
Thoughts on Bidao Planning of the Shantou Rongjiang Basin
Guiling Mu
1,2,*
and Sen Wang
1,2
1
Pearl River Water Resources Research Institute, Pearl River Water Resources Commission, Guangzhou 510611, China
2
Key Laboratory of the Pearl River Estuary Regulation and Protection of Ministry of Water Resources,
Guangzhou 510611, China
Keywords: Wanli Bidao, the Shantou Rongjiang Basin, Construction Planning.
Abstract: High-quality construction of Wanli Bidao is version 3.0 of Guangdong's water treatment. Based on the
analysis of the Bidao basement in the Shantou Rongjiang Basin, we determined the current status of the Bidao
construction, identified the existing problems, analyzed the theme characteristics, and refined the Bidao
construction goals and overall layout. According to the existing problems and construction goals of the Bidao
construction, the specific construction tasks of the Bidao were determined item by item to provide technical
support for the Bidao construction in the Shantou Rongjiang Basin.
1 INTRODUCTION
Rongjiang is an important river along the east coast of
Guangdong. It originated from Phoenix Mountain in
Luhe County, Shanwei City. It flows from the
southwest to the northeast, passing through Jieyang
City and Shantou City, imports to the South China Sea
via Shantou Port.
The concept of Bidao was proposed in June 2018
(Lie Ruiming, 2020). The connotation, classification
and construction tasks of Bidao are very clear after
two years development. The high-quality
construction of Wanli Bidao is version 3.0 of
Guangdong's water treatment (Ma Xiangming, 2020).
Compared with the simpler water environment
management in the past, the construction of Wanli
Bidao has jumped out of the traditional model of
water treatment, and transformed into a water
treatment-based approach. It is implemented such as
rural revitalization, global tourism, flood control,
sponge city construction, characteristic waterways
and construction of "four good rural roads" as a
whole, water and shore co-governance, and finally
realize the co-construction, co-governance and
sharing of beautiful ecological environment (Li
Junfei, 2020). The pilot Bidao has given birth to the
vigorous development of the "water economy" in
various places. The rivers and lakes have changed
from the objects of money spent to the treasures of
improving the ecological environment, enhancing the
value of urban land, supporting industrial upgrading,
and driving rural revitalization. They have formed a
series of distinctive waterfront economic belts, and
carried out of Guangdong characteristics in practicing
the ecological development concept of "green water
and green mountains are golden mountains and silver
mountains".
Through thorough study of the concept and
connotation of Bidao, this paper analyzes and
identifies the base of Bidao construction in the
Shantou Rongjiang Basin, determines the goals and
specific tasks of Bidao Construction, and helps the
Shantou Rongjiang Basin build a comprehensive,
diversification and demonstration eco-tourism axis
integrating sports and leisure, sightseeing and
recreation, and education and display.
2 BASE ANALYSIS
The Shantou Rongjiang has a total length of about
60km and a catchment area of 334.21km
2
. It is a tidal
section, starts from the junction of Shantou City and
Jieyang City, and flows through Chaoyang, Jinping,
and Haojiang District, and finally ends at Mayu Island
and merges into the South China Sea. The Shantou
Rongjiang is an important golden channel in eastern
Guangdong.
Mu, G. and Wang, S.
Thoughts on Bidao Planning of the Shantou Rongjiang Basin.
DOI: 10.5220/0011863800003536
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment (ISWEE 2022), pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-639-2; ISSN: 2975-9439
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
5

2.1 Water Resources Status and
Problems
The Rongjiang basin has abundant water resources,
but the per capita water resources are relatively short.
The main stream of Rongjiang was included in the
tidal section before entering the Shantou city. So, the
inbound water is difficult to use, only above the
Chaoyang Wenzui sluice, Chaoshuixi draws water
from the Nanhe to provide irrigation water for more
than 6,667 hm
2
of farmland along the bank. It is a
water-stressed area. The per capita water resource in
the Rongjiang Basin is 1138 m³/person, which is
lower than the internationally recognized water
scarcity warning line of 1700 m³/person. Although the
Rongjiang has abundant transit water, it is already
salty water when it enters the country and cannot be
used. Basically, water for drinking and irrigation in
the basin comes from reservoir water and diversion
from outside the basin.
2.2 Water Security Status and
Problems
Natural disasters in the Rongjiang basin are serious,
and the capacity of flood control and drainage needs
to be enhanced. Rongjiang is an important flood
control and drainage channel for Jieyang and Shantou
city. Since Guangdong Province launched the special
disaster prevention and mitigation action in 2003, the
flood control capacity of this basin has greatly
improved. But the Rongjiang dike still has some
problems such as non-compliant sections and
unclosed dikes, which still threaten the lives and
property safety of the people. In addition, the Shantou
Rongjiang is a tidal section, and the tidal water is
irregular semi-diurnal. Once the waterlogged caused
by heavy rain in the basin encounters the high tide
water level of Rongjiang, it will cause waterlogging
in the cities along the line, causing urban paralysis and
major economic and property losses.
2.3 Water Environment Status and
Problems
The water quality of water function area is not up to
standard, and the water quality monitoring capacity is
insufficient. According to the "Shantou Water
Resources Bulletin", the annual average water quality
of the Rongjiang Control Station is IV, and has not yet
reached the water quality target of III. The number of
monitoring sections on the main stream of Shantou
Rongjiang is relatively lack, and there are no
monitoring sections at the entrance of larger tributary
confluences. It is impossible to grasp the water quality
of the tributaries and its influence to the main stream
water quality.
The management of river sewage outlets is
lacking, and some rivers are heavily polluted. The
Rongjiang Basin’s sewage outlet monitoring
capabilities are weak, monitoring methods are lacking,
law enforcement forces do not match the tasks, and
some enterprises have illegal discharges, excessive
discharges, and even illegal discharges. The urban and
rural domestic sewage in the Rongjiang Basin has not
been effectively collected and treated, and there is still
a gap between the target sewage treatment rate of
more than 93%. In addition, the imperfect treatment
facilities of urban and rural domestic garbage have
aggravated water pollution in the river basin and
caused part of the water surface garbage to float.
2.4 Water Ecology Status and
Problems
Ecological flow is insufficient in Rongjiang basin.
The Shantou Rongjiang has a high degree of
utilization of water resources, and the ecological flow
of the main tributaries is seriously insufficient,
especially during the dry season, which leads to the
deterioration of the self-purification capacity of water
bodies and aggravates water pollution.
The prevention and control of soil erosion needs
to be strengthened. According to the results of the
fourth remote sensing survey of soil erosion in
Guangdong Province and combined with field
surveys, the overall soil erosion in the Shantou
Rongjiang Basin is slight, but it’s the heaviest among
the river basins in Shantou City.
The compensation mechanism for ecological
protection of the Rongjiang basin has not yet been
established. As a cross-border river, the establishment
of ecological protection compensation mechanism is
an important mean to mobilize the enthusiasm of all
parties and protect the ecological environment.
2.5 Featured Resources and Recreation
System Status and Problems
As shown in Figure 1, there are 12 characteristic
natural ecological resources, 18 human and social
resources, and 5 special industrial economic resources
in Shantou Rongjiang Basin, each accounting for
38.7%, 38.3%, and 26.3% of the whole city. However,
the waterfront space lacks local characteristics. It is
specifically reflected in the lack of regional cultural
elements in various supporting facilities such as
paving, vegetation matching, garden construction
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
6

sketches, and lighting night scenes along the slow
waterfront roads along the line.
Relying on the "Shantou Greenway Network
Planning and Construction Implementation Plan",
combined with the construction of beautiful rural
demonstration villages, the current Shantou
Greenway construction has begun to take effect.
There are 3 greenways related to the Rongjiang Basin:
Haojiang Queshi Scenic Area Greenway, Jinping
Niutianyang Greenway from the west side of Queshi
Bridge to Gate 4, and Jinping Seaside Greenway from
Xidi Ferry to Huaqiao Park. The waterfront service
facilities in the Rongjiang Basin are the scenic road
system cabinets in the Niutianyang National Wetland
Park and the Huanwan District. The water recreation
facilities are mainly the Merchants Passenger Wharf
to the Mayu Island Wharf, and the inner bay night
cruise line. However, the landscape recreation system
lacks connection. Each resource node is relatively
isolated, has not yet formed an effective linkage. The
waterfront slow-moving track, post, leisure dock and
other recreational system facilities are relatively
lacking, and have not yet formed an effective
connection.
Figure 1: Distribution Map of Characteristic Resources in
Rongjiang Basin.
2.6 Waterfront Economic Belt Status
and Problems
The development of the waterfront economic belt still
needs to be further explored. In 2007, Shantou put
forward the strategic conception of the "Three
Economic Belts" as Eastern Urban Economic Belt,
Industrial Economic Belt, and Ecological Economic
Belt. At present, the planning of the waterfront
economic zone focuses on the coast and the main
stream of the Rongjiang, the tributary parts lack
corresponding planning. In addition, the construction
of the economic zone is still in the planning stage and
needs to be implemented quickly.
3 GENERAL LAYOUT
The Rongjiang is a green ecological corridor in
Shantou, with beautiful scenery and many historical
sites along the bank. It is rich in tourism resources.
From the analysis of Shantou’s main characteristic
resources, it can be seen that characteristic natural
ecological resources and humanistic and social
resources are most prominent in the Rongjiang Basin.
The Rongjiang Basin has the scarcest natural
landscape, the inner-city bay. It has characteristic
landscapes such as Mayu Island, Queshi Scenic Area,
the promenade, and the light show of Times Square.
"Shantou City Landscape Lighting Plan (2018-2030)"
pointed out that the core area of the inner bay will be
built into a world-class night tourist destination.
Therefore, the plan follows the theme
characteristics of "human ecology River Bay",
considers the city’s humanities and water veins, fully
combines the cultural characteristics of Chaozhou and
the activity needs of citizens and tourists, aiming to
create a comprehensive, diversified, and
demonstration ecological tourism axis that integrating
sports and leisure, sightseeing and recreation,
education and display.
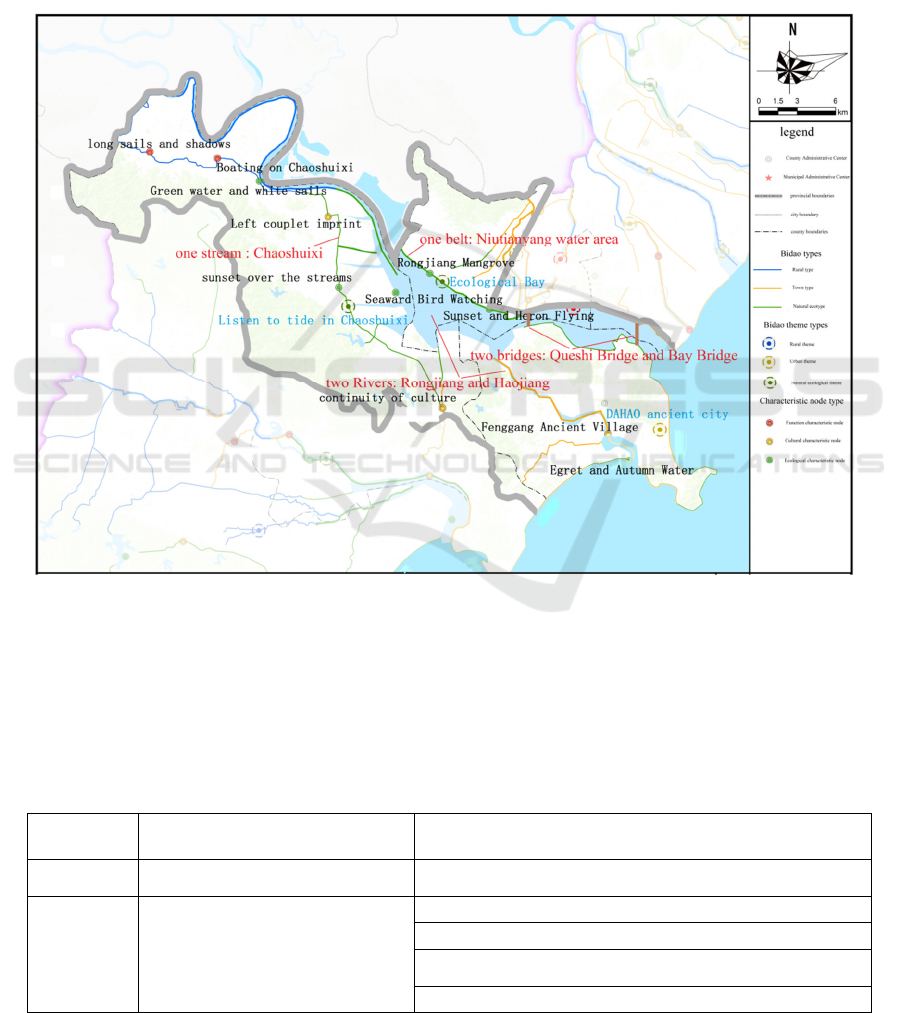
The pattern of the plan is "two rivers and two
bridges of humanity show, one stream and one belt of
natural beauty", as shown in Figure 2.
"Two Rivers" refers to Rongjiang and Haojiang.
With Rongjiang and Haojiang as the water vein,
relying on Niutianyang Wetland, Queshi Scenic Area,
Danying Ecological Park, Chaoshan Historical and
Cultural Expo Center, Dahao Ancient City, Fenggang
Ancient Village and other surrounding natural and
cultural resources, combining with local
characteristic culture, the plan praises the long history
and traditional culture of the Haojiang, and the natural
ecology and beauty bay of the Rongjiang through the
waterfront landscape design. "Two Rivers" focuses on
creating one river and two banks, creating water
landscape belt with clear themes and perfect
supporting facilities.
"Two bridges" refers to the Queshi Bridge and the
Bay Bridge. Relying on landmarks such as the
Customs Museum History Exhibition Hall, Shantou
Museum, Folk Museum, Customs Bell Tower near the
bridge, combined with Xidi Park, 1860 Cultural and
Creative Park, Small Park Opening Area, Zhongshan
Park, Laoma Palace Theatre, Waterfront Promenade
Park , Shipaotai Park, Tianhau Temple, Pearl Temple
and other cultural attractions, the plan rationally
Thoughts on Bidao Planning of the Shantou Rongjiang Basin
7
arranges multiple waterfront plazas, and integrates
murals, scenery walls, cultural corridors, art sketches
to comprehensively enhance the artistry and
interaction of public water spaces , aiming to create a
waterfront space full of popularity and vitality.
"One stream" refers to the Chaoshuixi. With water
as its vein, it creates a rooted in the urban ecological
corridor. With green as the bottom, it creates a
recreational resort with a blend of water and scenery.
With culture as its core, it creates a new Chaoyang
cultural travel line. "One stream" is built to create a
"Tide Listening" theme.
"One belt" refers to the Niutianyang water area,
starting at Xidong gate and ending at the No. 7 gate.
Combining Niutianyang Wetland with Mangrove
Wetland, "One belt" aims to create a natural
ecological landscape belt with Rongjiang Mangroves,
Happy Pastoral, Ecological Fisheries, and Sunset
Glows.
Figure 2: Planning Layout of Rongjiang Basin.
4 PLANNING TASK
In view of the current situation and problem analysis,
combined with the overall layout of the Bidao, we
determine 6 categories and 30 specific tasks of the
Bidao plan for the Shantou Rongjiang Basin, as
shown in table 1.
Table 1: Bidao Planning Task List of Rongjiang Basin.
Sub-item Existing problems Construction tasks
Water
resources
Relative shortage of per capita water
resources
Promote the Hanjiang-Rongjiang-Lianjiang water system connection
project
Water safety
flood control and drainage capacity needs
to be enhanced
Chaoyang Jinguanwei Mianbei Seawall Reinforcement Project
Sanyuwei Seawall Reinforcement Project
Reinforcement of 600m from Chaoyang Sanyuwei Seawall to City
Defense Project
Reinforcement of the seawall from Wutianwen dike to Leikou Bridge in
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
8
Sub-item Existing problems Construction tasks
Haojiang District
Standard Upgrading and Reconstruction Project of Seawall of Nanbin
Road, Haojiang District
Niutianyang No. 2, No. 5, No. 6 and No. 7 drainage ditches renovation
project
Wunangou Waterlogging Area Remediation Project
Newly built power stations as Tuolian, Li'an, Dongsha, Longhuguan,
and Huangcuowei
Reconstruction Sluices as Juding, Chaowei, Dayan, Yanzui, Chaocheng,
Xigang, Xitangwai, Hexi
Xilu River, Hexi River, Lianggang River treatment project
Reinforcement projects of 4 small reservoirs as Lingjiao, Shuijiling,
Dajiaoxia, Dongkeng, Haojiang District
Water
environment
Water quality is not up to standard
water environment management of Main stream and Hexi River, Xilu
River, Dagang River, Xigang River, Tuoji River
Treatment of 5 cases of black and odorous water bodies
Insufficient water quality monitoring
capabilities
Supplement water quality monitoring points at Chaoshuixi
Lack of management of sewage outlets
into the river
New sewage treatment plants as Jinping West District, Guanbu Town,
Hexi Town, Xilu Town and Jinzao Town
Carry out the cleanup of the forbidden areas in the waters of the
Haojiang Qingzhou Salt Field Section and Majiao Street Section
Residential environment improvement project for a total of 112 villages
in the 4 towns as Jinzao, Guanbu, Xilu and Hexi
Water ecology
Insufficient protection of ecological flow
Prepare a plan for determining and guaranteeing the ecological flow of
rivers and lakes in the Rongjiang Basin
The prevention and control of soil erosion
needs to be strengthened
Ecological Transformation of Hard Banks in the Basin
Hexi Reservoir Water Conservation Forest Construction Project
Construction of Shantou Mangrove Ecological Wetland Park and
preparation of watershed wetland protection plan
Ecological protection compensation
mechanism has not yet been established
Actively promote the establishment of river basin ecological
compensation mechanism
Landscape
and
Recreation
System
Waterfront space lacks local
characteristics
Create Niutianyang Wetland Park "Rongjiang Mangrove", "Seaward
Bird Watching", "Sunset and Heron Flying" landscape nodes
Create Chaoshuixi landscape nodes such as "continuity of culture" ,
"sunset over the streams", and " Green water and white sails "
Create Haojiang River landscape nodes such as "Egret and Autumn
Water" and "Fenggang Ancient Village"
The recreational system lacks connection
Create slow-moving trails throughout the basin, with 4 integrated post
stations and 33 convenient post stations
Waterfront
Economic
Belt
The development of the Waterfront
Economic Belt needs to be further
explored
Create the Rongjiang Inner Bay Bidao + Smart Tourism Industrial
Economic Belt
Create the Bidao on the south bank of the Rongjiang + agricultural
tourism industry economic belt
Create the Chaoshuixi Bidao + cultural tourism + rural revitalization
industrial economic belt
Create the Haojiang Bidao + Emerging and Vigorous Industrial
Economic Belt
5 CONCLUSION
On the basis of in-depth study of the concept and
connotation of Bidao, we analyzed and identified the
base of Bidao construction in the Shantou Rongjiang
Basin, determined the theme and characteristics of the
Shantou Rongjiang Bidao, and extracted the goals and
layout of the Shantou Rongjiang Bidao construction.
According to the existing problems and construction
goals of the Shantou Rongjiang Bidao, the specific
construction tasks are determined to guide the
construction of the Shantou Rongjiang Bidao. The
plan will help the Shantou Rongjiang Basin to build a
comprehensive, diversified, and exemplary eco-
tourism axis, which integrates sports and leisure,
sightseeing and recreation, education and display.
Therefore, the plan has a strong guiding significance.
Thoughts on Bidao Planning of the Shantou Rongjiang Basin
9

ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by Special Foundation
for National Science and Technology Basic Research
Program of China (2019FY101900), National Natural
Science Foundation of China (5170929), and the
Open Research Fund of Guangxi Key Laboratory of
Water Engineering Materials and Structures (GXHRI-
WEMS-2020-11)
REFERENCES
Lie Ruiming 2020 Research on the Master Plan of Wanli
Bidao in Guangdong Province Urban and Rural
Development 600(21) 47-48.
Ma Xiangming, Wei Jiming, Hu Xiumei, et al 2020 New
Idea of National Land and Space Ecological
Restoration: Guangdong Greenway and Blueway
Planning Planners, 317(17) 26-34.
Li Junfei, Li Huan, Yang Leisan 2020 Brief Discussion on
the Innovative Water Pollution Control Mode in
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
China Water & Wastewater 508(08) 9-14.
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
10
