
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of
Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
Weiwei Zhang
Tianjin University of Finance and Economics Pearl River College, Tianjin, 301811, China
Keywords: Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Data Mining, Index System, Expert Survey Method, Hierarchical Analysis
Method.
Abstract: The "mass entrepreneurship and innovation" has been raised to a national strategy, and the cultivation of
college students' innovation and entrepreneurship has become one of the urgent tasks of higher education
reform. This paper designs a model for cultivating college students' innovation and entrepreneurship based on
data mining technology. Firstly, we study the literature related to the cultivation of innovation and
entrepreneurship ability of college students, select the influencing factors to build the index system of
innovation and entrepreneurship ability cultivation, and determine the index level by expert survey method;
then, we introduce big data mining technology to match the characteristics of college students' innovation and
entrepreneurship ability cultivation, and use AHP hierarchical analysis method to establish the model of
innovation and entrepreneurship ability cultivation; finally, we calculate and analyze the weight of each
cultivation Finally, by calculating and analyzing the corresponding weights of each cultivation indicator, we
derived the main factors affecting the cultivation of college students' innovation and entrepreneurship ability,
and proposed the feasible ability cultivation strategies.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the continuous development of society and the
country's emphasis on education, the number of
college graduates in China is increasing, and the
employment pressure of college graduates comes with
it. While college students are facing employment
difficulties, there is a labor shortage phenomenon in
sociaty. This contradiction shows that there is a gap
between the college students cultivated by the current
college talent producing+ mechanism and the 21st
century enterprise talent demand. Under the
employment system of "Bidirectional options" for
college students, creative talents with innovative and
entrepreneurial consciousness and ability are more
welcomed by the society. This paper will conduct an
in-depth discussion and research on the factors
influencing the cultivation of innovation and
entrepreneurship among college students and
determine the weight of each influencing factor from
qualitative and quantitative perspectives, and propose
countermeasures and suggestions.
2 RESEARCH ON THE FACTORS
OF CULTIVATING
INNOVATION AND
ENTREPRENEURSHIP
ABILITY OF COLLEGE
STUDENTS IN GENERAL
COLLEGES AND
UNIVERSITIES
2.1 Index System for Cultivating
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Ability of College Students
According to Chu Mingchang (2014), "strengthening
the cultivation of college students' innovation and
practice ability is the core of education reform in
higher education", and that "college students'
innovation and entrepreneurship training program
project is an effective carrier to cultivate innovation
and practice ability" (Chu, Li, Gao, 2014). Dong
Yunfei and Zheng Libo (2014) believe that only
through optimizing the innovation and
90
Zhang, W.
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining.
DOI: 10.5220/0011898700003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 90-99
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

entrepreneurship curriculum system, establishing a
multidisciplinary and comprehensive mentor team
and building a practice platform for college students
can we promote and enhance the innovation and
entrepreneurship ability of college students (Dong,
Zheng, 2014). According to Tang Genli (2009), the
cultivation of innovation and entrepreneurship talents
requires universities to "create a campus culture that
encourages innovation and entrepreneurship, improve
the curriculum system of innovation and
entrepreneurship education, strengthen the
construction of innovation and entrepreneurship
teachers, cultivate innovation and entrepreneurship
student teams, strengthen the construction of
innovation and entrepreneurship practice bases,
enhance the practical activities, and strengthen the
support of the government and the community. "(Tang
2009) Zhang Jihe and Zhang Fan (2011), put forward
five countermeasures for the dilemma of cultivating
practical innovation ability of undergraduate students
in colleges and universities: "to construct personalized
talent cultivation goals; to strengthen the support of
practical teaching working conditions; to enrich and
optimize the construction of practical teaching team;
to establish a scientific and reasonable assessment and
evaluation system and to support students to conduct
scientific research practice training ". (Zhang, Zhang,
2011) Qian Xiaoming, Rong Huawei and Qian
Jingzhu (2014) believe that the "innovation and
entrepreneurship training program for college
students" education under the mentor ship system is
an effective way for higher education institutions to
do a good job in innovation and entrepreneurship
education and guide students to carry out innovation
and entrepreneurship training (Qian, Rong, Qian,
2014). In addition, Jiang Qian et al. (2016) gave the
path of cultivating innovation and practice ability of
college students from three levels, and believed that
students should cultivate interests and hobbies,
cultivate innovation consciousness, teachers should
establish the education idea of innovation and
practice, strengthen the construction of teaching team,
and "the interaction of scientific research and
teaching, innovation and practice in parallel, while the
school should create innovation and entrepreneurship
training system and build In order to promote the
orderly development of innovation and
entrepreneurship education, the school should create
an innovation and entrepreneurship training system
and build a network platform (Jiang, Liu, Hu, Wu,
2016). Chen Yong (2016) pointed out that universities
should strengthen the construction of full-time
teachers of innovation and entrepreneurship
education, enhance training in innovation and
entrepreneurship education, encourage teachers to
strengthen theoretical research on innovation and
entrepreneurship education, and actively create
conditions to encourage them to go deeper into
practice and cultivate them into groups with both
theoretical knowledge and practical experience (Chen
2016).
This paper constructs a five-dimensional structural
model that affects the cultivation of innovation and
entrepreneurship ability. The five dimensions are: 1.
Talent cultivation objectives and modes; 2. Training
and construction of faculty team; 3. Teaching Content
and Curriculum Design; 4. financial and policy
support; 5. Experimental and practical teaching
management. For the above 5 dimensional contents,5
experts and scholars were asked to carry out repeated
discussions and finally came up with 20 specific
influential contents. In this way, according to the
principle of AHP hierarchical analysis, this paper
divides the index system according to the target level,
criterion level and program level, and constructs the
hierarchical structure model of innovation and
entrepreneurship cultivation of college students in
local universities; Table 1 shows the evaluation
system of influence factors of innovation and
entrepreneurship cultivation in local universities.
Table 1 Evaluation system of factors influencing the cultivation of innovation and entrepreneurship in local Universities
Target layer Criterion layer Scheme layer
A:Cultivation
of innovation
and
entrepreneurial
ability in local
universities
B1 Talent
cultivation
objectives and
modes
C1 Clarify the goal of cultivating talents for innovation and entrepreneurship
education
C2 In-depth integration of innovation and entrepreneurship education with
professional education
C3 Establish a mentorship-based innovation and entrepreneurship training
program for college students
C4 Curriculum structure and teaching contents meet the needs of innovative
and entrepreneurial talents
B2 Training and
construction of
faculty team
C5 Create a team of teachers for innovation and entrepreneurship practice
C6 Establish a multidisciplinary comprehensive mentor team
C7 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship
C8 Use social power to form part-time teachers
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
91
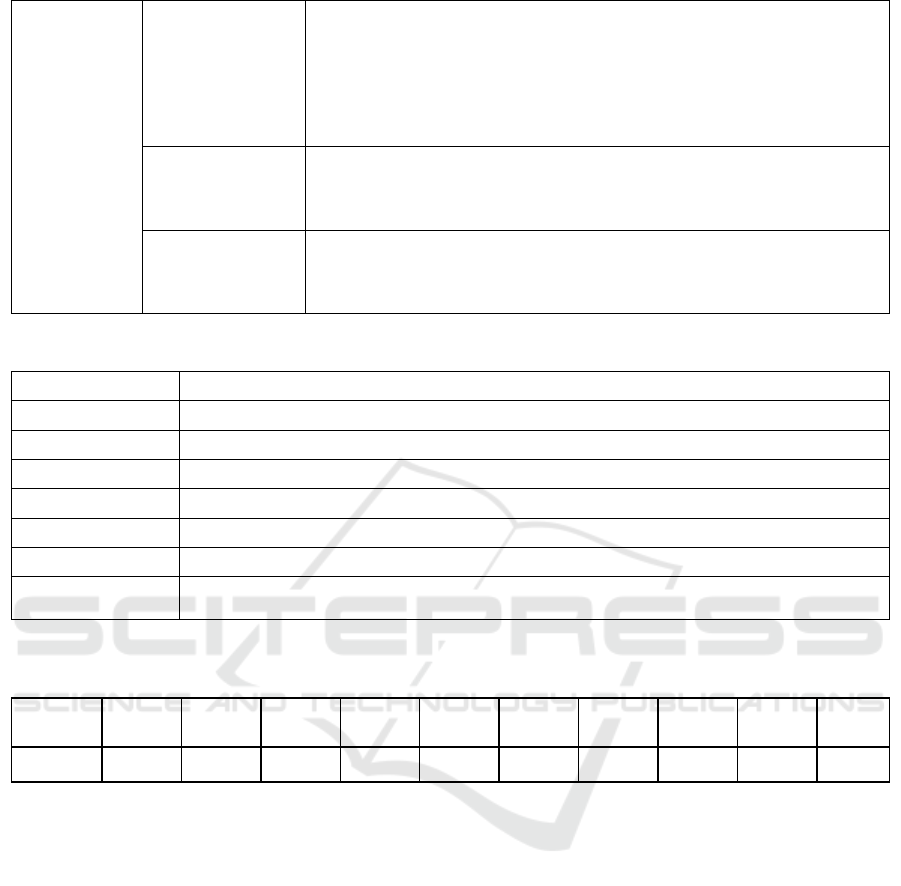
B3 Teaching
Content and
Curriculum Design
C9 Establish the Educational Ideology of Innovation and Practice
C10 Improve the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Curriculum System
C11 Conduct lectures on innovation and entrepreneurship knowledge
C12 Construct a classroom teaching mode that emphasizes both theory and
practice
C13 Establish a scientific examination and evaluation system for innovation
and entrepreneurship education courses
B4 Financial and
policy support
C14 Strengthen the support of practical teaching working conditions
C15 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship
C16 Create a campus culture that encourages innovation and entrepreneurship
C17 Stren
g
then the su
pp
ort from the
g
overnment and the societ
y
B5 Experimental
and practical
teaching
mana
g
ement
C18 Build a platform for innovation and entrepreneurship practice
C19 Cultivate innovative and entrepreneurial student teams
C20 Strengthen the construction of innovation and entrepreneurship practice
b
ases
Table 2 Significance scale meaning table
Importance scale Interpretation and description
1 Indicates that two factors have the same importance
3 Indicates that one element is slightly more important than the other
5 Indicates that one element is more important than the other
7 Indicates that one element is more important than the other
9 Indicates that one element is more important than the other
2, 4, 6, 8 is the median value of the above adjacent judgments
Inverse value
When i is compared with j, it is given the value of some criterion above; when j is compared with
i, the weight value is the inverse of that criterion
Table 3 Average random consistency indexRIstandard values (different standards are different,RIand the values may have
slight differences)
Matrix
orde
r
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
RI 0 0 0.58 0.90 1.12 1.24 1.32 1.41 1.45 1.49
2.2 Big Data Mining Technology
2.2.1 Establishing Hierarchical Structure
Model
Hierarchical analysis divides the goal, the factors to be
considered (decision criteria) and the decision object
into the highest level, the middle level and the lowest
level according to their interrelationship, and draws a
hierarchical structure diagram. The highest level
refers to the purpose of the decision, the problem to be
solved. The lowest level refers to the alternatives in
decision making. The middle level refers to the factors
to be considered, the criteria for decision making. For
the two adjacent layers, the higher layer is called the
objective layer and the lower layer is the factor layer.
2.2.2 Construction of Judgment Matrix
Using the consistency matrix method, factors are
compared with each other in pairs. If there be n factors
in a given stratum, X=
x
,x
,⋯,x
, if you want to
rank the degree of influence of n factors on an
objective at the upper level, a
is the result of
comparing the importance of factor i with that of
factor j. Table 2 shows the nine levels of importance
and their assigned values. The matrix formed by the
results of a comparison is called the judgment matrix.
A=a
×
=
a
a
a
a
⋯a
⋯a
⋮⋮
a
a
⋮⋮
⋯a
Where
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
92

a
=
1
a
The judgment descaling methods of the matrix
factors a
are as follows (Table 2).
The judgment matrix satisfies the property 1,
a
>0; 2, a
=
; 3, a
=1, is then a positive
reciprocal matrix.
2.2.3 Calculate the Single Ranking Weight
Vector and Do Consistency Test
The process of determining the degree of influence of
each factor at the lower level on a factor at the upper
level is called hierarchical single ranking. The degree
of influence is expressed in terms of weights, The
weights of each of the n influencing factors are
w
,w
,⋯,w
, then the judgment matrix is
A=
⎝
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎛
1
w
w
w
w
1
⋯
w
w
⋯
w
w
⋮⋮
w
w
w
w
⋮⋮
⋯1
⎠
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎞
Where
w
w
=
w
w
∙
w
w
That a
∙a
=a
i,j=1,2,⋯,n is, In the
positive and negative matrixA, if a
∙a
=a
, then
it is a consistent array.
Whether the hierarchical single ordering can be
confirmed, where, the unique non-zero characteristic
root of a consistent array of nth order is n; maximum
characteristic roots of nth order positive reciprocal
inverse array is λ≥n, when and only whenλ=n, A
is the consistent matrix.
Since λ continuous depends, a
,then more λ
larger than A, the more serious the inconsistency of A.
The consistency was calculated by index CI. The
smaller the CI is, indicating that the greater the
consistency is.
CI=
λ−n
n−1
When CI=0 , there is complete
consistency; when CIclose to 0, there is satisfactory
consistency; when CI is grow bigger, the
inconsistency grow more seriously.
For measuring the value of CI, stochastic
consistency indicator RI is introduced.
RI=
CI
+CI
+⋯+CI
n
where, the stochastic consistency indicator RI is
related to the order of the judgment matrix, and in
general, the greater the order of the matrix, the greater
the possibility of random deviation of consistency,
and its correspondence is shown in Table 3.
Considering that deviations from consistency may
be due to random causes, in testing whether the
judgment matrix is satisfactorily consistent, it is also
necessary to compare CI with the stochastic
consistency index RI, the test coefficients are derived
as follows
CR=
CI
RI
Generally, if,CR<0.1 then the judgment matrix
is considered to pass the consistency test, otherwise it
does not have satisfactory consistency.
2.2.4 Calculate the Total Ranking Weight
Vector and do the Consistency Test
Calculation of the weights of the relative importance
of all factors at a given level to the highest level (the
overall objective) is called the overall ranking of the
levels. A level has m factors A
,A
,⋯,A
, the
ranking of the total objective Z is a
,a
,⋯,a
. B
level has n factors, the hierarchical single ranking of
factor A
in upper level A is b
,b
,⋯,b
,j=
1,2,⋯,m, the total hierarchical ordering of the B
levels is:
B1:a
b
+a
b
+⋯+a
b
B2:a
b
+a
b
+⋯+a
b
⋯
Bn:a
b
+a
b
+⋯+a
b
The weight value of the total objective is.
a
b
The consistency ratio of the hierarchical total
ranking is
CR=
a
CI
+a
CI
+⋯+a
CI
a
RI
+a
RI
+⋯+a
RI
At CR<0.1 that time, the hierarchical total
ranking is considered to pass the consistency test.
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
93
2.3 Research Steps of
Countermeasures for Cultivating
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Ability of College Students
Take the cultivation of college students' innovation
and entrepreneurship ability as the target layer, each
factor of the evaluation system as the criterion layer,
and the cultivation countermeasures as the program
layer. Experts and scholars are invited to assign values
to the factors in the index system respectively
according to the importance scale meaning table
(Table 2).
2.3.1 Hierarchical Single Ranking
The judgment matrix of the criterion layer of factors
influencing the cultivation of innovation and
entrepreneurship ability of college students in local
universities is calculated. Among them, the weights
indicate the weights of the five influencing factors of
the criterion layer on the degree of influence of the
upper target layer. Table 4 shows the judgment results.
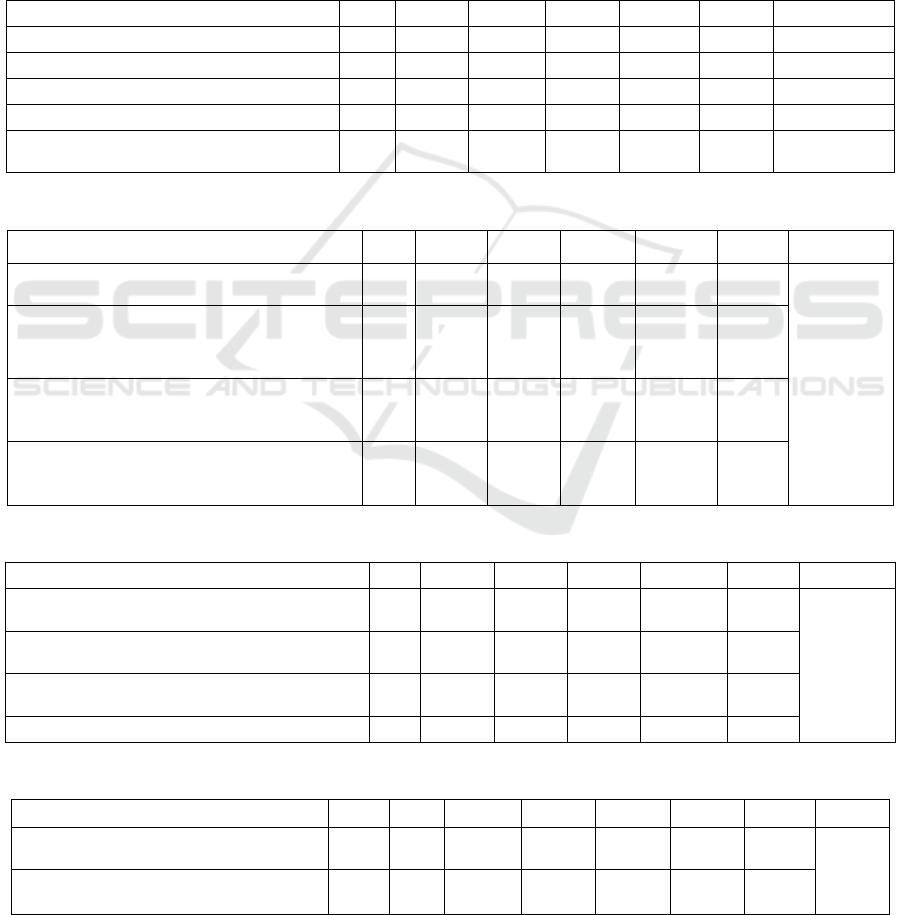
Table 4 Judgment matrix of the criterion layer
A B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 Wi
Talent cultivation objectives and modes
B1 1 1.9 2.5667 2.55 2.3667 0.2708
Training and construction of faculty team
B2 1.8167 1 3.8 3.6 3.2 0.3221
Teaching Content and Curriculum Design
B3 1.1567 0.2733 1 2.2667 2.2667 0.1599
Financial and policy support
B4 1.3567 0.2833 0.9 1 0.7667 0.1168
Experimental and practical teaching
mana
g
emen
B5 1.1667 0.3167 0.9 1.9 1 0.1303
Table 5 Judgment Matrix of Talent Cultivation Objectives and Modes Factors
B1 C1 C2 C3 C4 Wi λmax
Clarify the goal of cultivating talents for
innovation and entrepreneurship education C1 1 1.6 2.4667 1.1667 0.2689
5.4623
In-depth integration of innovation and
entrepreneurship education with professional
education
C2 1.1333 1 1.5333 1.3333 0.2274
Establish a mentorship-based innovation and
entrepreneurship training program for college
students
C3 0.8667 1.4667 1 0.9167 0.1912
Curriculum structure and teaching contents
meet the needs of innovative and
entre
p
reneurial talents
C4 1.85 2.04 2.2667 1 0.3125
Table 6 Judgment Matrix of Cultivation and construction of faculty Factors
B2 C5 C6 C7 C8 Wi λmax
Create a team of teachers for innovation and
entrepreneurship practice
C5 1 2.25 2.5 2.7 0.3543
5.4593
Establish a multidisciplinary comprehensive
mentor tea
m
C6 1.1833 1 1.9667 2.3667 0.2734
Create a training system for innovation and
entrepreneurship
C7 0.6833 1.2 1 2 0.2036
Use social power to form part-time teachers C8 0.65 1.1667 1 1 0.1688
Table 7 Judgment matrix of Teaching Content and Curriculum Design factors
B3 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 Wi λmax
Establish the Educational Ideology of
Innovation and Practice
C9 1 0.6833 1.5 1.0667 1.3667 0.153
6.6128
Improve the Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Curriculum System
C10 2.5 1 3.6 2.7 3.6 0.3478
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
94
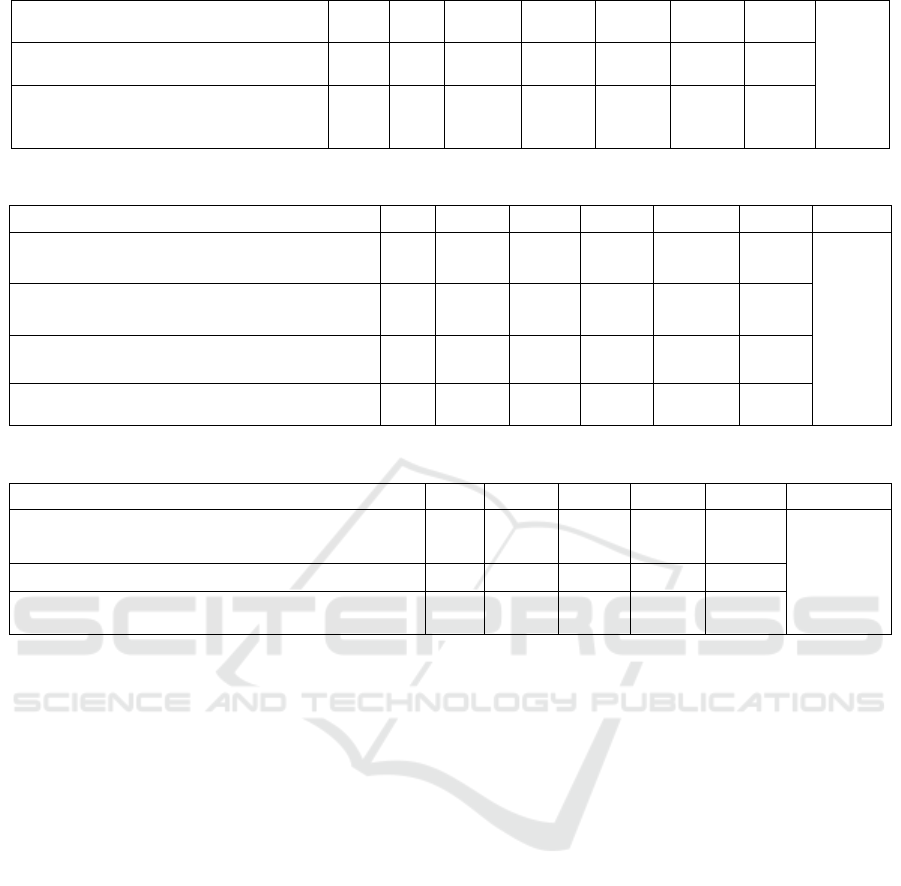
Conduct lectures on innovation and
entre
p
reneurshi
p
knowled
g
e
C11 1.35 0.29 1 0.8333 0.6333 0.1079
Construct a classroom teaching mode
that emphasizes both theory and practice
C12 2.65 0.6733 2.8667 1 3.4 0.2529
Establish a scientific examination and
evaluation system for innovation and
entrepreneurship education course
C13 1.84 0.3067 2.9 0.3 1 0.1384
Table 8 Judgment matrix of financial and policy support factors
B4 C14 C15 C16 C17 Wi λmax
Strengthen the support of practical teaching
working conditions
C14 1 2.3333 2.5667 2.3667 0.3286
5.8961
Create a training system for innovation and
entrepreneurship
C15 1.3667 1 3.6 3.2667 0.33
Create a campus culture that encourages
innovation and entrepreneurship
C16 1.15 0.2833 1 1.5333 0.1547
Strengthen the support from the government
and the societ
y
C17 1.28 0.8067 1.4667 1 0.1866
Table 9 Judgment matrix of Experimental and practical teaching management factors
B5 C18 C19 C20 Wi λmax
Build a platform for innovation and entrepreneurship
practice
C18 1 2.4667 2.5333 0.4396
4.1922
Cultivate innovative and entrepreneurial student teams C19 0.8833 1 1.2667 0.2463
Strengthen the construction of innovation and
entrepreneurship practice bases
C20 1.3567 1.65 1 0.3141
In Table 4, "Talent Cultivation Objectives and
Mode" and "Training and construction of faculty
team" have the highest weights, indicating that these
two factors are very crucial to the cultivation of
college students' innovation and entrepreneurship.
In Table 5, the highest weight is given to "Clarify
the goal of cultivating talents for innovation and
entrepreneurship education", which indicates that the
positioning of talents' goal is the platform to guide the
teaching practice afterwards.
In Table6, "Create a team of teachers for
innovation and entrepreneurship practice" has the
highest weight and plays a relatively important role in
"Training and construction of faculty team".
In Table 7, "Improve the Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Curriculum System" has the highest
weight, which indicates that reforming the innovation
and entrepreneurship curriculum and building a
classroom teaching mode with equal emphasis on
"theory and practice" are important aspects to improve
the innovation and entrepreneurship ability of college
students.
In Table 8, "Strengthen the support of practical
teaching working conditions" has the highest weight,
which indicates that the effective support of
supporting facilities is indispensable in cultivating the
innovation and entrepreneurial ability of college
students.
In Table 9, the highest weight is given to "Build a
platform for innovation and entrepreneurship
practice", followed by Strengthen the construction of
innovation and entrepreneurship practice bases, which
indicates that strengthening the practical activities is
the key to improving the innovation and
entrepreneurship ability of college students.
Tables 10 and 11 are the consistency tests of the
above judgment matrix.
It can be seen through Table 11 that the above
judgment matrix CR values are all less than 0.1, which
passed the consistency test, that is, when comparing
all the results together, there is no inconsistency in the
comparison results.
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
95
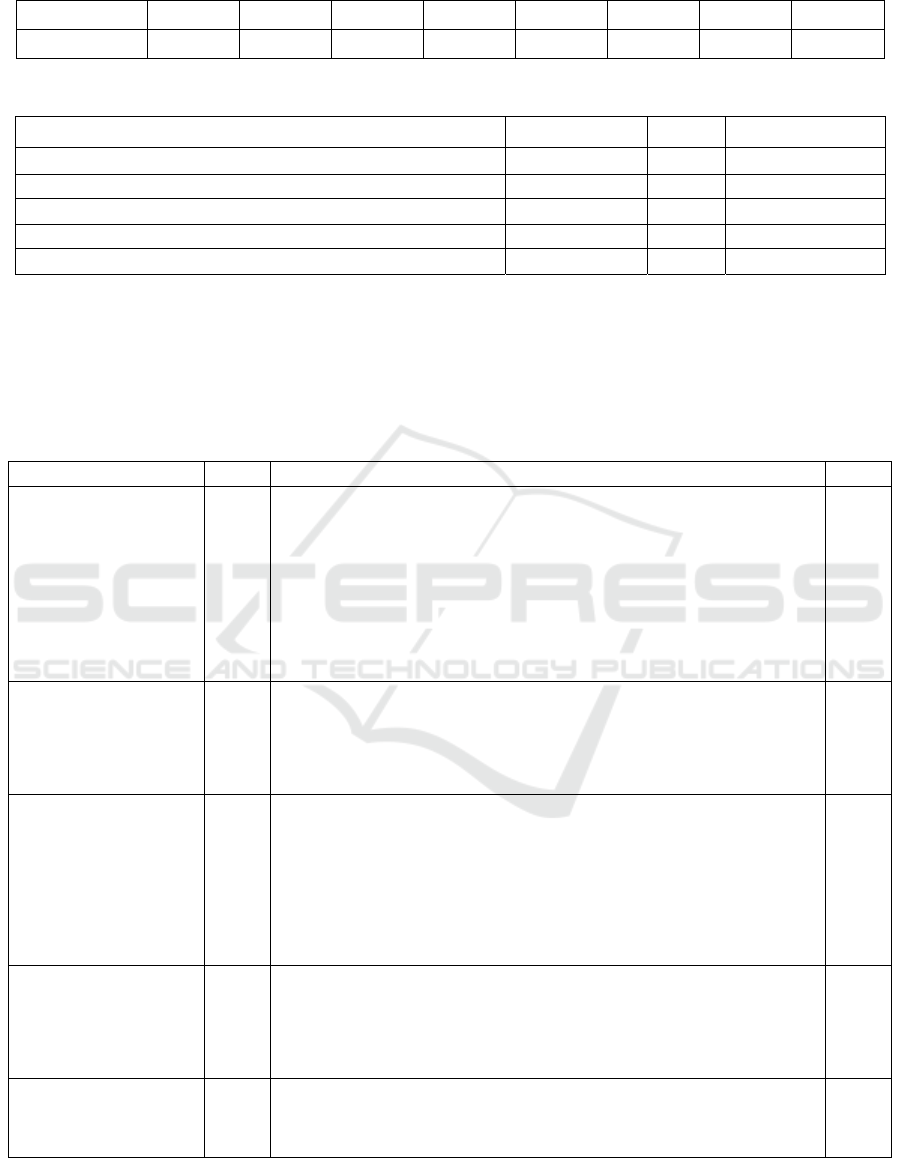
Table 10 Random consistency RI table
n-order 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
RI value 0.52 0.89 1.12 1.26 1.36 1.41 1.46 1.49
Table 11 Consistency test
Judgment matrix λmax CR (CR<0.1)
Talent cultivation objectives and modes 5.4623 0.080 Pass
Training and construction of faculty team 5.4593 0.050 Pass
Teaching Content and Curriculum Design 6.6128 0.090 Pass
Financial and policy support 5.8961 0.079 Pass
Experimental and practical teaching management 4.1922 0.052 Pass
2.3.2 Total Hierarchical Ranking
Based on the above research, we now rank the weights of
the indicator system of the factors influencing the cultivation
of innovation and entrepreneurship ability of local
university students, as shown in the following figure:
Table 12 Weight distribution of the index system of factors influencing the cultivation of innovation and entrepreneurship in
local universities
Criterion layer Weight Scheme layer Weight
B1 Talent cultivation
objectives and modes
0.2708
C1 Clarify the goal of cultivating talents for innovation and entrepreneurship
education
C2 In-depth integration of innovation and entrepreneurship education with
professional education
C3 Establish a mentorship-based innovation and entrepreneurship training program
for college students
C4 Curriculum structure and teaching contents meet the needs of innovative and
entrepreneurial talents
0.0728
0.0616
0.0518
0.0846
B2 Training and
construction of faculty
team
0.3221
C5 Create a team of teachers for innovation and entrepreneurship practice
C6 Establish a multidisciplinary comprehensive mentor team
C7 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship
C8 Use social power to form part-time teachers
0.1141
0.0881
0.0656
0.0544
B3 Teaching Content and
Curriculum Design
0.1599
C9 Establish the Educational Ideology of Innovation and Practice
C10 Improve the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Curriculum System
C11 Conduct lectures on innovation and entrepreneurship knowledge
C12 Construct a classroom teaching mode that emphasizes both theory and
practice
C13 Establish a scientific examination and evaluation system for innovation and
entrepreneurship education courses
0.0245
0.0556
0.0173
0.0404
0.0221
B4 Financial and policy
support
0.1168
C14 Strengthen the support of practical teaching working conditions
C15 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship
C16 Create a campus culture that encourages innovation and entrepreneurship
C17 Strengthen the support from the government and the society
0.0384
0.0386
0.0181
0.0218
B5 Experimental and
practical teaching
management
0.1303
C18 Build a platform for innovation and entrepreneurship practice
C19 Cultivate innovative and entrepreneurial student teams
C20 Strengthen the construction of innovation and entrepreneurship practice bases
0.0573
0.0321
0.0409
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
96
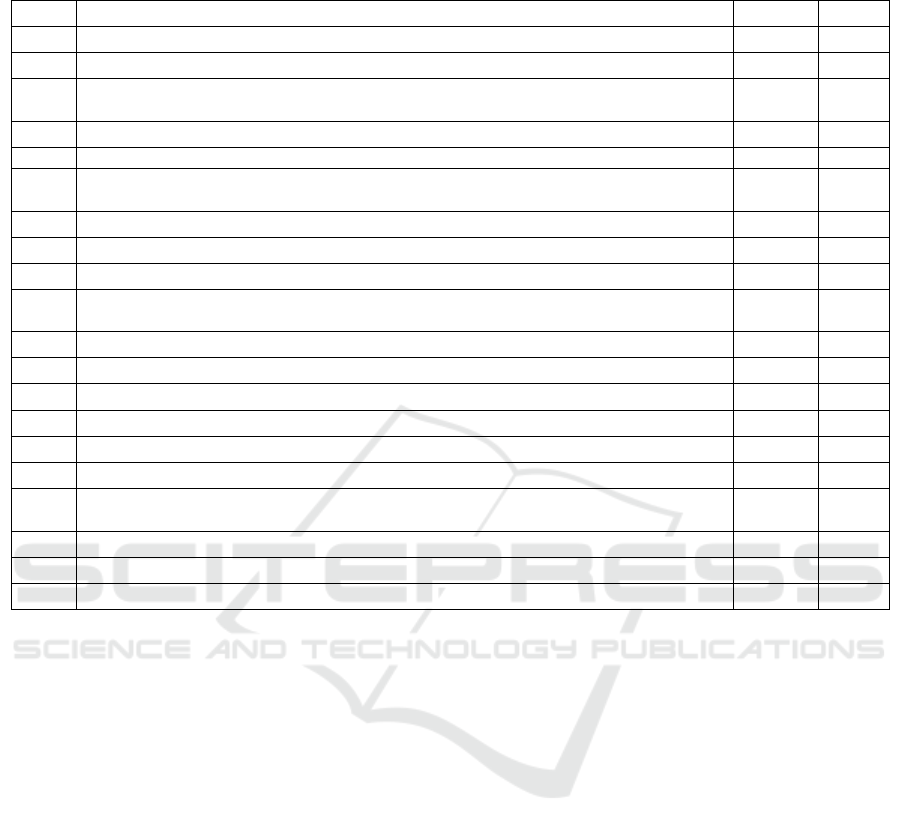
Table 13 The weighting of the index system of factors influencing the cultivation of innovation and entrepreneurship of college
students in local universities
No. Indicator Name Weight Rank
C5
Create a team of teachers for innovation and entre
p
reneurshi
p
p
ractice
0.1141 1
C6
Establish a multidisci
p
linar
y
com
p
rehensive mentor tea
m
0.0881 2
C4
Curriculum structure and teaching contents meet the needs of innovative and
entre
p
reneurial talents
0.0846 3
C1 Clarify the goal of cultivating talents for innovation and entrepreneurship education 0.0728 4
C7 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship 0.0656 5
C2
In-depth integration of innovation and entrepreneurship education with professional
education
0.0616 6
C18
Buil
d
a platform for innovation and entrepreneurship practice
0.0573 7
C10
Improve the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Curriculum Syste
m
0.0556 8
C8
Use social
p
ower to form
p
art-time teachers
0.0544 9
C3
Establish a mentorship-based innovation and entrepreneurship training program for
college students
0.0518 10
C20
Stren
g
then the construction of innovation and entre
p
reneurshi
p
p
ractice bases
0.0409 11
C12
Construct a classroom teaching mode that emphasizes both theory and practice
0.0404 12
C15 Create a training system for innovation and entrepreneurship 0.0386 13
C14
Strengthen the support of practical teaching working conditions
0.0384 14
C19
Cultivate innovative and entre
p
reneurial student teams
0.0321 15
C9
Establish the Educational Ideolo
gy
of Innovation and Practice
0.0245 16
C13
Establish a scientific examination and evaluation system for innovation and
entre
p
reneurshi
p
education courses
0.0221 17
C17
Stren
g
then the su
pp
ort from the
g
overnment and the societ
y
0.0218 18
C16
Create a campus culture that encourages innovation and entrepreneurship
0.0181 19
C11
Conduct lectures on innovation and entre
p
reneurshi
p
knowled
g
e
0.0173 20
Table 12 shows that the five influencing factors at
the guideline level can be ranked from the largest to
the smallest in terms of weight: Training and
construction of faculty team >Talent cultivation
objectives and modes> Teaching Content and
Curriculum Design >Experimental and practical
teaching management > financial and policy support.
Through Table 13, we can conclude that "Create a
team of teachers for innovation and entrepreneurship
practice" "Establish a multidisciplinary
comprehensive mentor team" Curriculum structure
and teaching contents meet the needs of innovative
and entrepreneurial talents" "Clarify the goal of
cultivating talents for innovation and entrepreneurship
education" "Create a training system for innovation
and entrepreneurship" "In-depth integration of
innovation and entrepreneurship education with
professional education"" Build a platform for
innovation and entrepreneurship practice" "Improve
the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Curriculum
System" and "Use social power to form part-time
teachers" ranked high. Although other indicators have
relatively low weights, they are also indicators that
cannot be ignored in the cultivation of college
students' innovation and entrepreneurship ability.
3 COUNTERMEASURES FOR
CULTIVATING INNOVATION
AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
ABILITY OF COLLEGE
STUDENTS IN LOCAL
COLLEGES AND
UNIVERSITIES
3.1 Improve the Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Education
System of College Students
To improve the innovation and entrepreneurship
education system of college students, it is necessary to
clarify the goal of cultivating talents for innovation
and entrepreneurship education, cultivate innovative
spirit and innovative thinking, improve innovation
and entrepreneurship ability, and promote students'
personalized development and comprehensive
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
97

quality. Formulate the route of cultivating innovative
and entrepreneurial talents, establish the collaborative
education mode of innovation and entrepreneurship,
and achieve the synergy of faculty and department,
school-school synergy, school-enterprise synergy and
government-enterprise synergy.
3.2 Create a Team of Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Practice
Teachers and a Multidisciplinary
Comprehensive Mentor Team
Schools can select teachers from various disciplines to
form innovation and entrepreneurship practice teams
and multidisciplinary comprehensive mentor teams,
not only to give students guidance on professional
knowledge, but also to better explore students' own
potential and give them positive guidance in actual
projects. The composition of the teachers in the team
is very important, and it is important to focus on the
teachers' practical experience in the industry and
provide them with opportunities for training and
upgrading, so as to create a team of teachers who
master the frontiers of their disciplines and industry
experience in innovation and entrepreneurship
practice. At the same time, using social power, we
invite entrepreneurs and start-ups to form a team of
part-time teachers to impart experience to students.
3.3 Reform the Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Curriculum
System
Reforming the innovation and entrepreneurship
curriculum is an important part of improving the
innovation and entrepreneurship ability of college
students. As the foundation of innovation and
entrepreneurship cultivation, the curriculum of
innovation and entrepreneurship for college students
should combine "method" and "knowledge",
"practice" and "theory", and build a classroom
teaching mode with equal emphasis on "theory and
practice". At the same time, innovation and
entrepreneurship education should be deeply
integrated with professional education to stimulate
students' learning motivation. The school establishes
a scientific assessment mechanism for innovation and
entrepreneurship education courses and makes
dynamic adjustments in teaching practice, so as to
constantly improve itself and keep pace with the
times.
3.4 Build the Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Practice
Platform
Building innovation and entrepreneurship practice
platform and strengthening the practical activities are
the keys to improve the innovation and
entrepreneurship ability of college students.
Theoretical knowledge and practical ability of
innovation and entrepreneurship of college students
can be tested through various practical links, and
continuously improved and enhanced through
practical training projects and so on. Through the
innovation and entrepreneurship practice platform,
students can not only experience the difficulties of
innovation and entrepreneurship, but also experience
the importance of teamwork, which is significant for
the improvement of college students' innovation and
entrepreneurship ability.
3.5 Promote the Synergistic
Cooperation among Government,
Enterprises, Universities and
Research Institutes
The government, universities and enterprises
cooperate with each other to provide service support
such as venue, capital and guidance for college
students' innovation and entrepreneurship by
integrating resources. Building an innovation and
entrepreneurship training system that integrates the
functions of innovation and entrepreneurship practice,
business incubation, innovation and entrepreneurship
training and innovation and entrepreneurship service
of college students with demonstration and leading
role can not only improve the ability of original
innovation, integrated innovation and re-innovation of
introduction, digestion and absorption of enterprises,
but also effectively improve the practical training
effect of innovation and entrepreneurship of college
students.
REFERENCES
Chen Yong. Exploration of innovation and
entrepreneurship education in higher education under
the perspective of "Internet +" [J]. Southern Journal of
Vocational Education.2016(03):84-87.
Chu Mingchang, Li Xiaomei, Gao Weixin. Practice and
Exploration of College Students' Innovation and
Entrepreneurship Training Program Project [J]. Journal
of Liaoning University of Technology (Social Science
Edition), 2014.16.4.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
98

Dong Yunfei, Zheng Libo. Thinking about the strategy of
cultivating college students' innovation and
entrepreneurship [J]. Heilongjiang Social Science,
2014.5.
Jiang Qian, Liu Xiaowei, Hu Guojie, Wu Bingye. Research
on the path selection of innovation and practical ability
cultivation of college students with innovation and
entrepreneurship competition as a carrier. Journal of
Liaoning University of Technology (Social Science
Edition).2016(02):89-91.
Qian Xiaoming, Rong Huawei, Qian Jingzhu. Practice and
reflection on the education of "college students'
innovation and entrepreneurship training program"
based on mentoring system [J]. Experimental
Technology and Management. 2014(07):21-23.
Tang Genli. Problems and countermeasures of
entrepreneurship education in China's colleges and
universities [J]. Enterprise and Education.
2009(03):53-54.
Zhang Jihe, Zhang Fan. Research on cultivating practical
innovation ability of undergraduate students in colleges
and universities--Based on the perspective of practical
teaching path [J]. China University Technology.
2011(10):70-71
Research on Cultivating Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Students in Local Universities Based on Data Mining
99
