
Study on Logistics Warehouse Dynamic Fire Risk Assessment Based
on Gustav Method
Wenhui Ju
1
, Guofeng Su
1
and Lizhi Wu
2
1
Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Heqing Road, Haidian District, China
2
China People’s Police University, Xichang Road 220, Anci District, Langfang, Hebei Province, China
Keywords: Logistics Warehouse, Gustav Method, Risk Assessment
Abstract: Modern logistics is a multi-faceted chain link comprised of storage, transfer, sorting, processing, and
distribution. Logistics warehouses, regarded as the most significant infrastructures in the supply chain, have
characteristics such as large building areas, multiple types, storage of miscellaneous goods, and fast goods
flow. In recent years, there has been an increase in the frequency of logistics warehouses fires resulting in
large socio-economic losses. Subsequently, a dynamic fire risk assessment method of logistics warehouses is
needed. Firstly, 52 fire accidents implied that the fire of logistics warehouses generally destroyed large-
destroyed areas, produced poisonous gases, spread rapidly, and led to the collapse of the warehouses.
Secondly, the investigation of logistics warehouses showed that the different ribbons of the logistics chain
had significant fire resources and risks. Thirdly, the fire risk analysis contributed to developing an index
system of fire risk for modernized logistics warehouses with the parameter weights being decided by the AHP
method and Delphi Method. Finally, a fire risk assessment method of modernized logistics warehouses was
developed by using the Gustav method. The users' feedback ascertained that the new method is feasible and
practical even to laymen of very little professional knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
Constructing logistics warehouses, which contributed
to the high-speed transportation of goods between
areas, became the most prevalent campaign because
the least time cost of transportation means optimized
social economics. COVIN-19 broke out the most
serious public health crisis, bankrupted countless
industries but boomed the logistics industry. Express
delivery has become one of the necessary parts of our
daily life. However, whether we under-evaluate some
potential social risks?
1.1 Status Quo of Logistics Warehouses
News broadcasted many logistics warehouse fire
accidents in recent years, including the Chinese
Jingdong warehouse fire in 2016, Amazon UK
logistics warehouse (BHX1) fire in 2017, Japanese
transportation logistics warehouse in 2018, and
Amazon American logistics center warehouse
(TEB6) fire in 2020. Logistics warehouse fires
always cause serious economic losses and casualties.
Logistics has been the tipping point of economic
rise among modern industries and an integral
parameter of financial evaluation. With the increasing
demands of logistics, advanced technologies and
transportation capacity, new automatic modernized
logistics warehouses with a clearance height of over
14m are being developed. As the most substantial link
within the logistics industry, how can we ensure its
safety development? One efficient way is to develop
a fire risk assessment method for modernized
logistics warehouses. The structure of the article is
shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The structure of the article.
110
Ju, W., Su, G. and Wu, L.
Study on Logistics Warehouse Dynamic Fire Risk Assessment Based on Gustav Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0011905900003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 110-114
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

1.2 Research Review
During the early years in the logistics industry,
scholars focused more on how to optimize the layout
of logistics warehouse based on the cost-benefit
model, Melendez 0. et al (2001) and M.Dai.s C.
(2010) suggested different optimization plans. These
optimized plans were not enough to prevent the
warehouse fire from occurring.
Subsequently, countries published their logistics
warehouse regulations for various aspects, including
the NFPA 230 Standard for the Fire Protection of
Storage (2000), National Standard of Canada, The
Building Code of Australia and Classification and
Requirement of Logistics Park of China (2017).
However, the regulations are hysteretic with the
development of warehouses. The new types of
logistics warehouses cannot satisfy the basic
requirement of fire protection in the code. Wenhui J.
(2017) chose nine typical logistics warehouses in
China and studied the contradictions between real
construction and fire department design requirements
to make the fire protection investment more
reasonable and feasible.
How can one value the risk of the logistics
warehouse? This can be done through a risk
evaluation method to ascertain the risk factors. Zang
L.and Zhang J. established an index system for
transportation warehouses using the fuzzy
comprehensive analysis method and the Analytic
Hierarchy Process (AHP). Wenhui J. (2016)
developed the Event and Fault Tree Analysis method
(EFTA) to explore the fire spread mechanism of
various cotton logistics warehouses.
2 FIRE RISK ANALYSIS OF
LOGISTICS WAREHOUSES
Fire risk analysis is an efficient tool to find the fire
risk factors. The general and special characteristics
should be analysed by fire accidents and features of
different functions respectively.
For the common characteristic, 52 fire accidents,
from 2005 to 2020, were collected with their
complete information and investigation reports.
There are four features of fire accidents in logistics
warehouses, larger destroyed areas, abundant toxic
and high-temperature smoke, faster spread speed at
the early fire stage, and collapse.
For the special ones, it depends on the features of
different processes. Warehouse types are defined by
location, application, and automatic degree, which in
effect lead to different fire characteristics. Generally,
storing, sorting, and processing are the essential
components of modernized logistics chains. Special
fire risk analysis can be studied by comparing these
three links.
2.1 Storing Area
Sorting has been the feature of the modernization of
logistics warehouses. Investigations show that
stochastic fluctuation of fire loads, complex
combustion sources, and electrical failure are
significant risk characteristics in the sorting area.
Although it is called ‘zero storage’ in the sorting
center, the storage time is no more than 4 hours, the
storage capacity randomly tips a peak every day as
such making it difficult to predict the fire loads. Duo
to its ‘zero storage’ nature, the sorting center is open
to every person, unsafety behaviours, smoking or
arson. This increases the propensity of a fire accident
more readily. Even though automatic equipment is
popular and advanced, its operation needs electricity.
In the 52 fire accidents analysed, 30% was as a result
of electrical failures, the highest of the loss.
2.2 Manufacturing Area
Manufacturing, including unpacking, thermoplastic,
and repackaging order goods, is the most complex
aspect of logistics warehouses. Lack of efficient fire
separations and high-temperature manufacturing
processes are the unique fire risks in this area.
To shrink the time interval between packing and
transportation, storing area is always close to the
manufacturing area, and the conveyor belts across the
firewall may times. Even some warehouses illegally
dismantle the fire separations. Thermoplastic needs
high-temperature conditions. If the good with the
high-temperature external surfaces, are put near
inflammable things, a fire is likely to occur.
3 INDEX SYSTEM OF FIRE RISK
ASSESSMENT FOR
MODERNIZED LOGISTICS
WAREHOUSES
Index system is a general method to evaluate logistics
warehouses’ fire risk. There exits quite a lot of index
systems that is different in either warehouse
categories or risk parameters. However, they cannot
satisfy the modernized classification with high-tech
and multi-function. Compared to the traditional
Study on Logistics Warehouse Dynamic Fire Risk Assessment Based on Gustav Method
111
warehouses, the modern ones have new fire risk
sources and the context-specific fire characteristics
ignored by any of the existed index systems.
Therefore, a need to construct an updated version of
the modernized logistics warehouse index system.
3.1 Construction Principle of Index
System
The science and efficacy of the risk evaluation index
system is dependent on whether the evaluation
parameters are chosen reasonably. The effect between
risk parameters of warehouses is complex enough as
hinted by several principles always reminded us
through the construction process.
Firstly, what is the main purpose of establishing
an index system? It’s to find out fire risk sources,
distinguish risk factors, make sure fragile spots are
eliminated or control the risks. Secondly, over-
comprehensive should be avoided. Too many risk
indexes may lead to an overlap of similar risk factors,
and it may cause an over-evaluated risk level leading
to a waste in fire protection investment.
Unfortunately, it is not feasible for users to check out
at first glance which fire risk should be eliminated
without personalized characteristics being included.
It is imperative therefore to consider special risk
characteristics for developing warehouses.
Fortunately, the research provides the basis for it.
3.2 The Parameters of the Index
System
According to the theory of two types of hazards and
the fire risk analysis, an optimized and multiple index
system of modernized logistics warehouses is
composed of four parameters in the first level, ten in
the second level, and thirty-two in the third level, as
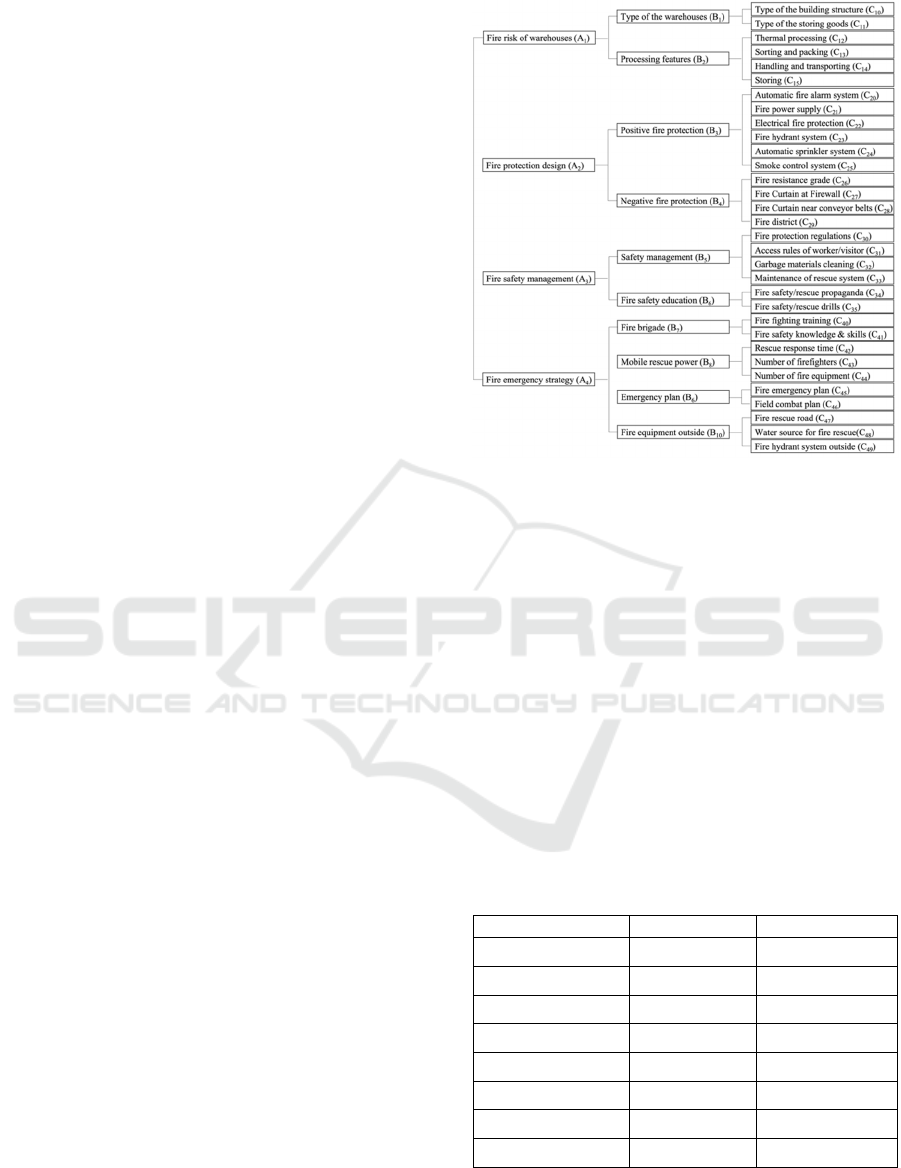
shown in Figure 2.
There are four noteworthy points in the new index
system. The first takes into account the risk of
different process characteristics (B
2
) into account.
The second one is that it considers the risk of fire
shutter in different parts, fire curtain at the firewall
(C
27
), and fire curtain near the conveyor belt (C
28
).
The third, safety management (B
5
) considers whether
the garbage materials cleaning is in time (C
32
). The
fourth, evacuation factors are omitted because the
investigation showed that the workers in modernized
logistics warehouses are few and familiar with the
evacuation plans.
Figure 2: The index system of fire risk assessment of
modernized logistics warehouses.
3.3 Weighted Parameters
Due to the lack of a database for logistics warehouses,
it is scientific to calculate the weight of parameters in
the index system was calculated using the AHP
method and the Delphi method based on the fire risk
analysis above. We invited more than ten renowned
first safety Chinese experts.
Two methods were used to determine the weight
of the judgment interval matrix, the relevant weight
between indicators. We used MATLAB to calculate
the weighted value of parameters and assess the
consistency. The result of the consistency test of the
judgment matrix is well, as is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Consistency test of judgment matrix.
Judgment matrix CR Consistency test
𝑅
←
0.0440 Yes
𝑅
0.0191 Yes
𝑅
0.0415 Yes
𝑅
0.0257 Yes
𝑅
0.0428 Yes
𝑅
0.0191 Yes
𝑅
0.0036 Yes
𝑅
0.0036 Yes
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
112

4 THE MODIFIED GUSTAV
METHOD FOR FIRE RISK
ASSESSMENT OF LOGISTICS
WAREHOUSES
When it is uncertain on which method to select
amongst the many evaluation methods, the status quo
and analysis of reasons should be considered. The
status quo shows that the lack of historical data of
logistics warehouse fire accidents excludes the
quantitative methods, and the research goal of
workers’ evaluation method decides that the new
method should be simple to learn and easy to operate.
4.1 Modified Gustav Method
Gustav method is a semi-quantitative risk analysis
method. It separates fire risks into two aspects, the
structure destroys of construction outside (GR) and
property loss and casualties of construction inside
(IR). The method constructs a rectangular coordinate
system, x-axis defined as GR against the y-axis as IR.
Two figures decide one point defined as risk level in
the rectangular coordinate system. In this way,
Gustav method could provide simple and feasible fire
protection plan to companies, even those who don't
have enough knowledge of fire prevention. However,
the traditional Gustav method can only determine a
fixable fire risk level. Considering the fire protection
status quo and fire risks analysis in modernized
logistics warehouses, it is necessary to modify the
traditional version to consist with fire risk
characteristics. So, we added dynamic factors into GR
and IR to account for the dynamic assessment.
For GR, we added mobile fire loads and their
inflammable degrees. We also considered the
different links, similar to categorizing the special fire
risks into storing, sorting and manufacturing areas.
𝐺𝑅 =
(𝑄
∙𝛼+𝑄
)∙𝑆∙𝐵∙𝑇
𝑊∙𝑅
(1)
𝑄
and 𝑄
, the mobile fire risk loads and fixable
fire risk loads respectively; 𝛼 , the inflammable
degree of 𝑄
; S, the building area; B, the risk
parameter of location; T, the function district
parameter; W, the fire resistance degree; 𝑅
, the
competency of the fire protection system.
For IR, we added the number of people as the
dynamic parameter of IR and multiplied it by 0.1 to
shrink the maximum value of IR to fit with the figure
interval of the x-axis.
𝐼𝑅 = 0.1𝐹 ∙ (𝐻 ∙ 𝜑) ∙ 𝐷 (2)
F, toxic degree of gases; H, the risk degree; 𝜑, the
number of people; D, the loss degree of property.
All value of each parameter above obeys some
regulations. The original parameters values are same
as the traditional Gustav method, while the figures of
adding parameters are according to the status quo of
building codes or other regulations. The details of the
figures are available on request.
4.2 The Procedure of Dynamic Fire
Risk Assessment of Modernized
Logistics Warehouses
The research above establishes a dynamic fire risk
assessment to fit modernized logistics warehouses.
Assessors should therefore know how to use it, and
the procedure of the method illustrates as follow.
Firstly, the assessor should investigate the basic
data of an assessed warehouse. At the same time, the
assessor should record the fire risk resources and
hidden hazards. In this step, the assessor can
determine some values of fixable parameters in the
modified Gustav method.
Secondly, the assessor should choose an area to
record the data of dynamic parameters at least two
days (without maximum limitation), including the
mobile fire loads, the number of workers. This helps
to bring out average value of each dynamic parameter
comes out.
Thirdly, the value of each parameter in the
modified Gustav method should be multiplied with
the corresponding weighted value in the index system,
to bring out the fire risk level comes out.
4.3 Empirical Study
The sorting center of JingDong Gu’an Logistics
warehouse was chosen. It is 20762.28m
2
, separated
into three fire compartments, and installs automatic
sorting equipment. This warehouse is used to sort
electronic household appliances, mobile phones,
laptops, foods, and some wine.
We chose 15-time points every day to record the
data of the mobile fire loads and the number of people,
and the recording work continued for one week.
Three periods, 01:00 to 7:00, 11:00 to 14:00, and
18:00 to 21:00 were deleted because workers rested
during these periods. It was assumed that there was
no fluctuation of fire risk, although some few parts
continued working actually.
According to the investigation of the sorting
center of the logistics warehouse, by adding data from
the record, each parameter’s value, the average value
Study on Logistics Warehouse Dynamic Fire Risk Assessment Based on Gustav Method
113
of one week’s records, in the modified Gustav
Method could be determined, as the table 2 shows.
Table 2: The value of GR & IR in Jingdong sorting center
of logistics warehouse.
Time GR IR Time GR IR
7:00 0 0 17:00 3.99 2.16
8:00 0.35 2.16 18:00 5.32 1.08
9:00 1.24 2.16 21:00 3.11 2.16
10:00 1.95 2.16 22:00 3.73 2.16
11:00 2.57 2.16 23:00 2.84 2.16
14:00 2.75 1.08 00:00 1.15 2.16
15:00 2.40 2.16 01:00 0.53 2.16
16:00 3.19 2.16
—
—
—
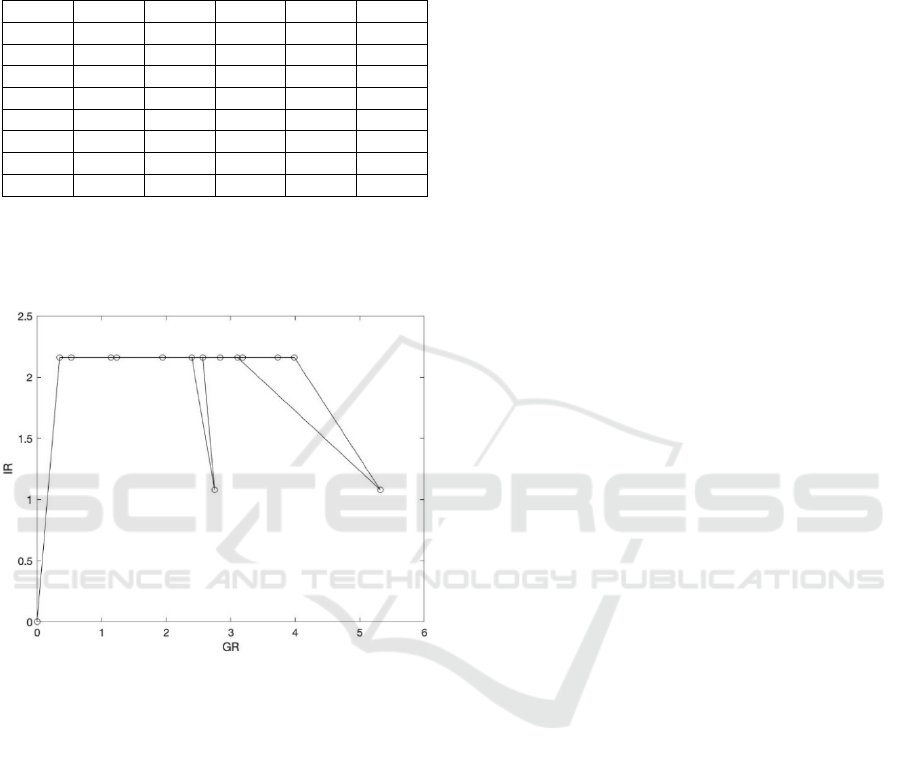
Putting all the figures into x-axis and y-axis
respectively, a graphic, implying the fluctuation of
fire risk in sorting center of logistics warehouse, is
shown as Figure 3.
Figure 3: The fluctuation of fire risk level in sorting center
of logistics warehouse.
According to Figure 3, three points are lower than
others, respectively corresponding to 7:00, 14:00, and
18:00. It is obvious that when the sorting center is
operating, the fire risk is higher. However, comparing
the three lower points, the fire risk at night is still
higher relative to the morning. The manager said that
the reason might be that some orders, paid through the
e-commerce platform, were at night. When the
worker picked out the goods and transported them to
the sorting center, the workers had to work overtime,
but the extra time was excluded from the record.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The research develops a dynamic fire risk assessment
method based on the Gustav method.
Firstly, based on investigations of fire accidents
and reports of modernized logistics warehouses, the
research implies the status quo of fire safety, analyses
the fire features, and concludes special characteristics
for different links in logistics warehouses.
Secondly, the research constructs a new index
system of modernized logistics warehouses, and
emphasizes the effect of warehouse types, packing
garbage, operating processes, and fire roller shutters.
Thirdly, the research modifies the Gustav method
by adding dynamic fire risk factors, mobile fire loads,
and the number of workers. Through the assessment
of the fire risk in Jingdong Gu'an sorting center of
logistics warehouses, the result validates the
reliability and efficacy of the new assessment
method.
When reviewing the research, we think some
aspects could be improved. In the empirical study, the
type of the function area is too single to make a
comparison, and the time length of the record is too
short to find enough routines of fluctuation. And the
research started on a general workday, not on a
special days like shopping festivals, which may raise
the peak figure of the mobile fire loads. Moreover, the
new method could be modified to be a quantitative,
provided enough data of logistics warehouses and
change the method of calculating the weight of
parameters. Other details pertaining to investigation
and calculation that were not presented in this paper
are available on request, if needed.
REFERENCES
Moore, R., Lopes, J., 1999. Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SCITEPRESS.
Smith, J., 1998. The book, The publishing company.
London, 2
nd
edition.
Melendez O, Maria F., 2001. Bonded Logistics Zone under
the Influence of Basic Traffic Construction. J.
Log&Trans.Rev. 21 1-4.
M.Dai.s C., 2010. Study on Layout Optimization of the
Regional Logistics System Master’s Thesis. J. Bus.
Log. 11 43-5.
NFPA, 2000. Standard for the Fire Protection of Storage.
American Elsevier.
Standardization administration, 2017. Classification and
Planning Fundamental Requirements of
Logistics
Park. China: Standards Press of China.
Wenhui J. and Yifu L., 2017. Conf. 3rd E-commerce &
Contemporary Economic Development (China: Xi’an)
p 216-21.
Wenhui J., 2016. Proc. Engineering vol 135 (China:
Guangzhou/ American Elsevier) p 417-25.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
114
