
E-Government Towards Smart City: Using of the "SIKESAL"
Application to Improve Public Services in Jambi City
Diva Umayah
1
, Titin Purwaningsih
1
, Dimas Subekti
2,*
and Misran
2
1
Department of Government Affairs and Administration, Jusuf Kalla School of Government, Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Government Affairs and Administration, Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: E-Government, Smart City, Public Service, SIKESAL Aplication.
Abstract: The use of applications by the government is one of the ways to provide public services today due to the
rapid development of technology and information. Therefore, this study aims to explain using the
"SIKESAL" application created by the Jambi City Government to improve public services. This research
method is qualitative, using a descriptive approach. This study uses NVIVO 12 plus software to analyze the
data. Findings in this study, the "SIKESAL" application has a main menu with the name "send the report"
used for reporting. The application also has a menu that contains an archive of complaints that have been
reported, as well as seeing responses from regional organizations. The actors involved in using the
"SIKESAL" application are the Jambi City regional apparatus organization and the application user
community. The Department of Communication & Informatics has a role as the leading implementer and
the secretariat of complaints. Then the response of the people of the city of Jambi using the "SIKESAL"
application is dominant to negative. The adverse reaction to using the "SIKESAL" application is more for
technical reasons so that the essence of public services is disrupted.
1 INTRODUCTION
Public services are part of a network of players
whose direct and indirect interactions do not exist in
isolation but rather as part of a larger ecosystem.
The use of applications is one of the ways of public
service today because of advances in technology and
advanced information used by humans(Hodgkinson,
Hannibal, Keating, Chester Buxton, & Bateman,
2017). Jambi City is one area that receives guidance
from the Indonesian government to implement
intelligent cities in improving public services. Jambi
City's use of information and communication
technology has been contained in the first vision and
mission of the Jambi City Medium Term
Development Plan 2018-2023, namely strengthening
the bureaucracy and improving information
technology-based public services(Nugroho, 2020).
"SIKESAL" is an application for complaints and
aspirations submitted by the people of Jambi City to
the Jambi City government in the form of online
contributions of thoughts, ideas, suggestions, or
complaints that can only be explicitly accessed by
people who have a Jambi City Population
Identification Number. However, some problems are
the absence of a particular budget from the Jambi
City Regional Budget for developing the
"SIKESAL" application. Then the lack of
socialization of the "SIKESAL" Application, which
is only about 0.16% (1000+) of Jambi City residents
who download this application. As well as the
incompatibility of implementing this application
with the established regulations, such as when
responding to public reports that are old/exceeding
the standard limit(Ahmad, 2021).
The importance of this research is because the
"SIKESAL" application was launched as a form of
improving public services for the Jambi City
government. So its use in the community becomes a
vital component to be considered a reference for the
successful implementation of the policy. The
performance of public services is the government's
effort to fulfill every community's basic needs and
civil rights for goods, services, and administrative
services provided by public service
providers(Usman, 2011).
Several previous studies are pertinent to this
topic, which addresses the WeLive framework, a set
12
Umayah, D., Purwaningsih, T., Subekti, D. and Misran, .
E-Government Towards Smart City: Using of the "SIKESAL" Application to Improve Public Services in Jambi City.
DOI: 10.5220/0011821300003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 12-18
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of tools that combines Open Innovation, Open Data,
and Open Data Services paradigms to enable co-
created urban apps(Emaldi, Aguilera, López-de-
Ipiña, & Pérez-Velasco, 2017). In Germany, mobile
crisis applications are being used. Mobile crisis
applications, which are relatively new public
services for citizens and are specifically meant to
spread disaster-related information and
communication between authorities, organizations,
and citizens, are increasingly being investigated by
crisis informatics(Kaufhold, Haunschild, & Reuter,
2020). Contact tracing is a typical surveillance
technique for locating, analyzing, and managing
persons who have been exposed to novel infectious
illnesses. COVID-19 is managed through mobile
phone apps that employ a digital technology
approach known as "proximity tracking" (Pillai,
Siddika, Hoque Apu, & Kabir, 2020). The
determinants of citizens' future use of government-
provided mobile applications(Reddick & Zheng,
2017). Citizen-government applications in
information use, service use, and participatory use. It
explores the impact of such use on citizen
compliance and the mediating role of trust in
government(Wang, Chen, Xu, & Leng, 2020).
Based on this explanation, several previous
studies focused on how the application works and
the determinants of people using government
applications. So the novelty of this research is the
focus on the use of applications launched by the
government to improve public services. Therefore,
this study aims to explain using the "SIKESAL"
application created by the Jambi City Government to
improve public services.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Smart City
The term "smart city" refers to using ICT to
sense, analyze, and integrate critical data from
core municipal systems. Smart cities may
simultaneously respond intelligently to a variety
of needs, including daily life, environmental
protection, public safety, and local services, as
well as industrial and commercial activity
(Zhang, 2010). The phrase "smart city" refers to
the idea of applying the "smart planet" concept
to a specific place to create informative and
integrated city administration. It's also the
successful combination of intelligent planning
principles, intelligent building processes,
intelligent management methodologies, and
innovative development strategies(Su, Li, & Fu,
2011).
The way cities organize policymaking and
urban expansion is changing due to information
and communication technologies. Smart Cities
use information and communication technology
to alter city infrastructure and services in
various disciplines, including economy,
environment, mobility, and governance(Bakıcı,
Almirall, & Wareham, 2013). Intelligent city
policies foster new methods of conceiving,
organizing, and controlling the city and its
flows while imbuing the city with a new moral
order by establishing technical parameters that
distinguish between "good" and "bad" cities. As
a result, the smart city could effectively
generate docile subjects and political legitimacy
processes (Nam & Pardo, 2011).
2.2 E-Government in Public Service
E-government will improve public services by
transforming the functioning of public sector
organizations. E-government can improve
public service delivery by boosting efficiency,
lowering operational costs, increasing access to
services, and raising consumer satisfaction
(Osei-Kojo, 2017). E-government is constantly
evolving for various reasons, including
providing high-quality services to citizens and
businesses, improving public sector efficiency,
reducing government administrative burden,
allowing for cost savings in government
administration, and increasing government
decisions and actions transparency. "The use of
ICTs in public administrations combined with
organizational reform and new skills to improve
public services and democratic processes and
strengthen support for public policy," according
to this definition. E-government is seen as a
catalyst for improved government and higher
public value (Georgiadis & Stiakakis, 2010).
E-government applications improve the
public sector's cost efficiency and effectiveness
and bring about a revolutionary change in
public service delivery, administration, and
public involvement. Because of the use of ICT
E-Government Towards Smart City: Using of the "SIKESAL" Application to Improve Public Services in Jambi City
13

to improve life and work inside a city in
significant and fundamental ways, technology
is critical for being a smart city. When it comes
to tackling those political, administrative,
democratic, or material difficulties, ICT
applications can help(Díaz-Díaz, Muñoz, &
Pérez-González, 2017). E-government is the
application of information and communication
technology (ICT) to improve the execution of
traditional government duties and services. To
reform the government bureaucracy, traditional
governance necessitates the establishment of E-
Government. As a result, e-government is
intended to allow government agencies to
provide timely and accurate services to all
stakeholders. It is expected that implementing
E-Government will result in changes in the
form of better public services. The goal of e-
government is to increase the efficiency of
government services to citizens(Nurjanah,
Mutiarin, & Kasiwi, 2021).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research method is qualitative and uses
NVIVO 12 plus software to analyze the data.
The feature used in NVIVO 12 plus to analyze
data is the project map. This feature is used to
display actors involved in implementing the
"SIKESAL" application in improving public
services in Jambi City. Another feature used in
NVIVO 12 plus is the crosstab query; this
feature displays public responses using the
"SIKESAL" application. The source of the
public response comes from reviews on the
playstore, this is because users comment a lot
about the "SIKESAL" application. This
research data collection technique uses library
research. The source of this research data comes
from the official website of the Jambi city
government. Then it is added with data
originating from credible national and regional
online media news and relevant scientific
journals. The period for data collection in this
study is from 2017 to 2021, and this is because
the "SIKESAL" application was launched and
began to be used by the people of the city of
Jambi at that time.
4 FINDING AND DISCUSSION
4.1 The Process of Using the
Application and the Actors
Involved
The "SIKESAL" application (Online
Community Complaint Information System) is
a Quick Win for Smart City implementation in
Jambi City. This "SIKESAL" application is
used as a form of community participation in
urban development so that suggestions and
aspirations, as well as community complaints,
can be conveyed quickly. In other words, public
complaints media, which are usually carried out
conventionally, are developed into application-
based complaints media. Through the
"SIKESAL" application technology are
expected to encourage effectiveness and
efficiency in resolving various public
complaints(Mahmudah, 2018). In essence,
complaints submitted by the public-to-public
servants are a response to public services
received by the community from public
servants. According to the Decree of the
Minister of Empowerment of State Apparatus
No. 118 of 2004 concerning the Handling of
Public Complaints, public complaints are a
form of implementation of community
supervision submitted by the community, either
orally or in writing to the relevant government
apparatus, in the form of contributions of
thoughts, suggestions, ideas, complaints or
complaints made by the public constructive.
The availability of space to express aspirations
(voice) in the form of complaints and protests
against the implementation of government and
public services will play a significant role in
efforts to improve overall governance
performance. The public can use the
"SIKESAL" application owned by the City of
Jambi by downloading it on the Play store
channel using a device based on the Android
operating system. The admin of the
"SIKESAL" application is the Jambi City
government. The public must register how to
use the application by entering the family
identification number (NIK). Then enter the
user's data as an initial form of registration to
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
14

enter the application. After all the stages have
been filled in, the user can enter to use the
application. In the "SIKESAL" application,
there are features that the public can use to
report something.
In presenting the report, the user must fill in
several fields that have been provided in the
application. The user must fill in the report title
column, report description, suggestions, or
solutions that can be given. Then choose which
category of regional device organization must
resolve it and write down the full address of the
place of the complaint. After all the fields are
filled in, the "SIKESAL" application user must
attach a photo of his complaint so that the report
sent is clearer. The reporting history that has
been submitted will wait for a response from the
Jambi City regional apparatus organization
concerned to follow up. The Online Community
Complaints Information System (SIKESAL)
application has four accessible menus. See the
home menu to see the progress of the completed
report, famous problems, or the most active
users. While the other three menus contain
archives of complaints that have been reported
and see responses from regional device
organizations, then a menu about regional
device organization ratings & user profiles. The
presence of this application is expected to make
the people of Jambi City able to assist the
government in reporting problems that exist in
the community through E-Government. This is
certainly in line with the vision & mission of the
City of Jambi to become a Smart City
Government (Ahmad, 2021).
Understanding the roles that players such as
public legal entities and natural persons play in
inter-organizational digital public services is
critical for digital government success. An actor
role (or role) is defined as "the responsibility for
performing specified behavior, to which an actor
may be allocated, or the part played by an actor
in a given action or event" (Wouters, Janssen, &
Crompvoets, 2021). In the context of the
application "SIKESAL," several actors are
involved, both Jambi City government agencies
and the community itself. Figure 1 attempts to
map the actors involved in the use of the
"SIKESAL" application.
Figure 1: Actor involved.
Figure 1 shows some of the actors involved
in using the "SIKESAL" application. The actors
involved in the "SIKESAL" application are the
regional government organizations of the Jambi
city government and the community. The
SIKESAL application is directly connected to
the local government organization of the Jambi
city government. This means that complaints or
reports submitted by the community through
the application can be directly directed to the
relevant agencies or in their fields. The
Department of Communication & Informatics
has a role as the leading implementer and the
secretariat of complaints. Jambi city
government, regional apparatus organizations
involved with the "SIKESAL" application
include Regional Development Planning
Agency, Regional Personnel, and Human
Resources Development Agency, Regional
Financial and Asset Management Agency,
Regional Tax and Retribution Management
Agency, National and Political Unity Agency,
Education Office, Health Service, Public
Works, and Spatial Planning, Public Housing
and Settlement Areas, Social Service,
Population Control and Family Planning Office,
Community Empowerment Service, Women,
and Child Protection, Environment Service,
Population and Civil Registration Service,
Transportation Service, Communication and
Information Service Office, Manpower Office,
Cooperatives and Small and Medium
Enterprises, One-Stop Investment and Service
E-Government Towards Smart City: Using of the "SIKESAL" Application to Improve Public Services in Jambi City
15
Office, Archives and Library Service, Youth
and Sports Service, Tourism and Culture
Office, Trade and Industry Service, Fire and
Rescue Service, Agriculture and Food Security
Service.
In this context, it has been suggested that
clarity of roles and underlying duties among
collaborating public organizations is a crucial
element for digital government success.
Defining and assigning actor roles might help to
alleviate governance issues caused by
interdependencies among participants. This is
especially true for inter-organizational digital
public services, which necessitate collaboration
among many players to link building blocks
that form integrated service chains that supply
various services.
4.2 App User Public Response
In practice, ICTs have begun to play an
essential role in all areas of human life,
including political processes, electoral
participation mechanisms, and public services.
ICT is used to make things easier for all matters
and the establishment of transparency. Then,
the response from users becomes very
important to see the success of the
implementation of the ICT(Haryadi, Nurmandi,
Muallidin, Kurniawan, & Salahudin, 2022). In
the context of using the "SIKESAL"
application, various responses emerged from
the user community. This response can be seen
in the review column in the play store. Figure 2
shows the reaction of the community of users of
the "SIKESAL" application which is managed
through the NVIVO 12 plus crosstab query.
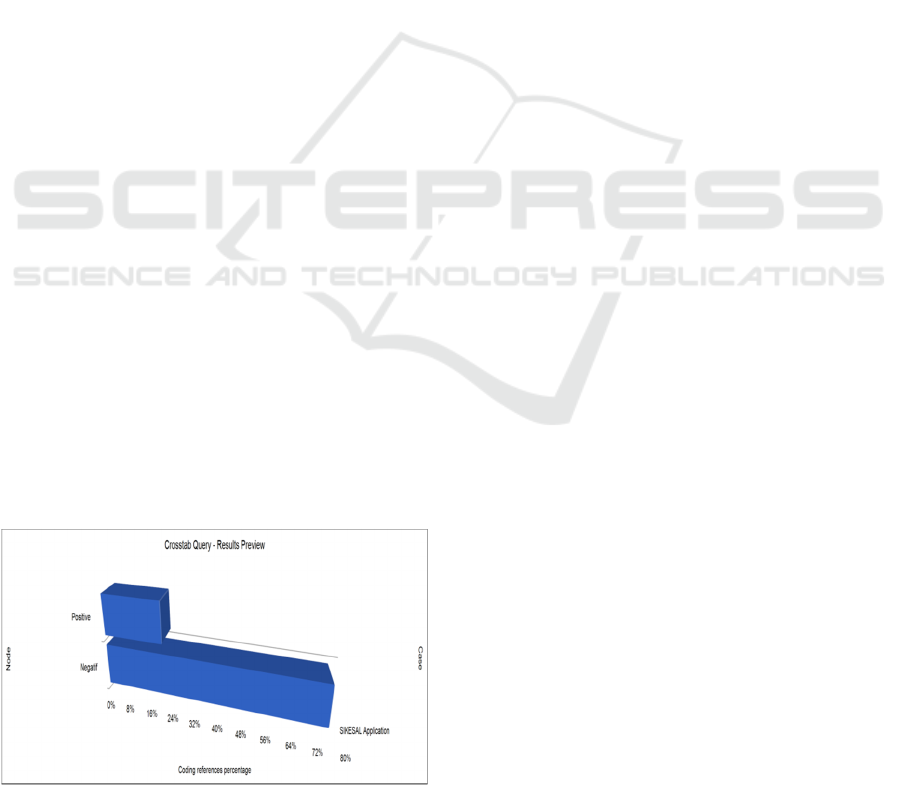
Figure 2: Public Response.
Figure 2 shows the public response to the
"SIKESAL" application, both negative and
positive. The user community of the
"SIKESAL" application who gave a positive
response was 22.00%, while those who gave a
negative response were more than 77.00%. This
shows that although the "SIKESAL"
application has a good purpose in its
application, it still has not received a good
response from the people of the city of Jambi.
In principle, the emergence of Artificial
Intelligence, or what is commonly referred to as
intelligent applications, has significantly
impacted life. Because it focuses on the
artificial reproduction and modification of
human intelligence to construct intelligent
machines, dealing with a quickly changing
world and being adaptable to intelligent
technologies can help people be more creative,
productive, and survive. Artificial intelligence
will assist the government in freeing up
resources by automating mundane jobs,
resulting in improved public service(Kasiwi,
Nurmandi, Mutiarin, & Azka, 2021).
The positive response from the user
community is that using the "SIKESAL"
application will bring benefits. Perceptions of
usefulness and convenience significantly affect
interest in using the "SIKESAL" application, an
instrument for the public to report complaints.
More than that, the positive response given by
the community to the "SIKESAL" application is
more to the initial purpose of the application as
a forum to convey aspirations to the
government. However, the negative response
received by the "SIKESAL" application is more
about its use which is still not well developed.
The application still has many technical
problems that make users uncomfortable using
it. The government needs to continue improving
the application's features so that people can
more easily access and complete the application
as an instrument of complaint.
The obstacle faced in using the "SIKESAL"
application is that the period given to the
agency to follow up on the report is too short,
resulting in the regulations governing
implementation not being implemented.
Another inhibiting factor, namely the absence
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
16

of a budget, also resulted in the lack of a
particular socialization program related to the
"SIKESAL" application which resulted in the
small number of downloads in this application,
and there were still many people who reported
manually. The role of agency heads in several
public sectors also seems to lack attention and
technical support in developing the "SIKESAL"
application due to the internal busyness of each
agency(Ahmad, 2021).
5 CONCLUSION
This study concludes that the Online
Community Complaints Information System
Application (SIKESAL) has four accessible
menus. The main menu with the name "send the
report" is used for reporting; in the application,
there is also a menu that contains an archive of
complaints that have been reported as well as
seeing responses from regional organizations.
The actors involved in using the "SIKESAL"
application are the Jambi City regional
apparatus organization and the application user
community. All regional government
organizations of the Jambi city government are
involved in using the "SIKESAL" application,
with the Communications & Information Office
having a role as the leading implementer and
the complaint secretariat. Then the response of
the people of the city of Jambi using the
"SIKESAL" application is dominant to
negative. The adverse reaction to the use of the
"SIKESAL" application is more for technical
reasons. Application development problems are
crucial in giving a negative response to the
"SIKESAL" application. This is because the
problem interferes with improving public
services using the "SIKESAL" application.
Although this research can explain the use of
the "SIKESAL" application to improve public
services in the city of Jambi, however, this
study has limitations, namely only defining the
use of one application in the city of Jambi.
Therefore, the recommendation for further
research is to compare two or more applications
used by the Jambi City government. This is to
more fully and clearly describe e-government
towards a smart city, especially in Jambi city.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is supported by the research and
innovation institute, Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta.
REFERENCES
Ahmad, Z. H. (2021). Pelaksanaan E-government Pada
Aplikasi Sistem Informasi Keluhan Masyarakat Online
(Sikesal) di Kota Jambi Tahun 2018-2019. Jom Fisip,
8(1), 1–12.
Bakıcı, T., Almirall, E., & Wareham, J. (2013). A Smart
City Initiative: the Case of Barcelona. Journal of the
Knowledge Economy, 4(2), 135–148.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-012-0084-9
Díaz-Díaz, R., Muñoz, L., & Pérez-González, D. (2017).
Business model analysis of public services operating
in the smart city ecosystem: The case of
SmartSantander. Future Generation Computer
Systems, 76, 198–214.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.01.032
Emaldi, M., Aguilera, U., López-de-Ipiña, D., & Pérez-
Velasco, J. (2017). Towards citizen co-created public
service apps. Sensors (Switzerland), 17(6), 469–481.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061265
Georgiadis, C. K., & Stiakakis, E. (2010). Extending an e-
government service measurement framework to m-
governement services. ICMB and GMR 2010 - 2010
9th International Conference on Mobile Business/2010
9th Global Mobility Roundtable, 432–439.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMB-GMR.2010.31
Haryadi, T., Nurmandi, A., Muallidin, I., Kurniawan, D.,
& Salahudin. (2022). Implementing “SIREKAP”
Application Based on Election for Improving the
Integrity of Election Administrators and Increasing
Public Trust. In Lecture Notes in Networks and
Systems (Vol. 319). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-
85540-6_21
Hodgkinson, I. R., Hannibal, C., Keating, B. W., Chester
Buxton, R., & Bateman, N. (2017). Toward a public
service management: past, present, and future
directions. Journal of Service Management, 28(5),
998–1023. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-01-2017-
0020
Kasiwi, A. N., Nurmandi, A., Mutiarin, D., & Azka, M. F.
(2021). Artificial Data Management in Reaching
Conditional Cash Transfer of Program Keluarga
Harapan (PKH) Utilizing Simple Addictive
Weighting. IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science, 717(1).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/717/1/012013
E-Government Towards Smart City: Using of the "SIKESAL" Application to Improve Public Services in Jambi City
17

Kaufhold, M.-A., Haunschild, J., & Reuter, C. (2020).
Warning the Public: A Survey on Attitudes,
Expectations and Use of Mobile Crisis Apps in
Germany. Proceedings of the European Conference on
Information Systems (ECIS), 1–16. Retrieved from
https://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2020_rp/84
Mahmudah, D. (2018). Persepsi Aparat Pemerintah Kota
Jambi terhadap Kegunaan dan Kemudahan
Penggunaan Media Pengaduan Berbasis Aplikasi.
Jurnal Studi Komunikasi Dan Media, 22(2), 123.
https://doi.org/10.31445/jskm.2018.220203
Nam, T., & Pardo, T. A. (2011). Conceptualizing smart
city with dimensions of technology, people, and
institutions. ACM International Conference
Proceeding Series, 282–291.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2037556.2037602
Nugroho, R. A. (2020). Mimpi Kota Jambi Menjadi Smart
City. Retrieved from kominfo.go.id website:
https://aptika.kominfo.go.id/2020/02/mimpi-kota-
jambi-menjadi-smart-city/
Nurjanah, A., Mutiarin, D., & Kasiwi, A. N. (2021). The
Use of Artificial Intelligent in Disaster
Communication between Government and Society
through E-Government in North Lombok. IOP
Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,
717(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-
1315/717/1/012038
Osei-Kojo, A. (2017). E-government and public service
quality in Ghana. Journal of Public Affairs, 17(3), 1–
8. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.1620
Pillai, S., Siddika, N., Hoque Apu, E., & Kabir, R. (2020).
COVID-19: Situation of European Countries so Far.
Archives of Medical Research, 51(7), 723–725.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.05.015
Reddick, C. G., & Zheng, Y. (2017). Determinants of
citizens’ mobile apps future use in Chinese local
governments: An analysis of survey data.
Transforming Government: People, Process and
Policy, 11(2), 213–235. https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-
11-2016-0078
Su, K., Li, J., & Fu, H. (2011). Smart city and the
applications. 2011 International Conference on
Electronics, Communications and Control, ICECC
2011 - Proceedings, 1028–1031.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECC.2011.6066743
Usman, J. (2011). Manajemen Birokrasi Profesional
Dalam Meningkatkan Pelayanan Publik. Otoritas :
Jurnal Ilmu Pemerintahan, 1(2).
https://doi.org/10.26618/ojip.v1i2.24
Wang, G., Chen, Q., Xu, Z., & Leng, X. (2020). Can the
use of government Apps shape citizen compliance?
The mediating role of different perceptions of
government. Computers in Human Behavior, 108,
106335.
Wouters, S., Janssen, M., & Crompvoets, J. (2021).
Understanding Actor Roles in Inter-organizational
Digital Public Services. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in
Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in
Bioinformatics), 12850 LNCS, 43–58.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84789-0_4
Zhang, Y. (2010). Interpretation of Smart Planet and
Smart City [J]. China Information Times, 10, 38–41.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
18
