the cross-basin hydropower cooperation
alliance is more dissatisfied with the distribution plan
y
. At this time, the total income of all participating
entities in the cooperative alliance (that is, the
collection of hydropower in each basin) is far less
than the cooperative added value
()vTS
generated
by it, and the stability of the distribution plan is poor.
When A is smaller, it means that the inter-basin
hydropower cooperation alliance is more satisfied
with the allocation plan
y
, showing that the
allocation plan is more effective.
Obtaining the solution of Equation (6) is
equivalent to finding the allocation plan that
minimizes the maximum overrun in the cooperative
alliance, that is, nucleolus
N
~
. What is more,
compared with the core that may be an empty set, the
nucleolus always exists and contains only one
element. First, the core of the cooperative game can
be found:
1
ii
n
i
i
yyd
yc
=
≥
=
(7)
In Equation (7),
c
represents the total income
Multi-Agent Cooperation Mechanism of Hydropower Plants in Central China Based on Raiffa Solution
327

obtained by hydropower in different river basins after
forming a cooperative alliance. The core of this set of
inequalities can be solved as follows:
() {( , ): }
ii i i i
Cv cyy yd y cyd=− ≤≤−
(8)
2.3 Solution Algorithm of Hydropower
Cooperation Game Model
The prerequisite for multiple game players to form a
cooperative alliance is still individual rationality. If
the cooperative alliance damages the interests of the
individual without compensation, the subject will
have the urge to withdraw from the alliance, and then
obtain greater benefits through its own actions or
strategies. Therefore, a “fair and reasonable”
distribution plan is very important in a cooperative
alliance, and the distribution plan is reasonable only
when it reaches the rational goals of the participating
subjects. Moreover, many scholars in the field of
game theory have explored the issue of “fairness of
distribution”, and representative solution concepts
include Nash-Harsanyi negotiation solution, Raiffa
value, etc. It can be deduced mathematically that the
negotiation solution is equivalent to the Raiffa value
(Lozano, 2020), and the method of obtaining the
solution of the cooperative game based on the
Shapley value is only suitable for the case where the
number of individuals in the set is not more than 3
(Eissa, 2021). In this study, there are more individuals
in the same and cross-basin cooperative game
alliances (
3n >
and
3
i
n >
). Therefore, the Raiffa
value is used to solve the solution of the cooperative
game distribution mode of hydropower in Central
China. The Raiffa value algorithm is carried out in the
following steps:
(1)For basin
i
, according to the profits of the
cooperation of
i
n
and
1
i
n −
sides, the lower limit
of the distribution of all sides, namely
,,,
1
1
i
n
i
ij ij ij
j
ii
B
x
bb
nn
=
=+ −
, is used as the basis of
distribution.
(2)When an individual
j
of basin
i
joins
the cooperation of
1n −
side
without
j
, the
increase in profit, namely the marginal benefit of
j
,
is calculate:
,
,
ij
iij
x
Bb=− .
(3)Assign
,ij
x
according to two steps.
Firstly, the individual
j
in the basin
i
and the
1
i
n −
side hydropower plant without
j
are
equally divided, and then the
1
i
n −
side
hydropower plant is divided equally, namely:
,,
,,,
,,,,[1,],
22(1)
ij ik
ikij ik i
i
xx
x
xx iIjk nkj
n
==+ ∈∈≠
−
(9)
(4) Taking j as
1, 2, , n
, repeat step (3), and
then sum and average, to get the final distribution as:
,
,
,,
1
11
[],,[1,]
22(1)
ij
i
ik
ijij i
jk
ii i
n
x
x
xxjkn
nn n
≠
−
=⋅+ + ∈
−
(10)
Substituting the vector
i
x
and
i
x
, Equation (10)
can be expressed as:
,,,
1
23
1
[],,[1,]
2( 1)
i
n
ii
ij ij ij i
j
ii i
Bn
x
bbiIj n
nnn
=
−
=+ − ∈∈
−
(11)
Equation (11) is the Raiffa equilibrium solution of
the cooperative game.
3 GAME DISTRIBUTION
SOLUTION OF INTER-BASIN
HYDROPOWER
COOPERATION IN HUNAN
PROVINCE OF CENTRAL
CHINA
In this paper, taking the typical provinces of Central
China and the typical river basins of Lishui in Hunan
as examples, the quarterly power generation and unit
power generation price of each hydropower plant in
the river basins of Hunan Province in 2020 are
substituted into the hydropower cooperation game
model and its solution algorithm in Central China, to
obtain the revenue distribution plan of the
hydropower cooperation game. In addition, since the
value corresponding to this solution can be regarded
as value or electricity, the RaiIffa solution is
normalized and converted into a proportional value
that is the proportion of cooperative game revenue
distribution based on the Raiffa solution to avoid unit
inconsistency, which is more convenient for practical
implementation.
Figure 2 shows the proportion of inter-basin
hydropower cooperation distribution in Hunan
Province in the Central China by quarter.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
328
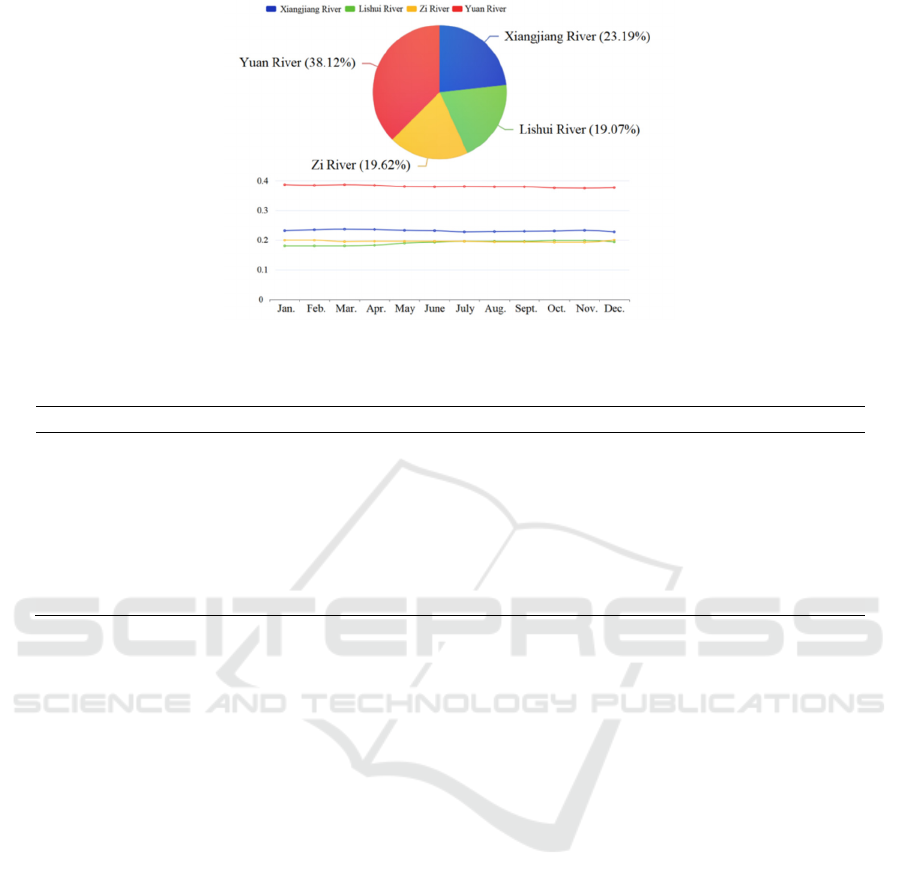
Figure 2: Proportion of income distribution based on multi-year average of Hunan hydropower inter-basin cooperation game.
Table 1: Cooperative game distribution share of power plants in Lishui river basin.
Power plant name The first quarter The second quarter The third quarter The fourth quarter
Jiang Ya
21.45% 7.48% 24.88% 27.68%
Guan Menyan
7.91% 10.81% 5.68% 6.38%
Changtan Rive
r
12.76% 11.24% 5.68% 6.38%
Yu Ta n 11.86% 9.93% 15.77% 11.86%
Chalin Rive
r
11.41% 11.38% 5.68% 6.38%
Zao Cit
y
11.90% 12.26% 19.16% 17.74%
San Jiangkou 13.03% 8.63% 12.64% 12.05%
Yan Zhou 9.67% 28.26% 10.52% 11.53%
It can be seen from Figure 2 that the Yuanshui
River Basin has the highest proportion (about 38%),
and the Lishui River Basin is the lowest (less than
20%). The Xiangjiang River and Zishui River Basins
are approximately equal, which is consistent with the
order of hydropower generation value in each basin
from high to low, embodying the principle that
individuals distribute revenue according to the
contribution to the team. Moreover, individuals with
a high proportion of power generation value need to
reduce the proportion of revenue sharing and give
profits to individuals with a low proportion of power
generation value to maintain the cooperative alliance.
Based on the profit distribution solution of the
cross-basin hydropower cooperation game in Hunan
Province, the distribution accuracy of the cooperation
revenue can be determined on the hydropower
alliances of each basin, further gaining the
distribution mechanism in each of the basin
hydropower cooperation alliances. Meanwhile, the
proportion of each power plant’s share of revenue be
obtained too. The following obtains the solution of
the Lishui Hydropower Cooperation Alliance in a
typical river basin, which is listed in Table 1.
It can be seen from Table 1 that the Raiffa value
of the hydropower plant cooperative alliance in a
single basin has different magnitudes from monthly.
Although the difference is small, and the fluctuation
range is not more than 2% in most cases, the
cumulative difference or cross-quarter difference is
significantly larger. The main reason for the
difference is that the power plants are different in
sensitivity to water regimes and their adjustment
capabilities, and there is a certain asynchrony in
production during periods of high water, flat water,
and low water, which shows that the quarterly Raiffa
value distribution method is more reasonable than the
annual Raiffa value distribution.
In addition, the cooperative alliance of a single
basin hydropower plant is formed to redistribute
benefits, which reflects the contribution of each
power plant to the single basin cooperative alliance.
In other words, power plants that can produce higher
electricity value each month account for a larger
proportion of the benefit distribution. However, the
proportion of profit distribution is not the same as that
of the monthly power generation value of each power
plant. For power plants with high power generation
value, the proportion of profits is lower than that of
their power generation value. Conversely, power
plants that account for the proportion of power
generation value can obtain a higher proportion of
revenue in cooperation, which is consistent with the
principle of the Raiffa value algorithm considering
Multi-Agent Cooperation Mechanism of Hydropower Plants in Central China Based on Raiffa Solution
329

the “marginal contribution of the team” and
“protecting the weak”.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the current practical problem that clean
energy is consumed inadequately due to malicious
competition among hydropower entities in Central
China, a hydropower cooperation game alliance in
Central China is established in this paper. Moreover,
with the help of the Raiffa solution algorithm, the
distribution plan of hydropower cooperative game
alliances in typical provinces and river basins in
Central China is calculated. It is proved that it is
feasible to establish a cooperative game alliance of
hydropower in Central China, and the distribution
plan is reasonable and incentively compatible. What
is more, the research methods and conclusions are of
practical guiding significance. In addition, the
hydropower cooperation alliance in Central China
will help regulate the power market and dispatch
order, thereby accelerating the consumption of clean
energy and promoting the realization of China’s
power generation carbon emission reduction and
“dual-carbon” strategic goals.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the State Grid
Huazhong Branch.
REFERENCES
Ambec, S., Ehlers, L. (2008). Sharing a river among
satiable agents. GAMES AND ECONOMIC
BEHAVIOR, 64(1), 35-50.
Eissa, R., Eid, M. S., Elbeltagi, E. (2021). Conceptual Profit
Allocation Framework for Construction Joint Ventures:
Shapley Value Approach. JOURNAL OF
MANAGEMENT IN ENGINEERING, 37(3).
Lozano, S., Soltani, N. (2020). A modified discrete Raiffa
approach for efficiency assessment and target setting.
ANNALS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH, 292(1),
71-95.
Wu, L., Zhu, Q. (2021). Impacts of the carbon emission
trading system on China's carbon emission peak: a new
data-driven approach. NATURAL HAZARDS,
107(3SI), 2487-2515.
Xiao, K., Li, F., Dong, C., Cai, Y., Li, Y., Ye, P., et al.
(2020). Unraveling effects of coal output cut policy on
air pollution abatement in China using a CGE model.
JOURNAL OF CLEANER PRODUCTION, 269.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
330
