
Characterization of Low Rank Coal as an Adsorbent Media through
Physical-Chemical Activation Using H3PO4-NaHCO3 as an Activator
Alwathan
1,3
, Siti Hamidah Mohd-Setapar
2,3
, Muh. Irwan
1
and Ramli Thahir
1
1
Department of Chemical Engineering, Politeknik Negeri Samarinda, Jalan Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo,
Kampus Gunung Lipan Samarinda, 75131, Kalimantan Timur Province, Indonesia
2
Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology (MJIIT), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Jalan Sultan Yahya Petra, 54100 UTM Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
3
Razak Faculty of Technology and Informatics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Jalan Sultan Yahya Petra, 54100,
UTM Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Keywords: Activation, Activated Carbon, Adsorbent, Low-Rank Coal, H
3
PO
4
-Nahco
3
Activator.
Abstract: The use of adsorbent media in the form of activated carbon is very necessary, especially in the refining
industry of a product or for handling waste, so far activated charcoal is mostly made from biomass as raw
materials such as coconut shell charcoal, wood, etc. However, by looking at the potential of coal in East
Kalimantan, which has quite abundant coal, especially low-rank coal which is not utilized optimally. Low-
rank coal or known as lignite has less economic value, this is due to its poor quality, low calorific value, and
high sulfur and ash content, making it unsuitable for use as an energy source. However, this low-rank coal
has the potential to be used as activated carbon which is an absorbent medium because it has a fixed carbon
content of 25-30%. As activated carbon, low-rank coal will be very useful to absorb impurities such as color
and dissolved metals. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of low-rank coal which
was activated chemically and physically using the H
3
PO
4
-NaHCO
3
activator. Coal was sieved with a size of
-100+120 mesh and then carbonized at 600
0
C for 3 hours. After that, 20 grams of charcoal was activated using
2.5M H
3
PO
4
-NaHCO
3
2.5M with variations in the activation process of combination activation and non-
combination at temperatures of 700
0
C and 800
0
C. The best results were obtained in the Physico-chemical
combination activation process at a temperature of 800
0
C with a water content of 4.14%; volatile matter
content of 9.58%; ash content of 13.45%; fixed carbon content of 72.81% and iodine absorption of 1163.5129
mg/g.
1 INTRODUCTION
Coal is one of the potential in Indonesia, which is an
energy resource commodity with the largest reserves
in the world. Coal is currently one of the main energy
sources. Indonesia has a large number of coal
reserves, many of which have not been exploited.
Coal exploration is being maximized to meet its use
as an alternative energy source.
East Kalimantan is one of the provinces in
Indonesia that produces the largest coal. Production
in 2017 was 86,101,658.68 tons. Low-rank coal is the
type that produces the most, which is 50% even
though it has a low heat. Subbituminous and
bituminous coal produced 36.6% while anthracite
11.6%.
The properties coal is a heterogeneous mixture of
solids and found in nature in different grades different
from low-rank coal, submit mine, bituminous, and
anthracite. The chemical elements in coal are divided
into 2, namely: organic compounds consisting of
carbon (C) (as aromatic/aliphatic), Hydrogen (H)
(present in the methyl group (-CH3), and the group
methylene (CH2-)), oxygen (O) (present in the
hydroxyl group (- OH), carboxyl (-COOH), carbonyl
(=C=O), and ether (-O-)), Nitrogen (N), Sulfur (S)
(present in the thiolic group (R-SH), and aliphatic
sulfide groups (R-S-R)), and Phosphorus (P). While
the inorganic elements are metals derived from
impurities such as Silica (Si), Aluminum (Al), Iron
(Fe), Calcium (Ca), and Magnesium (Mg).
Low-rank coal has not been utilized optimally
even though the amount is quite large in the territory
290
Alwathan, ., Mohd-Setapar, S., Irwan, M. and Thahir, R.
Characterization of Low Rank Coal as an Adsorbent Media through Physical-Chemical Activation Using H3PO4-NaHCO3 as an Activator.
DOI: 10.5220/0011761400003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 290-294
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of Indonesia. estimated Part of anthracite and
bituminous coal is only 0.3% and 14.3% each while
most are classified as low-rank coal. Low-rank coal
can be added value by making it an adsorbent, where
the low-rank coal must be activated first. Activation
is a process to increase the absorption of adsorbents
by physical means, namely by high-temperature
treatment. A chemical process can be done by adding
a chemical substance (activator) that aims to build
porosity and enlarge surface area (Kirk-Othmer,
1983).
As raw material for the manufacture of activated
carbon, various basic materials that have hydrocarbon
bonds can be used, in this research the coal with the
lowest rank is used. Activated carbon uses coal from
East Kalimantan as raw material requires more
difficult activation compared to raw materials derived
from wood, husks, coconut shells, and others so a
carbonization technique is needed first and a
combination of chemical and physical activation.
Chemical activation involves impregnation of a given
precursor with activating agents such as phosphoric
acid (H3PO4), chloric acid (HCl), nitric acid
(HNO3), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), and alkali metal
compounds. Research with chemical activation of
bituminous coal in East Kalimantan used a
combination of H3PO4-NH4HCO3 activator solution
as discussed in the previous discussion, but in this
research, NH4CO3 will be substituted with NaHCO3
The application of the use of adsorbents is usually in
adsorption technology, which is a process or
phenomenon of accumulation of substances on the
surface of other substances, such events are usually
referred to as absorption of adsorbate molecules. to
the adsorbent surface. (Treybal, 1981)
Adsorbents are solid substances that can absorb
certain components of a fluid phase. In general,
adsorbents are very porous materials. Because the
pores are usually very small, they can be referred to
as nanoparticles with large surface areas. Many
adsorbents that can be used including low-cost ones,
including natural materials, bio-sorbents, and
industrial and agricultural waste materials can be used
because they have a high carbon content and low
inorganic content (Akil Ahmad et al., 2015). One of
the adsorbents is activated carbon which is
amorphous carbon that has a large surface area and
internal volume so that it has a high adsorption
capacity (Ali et al., 2012). It is amorphous carbon that
has a large surface area and internal volume so that it
has a high adsorption capacity. Activated carbon was
a material that has many very small pores (Liu et al.,
2019). These many pores will be able to make
activated carbon have the ability to adsorb various
other substances that are close to it. the wider the
surface of the activated carbon, in principle, the more
pores it has to increase the surface area, then several
materials containing activated carbon will be present
(Jawad et al., 2019; Lilibeth et al., 1996). There were
at least 2 ways that can be done for activation, the first
is a physical process, namely by using a high
temperature, and the second is through a chemical
process, namely using certain chemicals that can be
in the form of acids or bases, or even a combination
of both (Han et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2020).
Research conducted by Ghafarunnisa et. al
(2017), namely the manufacture of activated carbon
through the carbonization and activation stages
carried out at a temperature of 600
o
C for 3 hours.
Activation is carried out twice, namely chemical and
physical activation. Chemical activation using a
single reagent, namely a solution of H
3
PO
4
, and a
combination reagent, namely a solution of H
3
PO
4
-
NH
4
HCO
3
at a temperature of 600
o
C for 2 hours
showed the best-activated carbon activated by the
combination reagents H
3
PO
4
2M - NH
4
HCO
3
2M and
H
3
PO
4
2.5M - NH
4
HCO
3
2.5M. In general, activated
carbon does not meet the standards of SNI 06-3730-
1995. However, this study shows that the single
reagent H
3
PO
4
and the combination reagent H
3
PO
4
and NH
4
HCO
3
are good reagents for chemical
activation.
In this study, H
3
PO
4
-NaHCO
3
activator was used,
the use of this activator will produce H
2
CO
3
and
Na
3
PO
4
compounds where Na
3
PO
4
can reduce ash
because it can bind calcium magnesium and silica
(Saragih, 2009) while H
2
CO
3
can dissolve calcium
(Tahrini, et al, 2009). The results to be achieved from
this study are focused on the effect of carbonization,
chemical activation using H
3
PO
4
-NaHCO
3
, physical
activation, and Combination Chemical-Physical
activation on the quality of activated carbon in order
to increase the economic value of low-rank coal
which is abundant in East Kalimantan as an
alternative raw material for making activated carbon.
2 METHODOLOGY
First, the brown coal is reduced to -100+120 mesh,
then carbonized at T=600
0
C for 3 hours, then
chemical activation of the carbonized brown coal is
soaked using 2.5 M H
3
PO
4
solution - 2.5 M NaHCO
3
in 8 hours. The immersion results obtained were then
washed with distilled water until the pH was neutral
and then placed in an oven to remove the water
content at a temperature of 105
0
C and physical
activation was carried out by heating at T=800
0
C for
Characterization of Low Rank Coal as an Adsorbent Media through Physical-Chemical Activation Using H3PO4-NaHCO3 as an Activator
291
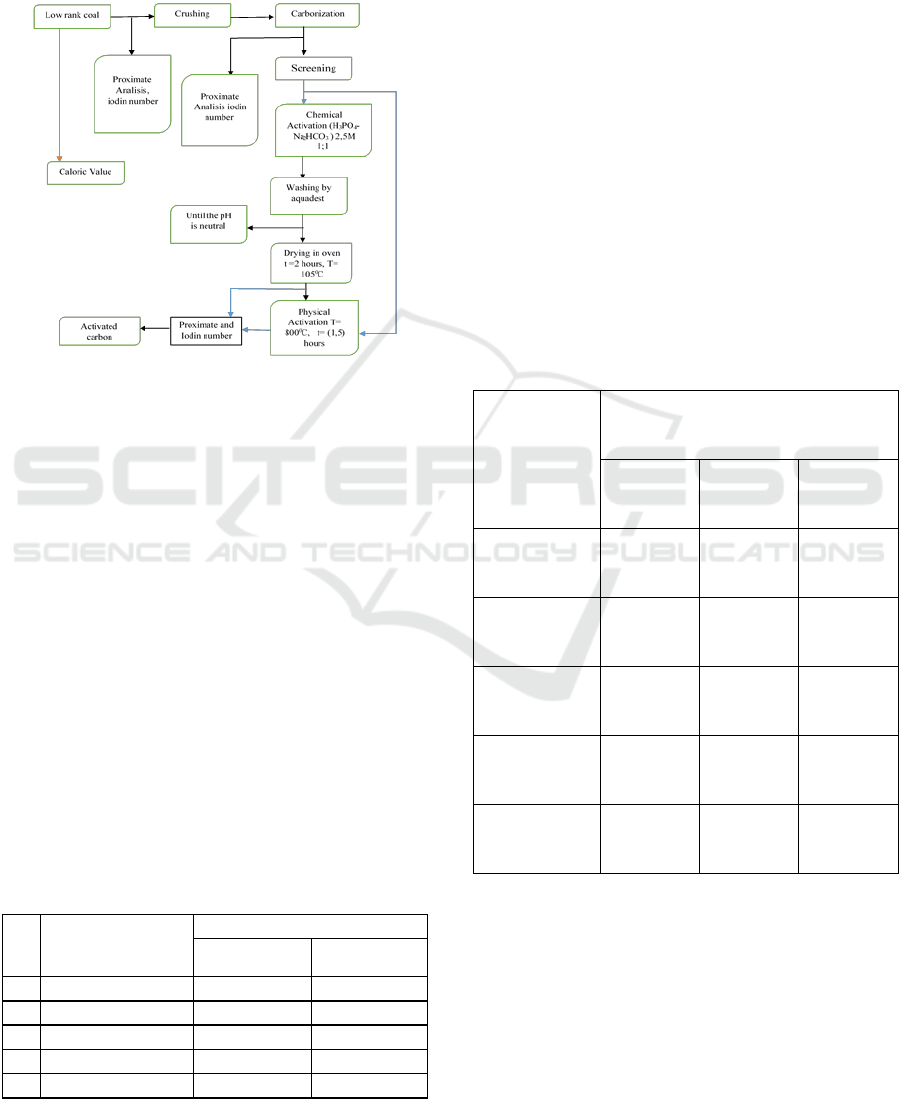
1 hours. remove it and let it cool in a desiccator then
perform proximate testing including analysis of
inherent moisture, ash content, volatile matter, fixed
carbon, and iodine absorption test. The procedure of
the process can be described as shown in the figure
below, namely in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Procedure of the process system.
The proximate analysis to determine the content
contained in brown coal activated carbon includes
water content analysis using the ASTM D7582-15
and iodine adsorption using titrasi iodometri.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The coal used in this study is low-rank coal. Testing
the calorific value of low-rank coal, the results show
that the calorific value of the coal used is 3804 cal.
The results obtained are analyzed after the
carbonization process is carried out to determine the
effect of carbonization on low-rank coal and is used
as the basis for the initial conditions of low-rank coal
before further activation, proximate analysis includes
analysis of water content, ash content, volatile matter
content and iodine absorption in table 1 below
Table 1: The effect of Carbonization process to proximater
parameter.
No
Parameter
Content
Low-Rank Coal
Low-Rank Coal
Crabonization
1
Moisture (%)
37,72
6,16
2
Ash (%)
5,49
8,27
3
Volatile Matter (%)
32,59
14,8
4
Fixed Carbon (%)
24,21
64,62
5
Iodin Number
103,145 mg/g
664,1745 mg/g
The characteristics of low-rank coal that have
been carbonized are affected by high temperatures
causing the surface area of low-rank coal to open but
it is not significant to become activated carbon,
obtained water content of 6,16%, volatile matter
content 14.80%, fixed carbon content 64.62%, ash
content 8.72% and iodine adsorption 664.1745 mg/g.
The value of iodine adsorption has a correlation with
the surface area of activated carbon, the greater the
iodine number, the greater its ability to adsorb
adsorbate or solutes. the carbonization process has a
significant effect due to the decomposition of organic
compounds that make up the structure of the material
to form methanol, vapor, tar, and hydrocarbons, this
is characterized by reduced volatile matter and
increased moisture content when carbonization is
carried out. But something different happens when
low rank coal is activated by using chemicals and
raising the temperature to 800
0
C to increase the
activation effect, the proximate results of the three
variation methods can be seen in table 2 below.
Table 2: The effect of Activation Process
Parameter
Activation Proccess
Chemical
activation
Pysical
activation
Chemical-
Physical
activation
Moisture
Content
(%)
6,78
4,44
4,14
Ash Content
(%)
11,92
16,01
16,45
Volatile
Matter
(%)
12,84
10,14
7,46
Fixed Carbon
(%)
67,52
69,40
67,81
Iodin Number
mg/g
689,3657
976,0039
1163,5129
Table 2 shows how the influence of the activation
activation process, the activation carried out includes
chemical and physical activation and combines both
physical and chemical activation. The following
graph below shows the the all of process effet to
proximate analyzed carried out on water content, ash
content, volatile content, fixed carbon and iodine
adsorption number, the following is graph 1 is about
the process efect to mosture content.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
292
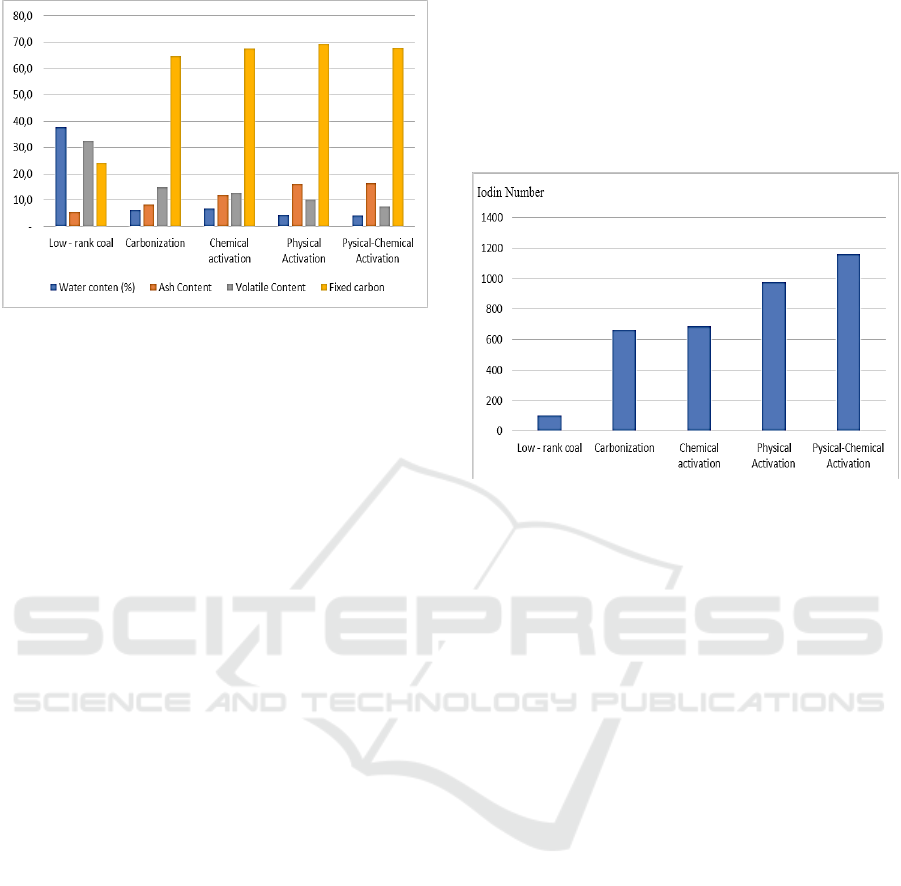
Figure 2: The time effect of brown coal activation.
Figure 2 Water content tends to decrease along
with different activation treatments, this is because
thermal and chemical effects have a significant
influence on the amount of bound water, the heating
process can encourage water particles trapped in the
coal, and chemical chemicals also have an influence
on the amount of water content for each activation
treatment, the water trapped in the cavities of the
activated carbon will be increasingly dehydrated by
the activating agent which results in more water being
absorbed by the activator because Na
3
PO
4
is a
compound which is a dehydrating agent..
This increase in ash content is due to the water
content in activated charcoal being much reduced
when heated, but the inorganic compounds that make
up the ash are relatively constant so that the
percentage of ash content will increase. The activator
substance also affects the amount of ash content if the
temperature used is relatively high with a longer time,
the ash content increases in the physico-chemical
activation process because the metals that make up
the activator material are oxidized to metal oxides.
The decrease in volatile matter levels is possible due
to the presence of volatile compounds that dissolve
with the addition of chemical activators on chemical
activation and evaporate during the physical
activation period at a temperature of 800oC. Acidic
compounds in the form of H
2
CO
3
break down into
H
2
O and CO
2
. The CO
2
generated from the thermal
activation period makes CO
2
trapped in activated
carbon which can encourage and increase levels of
volatile substances but the carbon content will remain
but is determined by the content of other impurities
such as water content, ash content and volatile
substances. The higher the moisture content, ash
content and volatile matter, the lower the fixed carbon
value. From the results of the study, it can be seen that
the increase in fixed carbon content is caused by a
decrease in water content and volatile matter, while
the ash content tends to increase due to the presence
of an activator composed of minerals.
Another important parameter is the iodine number,
as shown in the figure below which shows a
significant increase in iodine adsorption after
activation.
Figure 3: The effect activation process for iodin adsorption
number.
Based on Figure 3 shows the increase in iodine
uptake in each different process treatment. The
significant difference can be seen very clearly that the
iodine adsorption number increases very much after
being treated with carbonization and activation of the
initial low rank coal state, the optimum value
achieved exceeds the requirements of SNI No. 06-
3730-1995 which is 750 mg/g which in this study
physical-chemical activation gave the result of iodine
absorption of 1163.5129 mg/g. The use of chemical
compounds in the activation process causes activating
mineral elements to enter between the crystal
hexagon plates and separate the initially closed
surfaces and break the carbon chain of organic
compounds, contact time or immersion time has a
significant effect on activation. process. When
physical activation is carried out by heating at high
temperatures, the contaminant compounds that are in
the pores become more easily released. This causes
the active surface area to increase and increases the
ability of low rank coals to become good adsorption
agents.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The best results in the process of making activated
charcoal from browncoal from Kutai Kertanegara,
East Kalimantan based on variations in the activation
process treatment using and without using H3PO4-
Characterization of Low Rank Coal as an Adsorbent Media through Physical-Chemical Activation Using H3PO4-NaHCO3 as an Activator
293

NaHCO3 activator, the best conditions were obtained
in the combination treatment of physico-chemistry
with the results of the proximate parameter being
activation with a water content of 4.14%, ash content
16.45%, volatile content 7.46%, fixed carbon content
67.81% and iodine adsorption number 1163.5129
mg/g.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank the Research and
Development Center of the Samarinda State
Polytechnic which has funded this research, and also
to the Chemical Engineering Laboratory of the
Samarinda State Polytechnic as the research site. and
special thanks to Razak Faculty of Technology and
Informatics, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia who helped push this article
REFERENCES
Akil Ahmad, Siti Hamidah Mohd-Setapar, Chuo Sing
Chuong, Asma Khatoona, Waseem A. Wanic, Rajeev
Kumard and Mohd Rafatullah, (2015), Recent
Advances in New Generation Dye Removal
Technologies: Novel Search of Approaches to
Reprocess Waste Water , Jurnal Royal Society of
Chemistry
Ali I, Asim M, Khan TA (2012). Low cost adsorbents for
the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater.
Journal of Environmental Management 113: 170-183.
Han, Z., Guo, Z., Zhang, Y., Xiao, X., Xu, Z., & Sun, Y.
(2018). Adsorption-pyrolysis technology for recovering
heavy metals in solution using contaminated biomass
phytoremediation. Resources, Conservation and
Recycling, 129, 20-26.
Jawad, A. H., Ismail, K., Ishak, M. A. M., & Wilson, L. D.
(2019). Conversion of Malaysian low-rank coal to
mesoporous activated carbon: Structure
characterization and adsorption properties. Chinese
Journal of Chemical Engineering, 27(7), 1716-1727.
Kusdarini, et al, (2017). Production of Activated Carbon
from Bituminous Coal with H3PO4 Single Activation,
Combination of H
3
PO
4
-NH
4
HCO
3
, and Thermal. Adhi
Tama Institute of Technology Surabaya. Mining
Engineering.
Lilibeth l, Shigehisa I, Yuji I, Toshimitsu M (1996)
Research and Development of Carbon Compositesfrom
Wood Charcoal for Environmental Clean-up and their
Applications. Wood research Journal 83: 43-46.
Liu, J., Zhang, Q., Liang, L., & Huang, W. (2019). Study on
the Catalytic Pyrolysis Mechanism of Lignite by Using
Extracts as Model Compounds. Catalysts, 9(11).
doi:10.3390/catal9110953
Patmawati, Y and Kurniawan, A. (2017). Utilization of East
Kalimantan Lignite Coal into Activated Carbon.
Samarinda State Polytechnic. Chemical Engineering.
Rahim, M and Indriyani, O.S. (2010). Production of
Activated Carbon from Low Rank Coal. Journal of
Perspective Media Technology. Thing. 40-44.
Saragih, R. (2009). Determination of Phosphate Levels in
Recovery Boiler Feed Water by UV-VIS spectrometry
method at PT Toba Pulp Lestari, Tbk- Porsea.
University of Northern Sumatra. Medan.
Tahrini, W et al. (2009). Effect of Carbonic Acid (H
2
CO
3
)
on the impact strength of limestone aggregates.
Udayana University. Denpasar.
Treybal, R. E. (1981), Mass Transfer Operation.
SingaporeMcGraw-Hill Book Company
Yan, J., Liu, M., Feng, Z., Bai, Z., Shui, H., Li, Z., Yan, H
(2020). Study on the pyrolysis kinetics of low-medium
rank coals with distributed activation energy model.
Fuel, 261. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116359
Kirk-Othmer, E. (1983). of Chem. Tech.,, 1, 733-739.
Ghafarunnisa, D. (2017). Pemanfaatan Batubara Menjadi
Karbon Aktif dengan Proses Karbonisasi dan Aktivasi
Menggunakan Reagen Asam Fosfat (H3PO4) dan
Ammonium Bikarbonat (NH4HCO3). ReTII..
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
294
