
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based
on Bibliometrics
Qian Cui and
Zhimo Zhao
Department of Public Affairs and Administration, University of Electronic
Science and Technology of China,
Chengdu, China
Keywords: Digital Governance, Bibliometrics, Knowledge Structure.
Abstract: In the past decades, digital governance has developed into an important research field, which deserves a sys-
tematic review and evaluation of its research status, topic evolution, and research prospects. Based on the
Bibliometrics package, Vosviewer, and Citespace software, this study conducts bibliometric analysis in the
field of digital governance research. The literature sample for this study is obtained from the Web of Science
database, containing 2258 articles. First of all, through the analysis of the number of papers published, deter-
mine the publication trend of digital governance research. Secondly, through the citation analysis between
authors and literature, the highly cited authors and important literature in the field of digital governance are
discussed. Finally, through the knowledge structure analysis of the digital governance research field, includ-
ing author, journal co-citation analysis, topic evolution analysis, and other methods, the topic evolution and
future research direction of digital governance research are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital governance refers to the behavior process of
related affairs involving enterprises, social organiza-
tions, individuals, and other multiple subjects under
the government's leadership, aiming to improve the
level of digital governance by enabling the govern-
ance system through digital technology. Digital gov-
ernance is a multi-level, complex, and dynamic re-
search topic, involving communication, public man-
agement, law, network security, and other disciplines.
And there is a lack of systematic research review on
digital governance. By means of bibliometrics, this
paper deeply analyzes the research topic of digital
governance and its dynamic changes deeply analyze
the existing research content of digital governance,
points out the shortcomings of existing research on
digital governance and puts forward research pro-
spects based on this.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 Bibliometric Method
Bibliometrics is a method based on mathematics, sta-
tistics, and information science to study the develop-
ment trend and subject field of a discipline through
bibliometrics, knowledge graph, data visualization,
and other relevant technical means. The commonly
used tools of bibliometrics mainly include
Vosviewer, Citespace, and the bibliometric toolkit in
R language. This paper uses these three tools to con-
duct an in-depth analysis of the research status of dig-
ital governance.
2.2 Bibliometrics Toolkit in R
Language
Bibliometrics is an R package based on literature net-
work analysis. Compared with other R packages used
for bibliometrics, Bibliometrics has more powerful
functions and a more simple and direct presentation.
The categories of functions of Bibliometrics include
data import, descriptive statistics, co-occurrence ma-
trix presentation, knowledge graph rendering, etc.
Cui, Q. and Zhao, Z.
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based on Bibliometrics.
DOI: 10.5220/0011738700003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 413-422
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
413

This paper attempts to use the toolkit to conduct cita-
tion analysis and theme evolution analysis of relevant
literature on digital governance.
2.3 Vosviewer
Vosviewer is a Java-based free software oriented to
literature data, suitable for the analysis of modular
non-project networks, focusing on the visualization of
scientific knowledge. The core idea of the software is
"co-occurrence clustering," the idea that if two events
occur at the same time, then there is a degree of cor-
relation between them. There are many kinds of rela-
tionships that vary in strength and relationship to each
other. Different types of clusters can be found by
clustering the measurement indicators of relationship
strength and direction. This paper will use this soft-
ware to complete the co-citation analysis and litera-
ture coupling analysis of the digital governance liter-
ature.
3 CITESPACE
Citespace is an information visualization tool devel-
oped by Professor Chaomei Chen from Drexel Uni-
versity in the United States, which is specially used
for academic literature analysis. It is suitable for mul-
tivariate, time-sharing, and dynamic complex net-
work analysis, and can detect hot topics and their evo-
lution in a certain discipline or field. At present, it has
been widely used to detect and analyze the changing
trend of the research frontier, the relationship be-
tween the research frontier and the knowledge base,
and between different research frontiers. This paper
tries to use Citespace software to conduct a co-cita-
tion analysis of digital governance research literature.
4 DATA COLLECTION
In order to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the field
of digital governance, we first collected data from the
Web of Science, including the Citation Index of Nat-
ural Science and Social Science, SCI and SSCI), and
choose 1999-2022 as the literature research time of
digital governance. The main reason for choosing to
start the study in 1999 is that the relevant search terms
are locked in "digital governance". The first title re-
sult is "Winds of Change: Digital technology, trans-
action information, and Intellectual Property manage-
ment" (Tang, 1998). This paper focuses on the impact
of digital governance on global and digital market
formation. After discussion, this paper is considered
the beginning of research related to digital govern-
ance. The research period 1999-2022 is chosen to
help find all articles on digital governance research by
keyword. Then, based on the researchers' understand-
ing of the field of digital governance, "digital govern-
ance", "e-government", "data governance", "algorith-
mic governance" and "platform governance" are se-
lected as the final keywords of digital governance re-
search. Then, the relevant keywords of the selected
digital governance are extracted and analyzed. Fi-
nally, 2258 articles were selected for bibliometric
analysis.
Then the collected data text is analyzed bibliomet-
rically. Firstly, the built-in function of Web of Sci-
ence is used to analyze the number of published arti-
cles included. Then, the Bibliometrics toolkit is used
to analyze the number of published articles, authors,
and citations, followed by word frequency analysis
and topic evolution analysis. In addition, Vosviewer
and Citespace are used for co-citation analysis. Fi-
nally, the research prospect is prospected according
to the analysis results.
5 RESULT
5.1 Annual Publication Trend
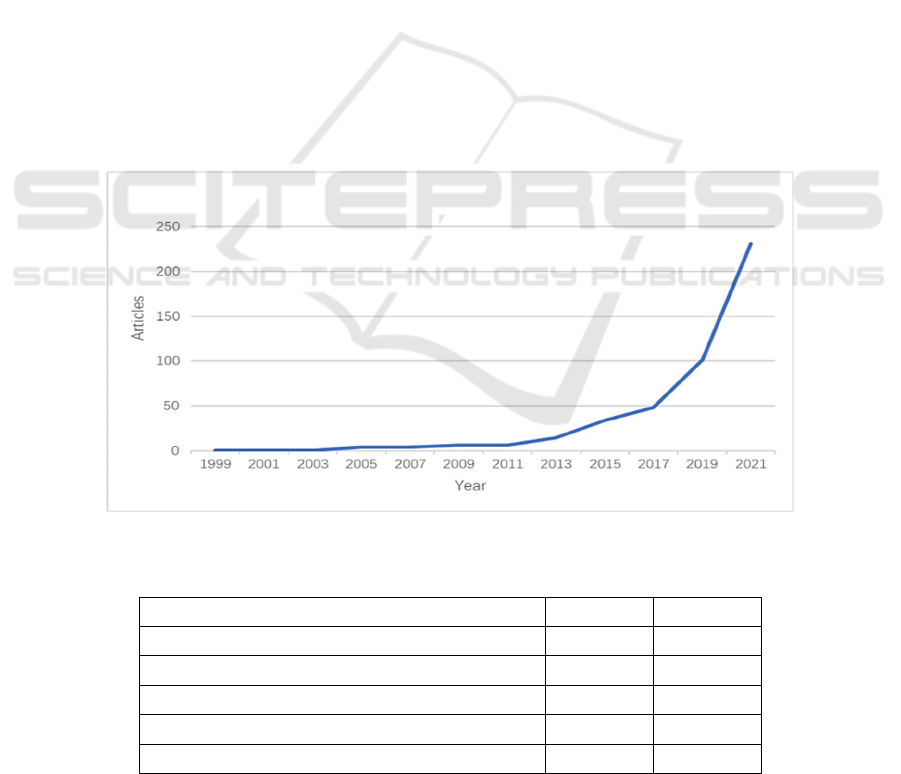
As shown in Figure 1, scholars begin to publish pub-
lications on digital governance in 2003 according to
the time distribution of publication years. The number
of publications on digital governance fluctuates in the
single digits from 2003 to 2011 and increases signifi-
cantly each year from 2011 to 2021. In particular, in
the past two years, the annual increase in articles
reached more than 50. The increase in the number of
papers indicates that digital governance has attracted
more and more attention from the academic commu-
nity, and a large number of research results have been
published exploring the technological construction,
application scenarios, policies, and regulations of dig-
ital governance, etc. This shows that the research field
of digital governance is still in the stage of rapid de-
velopment, the research results are constantly emerg-
ing, and the research prospect is relatively broad.
5.2 Source of Publication
Using the R language Bibilometrics toolkit for "the
most relevant articles" function, to explore digital
governance-related articles of use, The results are
shown in Table 1. Based on the distribution of articles
across journals, the most popular digital governance
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
414
study is Government Information Quarterly, with 36
articles.
Government Information Quarterly is an interna-
tional journal exploring the intersection of policy, in-
formation technology, government, and the public.
This is followed by sustainable development, with 32
and 20 papers published, respectively. The main
themes of Sustainability include definition and quan-
tification of sustainability; sustainable economic de-
velopment and enterprise management. Among them,
the articles related to digital governance published in
this journal mainly discuss digital governance in en-
vironmentally sustainable development and the inter-
relationship between digital governance and sustain-
able governance. In third place is Big Data & Society,
which publishes articles related to digital governance,
mainly including urban case studies of digital govern-
ance and cross-country comparative studies of data
governance.
At the same time, the H index and G index can be
used to comprehensively judge the journal contribu-
tion of digital governance research. The H-index, also
known as the H-factor, is a measure of academic
achievement and represents high citations. It can be
used to evaluate the productivity and citation impact
of relevant publications. The G index is the derivative
index of the H index, which can "average" highly
cited articles to more articles to a certain extent. H in-
dex and G index have both advantages and disad-
vantages, so this paper tries to incorporate both in-
dexes into the evaluation of journal contribution. The
results show that if the H index is used as the evalua-
tion criterion, the index value of Government Infor-
mation Quarterly is 18, ranking first. Public Manage-
ment Review and Sustainability rank second and
third. If the G index is used as the ranking standard,
the Government Information Quarterly is still ranked
first, and Sustainability and Public Management Re-
view is followed by second and third. Through the
above three indicators, it can be seen that the number
of relevant articles published by the Government In-
formation Quarterly, G index, and H index rank first
place in the theme of digital governance. Therefore,
this journal is a core journal in the field of digital gov-
ernance.
Figure 1: Annual Scientific production between 1999-2021 [Self-drawing].
Table 1: Ranking of publication sources based on the number of articles [Self-drawing].
Sources G index H index
Government information quarterly 30 18
Sustainability 17 10
Public management review 15 10
Information communication & society 12 6
Big data & society 10 8
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based on Bibliometrics
415
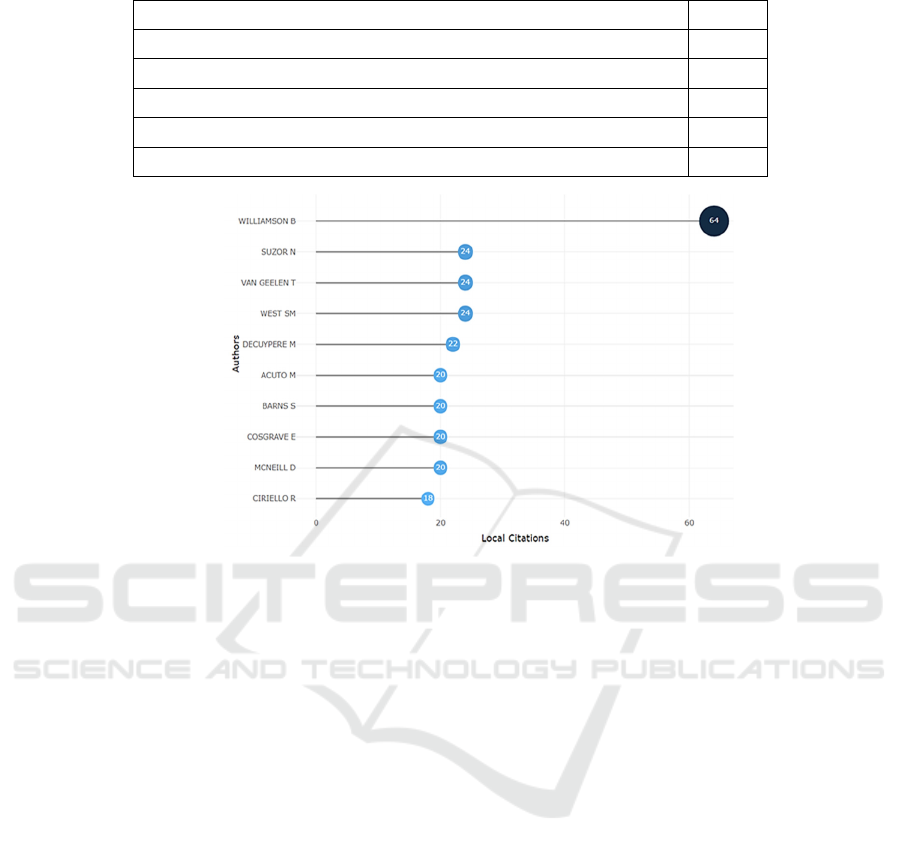
Table 2: Ranking of publication sources based on G index and H index [Self-drawing].
Sources Article
Government information quarterly 32
Big data & society 20
Canadian public administration-administration Publique du Canada 18
International journal of operations& production management 15
Information communication & society 14
Figure 2: Most cited authors within the examined documents [Self-drawing].
5.3 Citation Analysis
Author-cited Analysis.
Citation analysis is used to study the most frequently
cited authors and documents in the academic field.
The number of citations generally represents the con-
tribution of the author or literature to the academic
field. In this paper, the "Most Relevant Authors" fea-
ture in the Bibliometrix toolkit is used to analyze the
most frequently cited Authors in the digital govern-
ance domain, and the results are shown in Figure 2. It
can be seen that WillamSon B is the most cited author
in the field of digital governance, with the number of
citations reaching 64 times. Suzor N, Van Gleen T,
and West S M rank joint second, respectively, with
the number of citations being 24 times.
Literature-citation Analysis.
The literature citation analysis method in the Biblio-
metrics toolkit is mainly implemented through local
literature citation analysis and global literature cita-
tion analysis. This paper tries to use these two meth-
ods to conduct a citation analysis of the relevant liter-
ature on digital governance. At the same time, the
function of "Most Local Cited Documents" in the
Bibliometrix toolkit is used to analyze the Most Cited
local literature in the field of digital governance, and
the analysis results are shown in Table 3. It can be
seen that Williamson B's article "Digital Education
Governance: Data Visualization, Predictive Analyt-
ics, and 'Real-Time' Policy Instruments' are the top
citation with 16 citations (Williamson, 2016). This ar-
ticle focuses on a case study of digital education data
systems, to explore the choice and application of pol-
icy tools for digital education governance. The author
of the second most cited article is still Willamson B,
which mainly discusses the emergence and applica-
tion of digital governance technology in British pub-
lic education (Williamson, 2015). The third to fifth
articles focus on the value assessment of the govern-
ance legitimacy of online intermediaries (Suzor,
2018), the Web presence and improvement measures
of educational digital governance (Barns, 2017), and
the current status and challenges of digital infrastruc-
ture governance (Fung, 2015).
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
416
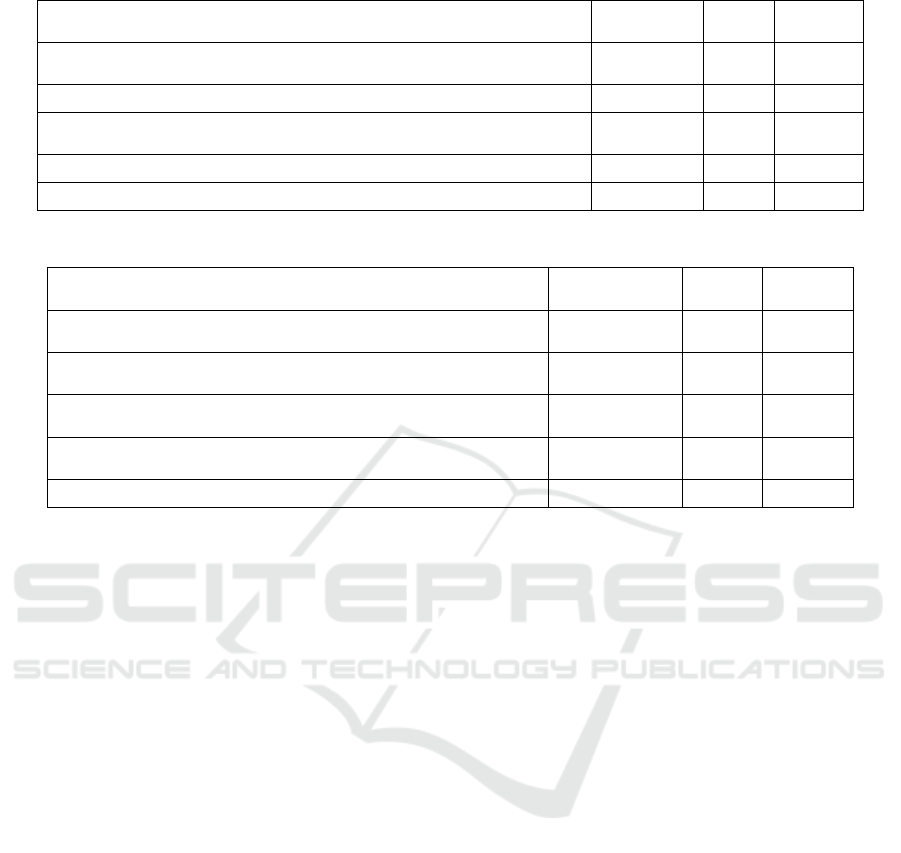
Table 3: Ranking of articles based on Global citations [Self-drawing].
Title Author Year
Global
citations
Putting the Public Back into Governance: The Challenges of Citizen Par-
tici
p
ation and Its Future
Fung A 2015 365
Digital government evolution: From transformation to contextualization Janowski 2015 190
The second wave of digital-era governance: a quasi-paradigm for the
g
overnment on the Web
Margetts H 2013 164
What is platform governance? Gorwa, R 2019 140
Big data in the policy cycle: Policy decision-making in the digital era Hoechtl, J 2016 101
Table 4: Ranking of articles based on Global citations [Self-drawing].
Title Author Year
Local
citations
Digital education governance: data visualization, predictive ana-
l
y
tics, and 'real-time'
p
olic
y
instruments
Williamson B 2016 19
Governing software: networks, databases and algorithmic power
in the di
g
ital
g
overnance of
p
ublic education
Williamson B 2015 13
Digital Constitutionalism: Using the Rule of Law to Evaluate the
Legitimacy of Governance by Platforms
Suzor n 2018 12
Diagrams of Europeanization: European education governance in
the di
g
ital a
g
e
Decuypere M 2016 11
Digital Infrastructures and Urban Governance Barns S 2017 10
Fung A's article "Bringing the Public Back to
Governance: The Challenge of Civic Engagement
and Its Future" is ranked number one in the world's
most cited literature (Fung, 2015). This paper mainly
discusses the value orientation of participatory gov-
ernance. It also highlights the challenges to participa-
tory governance posed by the development of digital
technologies and the growing demands of citizens for
personalized governance. Janowski's article, which
presents a phased model of the evolution of digital
government and provides some evidence to explain
the phased model, comes in second (Janowski, 2015).
The third to fifth literature mainly discusses the gov-
ernance model in the digital era (Margetts, 2013), the
interdisciplinary research paradigm of platform gov-
ernance (Gorwa, 2019), and ICT for policy decisions
(Hochtl, 2016).
Citation analysis only shows the contribution of
authors and documents in the field of digital govern-
ance research to the academic field. However, as a
dynamic research system, the digital governance re-
search field needs to understand the knowledge struc-
ture of digital governance. Knowledge structure
shows research structure and dynamic presentation in
academic research. At the same time, the knowledge
structure is helpful to determine the main theme of
digital management and explore the dynamic changes
between theme analysis, in order to further under-
stand the digital governance research in the field of
knowledge structure, the next will be led by the au-
thor, literature analysis, frequency analysis, theme
evolution analysis, to further explore digital govern-
ance research field.
5.4 Co-Citation Analysis
Author Co-Citation Analysis
The basic assumption of the author co-citation analy-
sis method is: that when the literature of two authors
is cited by the literature of the third author at the same
time, then there is a co-citation relationship between
the two authors. The higher the frequency of co-cita-
tion between two authors, the closer the academic re-
lationship between scholars is. Then, by clustering,
multi-dimensional scale analysis, and other statistical
methods, the author identifies the scientific commu-
nity in the academic field. This paper visually pre-
sents relevant literature on digital governance through
co-citation analysis of Vosviewer software, and the
results are shown in Figure 3. Among them, node size
represents the frequency of authors' common cita-
tions, and different colors of nodes represent different
clusters formed by authors' research.
The co-citation analysis based on the authors re-
veals four clusters formed by digital governance re-
search. As can be seen from Figure 3, the co-cited
sources of the cluster are public institutions repre-
sented by the European Union and the European
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based on Bibliometrics
417
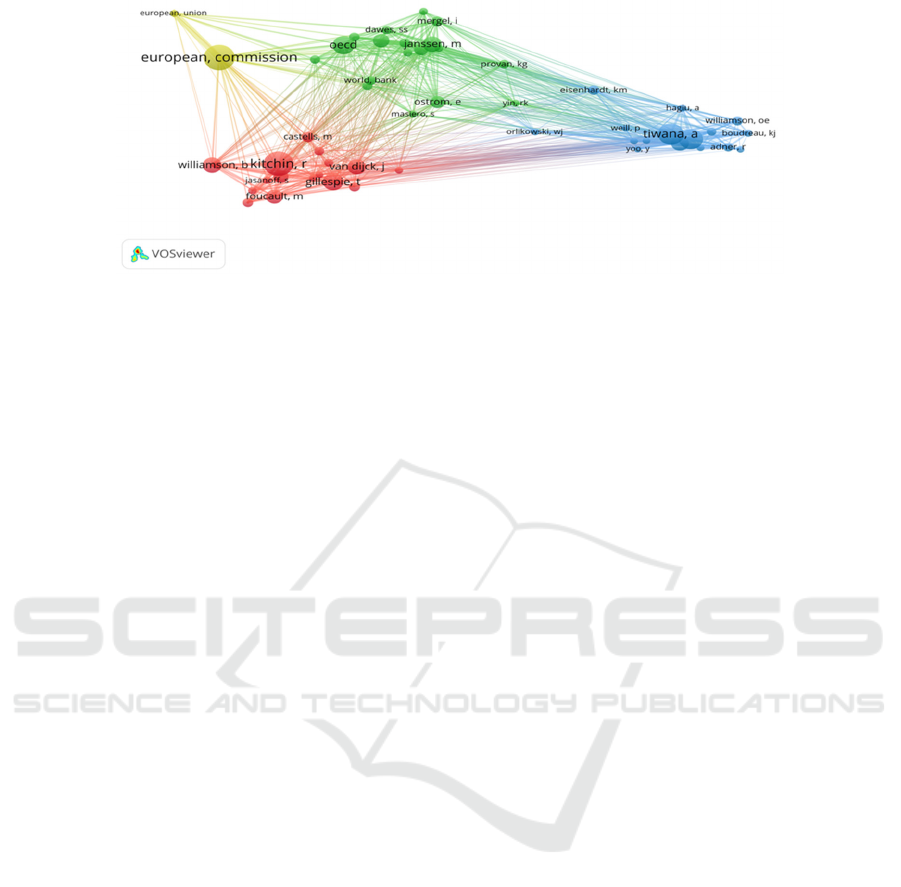
Figure 3: Author co-citation analysis [Self-drawing].
Commission. The cluster mainly involves the formu-
lation of digital governance regulations, the improve-
ment of digital governance policy documents, and the
formulation of national data security regulations and
problem governance. The second basic cluster is
formed around Janssen M, Dunleavy P, and other au-
thors. The research on citizen participation, citizen
empowerment, blockchain governance, digital plat-
form governance, and governance in the digital age is
the core of this cluster. The core authors of the third
cluster mainly include Kitchin R and Williamson B.
This cluster mainly discusses smart city governance
and smart education governance, and the fourth clus-
ter mainly discusses the governance application and
improvement of information technology.
Literature Co-Citation Analysis
The "literature co-citation" function in Citespace soft-
ware is used to conduct knowledge graph analysis on
the paper texts collected by digital governance re-
search. After entering the software and selecting the
project, the time and slice parameters are adjusted,
and the clipping function and path-finding function
are canceled. After selecting "Reference" as the anal-
ysis target, click visualization. After the data visuali-
zation is completed, the Citespace menu bar is used
to adjust the size of labels and lines, and the image
position is adjusted to perform clustering processing.
The TF-IDF algorithm is chosen for clustering pro-
cessing because it has obtained a general consensus
in acad demia. After that, satisfactory maps are ob-
tained by clustering labels and algorithms, and fi-
nally, four digital governance literature clusters are
obtained by literature co-citation analysis. The first
type of literature cluster is named "Public Health
Data".
The literature in this field focuses on the risks and
challenges faced by public health governance in the
era of big data, as well as the countermeasures. The
second kind of literature cluster mainly discusses the
influence and function of the digital economy on so-
cial governance and emergency management. Niu,
FJ, for example, based on the survey of four different
types of employees, adopts a structural equation
model approach to explore the role and mechanism of
the digital economy on socio-economic reform and
governance (Niu, 2022)
.
The results show that there
is a certain degree of relationship between the digital
economy and the social governance system, and the
sustainable digital economy system confirms the me-
diating effect between them. With this revelation, the
government should grasp the connection between
digital economy and governance, and promote digital
economy and digital governance level. The third kind
of literature cluster mainly focuses on data govern-
ance. The main contents of this research focus on the
core ownership, nature, rights, and interests of data
and the discussion of many rights and obligations in
the process of digital governance, such as personal
privacy, data property rights, and digital sovereignty.
The fourth type of document clustering is named
"joint research agenda", this topic mainly discusses
the constitutional governance platform management,
digital and other emerging research fields of digital
governance, needs joint efforts of the scholars to de-
velop related technical framework, to promote the
emerging research paradigm in the field of digital
management to further improve, further enrich the re-
search theory.
5.5 Word Frequency Analysis
Word frequency analysis is a common statistical anal-
ysis technique used in information retrieval and text
mining, which is used to analyze the number of repe-
titions of a word in a text or material database. Word
frequency analysis helps to clarify the key themes
emerging from digital governance research. In this
study, the number of words in the keyword module of
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
418
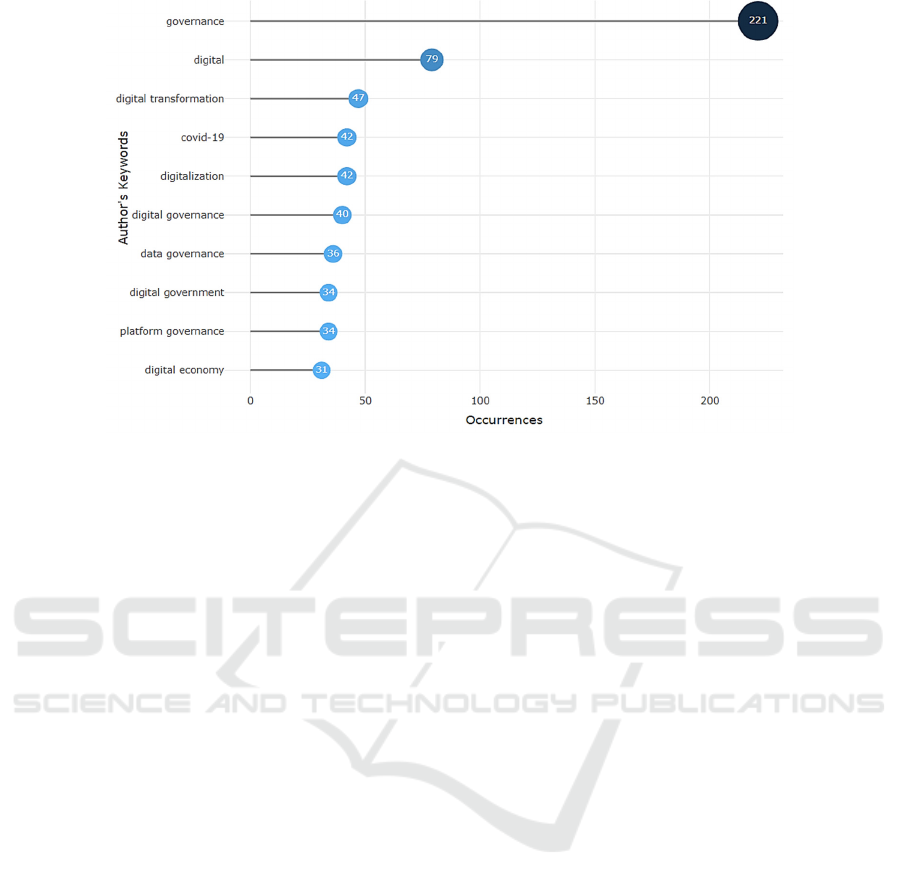
Figure 4: Word frequency analysis [Self-drawing].
the paper is selected as the measurement index, be-
cause the keyword module is more suitable for the
topic expressed in the paper, so the selected words are
more representative. Therefore, through the Biblio-
metrics toolkit in R language, the word frequency
analysis function is used to conduct word frequency
statistics for the keyword module of the relevant lit-
erature on digital governance and the results are
shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that:
The word "governance" appears the most, and the
number of occurrences reaches 221 times. Digital
governance, in the final analysis, is to achieve reason-
able and effective governance of digital scenes, digi-
tal business forms, digital economy, and other rele-
vant digital scenes through digital technologies such
as big data, artificial intelligence, and blockchain.
The terms "technology" and "technological transfor-
mation" rank second and third. It can be seen the im-
portance of the application of digital value technol-
ogy. Digital management is inseparable from the uni-
versal application of technology. Digital management
is equivalent to management with technology to some
extent. Through the application of relevant digital
technologies, governance institutions promote the
modernization, intelligence, and automation of gov-
ernance models.
The term "COVID-19" ranks fourth the number of
times, which reflects the academic community's
widespread concern about the optimization and im-
provement of the global digital governance model.
For instance, Lee and other scholars discuss the spe-
cific role of digital governance in the process of sup-
porting public crisis management in the context of the
COVID-19 pandemic by integrating the relevant
analysis framework through the case study of South
Korea (Lee, 2020).
The academic discussion on
COVID-19 and digital governance provides benefi-
cial enlightenment for the governing bodies to apply
digital governance technology such as health codes to
the practice of public crisis.
"Data governance" is even more frequent, appear-
ing 36 times. Human society has entered the era of big
data, and data elements have become the most critical
digital resource. The main content of digital govern-
ance research focuses on the core ownership, nature,
rights, and interests of data, and discusses many rights
and obligations in the process of digital governance,
such as personal privacy, data property rights, digital
sovereignty, and so on. Therefore, many scholars
have discussed the connotation and system improve-
ment of digital governance from the perspective of
data.
5.6 Strategic Map Visualization
Analysis
On the basis of word frequency analysis, the visual
analysis of strategic maps is helpful to better under-
stand the research topic of digital governance. The
strategic map is composed of two dimensions: cen-
trality and density. Centrality is a measure of the im-
portance of a topic in a research field, and a strategic
density map is drawn by centrality and density, and
the "thematic map" function is realized by the Biblio-
metrix toolkit function. The result is shown in Figure
5.
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based on Bibliometrics
419
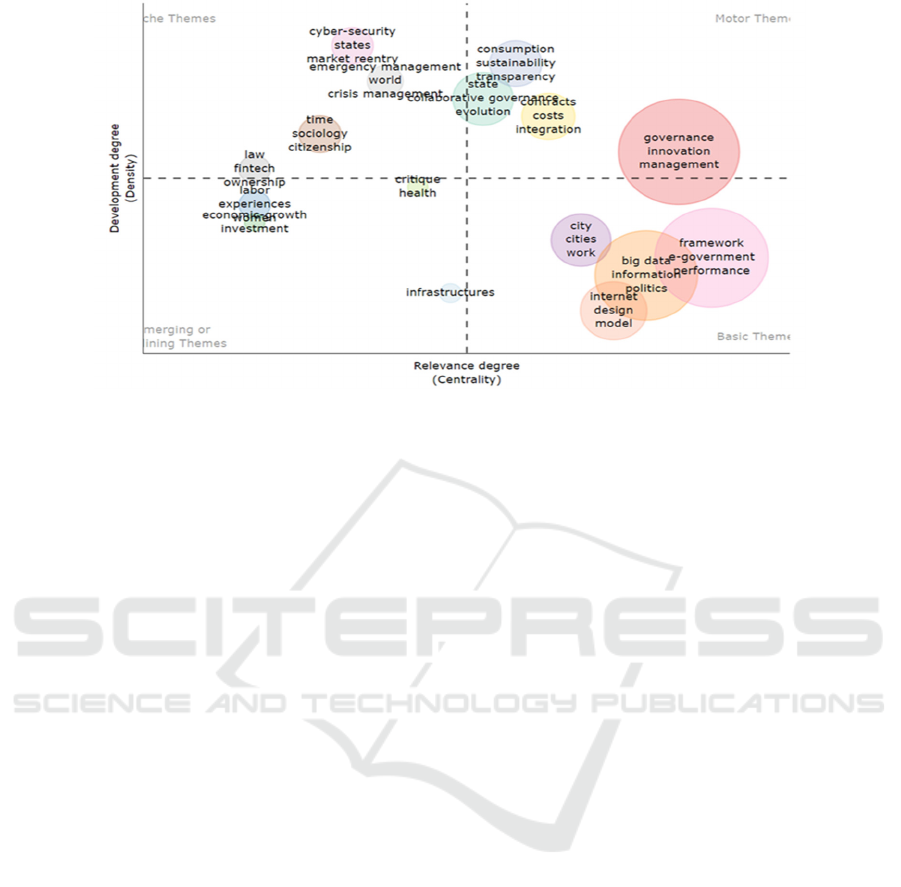
Figure 5: Strategic map visualization analysis [Self-drawing].
The topic located in the fourth quadrant of the
strategy diagram is called the core topic, and it is the
core of all research topics. The core themes of digital
governance mainly include "digital governance inno-
vation", "e-government", "big data governance",
"digital city", "Internet platform governance" and
other related topics. Themes in the second quadrant
of the strategic map are also known as "mobile
themes". The theme of the movement represents the
development theme in the field of digital governance,
which is of great significance to the research of digital
governance. "Digital governance innovation" and
"digital cooperative governance" are the movement
themes of digital governance. The topics covered by
"digital governance innovation" mainly include "gov-
ernance", "innovation" and "management", while the
topics covered by cooperative governance hotspots
include "state", "cooperative management", "docu-
ment analysis" and "evolution". The topic density of
the ecological theme is high, but the centrality is low.
These issues have little impact in areas where internal
links have been established, but their external im-
portance is negligible. "Cyber security" is one of the
ecological themes of digital governance, mainly in-
volving global security digital governance, cyber se-
curity digital governance capacity building, digital
trade and so on.
The topic density of the ecological theme is high,
but the centrality is low. These issues have little im-
pact in areas where internal links have been estab-
lished, but their external importance is negligible.
"Cyber security" is one of the ecological themes of
digital governance, mainly involving global security
digital governance, cyber security digital governance
capacity building, digital trade security strategy, etc.
Emerging or declining topics have low density and
relevance, and may be new or disappearing topics.
Topics in this category include "digital infrastruc-
ture", "digital workforce", "Digital economy and dig-
ital investment", "smart healthcare", etc.
The visual analysis of strategic maps helps to un-
derstand hot themes, movement themes, ecological
themes, and emerging or declining themes of digital
governance, and plays an important role in under-
standing the core concepts of key themes of digital
governance. However, from the time dimension, the
specific situation of the conceptual structure change
in the digital governance domain is not clear. There-
fore, this paper will introduce the theme evolution
analysis method to analyze the evolution of the digital
governance theme in chronological order and discuss
the emergence, development, and evolution process
of the digital governance theme in detail.
5.7 Theme Evolution Analysis
Through visualization tools such as the Sankey dia-
gram, the topic evolution analysis of the digital gov-
ernance research field is carried out. The reason why
the Sankey diagram is used for topic evolution analy-
sis is that the Hat Sankey diagram can effectively de-
scribe the flow of one set of data to another, and can
also reflect the size of the specific data flow through
the block, suitable for topic evolution analysis. At the
same time, this way can be proved by dividing and
comparing different periods. Using the thematic evo-
lution function in the toolkit of the Bibliometrics
package in R language and the time function for time
slicing, 1999 and 2010 are used as the starting point
and compound point of the research to analyze the
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
420
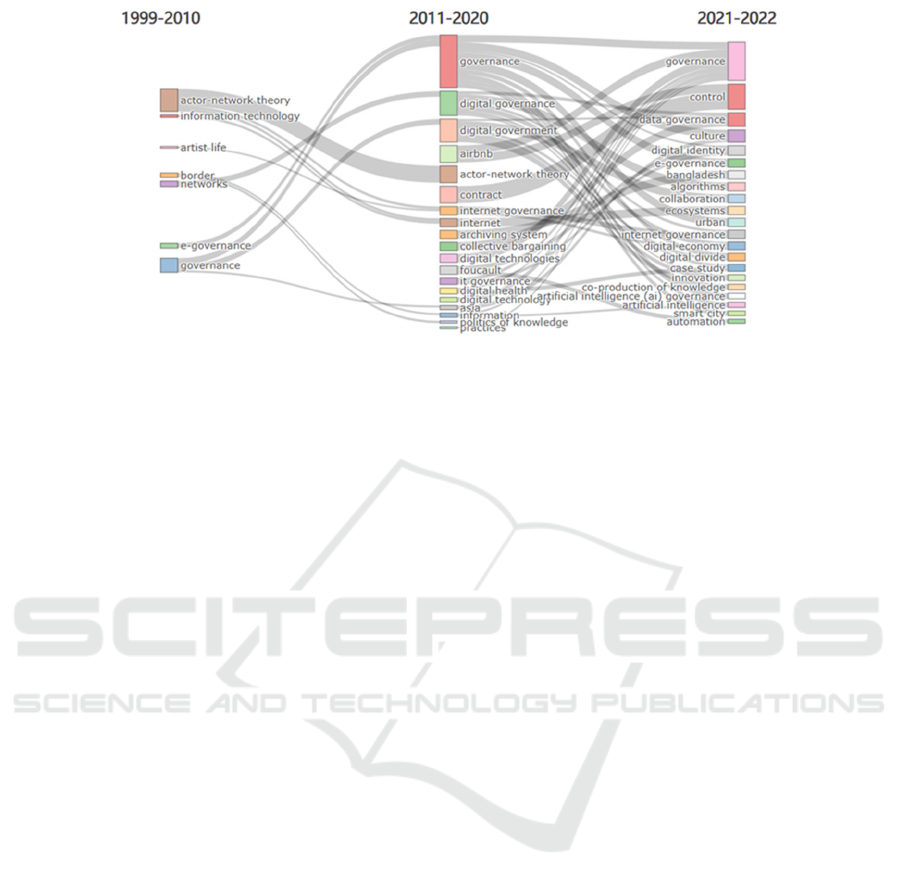
Figure 6: Theme evolution analysis [Self-drawing].
theme evolution of the collected digital governance-
related literature. The results are shown in Figure 6.
In the first period, from 1999 to 2009, "actor-net-
work theory" is the biggest theme in the development
of this field. The actor-network theory provides the
basic theoretical support for digital governance re-
search and the participation mode of governance sub-
jects. For example, other topics include "information
technology", and "e-government. The reason for the
small number of topics is mainly that the research on
digital governance was still in its infancy at that time.
In the second period, from 2009 to 2019, more re-
search topics appear in the field of digital governance,
and relatively important research topics appear in this
period. Digital government is one of them. In addi-
tion, during this period, many new research topics ap-
peared in the field of digital governance, such as al-
gorithm management, application of algorithm tech-
nology, discussion of algorithm discrimination, and
construction of algorithm supervision model. The
emerging themes also include digital health govern-
ance and digital cooperative governance, etc. These
emerging themes mark the research trend and re-
search frontier of algorithmic governance.
In the third stage, the research topics of digital
governance have further changed, and many new re-
search topics have emerged, such as the phenomenon
of convergence in digital governance, smart agricul-
ture, data governance, Internet platform governance,
digital governance under COVID-19, digital trade,
digital finance, etc. At the same time, the basic
themes. That is, the themes of digital government, e-
government, and governance have been further deep-
ened and developed, the research content has been
continuously expanded and the research results have
been constantly fruitful.
6 CONCLUSION
Based on the Bibliometrix toolkit in R language,
Citespace, and Vosviewer software, this paper dis-
cusses the contribution of authors, literature, and jour-
nals in the research of digital governance to the per-
formance of this research field. At the same time, it
discusses the knowledge structure of the field of dig-
ital governance through the co-citation analysis of au-
thors and literature. Preliminary results are obtained:
Government Information Quarterly is the core
journal in this field, and this journal contributes 32
relevant articles to the field of digital governance re-
search. These articles mainly discuss the choice of the
digital governance model and the case analysis of dig-
ital governance countries and cities. Other core jour-
nals in the field of digital governance research include
Sustainability, Public Management Review, Big Data
& Society, etc. After that, the core authors and litera-
ture of digital governance research are identified
through citation analysis. It is found that Williamson
B, Suzor N, Van Gleen T West S M, and others are
the core authors in this field.
Through author co-citation analysis and literature
co-citation analysis, the knowledge cluster of digital
governance research is deeply analyzed. At the same
time, the rise and fall of digital governance research
themes are understood through theme evolution anal-
ysis. The results show that the phenomenon of citizen
collaboration in digital governance, smart agriculture,
data governance, and platform governance become
the frontier directions of digital governance research.
At the same time, there are also the following de-
ficiencies in the research process to be improved;
First of all, bibliometric technology itself has some
Research Progress and Trend Analysis of Digital Governance Based on Bibliometrics
421

shortcomings. Bibliometric technology can only pro-
vide a snapshot of the research field. Researchers
need to combine context, discourse analysis, and nar-
rative analysis to have a more detailed understanding
of the research content. The second is the limitation
of data sources. Core journals in English included in
the Web of Science require high impact factors,
which may exclude good works from newly pub-
lished journals. Based on the above research deficien-
cies, the deficiencies of bibliometric analysis can be
improved through text narrative analysis, meta-anal-
ysis, and other research methods. At the same time,
the index scope can be expanded to include more and
higher quality digital governance articles in the re-
search scope.
REFERENCES
Barns, S., et al., Digital Infrastructures and Urban Govern-
ance. Urban Policy and Research, 2017. 35(1): p. 20-31.
Fung, A., Putting the Public Back into Governance: The
Challenges of Citizen Participation and Its Future. Pub-
lic Administration Review, 2015. 75(4): p. 513-522.
Gorwa, R., What is platform governance? Information
Communication & Society, 2019. 22(6): p. 854-871.
Hochtl, J., P. Parycek, and R. Schollhammer, Big data in
the policy cycle: Policy decision making in the digital
era. Journal of Organizational Computing and Elec-
tronic Commerce, 2016. 26(1-2): p. 147-169.
Janowski, T., Digital government evolution: From transfor-
mation to contextualization. Government Information
Quarterly, 2015. 32(3): p. 221-236.
Lee, D., K. Heo, and Y. Seo, COVID-19 in South Korea:
Lessons for developing countries. World Development,
2020. 135.
Margetts, H. and P. Dunleavy, The second wave of digital-
era governance: a quasi-paradigm for government on
the Web. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Soci-
ety a-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences,
2013. 371(1987).
Niu, F.J., The Role of the Digital Economy in Rebuilding
and Maintaining Social Governance Mechanisms.
Frontiers in Public Health, 2022. 9.
Suzor, N., Digital Constitutionalism: Using the Rule of Law
to Evaluate the Legitimacy of Governance by Plat-
forms. Social Media and Society, 2018. 4(3).
Tang, P. and W. Hulsink, The winds of change: digital tech-
nologies, trading information and managing intellectual
property rights. International Journal of Technology
Management, 1998. 15(8): p. 869-894.
Williamson, B., Digital education governance: data visual-
ization, predictive analytics, and 'real-time' policy in-
struments. Journal of Education Policy, 2016. 31(2): p.
123-141.
Williamson, B., Governing software: networks, databases
and algorithmic power in the digital governance of pub-
lic education. Learning Media and Technology, 2015.
40(1): p. 83-105.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
422
