
Analysis of the COVID-19 Communication on Twitter via Multilayer
Network
Milan Petrović
1,2 a
, Zoran Levnajić
3b
and Ana Meštrović
1,2 c
1
Faculty of Informatics and Digital Technologies, University of Rijeka, R. Matejčić 2, Rijeka, Croatia
2
Center for Artificial Intelligence, University of Rijeka, R. Matejčić 2, Rijeka, Croatia
3
Complex Systems and Data Science Lab, Faculty of Information Studies in Novo Mesto, Novo Mesto, Slovenia
Keywords: Multilayer Network, Social Network Analysis, Twitter, Covid-19 Communication.
Abstract: In this paper we describe a multilayer network based framework for the representation of online
communication in social media. More precisely, we define the formalism that captures knowledge about the
users, actions and messages in social networks such as Twitter. We present a possible application of the
proposed framework for the analysis of COVID-19-related communications on Twitter in the Croatian
language during the third wave of the pandemic. Given the multilayer network of six layers, we first calculate
and analyse set global and local network measures. In the second step, we perform the grouping of the tweets
by using community detection algorithm and k-means clustering of tweets represented as vectors composed
of centrality measures across the layers. As a result, the proposed multilayer framework provides an insight
into the crisis communication in terms of quantifying users' actions and the amount of tweeting and retweeting
about the specific topics related to COVID-19.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media plays a significant role in global crises,
such as the COVID-19 pandemic. It serves as a key
communication platform, and it is a potential source
of valuable information (Cuello-Garcia et al., 2020).
It affects the public perception and may influence
political communication and policy-making activities
(Cinelli et al., 2020). During the last two decades,
social media has amplified the spread of information,
as well as misinformation and disinformation which
may cause an infodemic as a negative side effect
(Eysenbach, 2002). Recent studies confirm that
(social) media influences human behavior in the
context of disease transmission and thus may affect
the spread and control of infectious diseases (Bedson
et al., 2021; Xiaet al., 2019). Hence, for both reasons
(positive and negative effects of social media), social
media monitoring is important for a better
understanding of crisis communication.
Modelling social media via networks is a
powerful tool to analyse relationships and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5302-9366
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9025-9344
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9513-9467
communication between individuals. This
representation is highly useful in modelling various
social phenomena and has been widely studied in
numerous research papers. Lately there has been a
great deal of network-based research related to
COVID-19 communication in social media (Ahmed
et al. 2020; Caldarelli et al., 2021; Mattei et al., 2021).
However, a single network can represent only one
type of relationship among users and thus might not
capture all the important properties of the
communication. The more appropriate approach is to
use a multilayer network that can represent different
layers of relationships in social networks. The main
goal of this study is to define a framework based on
multilayer network and to apply this framework in the
task of COVID-19 related communications on
Twitter.
The analysis of multilayer networks is an
emerging field that can capture various sorts of
relationships over heterogeneous data (Boccaletti et
al., 2014; Kivelä et al., 2014). We have already shown
that a multilayer network structure is fundamentally
PetroviÄ
˘
G, M., LevnajiÄ
˘
G, Z. and MeÅ ˛atroviÄ
˘
G, A.
Analysis of the COVID-19 Communication on Twitter via Multilayer Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0011939700003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 377-384
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
377

more expressive than individual layers in the
examples of modelling a multilayer language network
(Martinčić-Ipšić et al., 2016) and multidimensional
knowledge network (Vukić et al., 2020).
Social networks have already been modelled as
multilayer networks in different ways and for various
tasks in some previous studies, such as (Singh et al.,
2020; Sheikh et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). Some
of these approaches modelled Twitter as a multilayer
network based on retweet, quote, mention and reply
layer as, for example, in the task of disinformation
detection (Pierri et al., 2020). Solé et al. examined
Twitter and Instagram as a multilayer network of two
layers and proposed centrality measures for ranking
the users (Solé et al., 2020). Fewer studies consider
multilayer networks of tweets and even fewer
research combine heterogeneous sources of social
networks. Some examples of such approaches include
the analysis of the two layers based on hashtags
(Türker and Sulak, 2018) and the construction of the
two layers of Twitter based on followers and tweets
(Bindu et al., 2020), used for community detection.
There is still a lack of research that applies
multilayer networks to model social network
communications as multiple layers of heterogeneous
data that include both, users and messages. To
overcome this gap, we propose a framework that uses
a multilayer network to represent messages as nodes
in one layer and users as nodes in other layers. This
way it is possible to capture more details of the
communication on social networks such as the users’
activities and properties of posted messages. More
precisely, we model this communication by defining
five layers of users’ activities and one more layer
representing messages. In the case of Twitter these
aspects include various users’ actions such as retweet,
reply, quote, mention and follow plus one additional
layer dedicated to tweets. It is also possible to include
the metadata of tweets as an additional set of
attributes.
The objective of this research is to define a
general formalism that can capture different aspects
of communication on Twitter and then to apply this
formalism in analysis of COVID-19 related
communications on Twitter. We formalised this
model as a communication multilayer framework,
and we applied this framework to the task of
analysing COVID-19 communications on Twitter.
For this purpose, we collect a representative sample
of Twitter communication in the Croatian language
during the third wave of the pandemic including a
total number of 32,193 tweets. Within the proposed
framework, we calculate global and local network
measures and describe the structural properties of
twitter communication. Next, we analysed the
different subset of tweets in terms of structure,
semantic and sharing properties. The proposed
approach sheds light on users’ actions and themes
related to COVID-19 and may be used to advise the
authorities how to better communicate during the
healthcare crisis. In general, the proposed framework
can be applied to other similar situations when better
understanding of the crisis communication is needed.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Multilayer Framework
According to (Boccaletti et al. 2014) a multilayer
network is defined as a pair:
ℳ
=(G, C)
(1
)
where
G ={𝐺
;𝛼𝜖
{
1, … , 𝑚
}
}
(2
)
is a family of networks (graphs) 𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
)
called network layers of ℳ and C ={𝐸
⊆𝑉
×
𝑉
;𝛼,𝛽𝜖
{
1, … , 𝑚
}
,𝛼 ≠ 𝛽} is the set of
interconnections between nodes of different layers
𝐺
and 𝐺
where 𝛼≠ 𝛽.
Layers are annotated as numbers from the set
{
1, … , 𝑚
}
, where 𝑚 is the number of layers.
Multilayer networks can be directed or undirected,
weighted or unweighted. Communication in social
networks is best captured with the weighted and
directed multilayer network.
Additionally, we introduce and consider a set T
of all metadata related to posted textual messages.
The concrete metadata that is used may vary
depending on the task. However, this set includes all
messaging metadata that is available. In the case of
Twitter, this metadata includes information such as
the number of retweets, quotes, mentions, etc.
Additionally, this set may contain text embedding
provided by the language model that captures the
semantic of the text message. All these data is
represented as vectors and can be later used for
detailed examinations of the messages. In the context
of network analysis, these vectors are actually the
attributes of nodes that represent messages.
Finally, the communication multilayer framework
is defined as a tuple:
𝐶
ℳ
𝐹=(
ℳ
, T)
(3
)
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
378

2.2 The Networks Construction and
Analysis
For the network construction we first collected
dataset of 32,193 COVID-19 related tweets. Data is
collected using tweepy, a Python library for accessing
the Twitter API. For the purpose of this preliminary
study, we collected Twitter data posted in the period
from February 15, 2021 to May 31, 2021 covering the
time of the third pandemic wave in the Republic of
Croatia.
Given the framework 𝐶ℳ𝐹 , we model Twitter
data into five layers, thus 𝑚=6. Each layer represent
one aspect of communication on Twitter as follows.
𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a user retweet layer where Twitter
users are nodes. Two nodes 𝑖 and 𝑗 are connected with
the directed link if user 𝑗 retweets user 𝑖. The weight
represents the number of retweets. 𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a
user reply layer where Twitter users are nodes and
two nodes 𝑖 and 𝑗 are connected with the directed link
if user 𝑗 replies to user 𝑖. The weight represents the
number of replies. 𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a user quote
layer where Twitter users are nodes and two nodes 𝑖
and 𝑗 are connected with the directed link if node 𝑗
quotes user 𝑖. The weight represents the number of
quotes. 𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a user mention layer where
Twitter users are nodes and two nodes 𝑖 and 𝑗 are
connected with the directed link if user 𝑗 mentions
user 𝑖.The weight represents the number of mentions.
𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a user follow layer where Twitter
users are nodes and two nodes 𝑖 and 𝑗 are connected
with the directed link if user 𝑗 follows user 𝑖 . All
weights are set to 1 since this layer is an unweighted
network. 𝐺
=(𝑉
,𝐸
) is a tweets layer where
Twitter messages are nodes and two nodes 𝑖 and 𝑗 are
connected with the directed link if message 𝑖 and 𝑗
have at least one word and/or hashtag in common. The
connection is established according to the timeline;
from the first tweet to the second tweet. The weight
represents the number of common words/hashtags.
Illustration of this model is represented in Figure 1.
Interconnections between nodes of different
layers are defined in the way that for the first five
layers (which may be described as multiplex), links
are connecting the same nodes. The weight of the
interconnection links is set to 1 and the directions are
set from the upper layer to the lower layer. However,
in this case, the order of layers is arbitrary and
directed links are necessary only because the rest of
the multilayer network is directed. Additionally, we
construct directed links from users represented as
nodes on the fifth layer to the tweets represented as
nodes on the sixth layer. Node 𝑖 is connected with the
node 𝑗 if user 𝑖 posted a tweet 𝑗. Analogously, we
construct interlinks between the other layers and the
sixth layer: we connect the user with the tweet
according to the user’s actions. In this case, the
hierarchy of the layers is natural because it represents
the direction of the relationship from the user to a
certain tweet.
The first step of this approach is the analysis of
the global properties for all layers. We pick a set of
global network measures: average degree, average
strength (in/out), network density, average path
length, diameter, reach, global efficiency, average
clustering coefficient (weighted/unweighted),
average degree centrality, transitivity and modularity.
The second step is the grouping of messages using
two different approaches: (i) the Louvain algorithm
(Blondel et al., 2008) and (ii) k-means clustering of
tweets represented as vectors. Tweet vectors are
constructed using local node measures: in/out-degree,
in/out-strength, hubs and authorities. Hubs and
authorities, also known as HITS (Hyperlink-Induced
Topic Search) were initially introduced by Jon
Kleinberg (Kleinberg, 1998) for ranking web pages.
The idea behind applying these measures in the
directed social networks is that authorities will highly
rank nodes with many followers, replies, retweets,
quotes or mentions, while hubs will highly rank nodes
that retweet, reply, quote, mention or follow many
other nodes. After calculating four measures for all
six layers, a tweet is represented as a 24-dimensional
vector. For the purpose of this second step, we need
to combine heterogeneous data from ℳ, such as the
number of interlinks from 𝐺
to 𝐺
, with the texts
from the set T. This approach provides knowledge
about the possible similarities of messages, the
quantity of messages in a group and how certain
groups of messages are spreading.
Figure 1: Multilayer network diagram.
Analysis of the COVID-19 Communication on Twitter via Multilayer Network
379
3 RESULTS
3.1 Network Structure on the Global
Level
The global network measures for all six layers are
reported in Table 1. Although the first five layers
represent users, each layer includes different number
of nodes because we take into account only users that
are involved in observed relationships. Thus, the
Follow layer includes only nodes (users) that posted
tweets from the Tweets layer; and Mention layer
includes only nodes (users) that are mentioned in
tweets from the Tweets layer. Furthermore, the
relation of following is the most common and the
number of links that represent following is always
higher that number of links that represent replying,
retweeting, mentioning and quoting. Consequently,
the number of nodes and links across layers
substantially varies. For example, the Follow layer
has lower number of nodes, but the highest number of
links comparing the first five layers. Next, if we
compare only the first four layers that represent users’
actions, it seems that mention is the most frequent
action, while quote is very rare within COVID19
related communications on Twitter. Among these
four layers, mention and reply layers have the highest
values of average degree and in-strength measures.
This means that the users involved in this
communication replied and mentioned much more
often than retweeted and quoted.
Furthermore, all four layers have similar diameters
and low clustering coefficients, which may indicate
that these are small world networks. The reply layer
has the highest values of average path length and
reach, which can mean that the users are not so
closely connected in the case of replying. The
differences between layers can also be noticed in the
values of modularity measure. Retweet and quote
layers have values of modularity higher than 0.5,
which means that in these actions, users are better
grouped into communities than in mention and reply
layers.
On the other side, the layer that represents the
action of following is somewhat different than the
first four layers. In this sample of the dataset, we
cannot include users with protected profiles, therefore
the number of nodes is smaller than the real number
of users involved in COVID-19 communications.
However, even based on this data it is obvious that
the follower layer has more connections, and it is
much denser than the first four layers. Consequently,
the diameter is lower, indicating that all users are
relatively close which is the usual property of social
networks. However, the average path length is higher
than in the first two layers. This property is expected,
because following somebody does not automatically
imply actions of replying, retweeting, quoting and
mentioning.
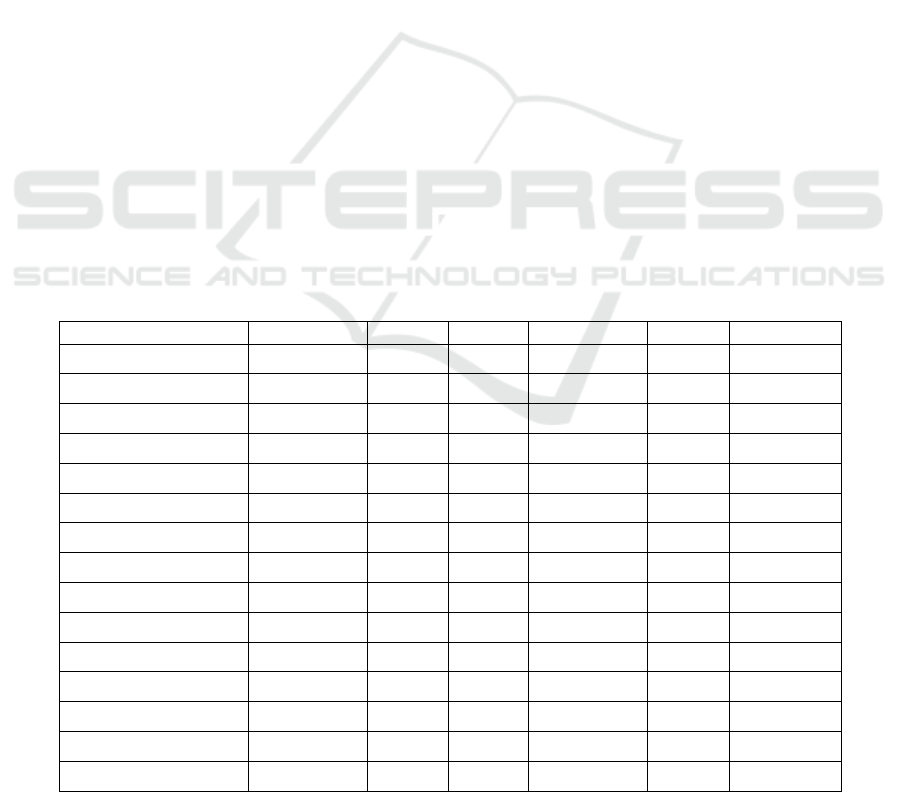
Table 1: Global network measures across layers.
Measure/Layer Retweet Reply Quote Mention Follow Tweets
total nodes 1543 2582 190 4963 1240 32,193
total edges 2141 6292 157 12,145 58,179 56,844,682
average degree 2 .7751 4.8737 1.6526 4.8942 93.837 3531.49
avg in-strength 0.8782 1.1311 0.6636 1.0993 - 1.0957
avg out-strength 0.7912 0.6818 0.5373 0.4636 - 1.0919
network density 0.0009 0.0009 0.0044 0.0005 0.0379 0.0548
avg. path length 0.0239 0.7214 0.0182 0.0007 2.2544 /
diameter 14 14 15 14 6 /
reach 0.1692 0.4073 0.0592 0.0299 0.021 /
global efficiency 0.1275 0.1807 0.0458 0.1641 0.4838 /
avg. clust. coeff. (uw) 0.016 0.0259 0.0037 0 0.3509 /
avg. clust. coeff. (w) 0.0001 0.0001 0.0003 0 - /
avg. degree cent. 0.0018 0.0019 0.0087 0.001 0.0757 0.1097
transitivity 0.0096 0.0329 0.0036 0 0.2959 /
modularity 0.5413 0.1882 0.7724 0.145 0.0008 0.0004
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
380
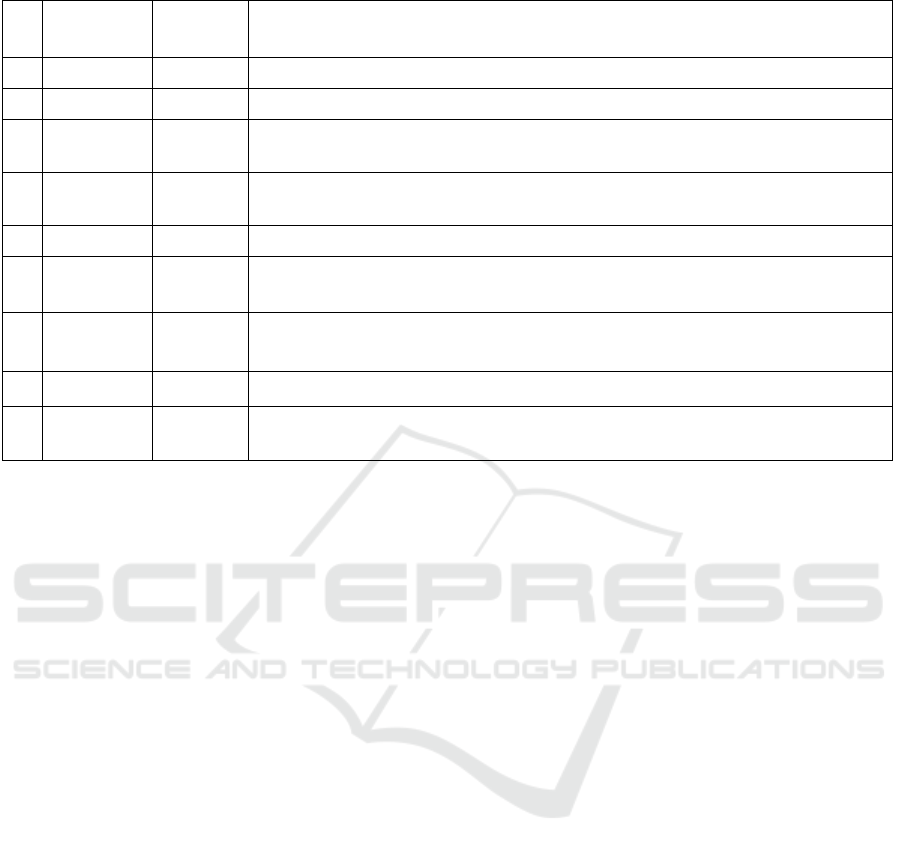
Table 2. Communities detected in a tweet layer.
#
Number of
tweets
Avg. no.
of rt
10 most frequent terms
1 1,979 75.31 masks, mask, rt, wear, @usenname11, open, don't have, misinformation, know, man
2 3,298 23.26 pandemic, covid, rt, covid-19, #covid19, croatian, man, person, new, measure
3 5,806 18.56
infect, headquaters, new, newly-infected, measure, person, croatian, epidemiological,
number, county
4 7,582 17.7
#koronavirus, #dnevnikhr, coronavirus, rt, new, person, @koronavirus\_hr, croatian,
infect, corona
5 3,287 11.66 vaccines, vaccine, rt, dose, croatian, pfizer, patient, new, respirator, other
6 3,383 5.29
@usenname1, @usenname2, @usenname3, @usenname4, @usenname5,
@usenname6, @usenname7, @usenname8, @usenname9, @usenname10
7 3,495 4.47
hospital, doctor (\textit{male}), medical, therapy, rt, medicine, doctorate, doctor
(\textit{female}), know, all
8 4,387 1.11 vaccination, vaccinate, vaccine, man, vaccines, rt, dose, all, person, other
9 66 0.49
#unizg, #mojesveuciliste, #ostanimoodgovoran, @sveucilistezg, project, student,
attach, university, faculty, competition
The sixth layer introduces tweets as nodes and
thus has a completely different structure. It captures
the semantic aspect of communication. Due to the
large number of links, distance measures are not
calculated. This network is much larger than the
network of other layers with a higher number of edges
and consequently much higher average degree.
However, the values of the average strength are not
high in comparison to other layers. This can be
explained in the sense that many tweets have only one
word or a hashtag in common. This property of
tweets’ similarity is examined in more detail in the
next subsection.
3.2 Communities and Clusters of
Tweets
In the second step we analyse the properties of groups
based on structure, semantics and the amount of
tweeting and retweeting. As described in the
Methodology section, we perform the grouping of
tweets using two different approaches. The results are
shown in Table 2 and 3 reporting the number of
tweets, the average number of retweets (calculated
based on the number of interlinks from G1 to G6 ) and
the top ten most frequent terms (words) translated in
English for each group (extracted from the set T).
Note that the most frequent words may contain
hashtags (indicated by the “#” character) and user
mentions (indicated by the “@” character), the
metadata for retweets (indicated by “rt”) as these
terms are essential parts of a tweet.
In Table 2 we show the results of grouping tweets
from the layer G^6 into 9 communities sorted by the
number of average retweets. We analyse the content
of tweets and assign a topic to every community as
follows: #1 - masks and misinformation, #2 -
COVID-19 pandemic in general, #3 - headquarters
and epidemiology, #4 - COVID-19 news, #5 -
vaccines, #6 - user mentions, #7 - healthcare, #8 -
vaccination, #9 - education. This set of topic covers
some of the main themes related to COVID-19. Note
that vaccines and vaccination are formed as two
separate communities, however, we decided to
analyse these two groups together. The most tweeted
topics are related to the vaccination (7,674 tweets in
#5 and #8), COVID-19 news (7,582 tweets in #4) and
headquarters and epidemiology (5,806 tweets in #3).
The highly retweeted (on average around 75 retweets
of one tweet) is the group with the topic related to
masks and misinformation. Very low sharing (less
than 10 retweets on average) is detected for the
groups of tweets related to #6 - user mentions, #7 -
healthcare, #9 - education.
In Table 3 we report the results of clustering the
tweets into 10 clusters using k-means algorithm.
Analysis of the COVID-19 Communication on Twitter via Multilayer Network
381
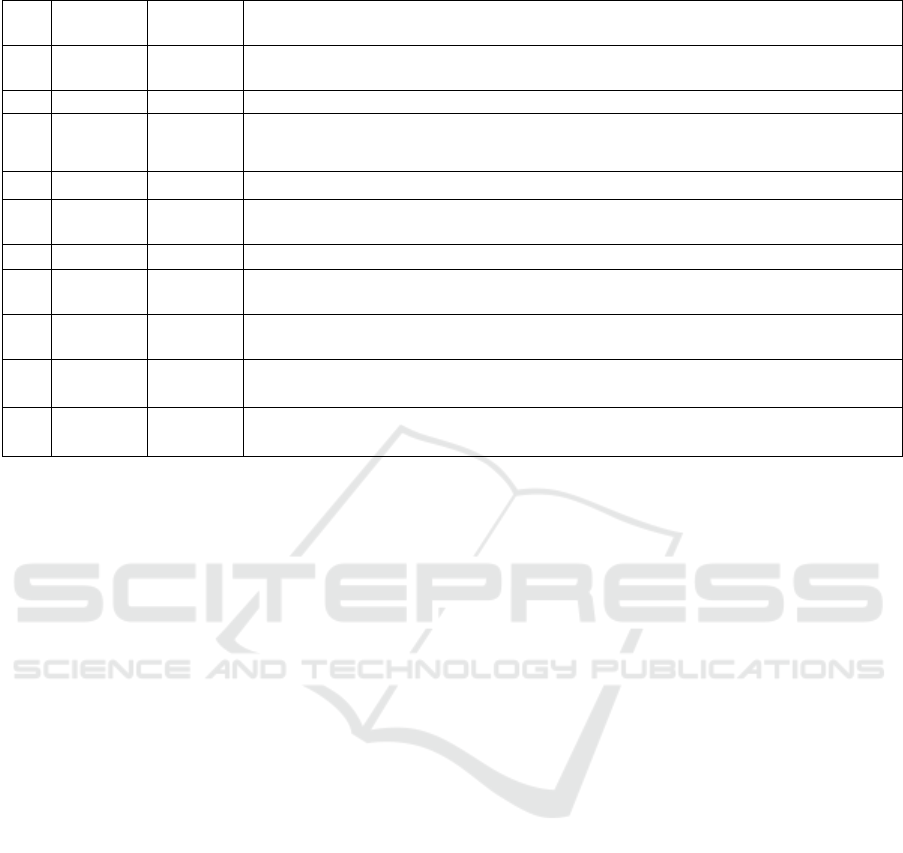
Table 3. Clusters of tweets constructed using k-means algorithm.
#
Number
of tweets
Avg. No.
of rt 10 most frequent terms
1 3,980 38.85
coronavirus, person, @koronavirus\_hr, new, infect, corona, #koronavirus, croatian,
hour, rt
2 15,661 24.68 rt, vaccination, @usenname1, vaccine, croatian, new, man, hospital, person, pandemic
3 180 10.1
rt, @koronavirus\_hr, @usenname12, vaccination, know, croatian, masks, get, vaccine,
measure
4 5895 5.9 vaccination, person, rt, @usenname1, new, croatian, man, vaccine, #hrvatski, #vijesti
5 334 3.47
@andrejplenkovic, rt, vaccine, dose, vaccination, \#covid19, @viliberos, @astrazenec,
@koronavirus\_hr, minister
6 3,088 1.55 rt, vaccination, vaccine, croatian, new, man, pandemic, covid, need, person
7 437 0.86
@dnevnikhr, \#koronavirus, rt, \#dnevnikhr, \#novatv, person, new, croatian, measure,
headquarters
8 782 0.64
\#dnevnikhr, \#koronavirus, rt, @novahr, cases, new, Croatian , #dnevniknovetv, number,
@koronavirus\_hr
9 319 0.12
@usenname1, @usenname4, @usenname3, @usenname5, @usenname9, @usenname2,
@usenname7, @usenname10, @usenname13, @usenname14
10 1,517 0.02
@usenname1, @usenname2, @usenname4, @usenname8, @usenname3, @usenname5,
@usenname6, @usenname15, @usenname7, @usenname14
Clusters are sorted by an average number of
retweets. According to the top ten most frequent
terms of each cluster, it is possible to recognise
differences within the structure of these clusters:
some clusters contain only mentions (#9, #10), some
contain hashtags (#5, #7, #8) cluster #6 contains only
words and metadata for a retweet. Some clusters are
a combination of terms with marks for mentions and
retweets (#1, #2, #3, #4). In the light of retweeting, it
seems that the clusters with a mixed structure (#1, #2,
#3, #4) have far more retweets than clusters with the
structure in which mentions (#9, #10) or hashtags (#7,
#8) are predominant. Tweets with a lot of mentions
referred to private communication, and for such a
cluster, it is expected to be less retweeted. The first
two highly retweeted clusters contain the highest
number of tweets as well. Furthermore, according to
the most frequent terms, we assign a predominant
theme for each cluster as follows: #1 - general terms,
#2 - vaccination, #3 - measures, #4 - vaccination, #5
- politicians, #6 - vaccination, #7 - news and
measures, #8 - number of new cases, #9 - mentions,
#10 - mentions.
It turns out that the largest and the most retweeted
clusters mention vaccination and pandemic measures.
This consideration of topics related to vaccination is
similar to the one based on the previous results with
communities. However, the topic detection of tweets
makes more sense in communities, while clusters
provide information about users’ actions.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we propose a multilayer network
framework for the representation and analysis of
communications in social media. We apply the
proposed framework to the analysis of COVID-19
related tweets.
On the global level we detect some general
properties of communication in social networks such
as the intensity of the communication and how well
these users are connected in terms of different
possible actions. Overall, in the case of COVID-19
related communications on Twitter in the Croatian
language, users are highly connected as followers,
while there are lower connection realised through the
actions of retweeting, replying, quoting and
mentioning. The most intense communication is
obtained via replies and mentions while the best
grouping into communities is achieved for users that
reply and quote.
Furthermore, by analysing local network measures
we get a better insight into the online communication
on Twitter related to COVID-19. Specifically, the
communities formed on G^6 represent semantically
similar groups of tweets pointing out the main
COVID-19 related topics that were in focus during
the third pandemic wave. According to our results the
most tweeted topics are related to vaccination,
COVID-19 news and headquarters and epidemiology,
while the most retweeted topic is related to masks and
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
382

misinformation. This approach can be further used as
a step in the task of topic modelling. Clustering based
on the data gathered from all six layers reveals the
patterns of users’ actions. In the case of COVID-19
communications on Twitter we recognise that the
majority of tweets contain vaccination, masks and
coronavirus as the most frequent terms. These are also
clusters of the most retweeted tweets.
This study is preliminary research and the first step
toward the modelling and understanding of the
multilayer communication network. In this approach,
we do not exploit the full potential of a defined
multilayer framework. There are several possible
directions of our future work, such as exploring other
possibilities of combining and analysing all the layers
and using more network measures, especially
centrality measures of the multilayer network.
Furthermore, we plan to extend this approach by
representing the Twitter message using the multilayer
network properties. This way, the message can be
represented as a vector composed of different
network features.
Moreover, the proposed approach can be applied in
the analysis of any other domain of communication
on Twitter.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported in part by the Croatian
Science Foundation under the project IP-CORONA-
04-2061, “Multilayer Framework for the Information
Spreading Characterization in Social Media during
the COVID-19 Crisis” (InfoCoV).
REFERENCES
Cuello-Garcia, C, Pérez-Gaxiola, G and van Amelsvoort, L
2020 Social media can have an impact on how we
manage and investigate the COVID-19 pandemic.
Journal of clinical epidemiology, 127, pp.198.
Cinelli, M, Quattrociocchi, W, Galeazzi, A, Valensise, CM,
Brugnoli, E, Schmidt, AL, Zola, , Zollo, F and Scala, A
2020 The COVID-19 social media infodemic.
Scientific Reports, 10(1), pp.1-10.
Eysenbach, G 2002 Infodemiology: The epidemiology of
(mis) information. The American journal of medicine,
113(9), pp. 763-765.
Bedson, J, Skrip, LA, Pedi, D, Abramowitz, S, Carter, S,
Jalloh, MF, Funk, S, Gobat, N, Giles-Vernick, T,
Chowell, G and de Almeida, JR 2021 A review and
agenda for integrated disease models including social
and behavioural factors. Nature Human Behaviour,
pp.1-13. 10
Xia, C, Wang, Z, Zheng, C, Guo, Q, Shi, Y, Dehmer, M and
Chen, Z 2019 A new coupled disease-awareness
spreading model with mass media on multiplex
networks. Information Sciences, 471, pp.185-200.
Ahmed W, Vidal-Alaball J, Downing J and Seguí FL 2020
COVID-19 and the 5G conspiracy theory: social
network analysis of Twitter data. Journal of medical
internet research. 6;22(5):e19458.
Caldarelli G, Nicola RD, Petrocchi M, Pratelli M and
Saracco F 2021 Flow of online misinformation during
the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy. EPJ Data
Sci 10:34.
Mattei, M, Caldarelli, G, Squartini, T and Saracco F 2021
Italian Twitter semantic network during the Covid-19
epidemic. EPJ Data Sci. 10, pp. 47.
Boccaletti, S, Bianconi, G, Criado, R, Del Genio, CI,
Gómez-Gardenes, J, Romance, M, Sendina-Nadal, I,
Wang, Z and Zanin, M 2014 The structure and
dynamics of multilayer networks. Physics reports,
544(1), pp.1-122.
Kivelä, M, Arenas, A, Barthelemy, M, Gleeson, JP,
Moreno, Y and Porter, MA 2014 Multilayer networks.
Journal of complex networks, 2(3), pp. 203-271.
Martinčić-Ipšić, S, Margan, D and Meštrović, A 2016
Multilayer network of language: A unified framework
for structural analysis of linguistic subsystems. Physica
A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 457,
pp.117-128.
Vukić, Đ, Martinčić-Ipšić, S and Meštrović, A 2020
Structural analysis of factual, conceptual, procedural,
and metacognitive knowledge in a multidimensional
knowledge network. Complexity pp 1-17.
Singh, LG, Mitra, A and Singh, SR 2020 Sentiment
Analysis of Tweets using Heterogeneous Multi-layer
Network Representation and Embedding. In
Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on EMNLP, pp.
8932-8946.
Sheikh, MM and Malick, RAS 2020 Community Detection
in a Multi-layer Network Over Social Media. In
International Conference on Complex Networks and
Their Applications (pp. 124-136). Springer, Cham.
Zhang, Y, Chen, W, Yeo, CK, Lau, CT and Lee, BS 2017
Detecting rumors on online social networks using
multi-layer autoencoder. TEMSCON, pp. 437-441.
Pierri, F, Piccardi, C and Ceri, S 2020 A multi-layer
approach to disinformation detection in US and Italian
news spreading on Twitter. EPJ Data Science, 9(1),
p.35.
Solé-Ribalta, A, De Domenico, M, Gómez, S and Arenas,
A 2014 Centrality rankings in multiplex networks. In
Proceedings of the 2014 ACM conference on Web
science, pp. 149-155.
Türker, I and Sulak, EE 2018 A multilayer network analysis
of hashtags in twitter via co-occurrence and semantic
links. International Journal of Modern Physics B,
32(04), p.1850029.
Bindu, PV, Mishra, R and Thilagam, PS 2018 Discovering
spammer communities in Twitter. Journal of Intelligent
Information Systems, 51(3), pp.503-527.
Analysis of the COVID-19 Communication on Twitter via Multilayer Network
383

Blondel VD, Guillaume JL, Lambiotte R and Lefebvre E
2008 Fast unfolding of communities in large networks.
Journal of statistical mechanics: theory and experiment.
9;2008(10):P10008.
Kleinberg, JM 1998 Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked
environment. In SODA, Vol. 98, pp. 668-677.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
384
