
Vulnerable Source Code Detection Using Sonarcloud Code Analysis
Alifia Puspaningrum
a
, Muhammad Anis Al Hilmi
b
, Darsih, Muhamad Mustamiin
and Maulana Ilham Ginanjar
Department of Informatics, Politeknik Negeri Indramayu, Jalan Lohbener Lama No. 08, Indramayu, Indonesia
Keywords: Source Code, Detection, Vulnerability, Code Analysis, SonarCloud.
Abstract: In Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), security vulnerabilities are one of the points introduced during
the construction stage. Failure to detect software defects earlier after releasing the product to the market causes
higher repair costs for the company. So, it decreases the company's reputation, violates user privacy, and
causes an unrepairable issue for the application. The introduction of vulnerability detection enables reducing
the number of false alerts to focus the limited testing efforts on potentially vulnerable files. UMKM Masa
Kini (UMI) is a Point of Sales application to sell any Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Product
(UMKM). Therefore, in the current work, we analyze the suitability of these metrics to create Machine
Learning based software vulnerability detectors for UMI applications. Code is generated using a commercial
tool, SonarCloud. Experimental result shows that there are 3,285 vulnerable rules detected.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC),
security vulnerabilities being one of point introduced
during construction stage. However, vulnerabilities
being one of issue which difficult to be detected until
it becomes apparent as security failures in the
operational stage of SDLC. (Kehagias, Jankovic,
Siavvas, Gelenbe, 2021). Failure to detect software
defect earlier after releasing product to the market
causes higher repairing cost for the company. So, it
decreases company reputation, violate user privacy,
and cause unrepairable issue for the application
(Cisco, 2019). In addition, techniques to detect
software vulnerabilities are needed before releasing
product (Shin, Meneely, Williams, Osborne, 2010).
To solve those problems, dedicated tools are available
on the market: e.g., Veracode (Veracode, 2020) and
SonarCode (Raducu, Costales, Lera, Llamas, 2019).
The introduction of vulnerability detection (usually a
binary classification of vulnerable and neutral parts of
the source code) enables reducing the number of false
alerts to focus the limited testing efforts on potentially
vulnerable files (Chowdhury, Zulkernine, 2010).
UMKM Masa Kini (UMI) is a Point of Sales
application to sell any kind Micro, Small and Medium
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7179-8847
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3696-0807
Enterprises Product (UMKM). Not only selling the
products, UMI also provides facilities for offline
transaction and facilities which can support the
development of UMKM. However, in construction
process, automated testing to detect vulnerable code
is a good way to save money and time. Therefore, in
the current work, we perform an analysis of the
suitability of these metrics to create Machine
Learning based software vulnerability detectors for
UMI application. Code is generated using a
commercial tool, SonarCloud.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Software Testing
Testing is an activity to evaluate software quality and
to improve it (Pan, 1999). In general, testing divided
into two namely black box and white box testing.
White box is a testing technique that uses Software
Under Test (SUT) or the software being tested as a
test guide to be carried out (Touseef, Anwer, Hussain,
Nadeem, 2015). In addition, Black Box Testing is not
an alternative solution to White Box Testing but is
Puspaningrum, A., Anis Al Hilmi, M., Darsih, ., Mustamiin, M. and Ilham Ginanjar, M.
Vulnerable Source Code Detection Using Sonarcloud Code Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011862600003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 683-687
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
683
more of a complement to testing things that are not
covered by White Box Testing.
2.2 Software Quality ISO 25010
Software quality can be assessed through certain
metrics, methods, as well as through software tests.
One of benchmarks for software quality is
(International Organization for Standardization) ISO
25010. ISO/IEC 25010 has eight characteristics to
measure software quality, including portability,
performance efficiency, reliability, security usability,
maintainability, compatibility, and functional
suitability.
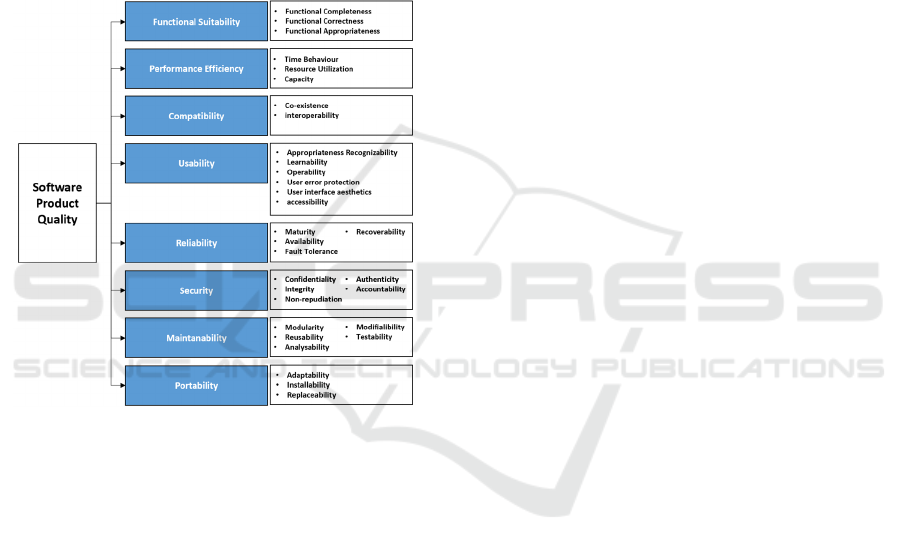
Figure 1: Product quality model ISO/IEC 25010.
Figure 1 is characteristics and sub-characteristics of
Software product quality model which consists of:
1. Functional Suitability is a characteristic to
measure which system provides functions
according to its requirement when used in
certain conditions.
2. Performance Efficiency is a characteristic to
calculate relative performance of the
resources when used in certain conditions.
3. Compatibility is a characteristic to measure
how a system share an information to other
systems and execute required functions
while sharing same hardware or software
environment.
4. Usability is a characteristic to measure
which system can be used to achieve the
specified goals effectively and efficiently.
5. Reliability is a characteristic to measure how
reliable a system can execute functions
under specified conditions for a certain
period.
6. Security is a characteristic to measure a
system in protecting information and data,
so that the system has a data access level
according to the type and level of
authorization.
7. Maintainability is a characteristic to
represent the level of effectiveness and
efficiency in the modification process for
system improvement in accordance with
adjustments and changes in the operational
environment.
8. Portability is a characteristic to represent the
level of effectiveness and efficiency of the
system in transferring from one device to
another.
2.3 SonarCloud
SonarCloud is an online automated software quality
analysis platform delivered by SonarQube, which is
used to collect code quality analysis data on linked
software from GitHub (SonarSource, 2014).
SonarCloud calculates several metrics such as
number of lines of code and code complexity and
verifies code compliance with a specific set of
"coding rules" defined for most common
development languages.
If the analyzed source code violates the coding
rules or if the metric falls outside a predefined
threshold, SonarCloud generates an "issue".
SonarCloud includes 3 quality models from ISO
25010 namely Reliability, Maintainability and
Security.
SonarCloud also classifies rules into five levels of
code severity, namely Blocker, Critical, Major,
Minor, and Info.
● Blocker: a bug with a high probability of
affecting the use of the application in
production.
● Critical: a bug with a low probability of
affecting application use in production or a
weak level of security.
● Major: lack of quality which can have a huge
impact on developer productivity. Like code
snippets not found and unused parameters.
● Minor: lack of quality which can slightly
impact developer productivity. Like too long
lines of code and minimal statements
● Info: not a bug or lack of quality but just a
finding from SonarCloud.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
684
3 METHOD
3.1 SonarCloud Pipeline
For experimental analysis, SonarCloud is used to
collect vulnerable source code to obtain analysis of
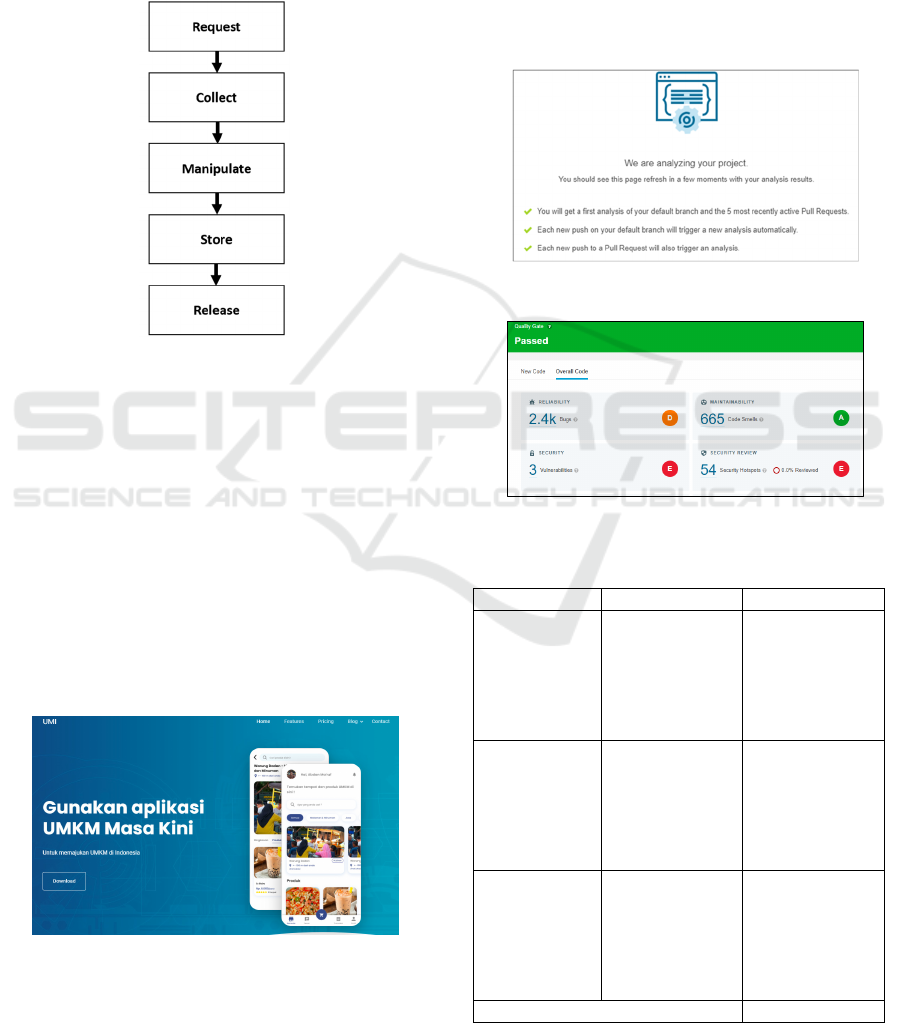
vulnerable code. Figure 2. show how SonarCloud
detects insecure in given code.
Figure 2: SonarCloud block diagram.
The first step is request SonarCloud REST API.
In the second phase, the crawlers collect source code
of the application. In the next phase, SonarCloud
manipulate by adding vulnerable lines as comments
at the end of the source code file. After that,
SonarCloud stores the result in the local file of the
system. The last step is releasing the dataset to the
community.
SonarCloud inspects the model according to ISO
25010 Standard, namely: reliability, maintainability,
security and classify into five categories then.
3.2 Dataset
Figure 3: Landing page of UMI website.
UMKM Masa Kini (UMI) is marketplace application
which store and generate finance administration. This
application has been developed since 2020. There are
19 functions in UMI.
4 RESULT
After scanning using SonarCloud as shown in Figure
4, SonarCloud generate a report, showing three
scopes of the application namely Reliability,
Maintainability, Security and its severity level as
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4: Analyzing project process.
Figure 5: SonarCloud report analysis.
Table 1: UMI severity level.
T
yp
e Severit
y
Rules
Bug
All 2,370
Info -
Mino
r
2,000
Ma
j
o
r
364
Critical 6
Blocke
r
-
Code Smell
All 665
Info -
Mino
r
74
Ma
j
o
r
356
Critical 233
Blocke
r
2
Vulnerability
All 3
Info -
Mino
r
-
Ma
j
o
r
-
Critical 1
Blocke
r
2
Total 3,285
Vulnerable Source Code Detection Using Sonarcloud Code Analysis
685
Overall code rating (reliability, maintainability,
security). The detail information of the report is
shown in Table 1.
After retrieving the source code, for each
vulnerability, a line is appended to the original
source. Result shows that there are 3.285 rules
detected as vulnerable code. Each issue namely bug,
code smell, and vulnerability are categorized into
severity level, namely: blocker, critical, major, minor,
info.
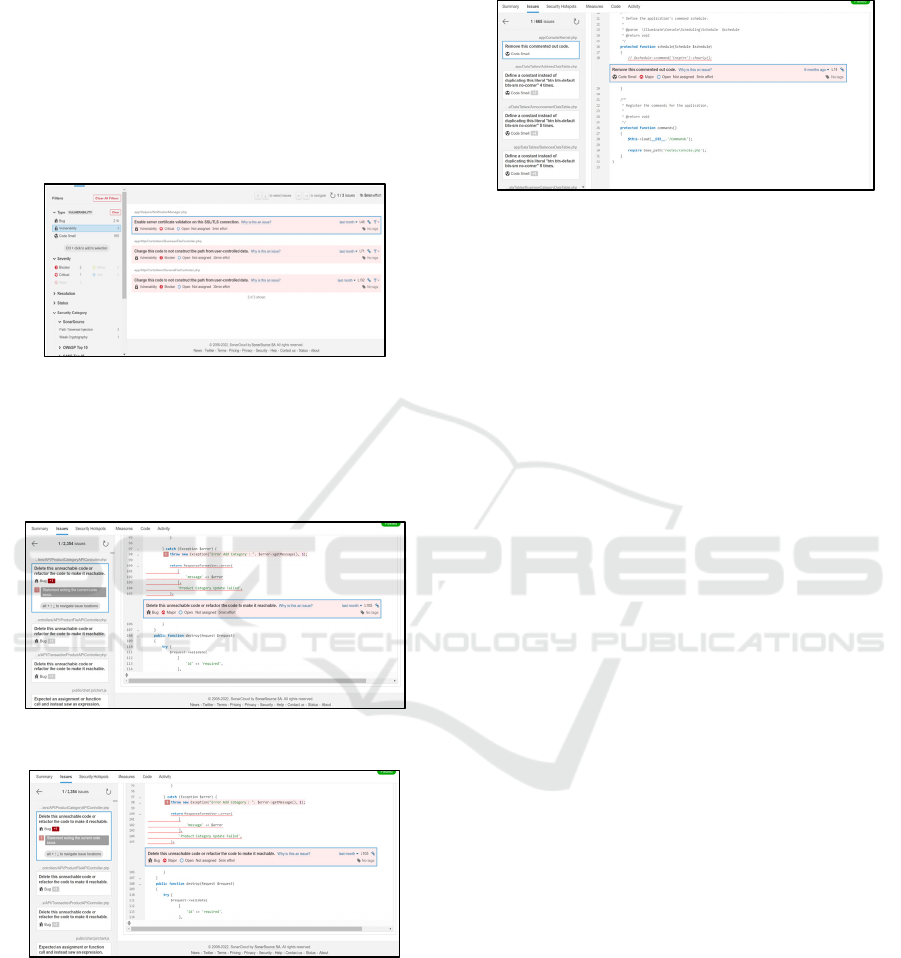
Figure 6: Vulnerability analysis.
There are three rules detected in vulnerability issue.
As shown as Figure 6, three rules are reported and
completed with each severity level. For each rule,
SonarCloud describes the issue as shown as Figure 7.
Figure 7: Sample code of vulnerability type.
Figure 8: Sample code of bug type.
For other issues such as code smell and bug
category are also analyzed as shown as Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
Every report can help developer to do
maintenance more efficient. However, one of limited
of SonarCloud’s web API is the one commonly
known as the 10,000-issue limit. This constraint
implies that every single request made will be
responded to only with the first 10,000 results.
Figure 9: Sample code of code smell type.
However, SonarCloud reports starting and ending
line and starting and ending offset (column) of the
vulnerability instead highlighting the vulnerable
code.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper analyzes vulnerable for UMI application
source code by using SonarCloud. Experimental
result shows that there are 3,285 vulnerable rules
detected. For the future work, highlighting the
vulnerable code instead of starting and ending line
and starting and ending offset (column) of the
vulnerability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by Pusat Penelitian
dan Pengabdian Masyarakat, Politeknik Negeri
Indramayu, as Penelitian Kerjasama Perguruan
Tinggi 2022.
REFERENCES
Kehagias, D., Jankovic, M., Siavvas, M., Gelenbe, E.
(2021). Investigating the Interaction between Energy
Consumption, Quality of Service, Reliability, Security,
and Maintainability of Computer Systems and
Networks. SN Comput. Sci., 2, 1–6.
Cisco (2019). Cisco Cybersecurity Series. Consumer
Privacy Survey. https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/
global/en_uk/products/collateral/security/cybersecurit
y-series-2019-cps.pdf.
Shin, Y., Meneely, A., Williams, L., Osborne, J.A. (2010).
Evaluating complexity, code churn, and developer
activity metrics as indicators of software
vulnerabilities. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng., 37, 772–787.
Veracode (2020). https://www.veracode.com/
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
686

Raducu, R., Costales, G. E., Lera, F. J. R., & Llamas, C. F.
(2019). SVCP4C: a tool to collect vulnerable source
code from open-source repositories linked to
SonarCloud. In Actas de las V Jornadas Nacionales de
Ciberseguridad: junio 5-7, 2019. Cáceres (pp. 191-
197). Servicio de Publicaciones.
Chowdhury, I., Zulkernine, M. (2010). Can complexity,
coupling, and cohesion metrics be used as early
indicators of vulnerabilities? In Proceedings of the 2010
ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Sierre,
Switzerland, 22–26 March 2010; pp. 1963–1969.
Pan, J. (1999). Software testing. Dependable Embedded
Systems, 5, 2006.
Touseef, M., Anwer, N., Hussain, A., Nadeem, A. (2015).
Testing from UML design using activity diagram: a
comparison of techniques. International Journal of
Computer Applications, 975, 8887.
SonarSource. SonarQube Docs—/api/issues. (2014).
https://docs.sonarqube.org/pages/viewpage.action?pag
eId=239218.
Vulnerable Source Code Detection Using Sonarcloud Code Analysis
687
