
Research on the Tripartite Evolution Game of Cooperative
Relationship of Collaborative Innovation Network of New Energy
Vehicle Industry under the Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises
Weiwei Liu
a
and Xianrong Lang
b*
School of Economics and Management, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
Keywords:
The Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises, New Energy Vehicle Industry, Collaborative Innovation Network,
Evolutionary Game.
Abstract:
The paper uses evolutionary game theory to establish an evolutionary game model and software simulation
to simulate the impact of the dominant roles of core enterprise on the evolution of collaborative innovation
network of new energy vehicle industry. The research shows that the dominant roles of core enterprises can
better guide the evolution of the cooperative relationship of the collaborative innovation network, the
network reward and punishment mechanism, collaborative innovation benefits distribution mechanism,
market risk taken mechanism and knowledge transfer mechanism all have an important impact on the
selection of multi-agent strategy behavior and the evoluti1on of collaborative innovation network, and the
strategy selection behavior of industry, university and research institutes has an important impact on the
exercise of the dominant roles of core enterprises.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the ever-increasing contradiction between
energy supply and demand, research and
development (R&D) and promotion of new energy
vehicles have become effective measures to alleviate
resource scarcity and environmental problems.
China's new energy vehicle market promotion level
ranks among the top in the world, but the
development of technology research and
development compared with Germany and other
automotive powers
is lagging behind (Tang, 2019).
Collaboration is conducive to identify and discover
direct or potential opportunities (Xu, 2018), build
rich information channels (Wang, 2020;
PEMARTIN, 2018) and collaborative innovation
networks are the ideal carrier for innovation in
strategic emerging industries such as new energy
vehicles (Jiao, 2015).
New energy vehicles and other strategic
emerging industries have great potential and growth
space, and dominance plays a great role in
improving network construction (Lovejoy, 2010).
Many scholars, such as Zhong Taiyong (Zhong,
2015), Sun Hongxia (Sun, 2018), Jiang Cailou
(Jiang, 2020)
from the perspective of government
leadership, have conducted important theoretical and
exploratory analysis of the government dominant
roles of collaborative innovation network of China's
new energy vehicle industry, the collaborative
innovation networks’ development of strategic
emerging industries under the dominant roles of core
enterprises are more effective than under the
dominant roles of government (Jiao, 2015), but there
are still certain research gaps in dominant roles of
core enterprises. Aiming at the existing research
gaps and combining the research results of relevant
scholars, this paper uses evolutionary game theory to
establish an evolutionary game model among
enterprises, URIs and core enterprises and software
simulation to simulate the impact of the dominant
roles of core enterprise on the evolution of
collaborative innovation network of new energy
vehicle industry.
2 EVOLUTIONARY GAME
MODEL CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Analysis of The Interests of Various
Members
(1) The core enterprises’ strategy space is positive or
342
Liu, W. and Lang, X.
Research on the Tripartite Evolution Game of Cooperative Relationship of Collaborative Innovation Network of New Energy Vehicle Industry under the Dominant Roles of Core Enterpr ises.
DOI: 10.5220/0011736500003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 342-347
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

negative exercising dominant roles, and its strategy
selection probability is
z
and
(1 )z−
(
[0,1]z ∈
). The
dominance of the core enterprise in the collaborative
innovation network is realized by reward and
punishment mechanism, collaborative innovation
benefits distribution mechanism, market risk taken
mechanism and knowledge transfer mechanism.
When the core enterprises actively exercises
dominant roles, the network management cost ‘
e
C
’
will be paid, but can obtain the subsidies ‘
3
G
’,
generate the innovative benefits ‘
c
R
’ with the
enterprises and URIs, and obtain the income
‘
12
(1 )PPR−−
’of the management network and at the
same time, take a corresponding market risk
‘
12
(1 )PPD−−
’, the core enterprises have a greater
voice for the allocation of the collaborative innovation
earnings; if the core enterprises are negatively
exercising dominant roles, it does not participate in
the cooperation, only helping the enterprises and
URIs to distribute the benefits and risk.
(2) The strategy space of the enterprises is
cooperation
()
x
or default
(1 )
x
−
When enterprises
choose to default, costs ‘
1
C
’ and obtains revenue
‘
1
R
’, and also gets betrayal benefits ‘
1
E
’, but if the
enterprises' unilateral default should pay a contract
‘
F
’, and have a reputation loss ‘
e
L
’. When the
enterprises’ choose cooperation, at the time,
collaborative innovation costs ‘
3
C
’, enterprises
always obtain government subsidies ‘
1
G
’ and
undertake marketization risks ‘
1
PD
’. If the core
enterprises actively exercise dominant roles,
enterprises can always have knowledge transfer
benefits ‘
e
R
’. If URIs choose to cooperate, the
enterprise and URIs have produced collaborative
innovation benefits ‘
R
’, and collaborative
innovation revenue is allocated among enterprises,
URIs and core enterprises with ‘
1
P
’, ‘
2
P
’
and‘
12
(1 )PP−−
’. if the URL choose default, the
enterprises receive compensation ‘
F
’.
(3) The strategy space of URIs is cooperation
()y
or default
(1 )y−
. When the URIs choose to default,
the independent innovation costs URIs ‘
2
C
’and
obtains benefits‘
2
R
’, and also gains betrayal benefits
‘
2
E
’, but if the unilateral default is required to pay
‘
F
’, and have a reputation loss ‘
u
L
’. When URIs
choose collaborative innovation, the costs are ‘
4
C
’
and marketization risks are ‘
2
PD
’, it always able to
obtain subsidies ‘
2
G
’
2.2 Payoff Matrix Construction
The payoff matrix of three populations under
dominant roles of the core enterprises is as follows.
The dynamic replication system of enterprises, URIs
and core enterprises can be obtained as follows:
11 1 11 31
22 2 22 42
3
() (1 )[( ) ( ) ]
() (1 )[( ) ( ) ]
() (1 )( )
x
ee
t
y
eu
t
z
CCC e e
t
d
V x x x PR PD E y R F z G C L C R
d
d
V y y y PR PD E x R F z G C L C R
d
d
Vz z z Rx Ry Rxy G C R
d
α
==− − − + + +++−−
==− − − + + +++−−
==− + − +−−
2.3 Stability Analysis
Table 1: Payoff matrix of three populations.
Strategy of
Core
enterprises
Strategy of
Enterprises and URIs
Payoff
Enterprises URIs Core enterprises
The positive
dominant
roles
(cooperation,
cooperation)
P
1
+R
e
+G
1
-C
3
-P
1
D P
2
+R
e
+G
2
-C
4
-P
2
D
12 3 12
(1 ) +G - (1 )
cee
PPRR C R PPD
α
−− + − −−−
(default, cooperation)
111 e
R
ECFL+−−−
24e
R
GFC++−
3cee
R
GC R
α
+−−
(cooperation, default)
13e
R
GFC++−
222
R
ECF
L
+−−−
3cee
R
GC R
α
+−−
(default, default)
11e
R
CL−−
22u
R
CL−−
3 ee
GC R
α
−−
The
negative
dominant
roles
(cooperation,
cooperation)
P
1
R+G
1
-C
3
-P
1
D P
2
R+G
2
-C
4
-P
2
D
12 12
(1 ) (1 )PPR PPD−− −−−
(default, cooperation)
111e
R
ECL+−−
24
GC−
0
(cooperation, default)
13
GC−
222u
R
ECL+−−
0
(default, default)
11e
R
CL−−
22u
R
CL−−
0
Research on the Tripartite Evolution Game of Cooperative Relationship of Collaborative Innovation Network of New Energy Vehicle
Industry under the Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises
343

Table 2: Eigenvalues of each equilibrium point corresponds to the Jacobi matrix.
Equilibriu
m poin
t
Eigenvalues
1
λ
Eigenvalues
2
λ
Eigenvalues
3
λ
1
(0,0,0)E
11 31e
GCLC R++−−
22 42u
GCLCR++−−
3 ee
GC R
α
−−
2
(0,1,0)E
11 111 31e
P
RPDE G C L C R−−+++−−
22 42
()
u
GCLCR−++−−
3Cee
RGC R
α
+−−
3
(0,1,1)E
11 1 11 31ee
PR PD E R F G C L C R− −+++++−−
22 42
()
eu
R
FG C L C R−++++−−
3
()
Cee
RGC R
α
−+−−
4
(0,0,1)E
11 31ee
R
FG C L C R++ + + − −
22 42eu
R
FG C L C R++ + + − −
3
()
ee
GC R
α
−−−
5
(1, 0, 0)E
11 31
()
e
GCLC R−++−−
22 222 42u
PR PD E G C L C R−−+++−−
3Cee
RGC R
α
+−−
6
(1, 0,1)E
11 31
()
ee
R
FG C L C R−++++−−
22 2 22 42eu
PR PD E R F G C L C R−−+++++−−
3
()
Cee
RGC R
α
−+−−
7
(1,1, 0)E
11 111 31
()
e
P
RPDE G C L C R−−−+++−−
22 222 42
()
u
P
RPDE G C L C R−−−+++−−
3Cee
RGC R
α
+−−
8
(1,1,1)E
11 1 11 31
()
ee
P
RPDE R FG C L C R−−−+++++−−
22 2 22 42
()
eu
P
RPDE R FG C L C R−−−+++++−−
3
()
Cee
RGC R
α
−+−−
Table 3: The judgment of the eigenvalues of each equilibrium point corresponds to the Jacobi matrix.
Equilibrium
point
Situation1-1
Situation
1-2
Situation
2-1
Situation2-2
Situation
3-1
Situation3-2
Situation
4-1
Situation4-2
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
123
,,λλ λ
1
(0,0,0)E
+++ ++- +-+ +-- -++ -+- --+ ---(ESS)
2
(0,1,0)E
+-+ +-+ +++ +++ --+ --+ -++ -++
3
(0,1,1)E
+-- +-- ++- ++- ---(ESS) ---(ESS) -+- -+-
4
(0,0,1)E
++- +++ +-- +-+ -+- -++ ---(ESS) --+
5
(1,0,0)E
-++ -++ --+ --+ +++ +++ +-+ +-+
6
(1, 0,1)E
-+- -+- ---(ESS) ---(ESS) ++- ++- +-- +--
7
(1,1, 0)E
--+ --+ -++ -++ +-+ +-+ +++ +++
8
(1,1,1)E
---(ESS) ---(ESS) -+- -+- +-- +-- ++- ++-
The conditions in each situation are as follows:
1-1: When
11 1311 12 2 2422 23
,,,
euee
PR PD G C R C L E P R P D G C R C L E G C R
α
−+−>−−+ − +−>−−+ >+
1-2: When
11 1311 12 2 2422 23
,,,
euee
PR PD G C R C L E P R P D G C R C L E G C R
α
− +−>−−+ − +−>−−+ <+
2-1: When
11 1311 12 2 24222 3
,,,
ee uee
P
RPDG C R C L EPRPDR FG C R E C LG C R
α
− +−>−−+ − +++−<+−− >+
2-2: When
11 1311 12 2 24222 3
,,,
ee uee
P
RPDG C R C L EPRPDR FG C R E C LG C R
α
− +−>−−+ − +++−<+−− <+
3-1: When
11 13111 2 2 2422 23
,,,
ee uee
P
RPDR FG C R E C LPRPDG C R C L EG C R
α
− +++−<+−− − +−>−−+ >+
3-2: When
11 13111 2 2 2422 23
,,,
ee uee
P
RPDR FG C R E C LPRPDG C R C L EG C R
α
− +++−<+−− − +−>−−+ <+
4-1: When
11 13111 2 2 24222 3
,,,
eee uee
PR PD R F G C R E C L P R P D R F G C R E C L G C R
α
− +++− <+−− − +++ − < + − − > +
4-2: When
11 13111 2 2 24222 3
,,,
eee uee
PR PD R F G C R E C L P R P D R F G C R E C L G C R
α
− +++− <+−− − +++ − < + − − < +
In summary, in situation 4-1 and situation 4-2 the
evolutionary stability strategy is (default, default,
play positive dominant roles) and (default, default,
play negative dominant roles),the two situations are
less in reality; in addition to these two situations, it
can be seen that the new energy vehicle industry
collaborative innovation network are more effective
under the positive dominant roles of core enterprise,
the dominant roles of core enterprise can better
guide the evolution of innovative network
partnerships, while how core enterprises play
dominant roles to make the enterprises and URIs
tend to cooperate more efficiently, is one of the
important directions of research.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
344
3 MULTI-BODY SIMULATION
AND ANALYSIS
In order to simulate the distribution law of the
situation and evolutionary stability strategy in
realities better, this paper uses software to simulate
the evolutionary process, and discuss the different
parameters’ influence to the network’s evolution
under the dominant roles of core enterprises.
According to the consultation of experts and
combined with the setting rules of simulation
parameters in related literature (Cao, 2020), setting
1
=6C ,
𝐶
=2,
3
=12C ,
𝐶
=5, 𝐶
=5,
=0.2
α
,
1
=9R ,
2
=7R ,
=30R ,
=7
c
R ,
𝐺
=2,
2
=1G ,
3
=2G ,
=9D ,
1
=12E ,
2
=9E ,
6, 4
eu
LL==,
6F = ;
1
0.5,P =
2
0.3,P =
12
(1 ) 0.2PP−− = , 7
e
R =
, setting the initial
cooperation willingness of enterprises, URIs and
core enterprises is 0.5.
3.1 The Influence of Reward and
Punishment Mechanism on the
Evolution of New Energy Vehicle
Industry under the Dominant Roles
of Core Enterprises
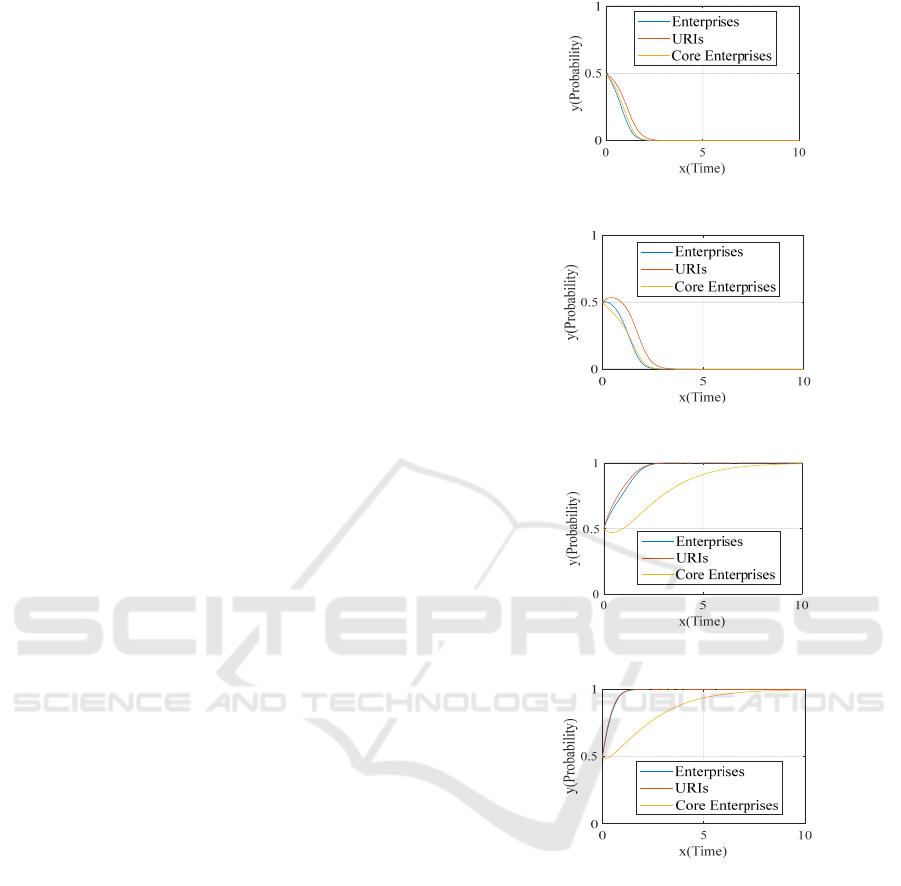
As can be seen from the figures, under low-intensity
rewards and punishment mechanisms, due to higher
betrayal benefits and lower default punishment, the
cooperation willingness of the enterprises and URIs
will show a decline and tend to default strategy, and
their collaborative innovation revenue is reduced, so
that core enterprises’ benefits of management
collaborative innovation network have reduced,
causes that core enterprises tend to adopt negatively
dominant roles; under the mid-intensity and
high-intensity rewards and punishment mechanisms,
the network reward highly the single cooperation,
and penal highly the single default, the cooperation
willingness of enterprises and URIs will rise and
higher collaborative innovation benefits have
produced, and core enterprises have obtained visual
management collaborative innovation benefits,
which tends to adopt positive dominant roles.
Figure 1: Evolution path under
1F =
.
Figure 2: Evolution path under 3F = .
Figure 3: Evolution path under
6F =
.
Figure 4: Evolution path under 10F = .
3.2 The Influence of Benefits
Distribution Coefficients and
Market Risk Taken Coefficients on
the Evolution of New Energy
Vehicle Industry under the
Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises
When 𝑃
=0.5,𝑃
=0.3,(1−𝑃
−𝑃
) = 0.2; 𝑃
=
0.7, 𝑃
=0.2,(1−𝑃
−𝑃
) = 0.1; 𝑃
=0.4,𝑃
=
0.4, (1 −𝑃
−𝑃
) = 0.2, the benefits distribution
coefficient and the market risk taken coefficient of
the enterprises, the URIs and core enterprises
basically meet the cost and elements investment
laws, the network ultimately tends to (cooperation,
Research on the Tripartite Evolution Game of Cooperative Relationship of Collaborative Innovation Network of New Energy Vehicle
Industry under the Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises
345
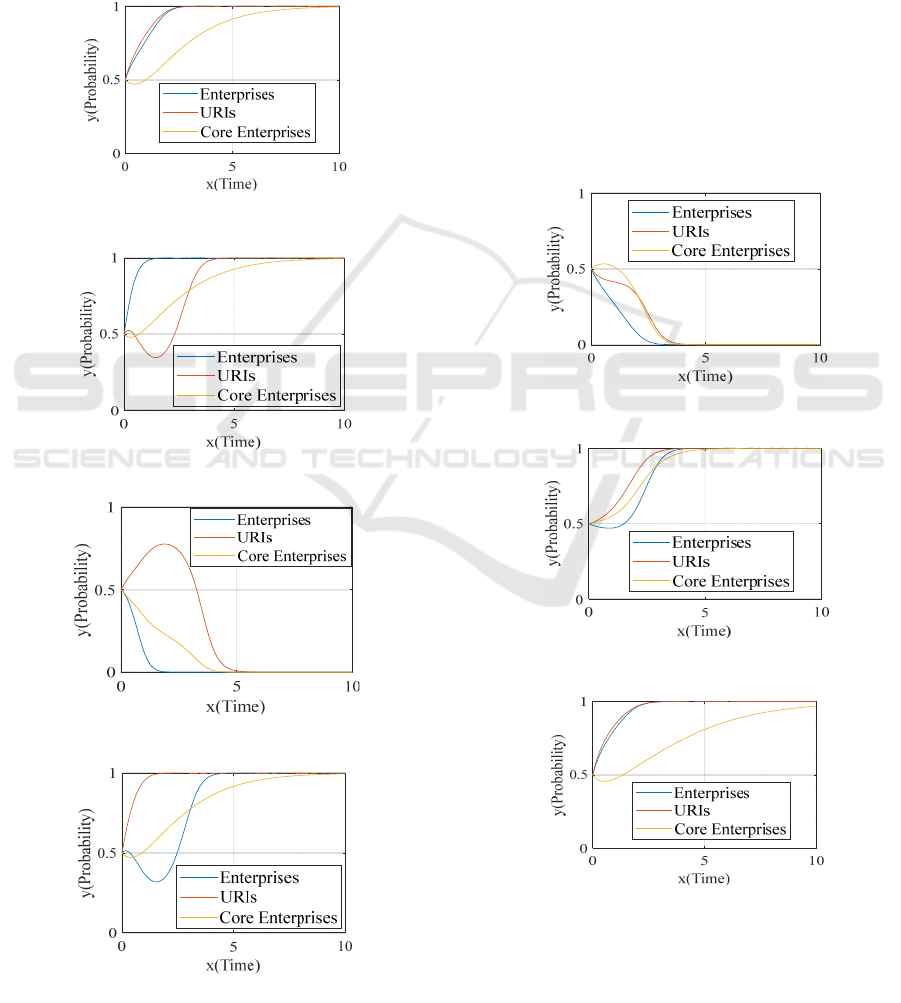
cooperation, play positive dominant roles).
When𝑃
=0.3,𝑃
=0.2, (1 −𝑃
−𝑃
)=0.5, the
core enterprises’ investments in the cost and
elements of the collaborative innovation project are
less than that of enterprises and the URIs, but the
benefits allocation coefficient is higher than the two,
enterprises and URIs adopt a default strategy and
produce small collaborative innovation benefits, the
core enterprises finally choose negative dominant
roles.
Figure 5: Evolution path under
10.5,20.3PP==
.
Figure 6: Evolution path under
10.7,20.2PP==
.
Figure 7: Evolution path under
10.3,20.2PP==
.
Figure 8: Evolution path under
10.4,20.4PP==
.
3.3 The Influence of Core Enterprises
Knowledge Transfer Revenue on
the Evolution of New Energy
Vehicle Industry under the
Dominant Roles of Core
Enterprises
Low core enterprise knowledge transfer is not
conducive for enterprise and URIs to knowledge
accumulation and technical breakthrough, higher
core enterprise knowledge transfer does not meet the
investment law of core enterprises, enterprises and
URIs obtain moderate core enterprise knowledge
transfer benefits, that is, core enterprises pay in
moderate core enterprises knowledge transfer costs,
it is good for multi-body selection cooperation
strategies and the optimal stability evolution of the
network.
Figure 9: Evolution path under 𝑅
=1.
Figure 10: Evolution path under 𝑅
=3.
Figure 11: Evolution path under 𝑅
=8.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
346
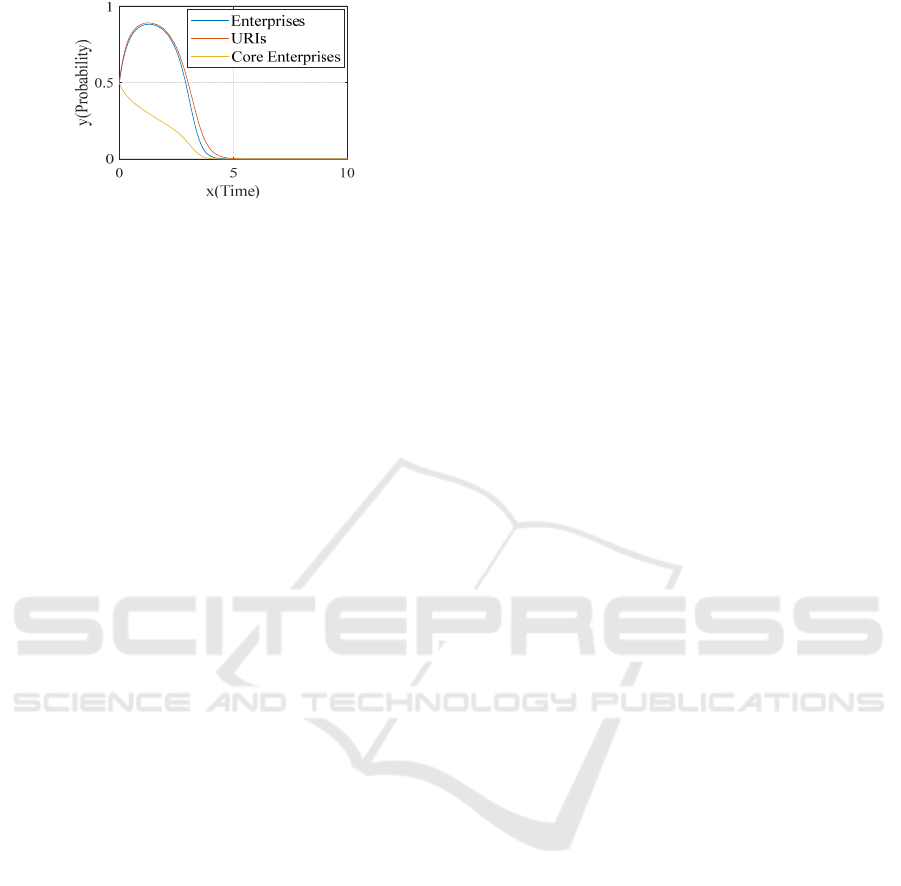
Figure 12: Evolution path under 𝑅
=12.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results and discussions presented
above, the conclusions are obtained as below:(1)
The new energy vehicle industry collaborative
innovation network is more effective under the
positive dominant roles of core enterprises; (2) The
dominant roles of core enterprises have an important
influence on multi-body strategic behavior and
collaborative innovation network evolution , and the
choice of subjects’ behavior selection has an
important influence on the dominant roles of core
enterprises as well; (3) With the increasing of the
reward for the only cooperation members and the
penalty for the only breaching members, enterprises
and URIs in the network have tend to the stable
strategy of cooperation, and the greater the
improvement, the faster the speed of cooperation;
(4)When the benefits distribution and the marketing
risk taken basically meet the cost and elements
investment laws, the network ultimately tends to the
optimal stability condition; (5)Enterprises and URIs
obtain moderate core enterprise knowledge transfer
benefits, that is, core enterprises pay in moderate
core enterprises knowledge transfer costs, it is good
for the optimal stability evolution of the network.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (71872056,
71302028, 71774037); National Social Science
Fund of China (17BGL204, 19BGL017); General
Project of Humanities and Social Sciences in the
Ministry of Education (19YJA630015).
REFERENCES
Cao Xia, Li Chuanyun, Yu juan, et al. Simulation of
Innovation Network Evolution Game of
Industry-University-Research Cooperation Under
Market Mechanism and Government Regulation: A
Case Study of New Energy Vehicle Industry [J].
Journal of Systems & Management, 2020, 29(03):
464-474. (in Chinese)
Changfeng Wang, Qiying Hu. Knowledge Sharing in
Supply Chain Networks: Effects of Collaborative
Innovation Activities and Capability on Innovation
Performance [J]. Technovation, 2020, 94-95: 102010.
Jiao Yuanyuan, Shen Zhifeng, Hu Qin. Research on
Partnership of Strategic Emerging Industry
Collaborative Innovative Network Under Different
Dominant Roles—A Case Study on Chinese IOT [J].
R & D MANAGEMENT, 2015, 27(04): 60-74. (in
Chinese)
Jiang Cailou, Zhang YING, Li Weiwei, et al. Evolutionary
Game Study between Government Subsidy and R&D
Activities of New Energy Vehicle Enterprises [J].
OPERATIONS RESEARCH AND MANAGEMENT
SCIENCE, 2020, 29(11):22-28. (in Chinese)
Lovejoy W S, Sinha A. Efficient structures for innovative
social networks [J]. Management Science, 2010, 56 (7)
PEMARTIN M, RODRIGUEZ-ESCUDERO A I,
MUNUERAALEMAN J L. Effects of collaborative
communication on NPD collaboration results: two
routes of influence [J]. Journal of Product Innovation
Management, 2018, 35(2): 184-208.
Sun Hongxia, Lv Huirong. Evolutionary Game Analysis
between Government and Enterprise in New Energy
Vehicles Market under New Subsidy Policy [J]. Soft
Science, 2018, 32(02):24-29+49. (in Chinese)
Tang Baojun, Wang Xiangyu, Wang Bin, et al. Analysis
and Prospect of China’s New Energy Vehicles
Industry Development Level [J]. Journal of Beijing
Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition),
2019, 21(02): 6-11. (in Chinese)
Xu J, Hou Q, Niu C, et al. Process Optimization of the
University-Industry-Research Collaborative
Innovation from the Perspective of Knowledge
Management [J]. Cognitive Systems Research, 2018,
52: 995-1003.
Zhong Taiyong, Du Rong, A Research of Subsidies for
New Energy Vehicles Based on Game Theory [J].
Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2015,
23(S1):817-822. (in Chinese)
Research on the Tripartite Evolution Game of Cooperative Relationship of Collaborative Innovation Network of New Energy Vehicle
Industry under the Dominant Roles of Core Enterprises
347
