
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
Chong Zeng
1,2 a
, Jiafeng Zhou
3b
, Zhongxi Lu
1c
, Yue Wu
1d
, Zicheng Nie
1e
and Hongji Yang
1f
1
School of Computer and Mathematical Sciences, University of Leicester, Leicester, U.K.
2
School of Mathematical and Engineering, Longyan University, Fujian, China
3
Creative Centre for ArtSciArch, Jilin Jianzhu University, Jilin, China
hongji.yang@leicester.ac.uk
Keywords: Synaesthesia, Creativity, Generation, Inducers, Concurrents, Cluster, Five Sensory.
Abstract: The key to creativity does not lie solely in the mental process. It is also regarded as a cultural or social activity.
Methods of supporting creative ideas generation have been studied and researched widely in various domains.
Among such studies, Gerald has summarized 172 methods that can be applied to creative ideas generation.
Although his research has covered the most used strategies, yet, synaesthesia as an incredible phenomenon in
which the stimulus arouses one or more additional sensory experiences has never been adopted as a strategy
to generate ideas. The aim of this research is to support creative ideas generation by merging computers and
synaesthetic experiences. Hence, a visual-related synesthesia-based creativity support system is proposed to
support creative ideas generation. Initially, synaesthesia is divided into synaesthesia clusters composed of five
sensory stimuli (e.g., visual-visual, visual-auditory) by analyzing synaesthetic experiences recorded in various
literature. Then, synaesthesia clusters related to vision were selected as the most prevalent synaesthetic
experience to generate a variety of rules. As a result, various rules are fused to produce numerous imaginative
elements for people to select, thus promoting the human imagination, and supporting creative ideas.
1 INTRODUCTION
Creativity is more than just a mental process; it is
also a cultural and social activity (Vidal 2009). In
general, creativity is defined and evaluated in a
variety of ways. For example, in terms of evaluation,
Boden considered that creativity is the ability to
generate “new, surprising, and valuable” ideas or
artifacts (Boden 2007). Meanwhile, Stein et al.
believed that creative work is a new work
acknowledged by a community as tenable, useful, or
pleasurable at some point in time (Stein 1953).
Generally speaking, creativity should simultaneously
fulfill the new, valuable, and acceptable criteria in
most cases.
The existing research proposed various
techniques to achieve the criteria mentioned above.
For instance, Boden proposed the most widely
accepted and classic technique in 2004: creativity can
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7764-1971
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7775-7728
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2455-8450
be acquired in three forms based on categorical
characteristics: combinational, exploratory, and
transformational (Boden 2004). It is easy to find
various creative support systems that employ a
variety of ways to aid in gathering relevant data and
the creation of ideas (Wang and Nickerson 2019). The
necessary and prerequisite condition for generating
creativity is the generation of creative ideas, which
have been the focus of creativity research. As early as
1998, Gerald studied 172 proposed approaches to idea
generation and summarized three positive elements
for generating creativity: strategies, tactics, and
enables, the latter two aimed at promoting the first
(Smith 1998). Specifically, methods such as idea
generation, brainstorming (Potter and Balthazard
2004), and mind mapping (Massetti 1996) are still
popular at present. Some studies employ a visual
technique to present stimuli to stimulate new ideas
(Wang, Cosley, and Fussell 2010; Wang, Fussell, and
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7156-9531
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9795-7666
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6561-3631
560
Zeng, C., Zhou, J., Lu, Z., Wu, Y., Nie, Z. and Yang, H.
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0011916000003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 560-570
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Cosley 2011).
Synaesthesia is an incredible phenomenon in
which the stimulus arouses one or more additional
sensory experiences (Grossenbacher and Lovelace
2001). It is worth noting that synaesthesia plays a
critical role in the development of sensory products,
and user-specific experiences can be obtained
through the imagination and creativity generated by
multiple sensory modes (Merter 2017).
Creative support systems are a typical tool for
enhancing human creativity through stimulating and
documenting the creative process and are often used
to stimulate the creative potential of individuals and
groups (Massetti 1996; Wang and Nickerson 2017).
2 RELATED WORKS
In recent years, synesthesia researchers have tended
to invest in the relationship between different types
of synesthesia, like how different types of
synesthesia fit together (Ward and Simner 2021)?
The relationship between different synaesthesia
forms and their ability to participate in art or
creativity (Lunke and Meier 2019). Especially,
researchers studied the effects of synesthesia on letter
representation in different languages, not only
English-speaking (Root et al. 2021). In addition,
researchers also believe that synaesthetes are more
creative than non-synesthetes due to the difficult
concepts that can be perceived (Mulvenna et al.
2003). Others consider that creativity and the
processing information ability can be improved by
activating more of the sense of non-synesthetes
(Merter 2017).
Some researchers considered that stimulus
relatedness is positively related to the idea quantity
and idea usefulness. Their study indicates that
remotely related stimuli, not unrelated stimuli, tend
to improve idea novelty. Such as the Wikipedia-
based approach to support creative idea generation
(Wang and Nickerson 2019). Others developed a
computational tool using a combination of ontology
and analogy to assist designers in generating creative
ideas in the early stages of design (Han et al. 2018)
.
3 METHODS AND
PROCEDURES
This study designed creative ideas support system
that inputs visual, auditory, and gustatory, and
randomly outputs pictures with shapes, numbers, and
colors through analyzing synaesthetic experience,
constructing rules between inducers and concurrents,
and summarizing and generalizing the rules. The
specific steps are as follows.
3.1 The Regular Conceptual Space
Recognition
It requires breaking the regular rules to achieve novel
and surprising results. Therefore, the first step is to
figure out the typical components of the regular
ideas. The standard components could be considered
as the rules constituting the conceptual space of the
specific meaning, themes or topics. For instance, if
the users aim to convey the meaning of cheerfulness,
the standard visual components might be the beers,
people's smiles and colourful background. To
achieve novelty, the typical components could be
replaced with other untypical components that are
remotely relevant. In this case, synaesthesia
experience would be helpful to find out the
corresponding components remotely relevant to the
typical components. We can consider standard
components as the inducers and unregular
components as the concurrences. The following steps
describe the process of matching inducers with
concurrences.
3.2 Classification of Synaesthesia
Types
Many researchers have extensively studied and
applied different classification methods for the
various synaesthesia forms: period-based (neonatal
and adulthood synaesthesia), timeliness-based
(momentary and permanent synaesthesia), function-
based (strong and weak synaesthesia) (Rogowska
2011), and so on. The following steps will be applied
to classify synaesthesia types:
Synaesthesia Clusters Adopted As the results of
studies indicate, 61 different forms of synaesthesia
have been recognized as of 2010 (Day 2016), and by
2022, 164 forms of synaesthesia have been
documented (Ward and Simner 2021). Furthermore,
researchers are frequently accustomed to defining
synaesthesia types through paring inducer and
concurrent (inducer-concurrent synaesthesia) (Ward
and Simner 2021), such as “grapheme-color
synaesthesia” implies letters or numbers evoke an
unusual color. This method of synaesthesia
definition based on synaesthetic phenomena is
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
561

intuitive but also leads to an overwhelming variety of
types and a lack of essential representation.
Accordingly, some methods named “synaesthesia
clusters” have been adopted by several researchers to
generalize and represent a group of related
synaesthesia types (Novich, Cheng, and Eagleman
2011; Ward and Simner 2021). It is notable that
Ward et al. classified synaesthesia clusters in terms
of common "concurrents" rather than common
"inducers” and selected 112 possible synaesthesia
types for cluster categorization after a
comprehensive assessment of 164 synaesthesia
types, ultimately summarizing eight synaesthesia
clusters and ranking their prevalence (which will be
utilized in my following software design) (Ward and
Simner 2021). In this classification model, the
synaesthesia clusters approach is also employed in
the classification of synaesthesia forms, and unlike
the approach proposed by Ward et al., a common
'inducer' will be applied as the aggregated instead of
a common 'concurrent'.
Intra- and Inter-modal Relationship One
possible way to elucidate the process of synesthesia
phenomena is widening the concepts of intra- and
inter-modality processes proposed by Marks (Marks
and Odgaard 2005). Specifically, Intramodal
synaesthesia signifies that the inducers and
concurrents being generated in the same modality,
e.g., seeing colors when seeing black numbers (Rich,
Bradshaw, and Mattingley 2005), whereas
Intermodal synaesthesia refers to inducers and
concurrents arising in different modalities, e.g.,
seeing images when hearing sounds (Baron-Cohen,
Wyke, and Binnie 1987). Regarding the previously
mentioned synaesthetic experience as one sensory
stimulus eliciting one or more sensory stimuli,
intermodal synaesthesia can be split into one-to-one
and one-to-many (multimodal), but the latter scarcely
exists and is excluded from discussion in this model
Five Sensory Modalities As mentioned earlier,
synaesthesia is evoked by sensory modalities.
Specifically, a wide variety of synaesthetic
experiences or phenomena are gained through five
human senses - visual, auditory, tactile, gustatory,
and olfactory. Accordingly, five sensory modalities
can be employed as both inputs to the inducers and
output to the concurrence in this categorization
model. 25 synaesthesia clusters were acquired
through arranging and combining the inputs and
outputs based on one-to-one modality: visual-visual
(visual to visual and the inducers in front), visual-
auditory, auditory-visual, and so on.
In 2011, some researchers pointed out that ninety-
eight percent of the tens of thousands of individuals
reported synaesthetic experiences were activated by
stimuli such as letters, numerals, or words (Novich et
al. 2011). That is, synaesthesia evoked by visual
stimuli predominates, which coincides with the
finding in 2022 that concurrents triggered by visual
stimuli were the most common through an
investigation of 164 possible synaesthesia types in
2925 self-referred synaesthetes (Ward and Simner
2021). Thus, the visual-related synaesthesia clusters
are the focus of the Synaesthesia Classification
Model, which contains nine visual-related
synaesthesia clusters, namely visual-visual, visual-
auditory, visual-tactile, visual-gustatory, visual-
olfactory, auditory-visual, tactile-visual, gustatory-
visual, and olfactory-visual. Furthermore, some
researchers have asserted that intramodal
synaesthesia plays a meaningless role in synaesthesia
classification (Jackson and Sandramouli 2012;
Novich et al. 2011; Ward and Simner 2021). Figure
1 shows the visual-related one-to-one synaesthesia
modality that will be discussed in this system.
Figure 1: visual-related one-to-one synaesthesia modality
3.3 Rules Construction
In this system, the construction of rules is derived
from the summarization and induction of various
synaesthetic experiences, each corresponding to a
synaesthetic experience. Specifically, the inability of
ordinary people (non-synaesthetes) to feel,
experience, or even imagine the spontaneously
generated synaesthesia concurrents when a stimulus
occurs can, to a certain extent, restrict the
imagination or association of people, and hinder the
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
562
support of creativity. An effective way to overcome
this limitation is to use the rules provided by this
system to help people imagine or associate with more
“infinite possibilities”. In addition, it is also
interesting to note that researchers are keen to focus
on the meaning of stimuli (inducer) (Boden 2007),
the effect of stimuli (Cytowic 2002), while the effect
or meaning of stimulus production (concurrents) has
been ignored. However, the rules are a mapping of
stimulus to the outcome, i.e., the inducer-
concurrents, which not only responds to the effects
of the inducers but also the concurrents, and it
corresponds to the whole process of computer input
and output, so the rules provided by this system can
effectively help people to come up with more
creative ideas.
Table 1 detail the rules generated by inducting
and summarizing the various synesthetic experiences
documented in the literature. It can be seen that most
rules are generated by visual-visual clusters,
followed by auditory-visual. In addition, the most
prevalent concurrents are color and shapes. It is
worth noting that the same inducers can arouse
different concurrents, meanwhile, the same
concurrents can be stimulated by different inducers.
In all, these features provide strong support for the
design of our systems.
Table 1: Rules based on synaesthesia clusters
Synaesthesia
clusters
Rules
Visual-visual
(1) Visual or visual motion triggering evokes color perception
Inducers: letters, shapes, numbers, swimming style, time units (months, years,
weekdays), numerous sequence units (shoe sizes, height, TV stations, body temperatures), name.
Concurrents: color (red, green, yellow, etc,)
(2) Visual triggering evokes space perception
Inducers: letters, numbers, time units, numerous sequence units.
Concurrents: shapes (circle, oval, ellipse, diamond, star, etc.), three-dimensional shapes,
spatial arrangement (columns, spirals.)
(3) Visual triggering evoke parity
Inducers: letters, numbers, time units, shapes, words.
Concurrents: feelings of oddness and evenness.
(4) Visual triggering evokes personalities
Inducers: letters, numbers, simple shapes, and even furniture.
Concurrents: rich and detailed personalities
Visual-auditory
((1) Visual motion induces auditory
Inducers: non-moving visual flashes, continuous visual motion
Concurrents: non-linguistic sounds (such as beeping, tapping, or whirring), pitches,
chords
Visual-tactile
(1) Visual or imaginary triggering evokes physical touch sensation
Inducers: others touch, pain
Concurrents: physical touch (pain)
(2) Visual evoke touches
Inducers: words, people names, numbers, letters, days, months
Concurrents: touch
Visual-gustatory
(1) visual triggering evokes tastes:
Induces: food, playing music words
Concurrents: emotional valence tastes (unpleasant, neutral, very pleasant tastes), food
flavor, shapes
Visual-olfactory
(1) Visual triggering evokes smells
Induces: words, Playing music, Months, Peoples names
Concurrents: flavors
Auditory-visual
(1) Auditory sensations evoke color imagery
Induces: Hearing words, Voices of different pitch, particular piano note, a tone at 2000
Hz, absolute pitch, being spoken to, complex jarring sounds
Concurrents: colors (dynamic, the color deepens as the pitch rises and decreases as the
p
itch decreases)
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
563

(2) Spoken or tone evoke words
Inducers: tone, being spoken to
Concurrents: words, reproduction out of the mouth (like ticker taper)
(2) Sounds evoke shapes or numbers
Inducers: sounds
concurrents: sha
p
es
(
d
y
namic random dots, s
q
uare, circles
)
, numbers
(
0,100, 400
)
Tactile-visual
(1) Tactile stimuli evoke visual motion
Inducers: tactile
Concurrents: visual sensation (movement, expansion, jumping)
(2) Tactile stimuli evoke color
Inducers: touch, thinking about touching
Concurrents: color
Gustatory-visual
(1) Taste evokes shapes:
Inducers: food taste
Concurrents: geometric shapes appear to morph over time (e.g., from pointed to round)
as the taste develops on the tongue
(2) Taste evokes colors:
Inducers: food taste
Concurrents: colors
Olfactory-visual
(1) Smell evokes shapes:
Inducers: food smell
Concurrents: geometric shapes
4 A CREATIVE IDEA
GENRATION SYSTEM
According to the construction of the previously
mentioned rules, the mapping of inducer and
concurrents are shown in Figure 2 through
summarizing and generalizing. Among them, the red
circle represents concurrents, and the blue one
represents inducer. Thus, a creative idea support
system consists of inducer and concurrents, creative
idea support through different search conditions.
There are two kinds of search ways:
Concurrents-inducer Concurrents are entered
into the system as a search condition, and can then be
output to display various inducers, followed by the
selection of one of the inducers to eject its properties.
For example, the user wants to find the colors
generated under various visual influences, “color” as
concurrents can be entered into the search box, then
inducers: “grapheme”, “swimming style”, “sequence
number” will be demonstrated, followed by clicking
on one of the inducers “swimming style”, the
properties can be output and displayed "butterfly",
“breaststroke”, “freestyle”, etc.
Inducer-Concurrents The inducer is entered
into the system as a search condition, the system then
selects the various matching concurrents. For
instance, “shapes” as inducer can be entered into the
search box, then concurrents such as “color”, “3D
shapes”, “parity”. will be displayed, followed by
kinds of properties.
4.1 System Implementation
Under current circumstances, the search technique of
inducer-concurrents is adopted in the creative idea
support system.
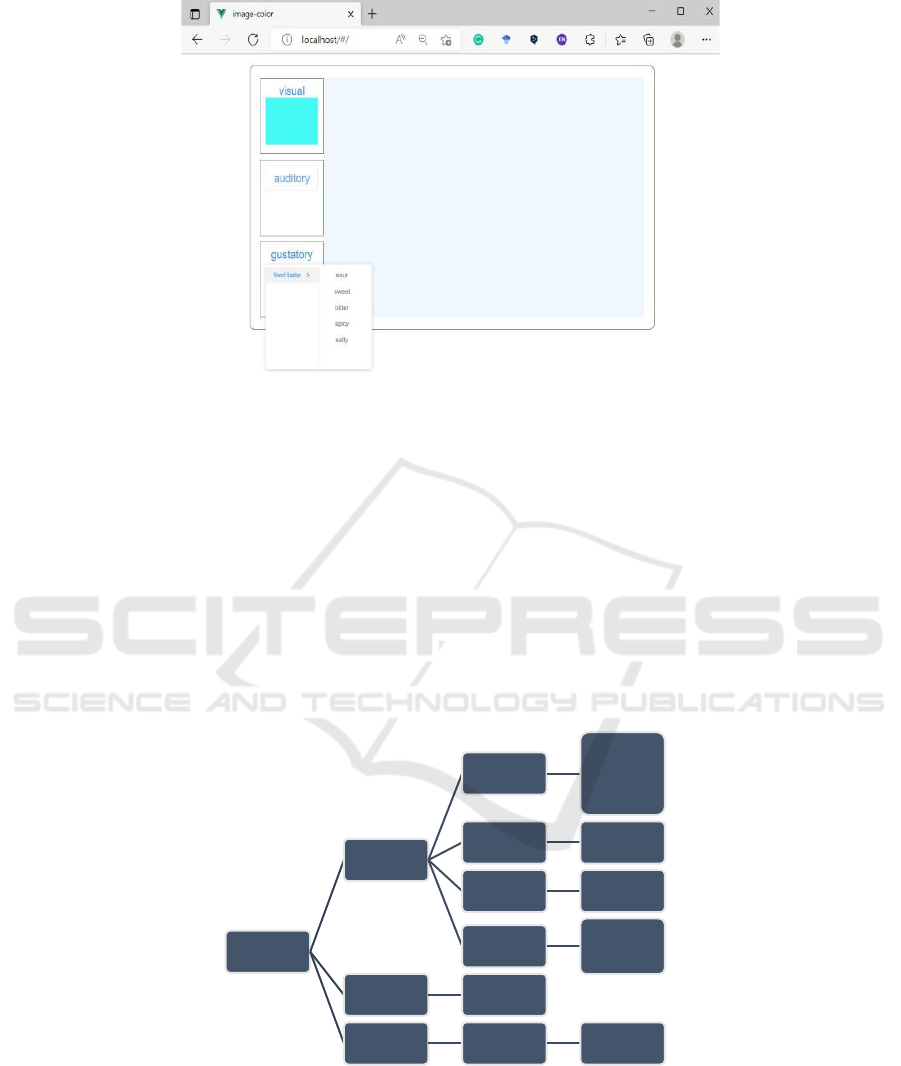
Input According to the previously generated
synaesthesia rules, the system input architecture
derived from the inducers is composed as shown in
Figure 2. In particular, the input architecture consists
of visual, auditory, and gustatory. Specifically, the
visual input selects English words, numbers, and
swimming postures; the auditory input selects sounds
and piano notes; the auditory selects food flavors. In
particular, the four special swimming styles can
trigger color vision in an intuitive picture selection
mode; the selection of sounds adopts the form of a
click-to-play to enable the users to hear a certain
sound; the food flavors are selected by clicking on
one of the taste sensations (sour, sweet, bitter, spicy
and salty). Screenshots of the system of showing
each of the three sensory input are shown in Figure
3.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
564

Figure 2: Input architecture of the system
(a) (b)
input
visual
english
words
name
week
Mon.,
Tue.,...Sun.
month
Jan.,
Feb.,...Dec.
numbers
sequence
number
height
shoe sizes
quantity
numbers
0~100
swimming
style
freestyle
breaststroke
butterfly
backstroke
auditory
sounds
car hoking
english words name
beep
piano notes
dol, re, mi, fa, sol, la,
tea, dol
gustatory food taste
sour, sweet, bitter,
spicy, salty
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
565
(c)
Figure 3: (a) the visual input of the system. (b) the auditory input of the system. (c) the gustatory input of the system
Output Similarly, the system output architecture
is based on the concurrents of the synaesthesia rules,
as shown in Figure 4. Three common concurrents
(shapes, numbers, and colors) are selected to form
the output picture. Specifically, colors are randomly
generated through visual input which contains twelve
colors (red, orange, yellow, etc.); shapes consist of
four types (animal, geometry, item, and botanical)
which can be randomly selected by auditory input;
numbers are randomly generated from 0 to 10 to
determine the number of shapes. Accordingly, the
final display is a fusion of three elements (shapes,
color, number) of visual output, where the color and
quantity of shapes are determined by visual and
gustatory inputs, respectively. For instance, “Eight
Blue Bottles” will appear on the screen after input, as
shown in Figure 5. It is worth noting that each input
will trigger a different output.
Figure 4: Output architecture of the system
output
shapes
animal
dog
cat
tiger
geometry circle
item
cup lamp
house
botanical
flower tree
grass
numbers 0~10
colors
twelve
colors
red orange
yellow
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
566

Figure 5: Output of the system
5 SYSTEM VALIDATION
The various matching rules of the system come from
the various types of synaesthesia recorded in Table
2. For example, the swimming style that arouses
people to perceive color is the swimming style
synaesthesia type; the piano notes that elicit people
to perceive shapes belong to the colored-hearing
synaesthesia type; food tasting that arouses people to
perceive numbers is the smell-shapes synaesthesia
type. In particular, English words that cause people
to perceive color belong to grapheme-color
synaesthesia - the most common form of
synaesthesia. In addition, swimming style
synaesthesia. Sequence-space synaesthesia are
classified as visual-visual clusters due to the colors,
letters, numbers, swimming style, time units
(months, years, weekdays), etc. are all perceived
visually.
Table 2 visual-related synaesthesia types
Synaesthesia
clusters
Synaesthesia types
Visual-visual
(1) Grapheme-color synaesthesia (Root et al. 2021; Simner and Bain 2013)
(2) Swimming style synaesthesia (Mroczko-Wąsowicz and Werning 2012; Nikolić et al.
2011)
(3) Sequence-space synaesthesia (Price and Mentzoni 2008; Sagiv et al. 2006; Smilek et al.
2007a)
(4) Stimulus-parity synaesthesia (Dumbalska et al. 2017)
(5)Ordinal linguistic personification (OLP) (Simner and Holenstein 2007; Smilek et al.
2007b)
Visual-auditory
(1) Visual-auditory synaesthesia (Noble et al. 2010)
(2) Hearing-motion synaesthesia (Rothen et al. 2017; Saenz and Koch 2008)
Visual-tactile
(1) Mirror-touch synaesthesia (MTS) (Banissy et al. 2009; Banissy and Ward 2007; Ward,
Schnakenberg, and Banissy 2018)
(2) Language-touch (Ward and Simner 2021)
Visual-gustator
y
(1) Lexical-gustatory synaesthesia (Cytowic 2003; Ward and Simner 2003)
Visual-olfactor
y
(
1
)
Lexical-smell s
y
naesthesia
(
C
y
towic 2002; Ward and Simner 2021
)
Auditory-visual
(1) Colored-hearing synaesthesia (Baron-Cohen et al. 1987; Jäncke and Langer 2011;
Lorusso and Porro 2010)
(2) Auditory-visual synaesthesia (Chun and Hupé 2013; Jackson and Sandramouli 2012)
(3) Lexical-gustatory synaesthesia (Luria 1987)
(
4
)
Ticker ta
p
er s
y
naesthesia
(
Chun and Hu
p
é 2013
)
Tactile-visual
(1) Touch-vision synaesthesia (Armel and Ramachandran 1999)
(
2
)
Touch-color s
y
naesthesia
(
Simner and Ludwi
g
2012
)
Gustator
y
-visual
(
1
)
Taste-sha
p
es s
y
naesthesia
(
C
y
towic 2003; Downe
y
1911
)
Olfactor
y
-visual
(
1
)
Smell-sha
p
es
(
C
y
towic 2003; C
y
towic and Wood 1982
)
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
567

6 CONCLUSIONS
We propose a creative support system that generates
creative ideas that can effectively broaden the mind
and provide more clues or ideas for human
association and imagination. It is worth noting that
whereas past approaches have chosen “concurrents”
as the synaesthesia classification. We adopt
“inducers” as the common classification.
Synaesthesia clusters formed on the basis of the five
senses (visual, auditory, tactile, gustatory, and
olfactory) essentially encompasses all synaesthetic
phenomena except for those related to emotions. In
addition, selected visual-related synaesthesia clusters
do not include about 1% of the synaesthetic
experiences, so the system basically reflects the
majority of the synaesthetic experiences. We
discover the mapping relationship between inducers
and concurrents through the analysis of synaesthesia
rules, which led to a more systematic approach to
creative idea support.
Furthermore, visual-related synaesthesia clusters
can also be expanded into related with auditory,
tactile, etc., so that the system can be classified
according to different sensory clusters, allowing for
a wide range of applications, especially in the
creation of human poetry, rhetoric, fiction, etc.
enhancing the richness of imagination or association
elements and cues. The system does not list all the
properties of the inducer, but only some basic
properties, such as “shape” only lists “rectangle,
triangle, circle”, so in the future, the system can be
improved by increasing the properties dictionary.
Creative support systems can be applied to in
assorted working domains such as knowledge
management, programming and music production.
Although such domains have different focus, but the
principles and the major elements have similar
features behind corresponding creative support
system (Hewett 2005).
In all, the diversity of creative ideas generation
methods is broad and abundant. But it is still very
new and rare to involve synesthesia in such domains.
Accordingly, it is believed that it is beneficial to
consider synesthesia’s nature and mechanism as a
potential approach to stimulate more creative ideas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost, I would like to give my deep and
sincere gratitude to this research’s advisor Prof.
Hongji Yang, for providing invaluable guidance
throughout this research. Besides my advisor, I
would like to thank Zhongxi for providing the
analysis of the creative support system and Yue’s
effort on designing the interface of the proposed
system. My warmest thank also goes to Zicheng, for
his insights into the relationship between
synaesthesia and creativity. Thank you again, for
supporting this research.
This work was supported by “Research on
people’s livelihood-oriented urban planning and
management in Jinlin Province, No. 2020
0101058FG”, and “Cloud-based urban visualization
integrated management platform based on big data
and knowledge system, No. 20210203146SF”.
REFERENCES
Armel, K. C. and V. S. Ramachandran. 1999. “Acquired
synesthesia in retinitis pigmentosa.” Neurocase 5(4):
293-96.
Banissy, M. J., R. C. Kadosh, G. W. Maus, V. Walsh, and
J. Ward. 2009. “Prevalence, characteristics and a
neurocognitive model of mirror-touch synaesthesia.”
Experimental brain research 198(2): 261-72.
Banissy, M. J. and J. Ward. 2007. “Mirror-touch
synesthesia is linked with empathy.” Nature
neuroscience 10(7): 815-16.
Baron-Cohen, S., M. A. Wyke, and C. Binnie. 1987.
“Hearing words and seeing colours: an experimental
investigation of a case of synaesthesia.” Perception
16(6): 761-67.
Boden, M. A. 2004. The creative mind: Myths and
mechanisms: Routledge.
Boden, M. A. 2007. “Creativity in a nutshell.” Think 5(15):
83-96.
Chun, C. A. and J.-M. Hupé. 2013. “Mirror-touch and
ticker tape experiences in synesthesia.” Frontiers in
Psychology 4: 776.
Cytowic, R. 2002. “Synesthesia: A Union of the Senses. 2-
nd ed.” MIT Press Cambridge, MA.
Cytowic, R. E. 2003. The man who tasted shapes: Imprint
Academic.
Cytowic, R. E. and F. B. Wood. 1982. “Synesthesia: II.
Psychophysical relations in the synesthesia of
geometrically shaped taste and colored hearing.” Brain
and Cognition 1(1): 36-49.
Day, S. 2016. Synesthetes: North Charleston: SC:
CreateSpace.
Downey, J. E. 1911. “A case of colored gustation.” The
American Journal of Psychology 22(4): 528-39.
Dumbalska, T., R. C. White, M. D. Duta, and K. Nation.
2017. “Automaticity in Stimulus-Parity Synaesthesia.”
i-Perception 8(6): 2041669517736323.
Grossenbacher, P. G. and C. T. Lovelace. 2001.
“Mechanisms of synesthesia: cognitive and
physiological constraints.” Trends in cognitive
sciences 5(1): 36-41.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
568

Han, J., F. Shi, L. Chen, and P. R. Childs. 2018. “A
computational tool for creative idea generation based
on analogical reasoning and ontology.” AI EDAM
32(4): 462-77.
Hewett, T. T. 2005. “Informing the design of computer-
based environments to support creativity.”
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies
63(4-5): 383-409.
Jackson, T. E. and S. Sandramouli. 2012. “Auditory-
olfactory synesthesia coexisting with auditory-visual
synesthesia.” Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology 32(3):
221-23.
Jäncke, L. and N. Langer. 2011. “A strong parietal hub in
the small‐world network of coloured‐hearing
synaesthetes during resting state EEG.” Journal of
neuropsychology 5(2): 178-202.
Lorusso, L. and A. Porro. 2010. “Coloured-hearing
synaesthesia in nineteenth-century Italy.” In
Neurology of music, pp. 239-56: World Scientific.
Lunke, K. and B. Meier. 2019. “Creativity and
involvement in art in different types of synaesthesia.”
British journal of psychology 110(4): 727-44.
Luria, A. R. 1987. The Mind of a Mnemonist: A Little
Book about a Vast Memory, With a New Foreword by
Jerome S. Bruner: Harvard University Press.
Marks, L. E. and E. C. Odgaard. 2005. “Developmental
Constraints on Theories of Synesthesia.”
Massetti, B. 1996. “An empirical examination of the value
of creativity support systems on idea generation.” Mis
Quarterly: 83-97.
Merter, S. 2017. “Synesthetic approach in the design
process for enhanced creativity and multisensory
experiences.” The Design Journal 20(sup1): S4519-
S28.
Mroczko-Wąsowicz, A. and M. Werning. 2012.
“Synesthesia, sensory-motor contingency, and
semantic emulation: how swimming style-color
synesthesia challenges the traditional view of
synesthesia.” Frontiers in Psychology 3: 279.
Mulvenna, C. M., E. M. Hubbard, V. S. Ramachandran,
and F. Pollick. 2003. “The relationship between
synaesthesia and creativity.” University of Glasgow.
Nikolić, D., U. M. Jürgens, N. Rothen, B. Meier, and A.
Mroczko. 2011. “Swimming-style synesthesia.”
Cortex 47(7): 874-79.
Noble, C., J. Mossbridge, L. Iordanescu, A. Sherman, A.
List, M. Grabowecky, and S. Suzuki. 2010. “Motion
induced pitch: A case of visual-auditory synesthesia.”
Journal of vision 10(7): 872-72.
Novich, S., S. Cheng, and D. M. Eagleman. 2011. “Is
synaesthesia one condition or many? A large‐scale
analysis reveals subgroups.” Journal of
neuropsychology 5(2): 353-71.
Potter, R. E. and P. Balthazard. 2004. “The role of
individual memory and attention processes during
electronic brainstorming.” Mis Quarterly: 621-43.
Price, M. C. and R. A. Mentzoni. 2008. “Where is January?
The month-SNARC effect in sequence-form
synaesthetes.” Cortex 44(7): 890-907.
Rich, A. N., J. L. Bradshaw, and J. B. Mattingley. 2005.
“A systematic, large-scale study of synaesthesia:
implications for the role of early experience in lexical-
colour associations.” Cognition 98(1): 53-84.
Rogowska, A. 2011. “Categorization of synaesthesia.”
Review of General Psychology 15(3): 213-27.
Root, N., M. Asano, H. Melero, C.-Y. Kim, A. V. Sidoroff-
Dorso, A. Vatakis, K. Yokosawa, V. Ramachandran,
and R. Rouw. 2021. “Do the colors of your letters
depend on your language? Language-dependent and
universal influences on grapheme-color synesthesia in
seven languages.” Consciousness and Cognition 95:
103192.
Rothen, N., G. Bartl, A. Franklin, and J. Ward. 2017.
“Electrophysiological correlates and psychoacoustic
characteristics of hearing-motion synaesthesia.”
Neuropsychologia 106: 280-88.
Saenz, M. and C. Koch. 2008. “The sound of change:
visually-induced auditory synesthesia.” Current
Biology 18(15): R650-R51.
Sagiv, N., J. Simner, J. Collins, B. Butterworth, and J.
Ward. 2006. “What is the relationship between
synaesthesia and visuo-spatial number forms?”
Cognition 101(1): 114-28.
Simner, J. and A. E. Bain. 2013. “A longitudinal study of
grapheme-color synesthesia in childhood: 6/7 years to
10/11 years.” Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 7: 603.
Simner, J. and E. Holenstein. 2007. “Ordinal linguistic
personification as a variant of synesthesia.” Journal of
Cognitive Neuroscience 19(4): 694-703.
Simner, J. and V. U. Ludwig. 2012. “The color of touch: A
case of tactile–visual synaesthesia.” Neurocase 18(2):
167-80.
Smilek, D., A. Callejas, M. J. Dixon, and P. M. Merikle.
2007a. “Ovals of time: Time-space associations in
synaesthesia.” Consciousness and Cognition 16(2):
507-19.
Smilek, D., K. A. Malcolmson, J. S. Carriere, M. Eller, D.
Kwan, and M. Reynolds. 2007b. “When “3” is a jerk
and “E” is a king: Personifying inanimate objects in
synesthesia.” Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 19(6):
981-92.
Smith, G. F. 1998. “Idea‐generation techniques: A
formulary of active ingredients.” The Journal of
Creative Behavior 32(2): 107-34.
Stein, M. I. 1953. “Creativity and culture.” The journal of
psychology 36(2): 311-22.
Vidal, R. V. V. 2009. “Creativity for problem solvers.” Ai
& Society 23(3): 409-32.
Wang, H.-C., D. Cosley, and S. R. Fussell. Year. “Idea
expander: supporting group brainstorming with
conversationally triggered visual thinking stimuli.” In
Proceedings of the 2010 ACM conference on
Computer supported cooperative work, edited by, pp.
103-06.
Wang, H.-C., S. R. Fussell, and D. Cosley. Year. “From
diversity to creativity: Stimulating group
brainstorming with cultural differences and
conversationally-retrieved pictures.” In Proceedings of
Generation of Creativity with Inspiration from Synaesthesia
569

the ACM 2011 conference on Computer supported
cooperative work, edited by, pp. 265-74.
Wang, K. and J. V. Nickerson. 2017. “A literature review
on individual creativity support systems.” Computers
in Human Behavior 74: 139-51.
Wang, K. and J. V. Nickerson. 2019. “A Wikipedia-based
method to support creative idea generation: The Role
of Stimulus Relatedness.” Journal of Management
Information Systems 36(4): 1284-312.
Ward, J., P. Schnakenberg, and M. J. Banissy. 2018. “The
relationship between mirror-touch synaesthesia and
empathy: New evidence and a new screening tool.”
Cognitive neuropsychology 35(5-6): 314-32.
Ward, J. and J. Simner. 2003. “Lexical-gustatory
synaesthesia: linguistic and conceptual factors.”
Cognition 89(3): 237-61.
Ward, J. and J. Simner. 2021. “How do Different Types of
Synesthesia Cluster Together? Implications for Causal
Mechanisms.” Perception: 03010066211070761.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
570
