
Study on the Influence of Government Subsidy on Farmers'
Willingness to Purchase Typhoon Index Insurance
Fang Song
1,2
, Xinyuan Wang
2
and Xuerong Xu
1, *
1
Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, College of Economics and Management, Fuzhou 350001, China
2
Concord University College, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350001, China
Keywords: Government Subsidy, Typhoon Index Insurance, Purchase Intention, Influence Factor.
Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to analyze the influencing factors of farmers' willingness to buy typhoon index
insurance from the perspective of government subsidy policy. In particular, the authors develop the binary
logistic regression model based on the survey data of 124 aquaculture farmers in Fujian Province. The results
showed that the age, input cost and the number of disasters affecting production except typhoon had a negative
effect on the willingness of aquaculture farmers to buy typhoon index insurance. In turn, the number of losses
due to typhoons in the past five years, attitude towards typhoon index insurance and satisfaction with subsidy
policy have a positive impact on the willingness of aquaculture farmers to buy typhoon index insurance. This
study helps to improve the risk guarantee system of aquaculture farmers and the government's subsidy policy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aquaculture industry is an important part of
China' s agriculture. Its output value accounts for 3.5
% of the total agricultural output value, and the total
production can reach 60% of the total world
aquaculture. However, in the contrast to the
prosperity of aquaculture, the development of
aquaculture insurance market in China is lagging
behind. As an industry with strong natural attributes,
aquaculture is affected by typhoon, drought, high
temperature, floods and other natural disasters, and
the situation of “poverty caused by disasters” is
endless. Moreover, in the aquaculture insurance
system is not complete, the huge losses caused by
disasters are almost borne by farmers themselves, the
industry's ability to resist risks is very weak.
Therefore, farmers and even the entire aquaculture
market demand for aquaculture insurance is
increasingly urgent.
In recent years, many scholars have studied the
influencing factors of farmers' willingness to
purchase agricultural insurance. Zheng et al.(2018)
investigated 1280 fishermen in three coastal cities of
*
Corresponding author. Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,College of Economics and Management, Fuzhou
350001,China.
E-mail: 31401969@qq.com.This paper is a phased research result of The National Social Science Fund Project “Statistical
Analysis of the Evaluation Index and Formation Mechanism of Rural Revitalization in China” (No. 19BTJ047)
China, and found that the degree of loss, fishermen' s
awareness of insurance and personal education have
a positive effect on purchase intention, but income
and breeding years have a negative impact on
purchase intention (Zheng, Zhao, 2018). Liu et al.
(2019) took a group of farmers who had suffered
excessive floods as the observation objects, and on
this basis, they searched for the second group of
observation objects who had not suffered floods but
had basically the same other conditions. Through the
investigation and study of the two groups of objects,
they concluded that farmers with corresponding
disaster experience had higher insurance purchase
intention (Liu, Tang, Ge, et al., 2019).
In addition, Oduniyi et al.(2020) used the
conditional value assessment method to locate the
influencing factors of farmers' willingness to buy
livestock index insurance, and found that farmers'
breeding experience, age, education, marital status,
awareness of insurance and family status have a
significant impact on purchase intention (Oduniyi,
Antwi, Tekana, 2020). Ali et al. (2020) randomly
sampled the northern region of Togo, West African
countries, and selected 704 farmer households as the
596
Song, F., Wang, X. and Xu, X.
Study on the Influence of Government Subsidy on Farmers’ Willingness to Purchase Typhoon Index Insurance.
DOI: 10.5220/0011752700003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 596-601
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

respondents to observe the specific factors that affect
the purchase intention of weather index insurance of
the respondents. The analysis shows that the length of
the drought period is the most important factor (Ali,
Egbendewe, Abdoulaye, et al., 2020). Budhathoki et
al. (2019) took the low-lying areas of Nepal as the
research area. Through investigating 350 farmers in
the region, they concluded that the main reason for
the low coverage of local agricultural product index
insurance was related to the pricing of insurance and
government subsidies (Budhathoki, Lassa, Pun, et al.,
2019).
Scholars have analyzed the influencing factors
based on different perspectives and theoretical
systems. However, due to the differences in
geological conditions, climate environment and the
degree of development of agricultural insurance in
different countries and regions, the factors affecting
purchase intention are also different. Most of the
existing literature focuses on the empirical research
of agricultural products in cotton, vegetables, grain
and other planting industries, and the research on
aquaculture insurance is insufficient (Tang, Yang,
Ge, et al., 2019; Roder, Hudson, Tarolli, 2019;
Mutaqin, Usami, 2019; Sarwary, Senthilnathan,
Vidhyavathi, et al., 2020; Shee, Azzarri, Haile, 2020).
Fujian Province is China's second longest land
coastline provinces, land coastline up to 3752
kilometers, accounting for about one sixth of the
country. There are many kinds of aquatic products in
the sea area, and a large number of aquatic organisms
with economic value. However, Fujian Province is
also a severely affected area by typhoon disasters,
which often brings a huge blow to farmers who have
invested high cost in the early stage. In response to
this situation, Fujian Fisheries Mutual Insurance
Association, jointly with Fujian Branch of China Life
and Property Insurance, tailored and launched the
aquaculture typhoon index insurance for the
aquaculture industry in Fujian Province, which was
officially issued and promoted throughout the
province in 2017. With the support of the
Government, the project incorporates a policy
dividend project to support agriculture and benefit
farmers, enjoying 30-40 percent of all levels of
financial subsidies, which greatly reduces the cost of
farmers' purchase. According to the latest “Pilot
Scheme of Typhoon Index Insurance for Aquaculture
in Fujian Province in 2020”, the provincial financial
subsidy of typhoon index insurance is 20% of the total
premium, and the minimum financial subsidy at the
city and county levels is 10%. Conditional cities can
increase the proportion of subsidies according to their
own conditions.
Presently, in order to attract aquaculture farmers
to buy the typhoon index insurance, the government
invested a lot of financial resources. So can these
subsidies increase the purchase intention of
aquaculture farmers as expected? What factors affect
farmers' purchase intention besides financial
subsidies? The exploration of these problems is
helpful to improve the relevant policies of policy-
oriented agricultural insurance, and provide reference
for whether the government provides subsidies and
benefits and what path to subsidize. This paper takes
aquaculture typhoon index insurance as the research
object, analyzes the influencing factors of farmers'
insurance purchase intention by the binary logistic
model based on the micro survey data of aquaculture
farmers in Fujian Province.
2 MECHANISM ANALYSIS
AND MODEL
CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Mechanism Analysis
2.1.1 Mechanism 1: From the Perspective of
Welfare Economics Theory
Traditional welfare economics believes that
increasing the total national income on the production
side and reducing the inequality of income
distribution on the distribution side could improve the
social economic welfare. Through the support and
promotion of typhoon index insurance, the
government establishes a reasonable financial
subsidy system to purchase farmers' fees, which can
improve the participation of aquaculture farmers in
typhoon index insurance, enhance the ability of
farmers to resist risks, and ensure the smooth progress
of the breeding process and the final production
income. This is conducive to the development of
agricultural economy, realize the redistribution of
agricultural part of national income, thereby
increasing the overall welfare of whole society.
2.1.2 Mechanism 2: Market Failure Theory
Perspective
Aquaculture typhoon index insurance as an example
of a class of agricultural insurance market, due to the
existence of moral hazard caused by information
asymmetry, the insurance company's business costs
increase, resulting in the insurance company related
business exit or increase premiums. However, at the
Study on the Influence of Government Subsidy on Farmers’ Willingness to Purchase Typhoon Index Insurance
597
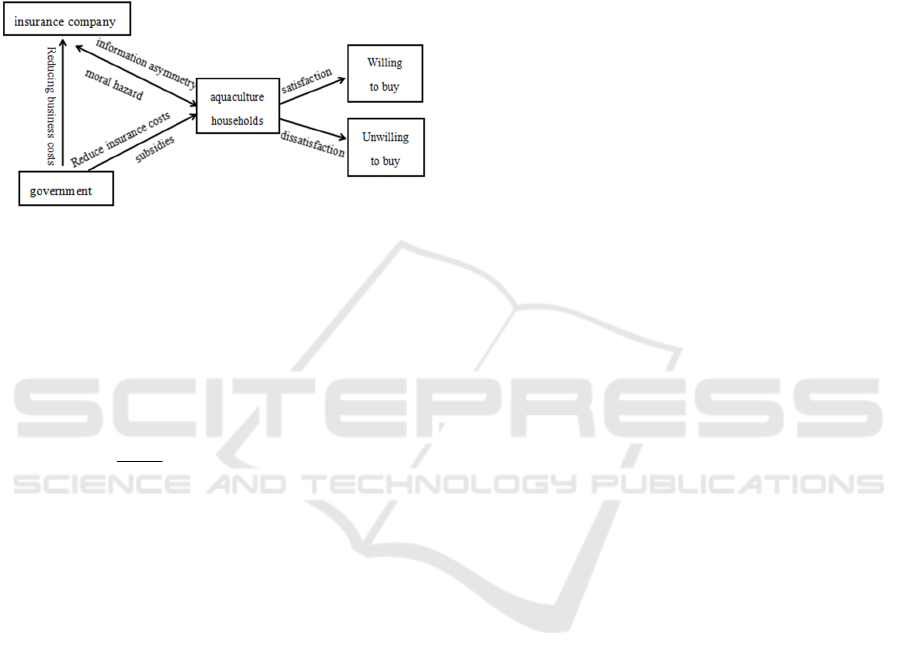
same time, increasing premiums also means that the
cost of farmers' purchase increases, which cannot
meet the insurance needs of farmers, and ultimately
leads to the failure of the relevant agricultural
insurance market. Therefore, the government reduces
the input costs of insurance companies and
aquaculture farmers through financial subsidies and
policy support, so as to solve market failure to a
certain extent.
Figure 1: Influence Mechanism of Financial Subsidies on
Purchase Intention of aquaculture households.
2.2 Model Construction
In order to study the impact of government subsidies
on the purchase intention of aquaculture farmers for
typhoon index insurance, the following binary
Logistic regression model was constructed:
++=
=
n
1
ii0
x
-1
ln
μββ
p
p
Y
(1)
In this model, Y is the dependent variable, when
Y=1, the farmers are willing to purchase the
insurance, in turn, when Y=0, they are unwilling to
buy. P is the probability of aquatic farmers purchasing
typhoon index insurance, and (1-P) is the probability
of non-purchase. The independent variables Xi (i=1,
2,..., n ) represents the factors that may affect
purchase intention. This model select government
subsidies as the key variables, select the age of
aquaculture farmers, farming area, annual investment
cost, the number of losses due to typhoon in the past
five years, in addition to typhoon, there are several
disasters affecting production, the understanding of
typhoon index insurance as the control variable.
0
β
is
the intercept items,
i
β
( i = 1, 2,..., n ) is the coefficient
of each factor, reflecting the influence of each factor
on purchase intention, and μ is the random
disturbance term.
3
DATA SOURCE AND
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
3.1 Data Source
The data used in this study were collected through a
questionnaire of aquaculture farmers in Fujian
Province conducted in 2021.The authors visited
Ningde, Xiapu, Changle, Luoyuan, Lianjiang,
Zhangpu and other major aquaculture producing
areas in Fujian Province, and investigated the
varieties including abalone, clam, yellow croaker,
spotted fish et,al. The survey mainly includes four
parts:(1) the basic characteristics of aquaculture
farmers, namely age and education level:(2) the
aquaculture related information of farmers, including
aquaculture area, annual cost of aquaculture and
annual income;(3) the typhoon disaster situation of
farmers, including the number of losses due to
typhoon in the past five years, the maximum loss
caused by typhoon and several disasters affecting
production in addition to typhoon;(4) the farmers'
awareness of the typhoon index insurance and
whether they are satisfied with the proportion of
government subsidies. After excluding disqualified
questionnaires, 124 valid responses were obtained.
3.2 Descriptive Statistics
Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics of seven
variables. The age span of aquaculture farmers
involved in the survey is large, and the youngest is 22
years old and the oldest is 75 years old. Aquaculture
information is represented by aquaculture area and
cost logarithm. Raising area due to varieties, funds
and other factors affect the individual gap is large, the
maximum reaches 185 acre and the minimum is only
1 acre. When farmers have invested a large amount of
money as a cost, paying premiums means that the cost
of expenditure will be further expanded, and the cost
of many farmers includes part of the borrowing. The
additional cost means that more money will be
borrowed, which virtually increases the degree of
another risk. Typhoon disaster situation is divided
into two control variables : the number of losses due
to typhoon in the past five years and several disasters
affecting production except typhoon. It can be seen
from Table 1 that each aquaculture farmer
participating in the survey has suffered four typhoon
attacks in the past five years on average. Due to the
different geographical locations and geographical
conditions, the number of wind disasters has reached
the maximum of nine.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
598
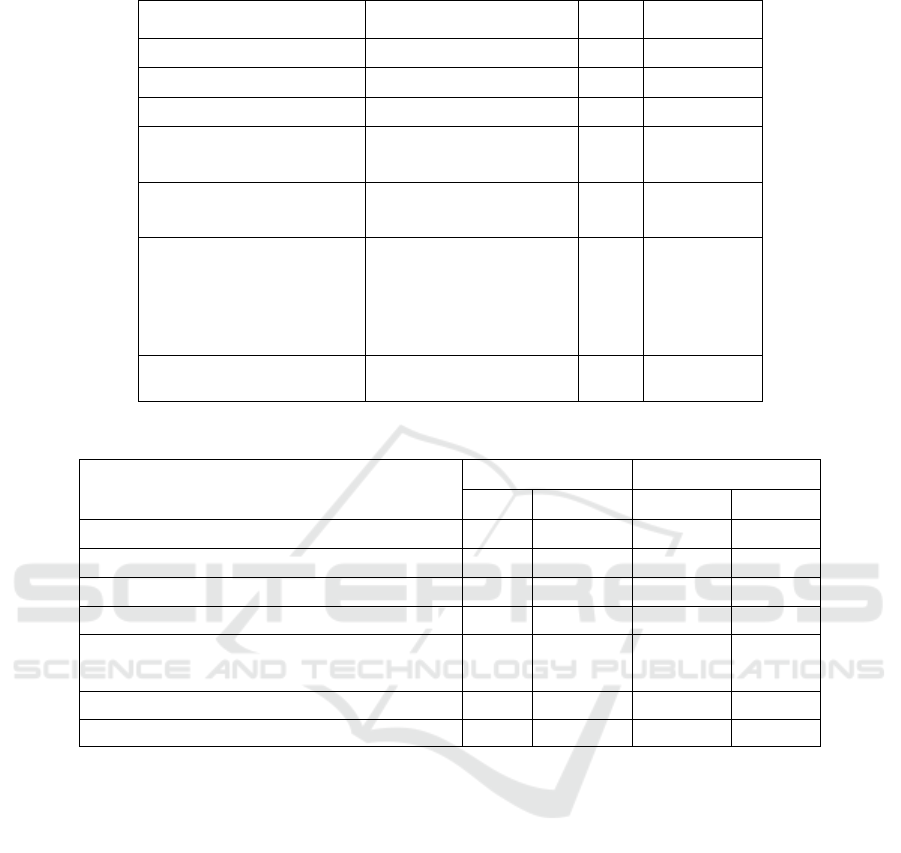
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of variables.
Variable Operational Definition Mean
Std.
Deviation
Age Years old 43.43 11.92
aquaculture area Acre 33.57 27.78
Log(cost) The logarithm of actual cost 3.02 .68
Number of typhoon losses
over the past five years
Number 4.02 2.32
Number of disasters affecting
production other than
t
yp
hoons
Number 1.45 0.87
Attitude towards typhoon
index insurance
1=Completely unimportant,
2=unimportant,
3=not essential
4=more important,
5=very important.
3.27 1.01
Satisfaction with government
subsidy policy
0=No,1=Yes 0.73 0.45
Table 2: Comparison of characteristics of aquaculture farmers willing and unwilling to buy typhoon index insurance.
Variable
Mean Std. Deviation
willing unwilling willing unwilling
age 41.24 49.21 11.27 11.83
aquaculture area 37.97 21.94 30.60 12.63
Log(cost) 3.20 2.56 0.59 0.68
Number of typhoon losses over the past five years 4.72 2.18 2.10 1.82
Number of disasters affecting production other
than typhoons
1.09 2.41 0.53 0.86
Attitude towards typhoon index insurance 3.71 1.97 0.74 0.72
Satisfaction with government subsidy policy 0.94 0.18 0.23 0.39
By comparing the data in the Table2, it can be
found that individual characteristics of two groups of
farmers willing and unwilling to buy typhoon index
insurance are significantly different : the age of
aquaculture farmers who are unwilling to buy
insurance is 8 years old on average higher than that of
those who are willing to buy insurance. The
aquaculture area and cost of the unwilling group were
16 acre and 1.7 less than the willing group,
respectively. In addition, the willing group has
experienced an average of two more wind disasters
that have caused losses over the past five years, while
the unwilling group has experienced an average of
two disasters affecting production other than
typhoons. In terms of attitude towards typhoon index
insurance, the willing group believes that the
insurance is more important than the unwilling group.
The gap between the two groups was the largest in
whether they were satisfied with the subsidy policy.
94% of the farmers in the willing group were satisfied
with the subsidy policy provided by the government,
while only 18% of the farmers in the unwilling group
were satisfied. Preliminary reflects the aquaculture
farmers' subsidy policy satisfaction has a strong
positive impact on purchase intention.
4 RESULTS ANALYSIS
SPSS23.0 and STATA15.1 soft wares were used for
binary logistic regression analysis of each variable.
The heteroscedasticity, multicollinearity and
robustness of the model estimation results are tested
and necessary corrections are made. Table 3 shows
the final results:
Study on the Influence of Government Subsidy on Farmers’ Willingness to Purchase Typhoon Index Insurance
599
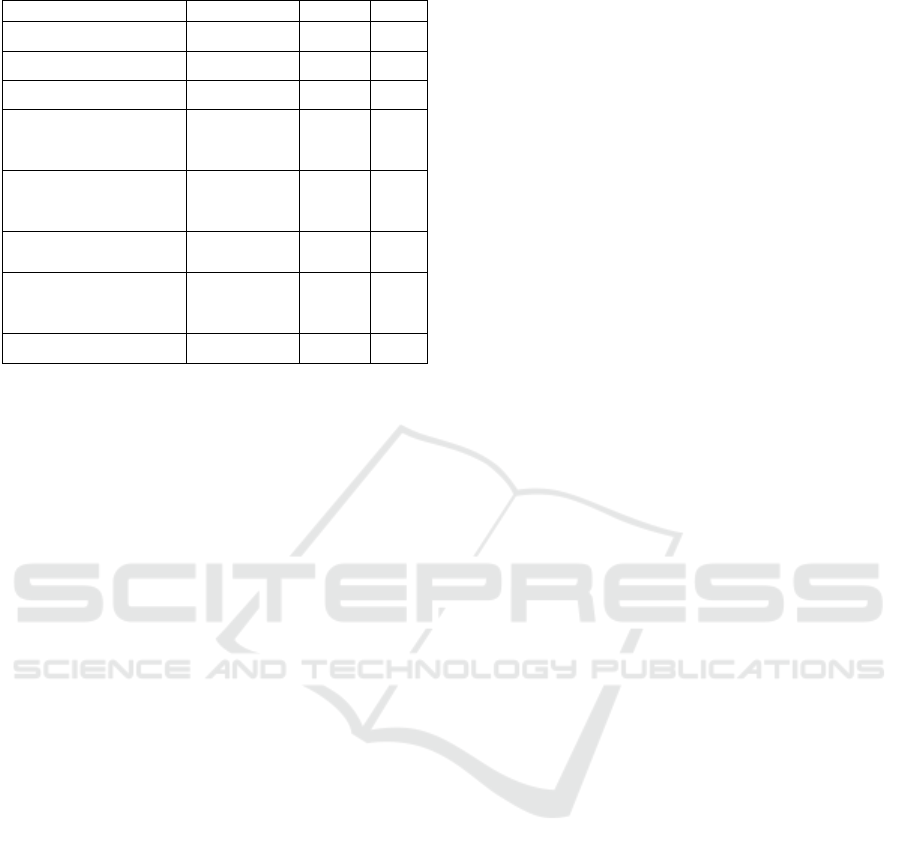
Table 3: Regression results of the binary logistic model.
Variable Coefficients t-value
p
age
-0.1218*** -2.93 0.003
aquaculture area
-0.0059 -0.17 0.865
Log(cost)
-3.6110*** -3.43 0.001
Number of typhoon
losses over the past five
years
1.2999** 2.17 0.03
Number of disasters
affecting production
other than typhoons
-2.8333** -2.36 0.018
Attitude towards
typhoon index insurance
7.0043*** 3.36 0.001
Satisfaction with
government subsidy
p
olic
y
9.6218*** 4.49 0.000
Constant
-5.6351 -1.23 0.217
Note:***,** reflect the 1%, 5%significance levels,
respectively
Individual characteristics of aquaculture farmers have
a negative effect on the willingness to buy typhoon
index insurance, and the statistical results are very
significant, which means that when the age of
aquaculture farmers is older, the willingness to buy
insurance will also decrease accordingly. This may be
because older farmers have lower acceptance of new
things than younger farmers. Older farmers seldom
use computers, smart phones and other equipment in
daily life, so they have fewer opportunities to contact
emerging insurance. Moreover, older farmers often
have richer farming experience, which helps them
avoid risks and resist disasters, so they have lower
demand for insurance.
The statistical results of aquaculture area are very
insignificant, contrary to the original expectations.
The reason may be due to the different varieties and
product value of farmers. The results of cost
logarithm factor are significant under 1 % confidence
interval, and the results have a negative impact on
purchase intention. Further analysis can be found that
aquaculture farmers with higher cost often have
longer farming experience, accumulated a lot of
farming experience, and have more solid disaster
resistance. Moreover, the scale of aquaculture
farmers' early investment costs is huge. If they buy
property insurance, it will be a additional investment
which will cause great economic pressure to them.
Therefore, this factor has a negative impact on
farmers' willingness to buy insurance.
The two variables of typhoon disaster are
significant within 5 % confidence interval. The
number of losses due to typhoons in the past five
years has a positive impact on purchase intention, and
more affected aquaculture farmers have a higher
purchase intention than3.669 times less affected
farmers. When aquaculture farmers lost more times
due to typhoon in recent years, it means buying
typhoon index insurance will be a wise choice. The
other variable has a negative effect on purchase
intention in the direction of several disasters affecting
production except typhoon. The types and times of
disasters that aquaculture farmers may encounter in
the breeding process are different due to different
breeding varieties and breeding regions. When the
types of disasters that aquaculture farmers face are
more, and the damage ability of each disaster is
equivalent, the cost-performance ratio of for a single
disaster will be weakened.
The attitude towards typhoon index insurance
pass the significance test at the level of 1%, and have
a positive effect. The corresponding coefficient is
large, and the occurrence ratio is 1101.327.
Therefore, when the coefficient is positive, it shows
that aquaculture farmers believe that the higher the
value and importance of typhoon index insurance, the
stronger the purchase intention. In fact, farmers'
awareness of the importance of typhoon index
insurance depends largely on whether they
understand the insurance itself and the size of their
risk awareness. When farmers understand the
insurance content more clearly and deeply, the
positioning of its importance will also change
accordingly.
As a key variable, the satisfactory of the subsidy
policy is significant under 1% confidence interval,
and the coefficient is the largest and positive of all
variables involved in the model, which means that
when aquaculture farmers are satisfied with the
subsidy policy provided by the government, their
willingness to buy typhoon index insurance will also
increase accordingly. At the same time, combined
with Table 2, it can be found that 94.44 % of the
farmers who are willing to buy the typhoon index
insurance are satisfied with the subsidy policy, while
only 17.65 % of the farmers who are unwilling to buy
the insurance group are satisfied with the
government's subsidy policy. The gap between the
two groups is as high as 5.35 times, which largely
reflects the important influence of the subsidy policy
in the decision whether the aquaculture farmers will
eventually buy the typhoon index insurance.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
600

5 CONCLUSIONS AND
IMPLICATION
The results show that :age, cost logarithm, the number
of losses due to typhoon in the past five years, several
disasters affecting production except typhoon,
attitude to typhoon index insurance and satisfaction
with subsidy policy are the six control variables
affecting purchase intention. Age, cost logarithm and
the directions of several disasters affecting yield
except typhoon are negative, and the other three are
positive. According to the research results, the
following suggestions are put forward :(1) The
typhoon index insurance should set different rates
according to the differences in breeding varieties to
meet the insurance needs of different types of
farmers; (2) Insurance companies should promote a
correlation system of aquaculture disaster insurance
such as typhoons and floods, red tide, and give
diverse concessions according to the correlation of
different disasters, so that the farmers reduce their
insured cost; (3) The fishery mutual insurance
associations should promote the relative natural
disaster insurance according to the breeding varieties,
and improve the farmers' awareness and risk
awareness of disaster insurance; (4) Governments
should enrich the ways of subsidies, such as the more
innovative “agricultural insurance + credit” policy
and so on. Diversified subsidy channels could
promote the purchase intention of farmers, and attract
more insurance buyers and provide a solid guarantee
for aquaculture.
REFERENCES
Ali, E.; Egbendewe, A.; Abdoulaye, T.; et al. Willingness
to pay for weather index-based insurance in semi-
subsistence agriculture: evidence from northern
Togo[J]. Climate Policy, 2020: 1-14.
Budhathoki, N.; Lassa, J.; Pun, S.; et al. Farmers' interest
and willingness-to-pay for index-based crop insurance
in the lowlands of Nepal[J]. Land Use Policy, 2019, 85:
1-10.
Liu, X; Tang, Y; Ge, J; et al. Does experience with natural
disasters affect willingness-to-pay for weather index
insurance? Evidence from China [J]. International
Journal of Disaster risk reduction, 2019, 33: 33-43.
Mutaqin,D.; Usami,K. Smallholder farmers' willingness to
pay for agricultural production cost insurance in rural
West Java, Indonesia: A contingent valuation method
(CVM) approach[J]. Risks, 2019, 7(2): 69.
Oduniyi, O.; Antwi, M.; Tekana, S. Farmers' Willingness to
Pay for Index-Based Livestock Insurance in the North
West of South Africa[J]. Climate, 2020, 8(3): 47.
Roder,G.; Hudson,P.; Tarolli,P. Flood risk perceptions and
the willingness to pay for flood insurance in the Veneto
region of Italy[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk
Reduction, 2019, 37: 161-172.
Sarwary,M.; Senthilnathan,S.; Vidhyavathi,A.; et al. Socio-
economic Impact of Climate Change, Adaptation and
Determinants of Willingness to Pay for Crop Insurance
in Central Agro-climatic Zone of Afghanistan[J].
Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology,
2020: 83-92.
Shee,A.; Azzarri,C.; Haile,B. Farmers’ willingness to pay
for improved agricultural technologies: Evidence from
a field experiment in Tanzania[J]. Sustainability, 2020,
12(1): 216.
Tang,Y; Yang,Y; Ge,J; et al. The impact of weather index
insurance on agricultural technology adoption evidence
from field economic experiment in China[J]. China
Agricultural Economic Review, 2019, 11(4):622-641.
Zheng, H.; Mu, H.; Zhao, X. Evaluating the demand for
aquaculture insurance: An investigation of fish farmers'
willingness to pay in central coastal areas in China [J].
Marine Policy, 2018, 96: 152-162.
Study on the Influence of Government Subsidy on Farmers’ Willingness to Purchase Typhoon Index Insurance
601
