
Low-Orbit Satellite Orbit Prediction Algorithm Based on Near-Polar
Circular Orbit
Delu Wei
1
, Chao Zhao
2
, Hangzai Luo
1
, Sheng Zhong
1
and Zhengwen Cao
1,*
1
School of Information Science and Technology, Northwest University, Xi’an, China
2
Xi’an Institute of Microelectronics Technology, Xi’an, China
Keywords: Low Orbit Satellite, Constellation Network, Orbit Prediction.
Abstract: Satellite orbit prediction is a significant research problem in visualizing low-orbit giant constellation networks.
However, due to the limited resources of the onboard network equipment, the existing satellite orbit prediction
methods are challenging to balance the accuracy and rapidity of the prediction. These traditional forecasting
methods tend to construct perturbation models and obtain accurate orbital dynamics equations for calculation.
Due to the complicated establishment of the perturbation model and the tedious calculation process, the
prediction accuracy of the low-order analytical solution is relatively low, and the calculation efficiency of the
high-order analytical solution is not high, which is not suitable for the orbit prediction of large-scale long-
period low earth orbit (LEO) satellites. This paper proposes an orbit prediction algorithm for LEO satellites
based on near-polar circular orbits. By simplifying the satellite motion model and using the least squares
method to fit the data errors, we finally obtain the position information of the LEO satellite constellation
network. Experimental results show that the method can perform orbit forecasting of large-scale LEO satellite
constellation networks while ensuring accuracy and rapidity compared with satellite tool kit (STK) software.
1 INTRODUCTION
In developing low-orbit giant constellation
networking visualization systems, satellite orbit
prediction technology is one of the key research
directions (Ren et al., 2019; Deng et al., 2021). The
prediction speed and accuracy play a vital role in the
design and optimization of inter-satellite link
visualization, which also directly reflects the
authenticity and reliability of the system. Currently,
most the satellite orbit prediction is based on the
classical mechanics model, which defines the
perturbation model by analyzing the satellites’ forces,
and then establishes the satellite orbit dynamics
equations and performs the orbit calculation through
the numerical integration method. For LEO satellites,
the main regenerative forces affecting the satellite
orbit calculation are the second-order band harmonic
terms of the earth’s non-spherical gravitational field,
atmospheric drag, other harmonic terms of the earth’s
non-spherical gravitational field, and the gravitational
force of the Sun and Moon. Since the accuracy of the
perturbation model is low, it can cause errors in the
traditional calculation methods. The other parameters
introduced by the perturbation model can lead to the
low prediction accuracy of the low-order analytical
solution and the cumbersome process of the high-
order analytical solution. (Wang et al., 2018).
This paper proposes a near-polar circular orbit-
based orbit prediction algorithm for LEO satellites.
The satellite motion model is simplified to a uniform
circular motion model with only the force provided by
gravity, and the computational errors caused by other
perturbations are fitted to the time-dependent primary
term by the least squares method and added to the
simplified satellite orbital dynamics equation to form
a new satellite orbital dynamics equation for orbit
calculation. By comparing the data obtained from the
high-precision satellite orbit prediction model in STK
software with a large amount of data obtained through
several experiments, the accuracy and feasibility of
the algorithm are verified. The fast and accurate
prediction of satellite orbit positions in the LEO giant
constellation network visualization system shown in
Fig. 1 is achieved with a limited computer system.
482
Wei, D., Zhao, C., Luo, H., Zhong, S. and Cao, Z.
Low-Orbit Satellite Orbit Prediction Algorithm Based on Near-Polar Circular Orbit.
DOI: 10.5220/0011953400003612
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing (ISAIC 2022), pages 482-487
ISBN: 978-989-758-622-4; ISSN: 2975-9463
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
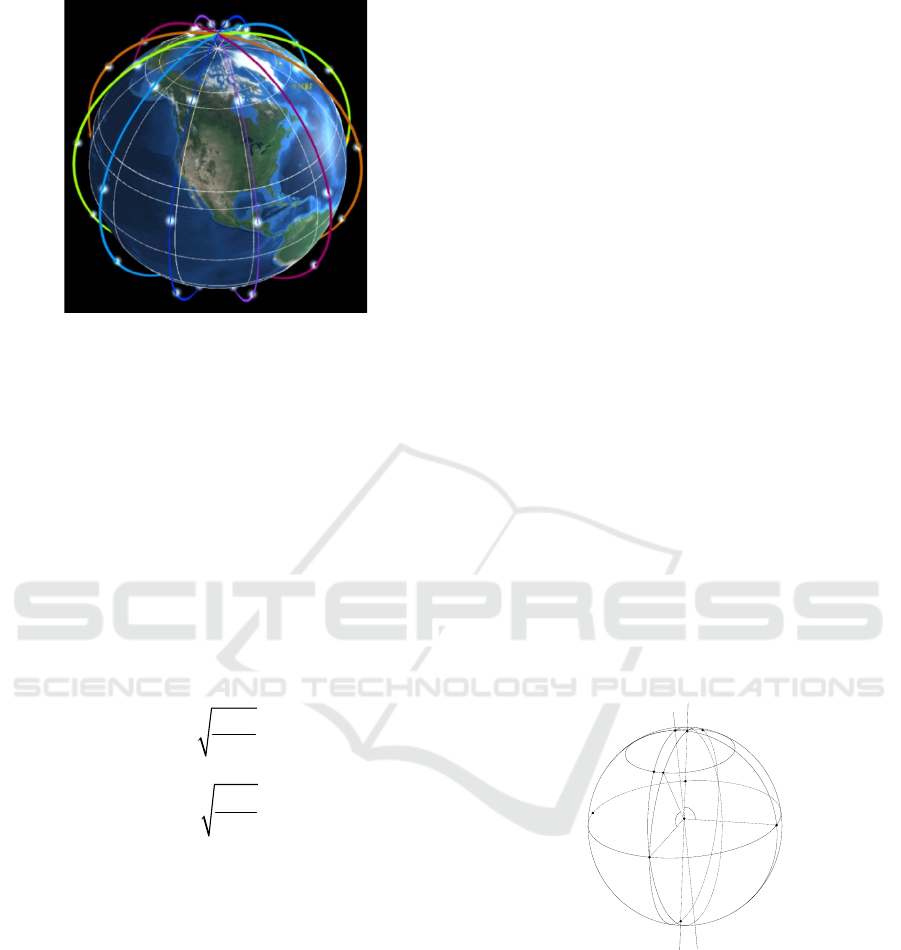
Figure 1: Visualization system diagram of constellation
networking.
2 SATELLITE CONSTELLATION
MOTION MODEL
2.1 The Law of Motion of the Satellite
Taking the near-polar circular orbit as an example, the
motion law of the satellite in an ideal state can be
simplified to a two-body problem (Ge et al., 2020).
According to the law of gravity, the linear and angular
velocities of the satellite orbiting at a given orbital
altitude
h
are calculated as:
GM
v
rh
=
+
(1)
GM
rh
ω
=
+
(2)
here
G
is the universal gravitational constant in
32
/( )mkgs⋅
,
M
is the total mass of the earth in
kg
,
r
is the mean radius of the earth in
m
.
2.2 Position Description of the Satellite
The position description of a satellite in a LEO
constellation network includes how to represent the
position of a point in the orbit and then consider how
to represent a point in the constellation network.
There are two main methods for describing the
position of a point in orbit: namely, phase
representation, and latitude and longitude
representation (Rabjerg et al., 2020).
In the phase representation, the orbit ascending
intersection point is specified as the 0 phase point. As
the satellite moves from south to north, the phase
varies between
(0, 2 )
π
. It increases linearly along the
direction of satellite motion, with the points on the
orbit corresponding to the phase values. In order to
extend the phase description method to the satellite
constellation, it is sufficient to add the orbit number
i
S
again, denoted by
(,)
i
S
ϕ
).
In the latitude-longitude representation, at any
moment, the subsatellite points of the satellite
uniquely map a latitude-longitude coordinate. The
satellite's orbit and the earth’s rotation will cause the
mapping relationship to change with time. The
latitude and longitude description method can be
directly extended to the constellation.
In order to illustrate the calculation process of the
longitude and latitude coordinates of the satellite
subsatellite, a typical satellite orbit model is
introduced as shown in Fig. 2. OA represents the
rotation axis of the earth, the orbital inclination can be
expressed as
i
, and the current phase angle of
satellite M is
ϕ
. Under the premise that the current
phase of the satellite is known, the latitude and
longitude of the satellite can be obtained according to
the geometric relationship in the Fig. 2 as follows:
1
sin (sin sin )
lat
i
θϕ
−
=
(3)
1
lng
tan (tan cos )i
θϕ
−
=
(4)
A
O
J
G
D
E
B
C
F
L
H
i
ψ
Figure 2: Satellite orbit model.
2.3 Location Distribution Strategy of
Satellites
Consider the problem of uniform coverage of the
satellite constellation network, the location
distribution of satellites can be carried out according
to the following strategy. Assume that a satellite
constellation network contains M orbits and N
Low-Orbit Satellite Orbit Prediction Algorithm Based on Near-Polar Circular Orbit
483

satellites on each satellite orbit, and the total number
of satellites in the constellation is S. The first orbit is
selected as the reference orbit, and the first satellite on
the first orbit is the reference satellite. The longitude
of the ascending node of the reference orbit is 0°, and
the initial phase of the reference satellite is 0 phase
point. The satellite orbit starts from the ascending
intersection point of the reference orbit and is evenly
distributed from west to east. The longitude
difference between adjacent orbits (
f
ϕ
Δ
) is
/
M
π
;
the satellites in the same orbit start from the 0 phase
point and are evenly distributed along the direction of
the increasing phase. The phase difference between
adjacent satellites in the same orbit (
s
ϕ
Δ
) is
2/N
π
.
From the above, for any satellite in the satellite
constellation network
mn
S
(denoting the n-th
satellite in the
m-th orbit, where
1, 2, ,mM=
,
1, 2, ,nN=
) the latitude and longitude of the initial
state can be expressed as:
1
0
( ) sin (sin sin )
lat
ti
θϕ
−
=
1
2
sin (sin(( 1) )sin )ji
N
π
−
=−
(5)
1
lng 0 0
( ) tan (tan cos )
js
ti
θθ ϕ
−
=+
1
( 1) tan (tan cos )
f
ii
ϕϕ
−
=−Δ +
(6)
Since the satellite constellation network is in
constant motion, the positions of the satellites in the
constellation are also changing. The satellite orbit
forecast is to calculate the position information of the
satellite at
t
based on the initial position of the
satellite and then to obtain the position information of
all the satellites in the entire constellation network at
t based on the distribution law of the satellites in the
constellation network. Considering the time factor,
the calculation formula of latitude and longitude is
rewritten as
1
( ) sin (sin ( ) sin )
lat
tti
θϕ
−
=
(7)
1
lng
() tan (tan ()cos)
jst
tti
θθ ϕ
−
=+
(8)
3 POSITION DATA ERROR
CORRECTION METHOD OF
SATELLITE
When using the satellite orbit motion model and
method composed of formula (1) to formula (8),
which is called the MNC model algorithm, the
obtained satellite position data has a significant error
compared with the data obtained by STK high-
precision orbit prediction model (MSGP4). The error
increases with the increase in prediction time.
The MNC calculation model simplifies the
satellite motion problem into a two-body problem.
This model does not consider the perturbation caused
by the second harmonic term of the earth’s aspheric
gravitational field, atmospheric resistance, and other
disturbances. It results in a significant error in the
calculation results.
Because of the difficulty of establishing an
accurate perturbation model and the complexity of
calculating the acceleration caused by each regression
force on satellite motion. The more orders of spherical
harmonic coefficients are considered in the
integration, the more time consumed. It is not
conducive to large-scale orbit position prediction and
visualization of LEO satellites with limited system
resources.
Therefore, in the subsequent, the least-squares
method is used for fitting. We fit the data errors
caused by various disturbances into polynomials
related to the running time and add them to the
original latitude and longitude calculation motion
model, which is called the MAC model. It solves the
problem that the data obtained by the MNC model and
the data obtained by the MSGP4 model have a
significant error. Under the condition of real-time and
accuracy, the position prediction and visualization of
large-scale LEO satellite constellation networks are
realized.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The target satellites in our experiments are low orbit
satellites in a near-polar circular orbit. A constellation
network of 6 orbits with 9 satellites in each orbit is
used as an example, and the satellites are distributed
according to the strategy described in subsection 2.3,
with an orbit inclination of 90°, and the experiments
are conducted under the settings of orbital altitudes of
500 km, 800 km, and 1000 km, respectively.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
484
The experimental environment was configured
with a processor AMD Ryzen 7 5800H with Radeon
Graphics 3.20 GHz, 16 GB of RAM, and an operating
system of 64-bit Windows 10 version 19044.1706.
4.1 Accuracy of Orbit Prediction
Algorithms for LEO Satellites in
near Polar Circular Orbit
Based on the given orbits, the satellite positions are
distributed according to the strategy proposed in the
previous section, and a satellite constellation network
is established. The initial latitude and longitude of all
satellites in the constellation network are obtained by
traversing the number of satellite orbits, the number
of satellites in orbit, and the latitude and longitude
position of any satellite at a given observation
moment is obtained by the latitude and longitude
calculation algorithm (MNC).
Without loss of generality, we selected any two
satellites among 54 stars with an orbital altitude of
500 km and observation time of 7 days for
position
data calculation and then compared them with the
position data calculated by the identical numbered
satellites in the same scale constellation network of
STK 11.6 software under the MSGP4 model, and the
error of the satellite latitude data obtained from the
MNC model experiment and the latitude data
obtained from the MSGP4 model in STK. The
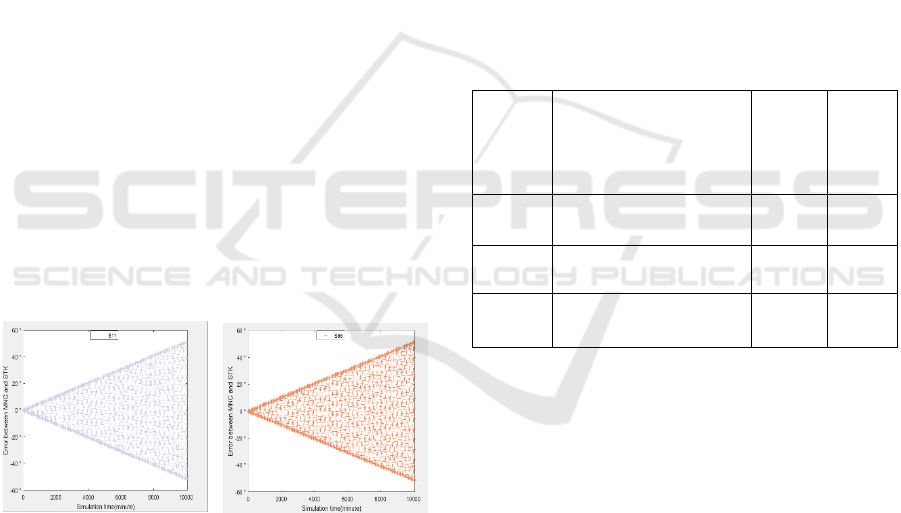
distribution of error with time is shown in Figure 3.
(a) Error of S11 (b) Error of S66
Figure 3: Error distribution plots.
Since our experiment is for a constellation of
satellites in a near-polar circular orbit, it can be seen
in the longitude calculation equation that when the
orbital inclination
i is 90, the longitude variation
depends only on the mean angular velocity of the
earth’s rotation
e
ω
. The value of the mean angular
velocity of the earth selected in the experiment is
consistent with the value set in the MSGP4 of STK
software. For the calculation of longitude, the errors
in the data obtained from the two models are minimal
and negligible (
3
10
−
). Therefore, only the errors in the
calculation of latitude are considered in this paper.
Figure 3 shows that the error in the latitude
direction is approximately linear for time. The
positive and negative error is that the latitude takes a
range of (-90°, 90°), and there are negative values.
Observing a large amount of data, it is found that the
error is positive when the satellite moves from south
to north and negative when the satellite moves from
north to south. Therefore, we set
d
as the direction
factor and find a primary polynomial by least squares
fitting
yatb=+
to fit the error curve to a time-
dependent primary term and add it to the latitude
calculation expression as an error correction term to
improve the accuracy of satellite position data
forecasting. The correction terms at three different
altitudes are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Expressions of correction terms at different orbital
heights.
Track
height
(km)
Correction
function
2
R
(fitting
degree)
RMSE
500
0.005094 0.00671yt=+
0.9996 0.294
800
0.004378 0.005281yt=+
0.9997 0.212
1000
0.003973 0.00312yt=+
0.9997 0.204
The correction term is added to the satellite
latitude calculation model to form a new calculation
model, which can be expressed as:
() ()
wt lat
tdyt
θθ
=+
(9)
here
d
is the orientation factor.
d
is -1 when the
satellite is moving from south to north,
d
is 1 when
the satellite is moving from north to south, and
()yt
represents the expression of the correction term at the
corresponding orbital altitude.
We refer to the satellite orbit prediction model
after adding the correction term as the MAC model.
By experimenting with the MAC model, the latitude
data of the satellite are calculated at three different
orbital altitudes. The latitude data of a satellite at three
different orbital altitudes are randomly selected and
compared with the latitude data of the corresponding
satellite in the MSGP4 model of STK. The error of
Low-Orbit Satellite Orbit Prediction Algorithm Based on Near-Polar Circular Orbit
485
the data obtained from the MAC model compared
with the MSGP4 model of STK and the error of the
data obtained from the MNC model compared with
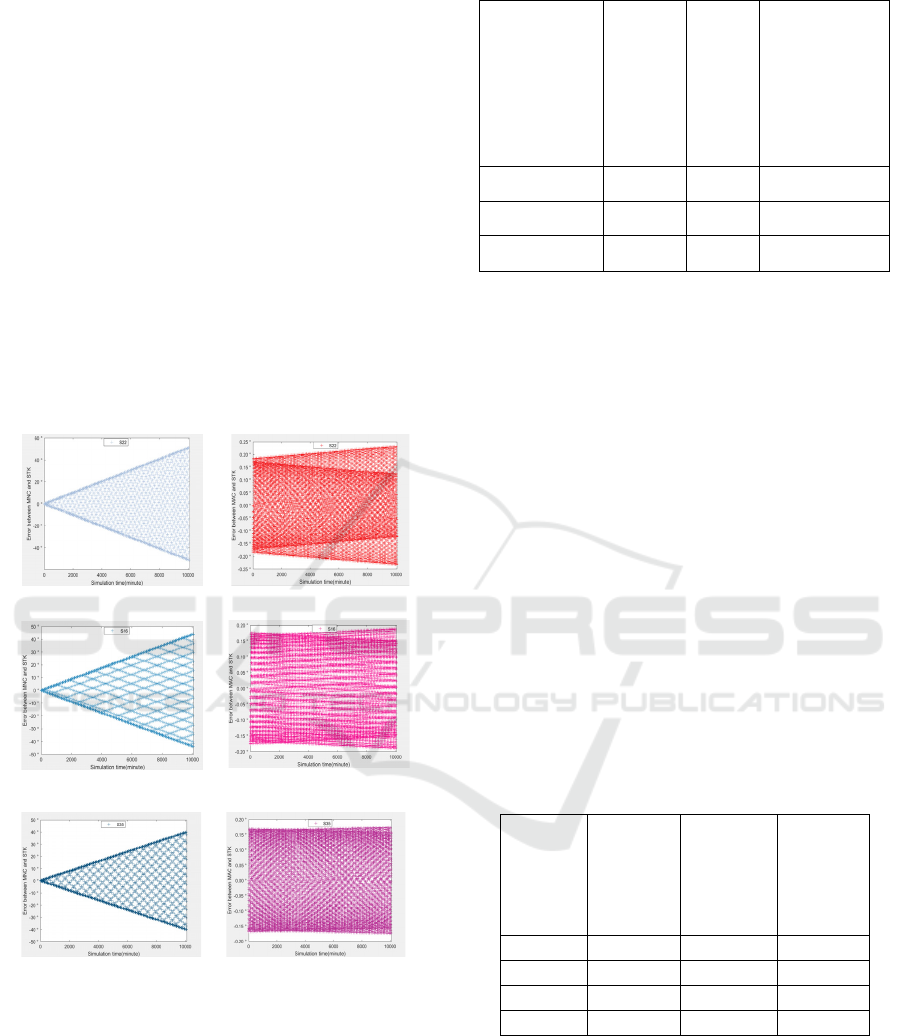
the MSGP4 model of STK are shown in Fig. 4. From
the figure, it can be seen that the data calculated by
the MAC model is closer to the data calculated by the
MSGP4 model in STK.
We experimentally tested the accuracy of the
satellite orbit prediction models for satellite
constellation networks with orbital altitudes of 500
km operating for 7, 15, and 30 days, and calculated
the correlation degree of the data obtained from the
MAC model proposed in this paper and the GSRPS
model in STK, calculated the MSE (mean square error)
of the data obtained from the two models, and
compared them with the MNC model. The
experimental results are shown in Table 2.
(a)Error of S22 on MNC (b)Error of S22 on MAC
`
(c)Error of S16 on MNC (d)Error of S16 on MAC
(c)Error of S35 on MNC (d)Error of S35 on MAC
Figure 4: Error comparison graph. (a) (b) with h = 500 km,
(c) (d) with h = 800km, (e) (f) with h = 1000km.
Table 2 Comparison of the accuracy of satellite orbit
prediction models before and after adding correction terms.
Satellite
constellation
network
operation
time
MSE
for
MNC
and
STK
MSE
for
MAC
and
STK
Order of
magnitude
improvement
in data
accuracy
7 days 754.41 0.0170 4.438×10
4
15 days 2810.45 0.0201 1.398×10
5
30 days 6309.11 0.0315 2.003×10
5
4.2 Superiority of Orbit Prediction
Algorithms for LEO Satellites in
near Polar Circular Orbit
The superiority of the near-polar circular orbit LEO
satellite forecasting algorithm in terms of execution
time is given in this subsection. The calculation
method proposed in this paper is applied to a network
of LEO satellites with different sizes of a near-polar
circular orbit, the orbital altitude is set to 500 km. The
operation time is set to 7 days, and the step size is 60
s. The position data of all satellites in the whole
constellation are calculated and output as a .txt file,
and the execution time of the MAC model algorithm
is obtained through experiments, and then compared
with the algorithm used by the MSGP4 model in STK
software, the experimental results are shown in Table
3.
Table 3 Comparison of the time consumption of the two
algorithms under different satellite constellation size.
Number
of
satellite
orbits
Number
of
satellites
per
orbit
STK
execution
time
(unit: s)
MAC
execution
time
(unit: s)
6 9 269.98 1.005
10 9 701.11 2.190
12 15 975.43 3.309
188 40 4263.61 13.278
With the increase of satellite constellation
network scale, the algorithm execution time gradually
increases. In the calculation of the orbit forecast of the
same scale satellite constellation network, the speed
of the algorithm used in this paper is nearly 300 times
higher than that of STK software, which can calculate
the position data of the large-scale LEO satellite
constellation network more quickly.
ISAIC 2022 - International Symposium on Automation, Information and Computing
486

5 CONCLUSION
This paper proposes a prediction algorithm for LEO
satellite orbits based on near-polar circular orbits.
Based on the prediction above model and algorithm,
the position data of the satellite at a given observation
moment and the time consumed by the algorithm
execution are obtained. In the experimental validation,
the predicted longitude and
latitude position errors are within the acceptable range
compared to the STK high-precision orbit prediction
model. Four orders of magnitude improve the
accuracy compared to before the correction term is
added, and the predicted position errors tend to be
stable for a time. The computation speed of the
algorithm proposed in this paper is nearly 300 times
higher than that of the STK software in the same scale
LEO satellite constellation, which is more suitable for
the long-period orbit prediction of large-scale LEO
satellite constellation networks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62071381),
Shaanxi Provincial Key R&D Program General
Project (2022GY-023).
REFERENCES
Deng, R.Q., Di, B.Y., and Song, L.Y.(2021). Ultra-Dense
LEO Satellite Based Formation Flying. IEEE
TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS(5).
Rabjerg, J.W., Leyva-Mayorga, I., and Soret, B. (2020).
Exploiting topology awareness for routing in LEO
satellite constellations.
Liang, J., Nan, X., and Zhang, J. (2011). Constellation
design and performance simulation of LEO satellite
communication system. International Conference on
Applied Informatics and Communication.
Ge, H., Li, B., Ge, M., Nie, L., and Schuh, H. (2020).
Improving low earth orbit (LEO) prediction with
accelerometer data. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1599.
Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, A., Xia, X., and Liu, X. (2021).
Deep learning-based channel prediction for LEO
satellite massive MIMO communication system. IEEE
wireless communications letters(10-8).
Ren, H., Chen, X., Guan, B., Wang, Y., and Peng, K.
(2019). Research on Satellite Orbit Prediction Based on
Neural Network Algorithm. the 2019 3rd High
Performance Computing and Cluster Technologies
Conference.
Bl, A., Hga, B., Mg, B., Ln, A., Ys, A., and Hs, B. (2019).
Leo enhanced global navigation satellite system
(LeGNSS) for real-time precise positioning services -
sciencedirect. Advances in Space Research, 63(1), 73-
93.
Li, S., and Wang, H. (2021). Research on navigation and
positioning technology based on opportunity signal of
low orbit satellite. Journal of Physics: Conference
Series, 1952(4), 042134 (13pp).
Wang, D. W., Tang, J. S., Liu, L., Ma, C. W., and Hao, S.
F. (2018). The assessment of the semi-analytical
method in the long-term orbit prediction of earth
satellites. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics, 42( 2),
239-266.
Low-Orbit Satellite Orbit Prediction Algorithm Based on Near-Polar Circular Orbit
487
