
Utilization of the Tukad Unda River
for the Development of Clean Water Services
Denpasar, Badung, Gianyar and Klungkung (Sarbagikung) Areas
I Nyoman Sedana Triadi, Ir. I Made Tapa Yasa, Ir. Made Mudhina, I G. L. Made Parwita,
I Nyoman Anom P. Winaya and Ketut Wiwin Andayani
Jurusan Teknik Sipil, Politeknik Negeri Bali,
Jl Kampus Bukit Jimbaran, Kuta Selatan, Kab. Bandung-Bali-8036, Indonesia
Keywords: Availability, Area, Need, Balance, Water, Development.
Abstract: The area of irrigated rice fields used by subak in the Unda River Basin is 3,891.89 ha, spread over the
Klungkung and Karangasem regencies. Specifically, the study of the discharge downstream of Tukad Unda
is in the Unda Dam, the irrigation area is called the Unda Irrigation Area, with a total area of 1,104.89 ha of
the Unda Irrigation Area. The population of Denpasar City in 2021 is 981,824 people, Badung Regency
696,850 people, Gianyar Regency 521,215 people and Klungkung Regency 181,989 people, currently trying
to fulfill clean water sourced from Tukad Unda water flow.To find out the potential of Tukad Unda
downstream in providing clean water, an analysis of its water availability and existing water needs was carried
out. Analysis of water availability with 90% reliability in the downstream Tukad Unda river was carried out
using frequency analysis based on the type of distribution of discharge data obtained in Tukad Unda. Analysis
of domestic and non-domestic water needs from 2020 to 2040 is based on the socio-economic development
conditions of the community. From the results of these calculations, an analysis of the water balance is carried
out, namely comparing the availability of water with the demand for water, so that the deficit or surplus is
known from time to time. The need for clean water in the Sarbagikung area until 2040 is 7,757 m
3
/s. The
planned allocation of water from Estuary of Tukad Unda Reservoir for the Sarbagikung area is 1,400
liters/second, covering 850 liters/second to meet the needs in South Denpasar District, 100 liters/second in
South Kuta District, 300 liters/second which will distributed to the Districts of Gianyar and Klungkung at 150
liters/second.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
Provision of drinking water is a basic need and socio-
economic right of the community that must be
fulfilled by the central and local governments. The
availability of drinking water is one of the
determinants in improving people's health, welfare,
and productivity in the economic field. Therefore, the
provision of drinking water facilities and
infrastructure is one of the keys to regional economic
development. (Minister of Public Works Regulation,
2007).
Specifically, the study of the discharge
downstream of Tukad Unda is in the Unda Dam, the
irrigation area is called the Unda Irrigation Area, with
a total area of 1,104.89 ha of the Unda Irrigation Area.
The current condition of the cropping pattern in the
Unda irrigation area is Paddy Paddy Palawija.
The increasing demand for water has caused
several problems in the process of providing adequate
quantity and quality of water supply. The population
of Denpasar City in 2021 is 981,824 people, Badung
Regency 696,850 people, Gianyar Regency 521,215
people and Klungkung Regency 181,989 people,
currently trying to fulfill clean water sourced from
Tukad Unda water flow
To find out the potential of Tukad Unda
downstream in providing clean water, an analysis of
its water availability and existing water needs was
carried out. Analysis of water availability with 90%
reliability in the downstream Tukad Unda river was
carried out using frequency analysis based on the type
of distribution of discharge data obtained in Tukad
Triadi, I., Yasa, I., Mudhina, I., Parwita, I., Winaya, I. and Andayani, K.
Utilization of the Tukad Unda River for the Development of Clean Water Services Denpasar, Badung, Gianyar and Klungkung (Sarbagikung) Areas.
DOI: 10.5220/0011876400003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 751-756
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
751

A
Eff
IRIR
DR 1157,0
21
+
=
Unda. Analysis of domestic and non-domestic water
needs from 2020 to 2040 is based on the socio-
economic development conditions of the community.
From the results of these calculations, an analysis of
the water balance is carried out, namely comparing
the availability of water with the demand for water,
so that the deficit or surplus is known from time to
time.
1.2 Problem Formulation
The formulation of the problem from the research on
Utilization of the Tukad Unda river for the
development of clean water services in the Denpasar,
Badung, Gianyar and Klumgkung (Sarbagikung)
areas is, how big the Tukad Unda river can be used
for the Sarbagikung area.
1.3 Purpose
The purpose of this study was to obtain answers to the
problems presented, is calculating how big the Tukad
Unda river can be used for the Denpasar, Badung,
Gianyar and Klungkung (Sarbagikung) areas.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Need for Irrigation
Taking into account the level of effectiveness and
efficiency of the water distribution pattern, the need
for irrigation water will be calculated based on a 15-
day period, this period is effective and efficient
enough to be implemented in the later operating
pattern. The methods that will be used in this analysis
are, (Kementrian Pekerjaan Umum, 2013).
Analysis of potential evapotranspiration (ETo)
using the Modified Penman method
ETo = ETo* . C (1)
Analysis of effective rainfall using the Basic
Year method, For Rice and For Palawija
Crop coefficient (Kc) based on FAO . method
Consumptive use (Etc)
Etc = Kc . Eto (2)
Efficient irrigation based on Planning Criteria
The need for clean water for rice is calculated
based on the formula.
IR1 = Etc1 + P + WLR + LP – Re (3)
Water Needs for Palawija .
IR2 = Etc2 – Rep (4)
water in the intake
(5)
2.2 Water Potential
Water potential is the amount of water contained in
water bodies, both as surface water and as
underground water. In the analysis of the amount of
water potential, it can be obtained through data series
from recording weir discharge, river or it could be
based on the mainstay discharge analysis by using
several methods of diverting the variance of rain
associated with the conditions of the existing
watershed. The method commonly used is the FJ
Mock method or the NRECA method, ( Soemarto
CD, 2011)
2.3 Strategy Management
Strategic management is defined as a way to guide
companies to achieve a number of goals, including
corporate responsibilities, managerial capabilities, to
administrative systems related to strategic decision
making, and operations.Strategic management is a
series of fundamental decisions and actions from the
highest management, which are applied by all
members of an organization, for the realization of
organizational goals. (Agrifa Masir, 2017)
2.4 Population
The calculation of the population is important,
because knowing the population of an area will be the
basis for making population policies at a certain time.
The province of Bali, which includes nine regencies
and cities, has a relatively varied population.
Population development in the province of Bali has
not been evenly distributed. As a result of the uneven
development of the region, especially related to the
development of the tourism industry sector,
community social centers, and government, which are
still in the district capital.
Calculation of the population using arithmetic,
geometric and least square formulas. To determine
the method used in each sub-district, the smallest
standard deviation value of the three approaches will
be determined. (Minister of Public Works Regulation,
2007).
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
752

2.5 Clean Water Development System
Part of a clean water distribution network system, are
the components that exist in a series of clean water
distribution network systems. These parts consist of
pipes and their connections, valves, pumps,
reservoirs, all of which must work properly.
Based on the instructions of the Integrated City
Infrastructure Development Program regarding
Guidelines for Planning and Technical Design for the
drinking water sector, it is stated that the raw water
sources that can be treated are springs, namely water
sources that are above the ground surface, shallow
wells, namely water sources resulting from
excavations or drilling depths. less than 40 meters
deep, deep wells, namely water sources from
excavation or drilling with a depth of more than 40
meters, rivers, namely water drainage channels
formed from upstream to empties into the sea or
lakes, lakes and water reservoirs, namely deep water
storage units a certain amount of which the water
comes from streams or rainwater reservoirs.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Scope of Research
The scope of the utilization of the Tukad Unda river
for the development of clean water services in the
Denpasar, Badung, Gianyar and Klungkung
(Sarbagikung) areas are:
Conduct a literature study or review of relevant
studies related to the remaining water in the
lower reaches of Tukad Unda
Measure the downstream Tukad Unda
instantaneous discharge
Analyzing the Tukad Unda discharge data based
on the Unda Dam discharge recording data,
AWLR, and rain data.
Analyzing the mainstay of the Tukad Unda debit
Analyzing the availability of Tukad Unda water
and current irrigation water needs
Analyzing the water balance downstream of
Tukad Unda
3.2 Data Source
The data source is a very important part related to the
validity of the data. With regard to the data to be
retrieved, the data that will be needed are as follows:
Daily rain data for 15 years from Besakih Rain
Station, Rendang Rain Station, Duda Rain
Station, and Klungkung Rain Station.
Data on debit recording at the Tukad Unda
AWLR Post for 15 years.
Data on debit recording in Unda Dam for 15
years.
Demographic data of the population, socio-
cultural facilities and infrastructure, tourism,
industry.
Clean water supply system data
Data on current sources of clean water
Clean water quality and quantity data
3.3 Measurement with Current Meter
The tool used to measure the flow velocity is a current
measuring instrument, which is commonly referred to
as a current meter. The main equipment commonly
used in measuring flow is a flow meter, including all
its accessories, namely a timer and a rotation counter,
a depth gauge, a width gauge, assembly equipment
and some additional tools. The selection of the use of
equipment and equipment must be adjusted to the
physical condition of the river being measured.
3.4 Analysis of Clean Water
Availability
In calculating the mainstay discharge using the basic
year planning method. The planning base year is a
reliable debit pattern where the debit pattern has
actually happened in previous years. The mainstay
discharge calculation is intended to find the
quantitative value of the available discharge
throughout the year, in the dry season and in the rainy
season.
3.5 Population Analysis
Calculation of the population using arithmetic,
geometric and least square formulas. To determine
the method used in each sub-district, the smallest
standard deviation value of the three approaches will
be determined.(Minister of Public Works Regulation
2007).
3.6 Clean Water Needs Analysis
The Directorate General of Human Settlements has
set the water usage standard for metropolitan cities of
190 liters/person/day, standard waterrequirements for
large cities at 170 liters/person/day, medium cities at
Utilization of the Tukad Unda River for the Development of Clean Water Services Denpasar, Badung, Gianyar and Klungkung
(Sarbagikung) Areas
753
150 liters/person/day, and small cities at 130 liters
people. /day.
3.7 Water Balance
The water balance is intended to determine how much
potential is available each month, as well as how
much water is needed. The Water Balance will know
the months of surfing as well as the months that are
in deficit. Mathematically, the calculation method for
obtaining the residual water discharge in this water
balance analysis is the mainstay discharge minus the
demand discharge.
3.8 Clean Water Supply System
Strategy
The clean water supply system strategy is carried out
by means of a literature study, with the development
of the concept of sustainable water source
management, based on the condition of the current
system that has been running, taking into account the
sustainability of clean water supply in the future.
Inventory of existing clean water sources and clean
water sources that are in the process of being built.
4 DISCUSSION RESULT
4.1 Population
Calculation of population using arithmetic, geometric
and least square formulas. Determination of the
method used in each sub-district will be determined
with the smallest standard deviation value of the three
approaches. (Minister of Public Works Regulation,
2007)
Table 1: Population of the Sarbagikung Area.
Districts
Projected population (person)
2020 2025 2030 2035 2040
Denpasar 962.900 1.057.362 1.165.838 1.285.734 1.418.286
Badung 683.200 750.730 816.460 880.390 942.520
Gianyar 516.300 539.827 563.645 588.099 613.217
Klungkung 180.780 186.824 192.869 198.913 204.957
Total 2.343.180 2.534.743 2.738.812 2.953.136 3.178.980
4.2 Water Demand Projection
The sub-district's domestic water needs are
determined based on the population. In 2020 and
2021, it is assumed that the service level has reached
80%, an increase of 5% annually, until in 2025 the
service level has reached 100%. Non-domestic needs
are 20% of domestic needs, water leakage is 20% of
total domestic and non-domestic needs. The total of
water needs is the sum of domestic, non-domestic,
and water leaks.
Table 2: Average Water Demand Capacity.
Districts
Average Water Demand Capacity (liter/second)
2020 2025 2030 2035 2040
Denpasar 1.925,80 2.643,41 2.914,59 3.214,34 3.545,72
Badung 1.255,95 1.764,52 2.001,67 2.153,88 2.347,57
Gianyar 929,31 1.176,09 1.303,79 1.361,04 1.419,81
Klungkung 306,77 371,4 417,88 430,98 444,08
TOTAL 4.417,83 5.955,42 6.637,93 7.160,24 7.757,18
4.3 Mainstay Debit Analysis
Mainstay debit is the amount of discharge available
to meet water needs with a calculated risk of failure.
In planning a water supply project, a reliable
discharge must first be sought, the purpose of which
is to determine the planned discharge which is
expected to always be available in the river
(Soemarto, 1987). The mainstay discharge is intended
to find the quantitative value of the available
discharge throughout the year, both during the dry
season and in the rainy season. The mainstay debit is
the minimum debit that can be guaranteed reliability
with a probability of P% or has a failure risk level of
(1-P%).
Table 3: Mainstay debit 90% at Weir Unda.
Descri
p
tion
Mainstay Discharge 90% in Unda Dam (m3/s)
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun
AWLR Debit Data 3,84 3,88 3,66 3,59 2,76 1,57
Recording Debit
Data at Unda Dam
7,95 6,23 7,62 8,22 7,54 5,97
FJ. Mock Debit
Data
7,20 12,50 7,00 6,50 3,70 0,20
Average 6,33 7,54 6,09 6,10 4,67 2,58
Descri
p
tion
Mainstay Discharge 90% in Unda Dam (m3/s)
Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
AWLR Debit Data 2,74 2,21 3,34 1,40 2,11 3,60
Recording Debit
Data at Unda Dam
6,41 5,40 4,24 3,76 7,56 5,61
FJ. Mock Debit
Data
4,70 1,50 4,30 2,10 1,20 7,60
Average 4,61 3,04 3,96 2,42 3,63 5,60
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
754
4.4 Irrigation Water Needs
The area of irrigated rice fields utilized by the Unda
Irrigation Area is 1,104.89 ha. The condition of the
existing cropping pattern in DI Unda is Paddy Paddy
Palawija, early planting of rice 1 is March 1, paddy 2
is on July 1 and palawija is on October 1st.
Table 4: Irrigation Water Needs in Unda Weir.
Descri
p
tion Irri
g
ation Water Needs in Unda Weir (m3/sec)
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun
Existing
Irrigation
Needs
0,04 0,68 1,46 0,59 0,56 0,77
Descri
p
tion Irri
g
ation Water Needs in Unda Weir (m3/sec)
Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
Existing
Irrigation
Needs
1,54 1,31 1,14 0,55 0,31 0,70
4.5 Water Balance
Water-balance is an analysis that describes the
utilization of water resources in a review area based
on a comparison between water demand and
availability. The calculation of the water balance is
intended to determine the remaining Tukad Unda
water after being used, which indicates a shortage or
excess of water, in the downstream part of the Tukad
Unda watershed, in terms of the availability of surface
water.
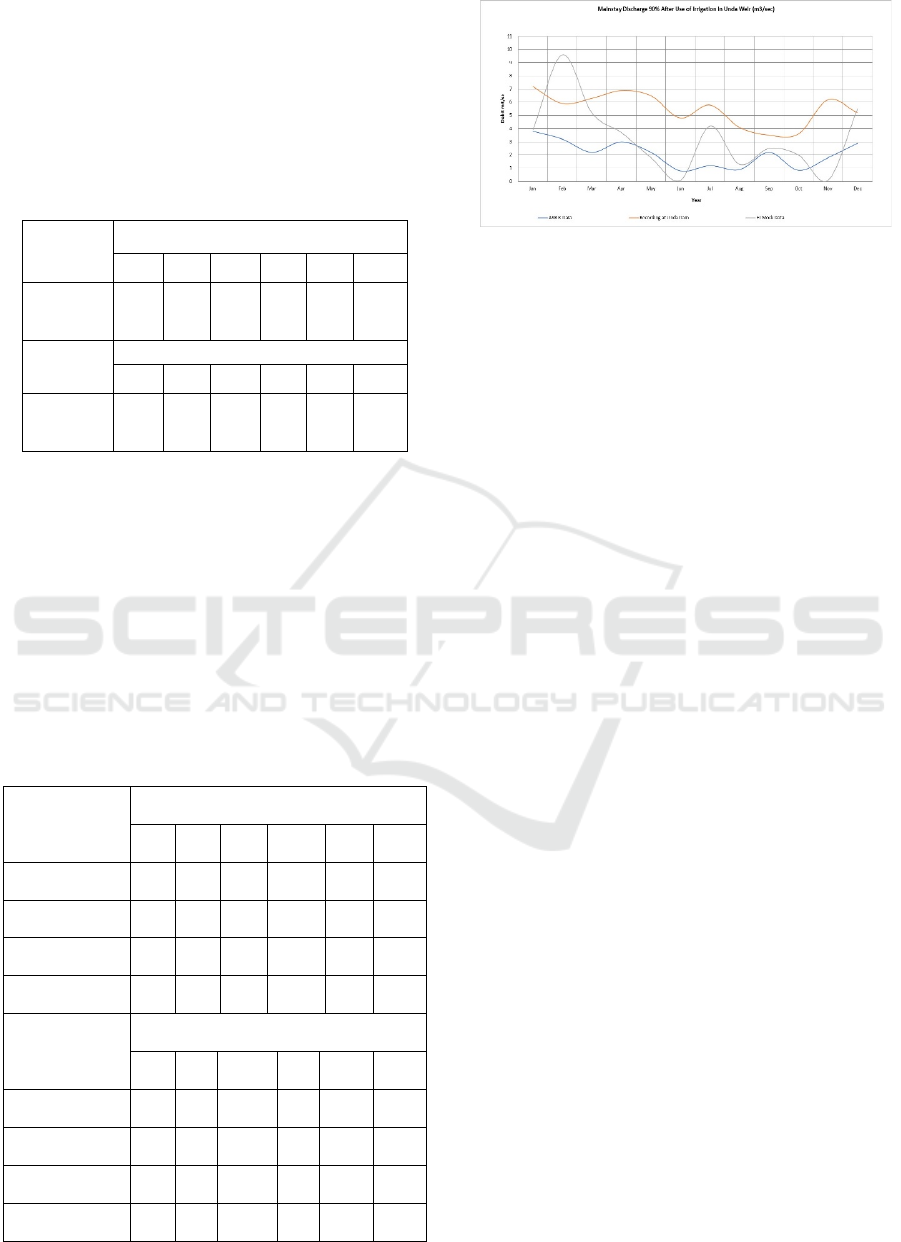
Table 5: Mainstay Discharge 90% in Unda Dam.
Description
Mainstay Discharge 90% After Use of
Irrigation in Unda Weir (m
3
/sec)
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun
AWLR Debit Data 3,80 3,20 2,20 3,00 2,20 0,80
Recording Debit
Data at Unda Dam
7,20 5,90 6,30 6,90 6,50 4,80
FJ. Mock Debit
Data
3,90 9,60 5,20 3,70 1,80 0,10
Average 4,97 6,23 4,57 4,53 3,50 1,90
Description
Mainstay Discharge 90% After Use of
Irrigation in Unda Weir (m
3
/sec)
Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
AWLR Debit Data 1,20 0,90 2,20 0,85 1,80 2,90
Recording Debit
Data at Unda Dam
5,80 4,10 3,50 3,60 6,20 5,20
FJ. Mock Debit
Data
4,20 1,30 2,50 2,00 0,10 5,50
Average 3,73 2,10 2,73 2,15 2,70 4,53
Figure 1: Mainstay Discharge 90% in Unda Weir
(Remaining Water downstream of the Unda Weir).
5 CONCLUSION
The conclusion of the research is :
The average value of the residual water
discharge in Tukad Unda is 3,638 m3/sec.
The need for clean water in the Sarbagikung
area until 2040 is 7,757 m3/s.
The planned allocation of water from Estuary of
Tukad Unda Reservoir for the Sarbagikung area
is 1,400 liters/second, covering 850
liters/second to meet the needs in South
Denpasar District, 100 liters/second in South
Kuta District, 300 liters/second which will
distributed to the Districts of Gianyar and
Klungkung at 150 liters/second.
REFERENCES
Agarwa (2000). Integarted Water Resources Managemen.
tehnicel Advisory Commitee (TAC). Global Water
Parnership (GWP) Stokholo. Sweden, Home Page of
GWP www.gwpforum.org
Agrifa Masir (2017). JISIP., Journal of Social and Political
Sciences. Vol 6. N0.2. PDAM Strategy in Improving
Clean Water Quality to Support Development in Batu
Tourism City.
Kementrian Pekerjaan Umum (2013). Criteria for Irrigation
Planning KP-01. Planning of irrigation networks.
Jakarta: Directorate General of Water Resources.
Minister of Public Works Regulation No.18/PRT/M/2007
(2007). Concerning Implementation of Drinking Water
Supply System Development.
Andito Sidiq Swastomo (2020). Sukowati Research and
Development Journal, Community-Based Rural Water
Supply System Sustainability.
Central Statistics Agency (2020). Denpasar City in Figures,
Badung Regency in Figures, Jembrana Regency in
Figures, Klungkung Regency in Figures.
Utilization of the Tukad Unda River for the Development of Clean Water Services Denpasar, Badung, Gianyar and Klungkung
(Sarbagikung) Areas
755

Beecher, Janice A (1995). Integarated Resources Planiing
Fundamentals, Journal of American Water Works
Assosiation (AWWA)
Chow, VT (1992). Open Channel Hydraulics. Bandung: PT
Erlangga.
Erwin Nugraha. (2009). Department of Planning
Engineering. Bandung Institute of Technology.
Joerson Loebis, Soewarno, Suprihadi B (1993). River
Hydrology, Jakarta: Public Works Publishing Agency
Foundation.
Kamulyan, P. Wiguna, I.P.A. and Slamet, A. (2017).
Assessment of the Sustainability of Community-Based
Drinking Water Supply System Management in Blitar
City. Ten November Institute of Technology Journal Of
Civil Engineering. 32(2). 60-6.
Kamiana, I. M. (2012). The technique of calculating the
discharge plan of the water structure. Yogyakarta:
Graha Ilmu.
Mock, F.J. (1973). Water Availability Appraisal. Basic
study prepared for FAO/ UNDP Land Capability
Appraisal Project. Bogor.
Minister of Public Works Regulation No.18/PRT/M/2007
(2007). Concerning Implementation of Drinking Water
Supply System Development
Soemarto CD (2011). Engineering Hydrology. Jakarta :
Erlangga.
Soewarno (1995). Hydrology Application of Statistical
Methods for Data Analysis. Bandung : Nova
Sudirman et al (2021). Irrigation Systems and Waterworks,
Publisher: Yayasan Kita Menukis . Medan.
Slamet Suprayogi (2020). Watershed Management.
Publisher : UGM Press. Yogyakarta.
Norken, I Nyoman (2003). Integrated and Sustainable
Development and Management of Water Resources (A
Challenge in Water Resources Management in
Indonesia), Paper in Seminar on Integrated and
Sustainable Development and Management of Water
Resources, F.T. UNUD, Denpasar.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
756
