
The Flexural Strength of Bacteria-Based Concrete for Sustainable
Materials
Mutia Gina Savira
1
, Ujang Ruslan
1
, Keryanti
2
and Luthfi Muhammad Mauludin
1
1
Civil Engineering Department, Politeknik Negeri Bandung, Jl. Gegerkalong Hilir, Bandung Barat, Indonesia
2
Chemical Engineering Department, Politeknik Negeri Bandung, Jl. Gegerkalong Hilir, Bandung Barat, Indonesia
Keywords: Flexural Strength, Bacillus Megaterium, Fly Ash, Cracks.
Abstract: Concrete is the most popular material used in construction. In fact, concrete lies in its resistance to
compressive forces. However, the drawback of the concrete materials is weak in tension. Because of its
weakness, it can cause cracks in the concrete. One way to handle cracks in the concrete is to make bacteria-
based concrete. In this research, the type of bacteria used in concrete mixing is Bacillus megaterium. The
purpose of this research is to study the effect of Bacillus megaterium on the flexural strength of concrete. The
bacteria proportions of 1% and 2%, which are adopted in this study, were combined with fly ash as an additive
material. The specimens were casted into beam molds sized (500x100x100) mm and then tested under a three-
point bending machine to observe its bending capacity. The flexural strength of bacteria-based concrete was
observed for some periods, namely 14 days and 28 days. From this research, it can be concluded that the
flexural strength of bacteria-based concrete was raised up to 14,64% compared to virgin concrete.
1 INTRODUCTION
In infrastructure, concrete structures are the most
popular structures. The advantage of a concrete
structure is its resistance to compressive forces. This
material is widely used because of its strength and
durability (Bashir et al., 2016). On the other hand, the
weakness of the concrete structure is weak tension.
From this weakness, concrete is quite sensitive to
cracking which can compromise the durability of the
concrete structure as a whole (Luthfi Muhammad
Mauludin & Rabczuk, 2021) so it can cause cracks in
the concrete. Starting from a small crack, then it
becomes a medium crack and finally into a large
crack. If small cracks are not treated immediately, it
will cause larger cracks so that it can trigger cavities
that can make the reinforcing steel corrosive. If
repairs are not immediately carried out, it will result
in structural failure (collapse) and can also threaten
human life.
Cracks in concrete must be carefully monitored
and periodically repaired for ensuring durability and
safety (Luthfi M. Mauludin et al., 2018). Small cracks
(microcracks) such as the one in that develop in the
concrete due to unbalanced (balanced) tensile forces.
Therefore, there is a self-healing concrete technology
with a mechanism to independently repair the cracked
part without human intervention in its maintenance
(Mauludin et al., 2018).The crack trajectory is highly
dependent on the inclusions in the material (Luthfi
Muhammad Mauludin & Rendragraha, 2022).
Because of that, the maintenance and repairs on
concrete structures are needed periodically according
to their needs and conditions. Meanwhile, the cost of
maintaining and repairing concrete structures is quite
high, Especially the crack that is located in difficult
area, such as in water or on the ground.
To solve this problem, bacteria-based concrete is
an alternative to many other conventional
technologies because they are environmentally
friendly, and have the ability to act as self-healing
agents (Tiwary, 2021). The active bacterial cells able
to convert the calcium lactate (CaC6H10O6) into
CaCO3 (Calcium Carbonate) using oxygen and water
(Tziviloglou et al., 2016).
In this study, a test will be carried out in the form
of the application of Bacillus megaterium bacteria
and calcium lactate which is inserted into the concrete
mixture.
986
Savira, M., Ruslan, U., Keryanti, . and Mauludin, L.
The Flexural Strength of Bacteria-Based Concrete for Sustainable Mater ials.
DOI: 10.5220/0011982900003575
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2022), pages 986-991
ISBN: 978-989-758-619-4; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Bacterial Concrete or Bacterial-Based Concrete is
intelligent concrete that exhibits human-like self-
healing characteristics that increase the strength of the
structure, especially under stress, and other
advantages such as the overall service life of the
structure were found to be increased, the effective
utilization of bacteria from corrosion, due to the
presence of water vapor generated used as a catalyst
to continuously maintain the quality of concrete, self-
healing concrete is better than traditional concrete
because of its environmentally friendly nature
(Ghodke & Mote, 2018).
Some researchers have conducted several
methods of self-healing concrete with using many
healing agents. Namely as follows.
a. Mauludin et al., 2018 in a journal article entitled
Computational modeling of fracture in
encapsulation-based self-healing concrete using
cohesive elements examined self-healing
concrete using computational methods carried
out with Abaqus, Python and Matlab software.
b. Rahmawan et al., 2021, in his journal entitled
Application of Bacteria as Self-Healing Agents
in Concrete, discuss the comparison of various
types of bacteria.
c. Gruyaert et al., 2016, in their journal entitled
Capsules with evolving brittleness to resist the
preparation of self-healing concrete. This
journal discusses the types of capsule shells.
Using polymer type capsules.
In previous studies, tests have been carried out
using encapsulated techniques both computationally
and experimentally, then there are studies using the
overall base material in the form of geopolymers and
there are studies that focus on the levels of Bacillus
megaterium bacteria which are effective for
increasing the compressive strength of concrete.
3 MATERIALS
3.1 Bacteria
The type of bacteria used in this research is namely
Bacillus megaterium. Bacillus bacteria can produce
as fillers for binding materials to shrink the capillary
pores of concrete to increase its strength and
durability (Andalib et al., 2016).
Bacillus megaterium is an organism that has
following characteristics: not filamentous, gram
positive, rod-shaped, produces endospores, catalase
positive, aerobic, nitrite negative and VP negative.
This kind of bacteris have endospore in the middle
of its cell. Bacillus bacteria have a positive effect on
the compressive strength of concrete and flexural
strength compared to conventional samples, and can
reduce water absorption (permeability) (Stanaszek-
Tomal, 2020).
The following is the classification of Bacillus
megaterium as listed in Figure 1:
Kingdom : Bacteria
Filum : Firmicutes
Kelas : Bacilli
Ordo : Bacillales
Famili : Bacillaceae
Genus : Bacillus
Spesies : Bacillus megaterium
Source: (Jayanti rusyda, 2014)
Figure 1: Bacillus megaterium Bacteria.
3.2 Fly Ash
Fly ash is used to stabilize the temperature of cement
so as not to harm the microbes inside. This type of
geopolymer has several advantages: more
environmentally friendly (in the manufacturing
process without releasing CO2 emissions into the
atmosphere), high workability (easy to flow or self-
leveling), more resistant to chemical attack (sulphate,
acid, and chloride), and more resistant to high
temperatures. Therefore, other substances are needed
such as Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) and Sodium
Silica (Na2SiO3) (Rizal et al., 2020).
The type of fly ash is grade 6 or class F which is
an active type of fly ash, it can be used as a binder not
only as a filler as listed in Figure 1.
4 METHODOLOGY
To carry out this research, good planning is needed so
that in its implementation it can run effectively and
efficiently. The type of this reasearch is experimental.
The Flexural Strength of Bacteria-Based Concrete for Sustainable Materials
987

Figure 2: Fly Ash.
The reseacrh was begun with studying the
previous studies on bacteria-based concrete. The
design the concrete with f’c 20 MPa specification,
was used ACI 211.1-1991 standard for 36 speciments.
The next step is testing the concrete materials. The
tests are Cement Specific Gravity (SNI 1527-2531-
1991), Cement Grain Fineness (SNI 03-1969/1970 –
ASTM C.127/128-95), Coarse Aggregate Gradation
Testing (SNI 03-1968-1990/ BS 410-1986),
Aggregate Moisture Testing (SNI-03-1971-1990),
Sludge Content Testing Passed through Sieve 200
(SNI 03-4142-1996/ ASTM C.117-95), and Organic
Fine Aggregate Testing (ASTM C.33-95).
Figure 3: The Preparation of Concrete Materials
After the materials test and mix design had been
done, the next step are preparation of the bacteria,
concrete materials as listed in Figure 3 and making
the speciments.
Figure 4: Bacteria Sample.
After prepared the media (nutrient agar) was
prepared with using autoclaved at 120°C for 15
minutes, then the media kept in the incubator at 35°C
and the colony of bacteria will growing there. After 3
days, the colony of bacteria will be moved into a
nutrient broth then shaked in 5 days along as listed in
Figure 4.
Figure 5: Concrete Casting Process.
To perform the flexural strength test, the bacterial
sample mixed with the concrete. When bacterial
concrete was casted, bacteria sample was added to the
water in ratio 1:100 (1% proportion) and 2:100 (2%
proportion). To cast the virgin concrete (conventional
concrete), no bacteria was added and no other
treatment was applied. The concrete casting process
is as listed in Figure 5.
Figure 6: The Bending Machine.
To do Flexural Strength Test, he standard that
used in this test is ASTM C.293. Flexural strength test
was performed on beam of size 100 mm × 100 mm ×
500 mm with three point bending. The testing was
conduct in 14 days and 28 days. Then tested under
three point bending machine as listed in Figure 6.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The following are the result of flexural strength in 14,
and 28 days, flexural strength values of virgin
concrete, Bacteria-based concrete (BBC) which
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
988
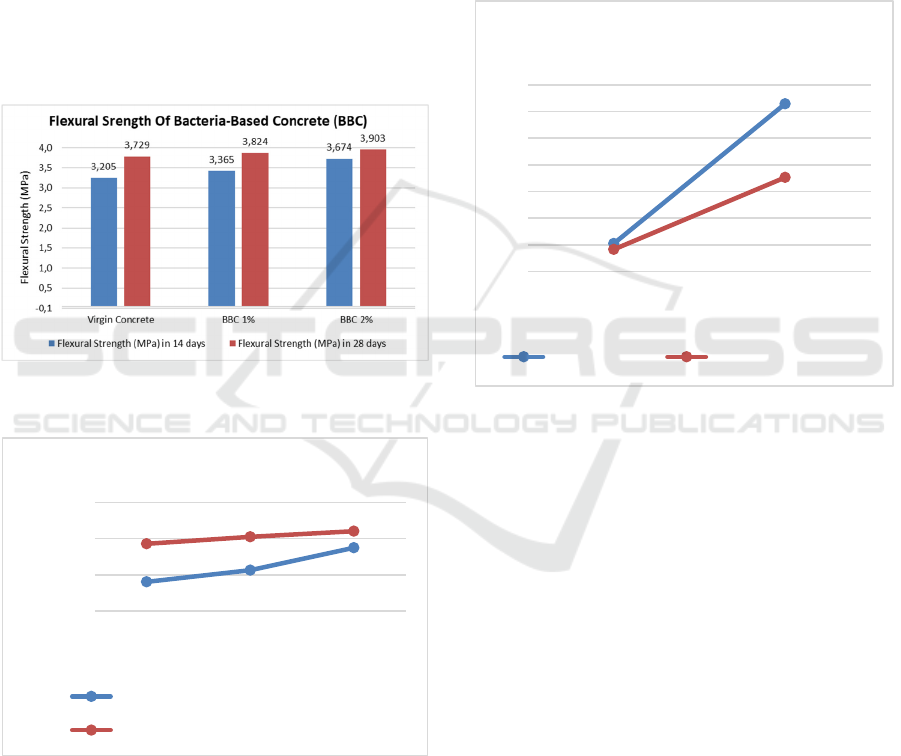
proportion are 1% and 2%, concrete with fly ash 2%,
then Bacteria-based Concrete with fly ash 2%
containing 1% and 2% bacteria proportions were
tested.
5.1 The Effect of Bacteria in
Conventional Concrete
After tested in 14 dyas of the specimens, there are a
trend increasing between the bacteria based-concrete
and virgin concrete the virgin concrete, concrete with
bacteria-based concrete 1% and bacteria-based
concrete 2% were tested and the result is increased
between the virgin concrete and the bacteria-based
concrete 2% as listed in Figure 7. The increasing is up
to 14,64%.
Figure 7: Graph Showing The Flexural Strength in 14 and
28 Days.
Figure 8: Graph Showing The Comparing Flexural Strength
in 14 and 28 Days.
Then, after 28 days, the virgin concrete, concrete with
fly ash 2%, bacteria-based concrete 1% and bacteria-
based concrete 2% were tested and the result is
increased between the virgin concrete and the
bacteria-based concrete 2% as listed in Figure 7. The
increasing is up to 4,44 for BBC 2 % and 4,64 for
BCC 1% compared with the virgin concrete as liested
in Figure 7.
So, the comparison between the 14 and 28 is listed in
. It shows that the result of an increasing trend of
bacteria-based concrete with a significant increase
between the virgin and the bacteris-based concrete
which bacteria proportion that the highest flexural
strength is 2% bacteria proportion.
5.2 The Effect of Bacteria in Fly Ash
Concrete
Figure 9: Graph Showing The Comparing Flexural Strength
of Virgin Concrete and Fly Ash Concrete in 14 and 28 Days.
Then, after 28 days, the virgin concrete, concrete with
fly ash 2%, bacteria-based concrete 1% and bacteria-
based concrete 2% were tested. And the Figure 9
shows that adding a fly ash in 2% could not increase
the flexural strength of virgin concrete.
The flexural test result in 14 days as listed in
Figure 10, is increased between the concrete + Fly
Ash 2% and the bacteria-based concrete 2%. The
increasing is up to 10,54% for BBC 2 % and for BCC
1%, there was degression into 8,13% compared with
the concrete+ Fly Ash 2%.
The following is the flexural result of adding 2%
fly ash into bacteria-based concrete 1% and bacteria-
based concrete 2% in 28 days as listed in Figure 10.
The comparison between 1% and 2% bacteria
proportion in 28 days was variated degression
between the concrete + Fly Ash 2%. For the BBC
1%+Fly Ash 2% the degression was 7,79% and for
the BBC 2%+Fly Ash 2% the degression was 7,79%
compared with the concrete + Fly Ash 2%.
3,205
3,365
3,674
3,729
3,824
3,903
2,8
3,3
3,8
4,3
Virgin
Concrete
BBC1% BBC2%
FlexuralStrength(MPa)
Comparisonbetween14and28days
FlexuralStrength(MPa)in14days
FlexuralStrength(MPa)in28days
3,205
3,729
3,183
3,453
3,1
3,2
3,3
3,4
3,5
3,6
3,7
3,8
FlexuralStrength
(MPa)in14days
FlexuralStrength
(MPa)in28days
FlexuralStrengthofVirginCncreteandFly
AshConcrete
VirginConcrete Concrete+FlyAsh2%
The Flexural Strength of Bacteria-Based Concrete for Sustainable Materials
989
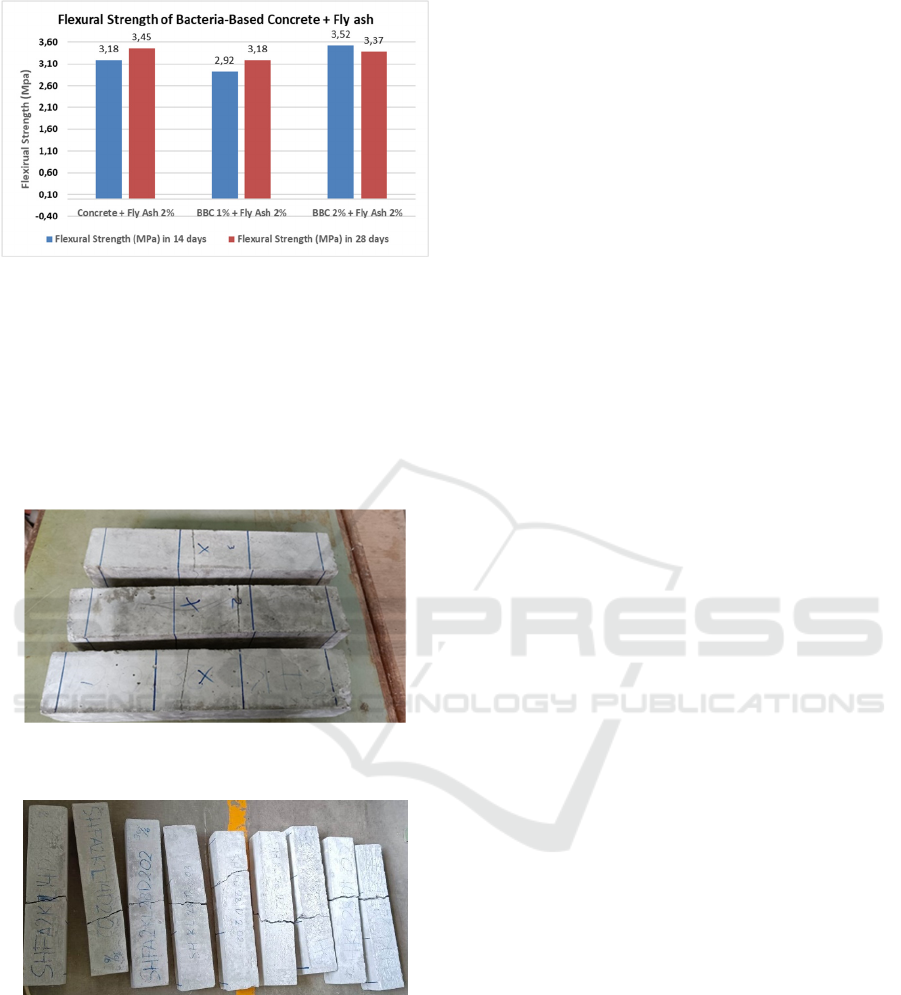
Figure 10: Graph Showing The Flexural Strength of fly ash
2% concrete, fly ash 2% + bacteria 1% concrete , and fly
ash 2% + bacteria 2% concrete in 28 Days.
5.2 The Specimens After Flexural
Strength in 14 Days and 28 Days
The following are the condition of specimens after
flexural strength test as listed to Figure 11 and Figure
12.
Figure 11: The Specimens After Flexural Strength Testing
Conditiosns.
Figure 12: The Crack Pattern of Specimens After Flexural
Testing.
6 CONCLUSION
The goal of this research was to see how bacteria
(Bacillus megaterium) affected the flexural strength,
of conventional (virgin concrete) and bacteria-based
concrete. The results of this study can be concluded
as follows:
Based on the test results, this bacteria-based
cocrete is a promosing material, by using
bacteria-based concrete could reduce to use
cement materials and forthemore it will be a
sustanable materials.
The concrete samples were evaluated for
flexural strength in both conventional and
bacterial concrete. By applicated the bacteria in
concrte, it was positively affected to increase the
flexural strength compared with the virgin
concrete. The higher the proportion of bacteria,
it can make the higher flexural strength. In
comparison to ordinary concrete, the flexural
strength of bacillus megaterium as bacteria-
based concrete by 14,64% while the fexural
sstrength of adding fly ash 2% is 8,91%.
By adding fly ash 2% and tested in 14 and 28
days, it doesn’t shows that the result is increased
the mechanical properties compared with the fly
ash concrete + bacteria. Due to the fly ash as an
additive could make another condition of
bacteria, so it could not be affected for the
flexural strength.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by Politeknik Negeri
Bandung (POLBAN) through Post Graduate
Research Grant Program (PPS) in 2022.
REFERENCES
Andalib, R., Abd Majid, M. Z., Hussin, M. W., Ponraj, M.,
Keyvanfar, A., Mirza, J., & Lee, H. S. (2016). Optimum
concentration of Bacillus megaterium for strengthening
structural concrete. Construction and Building
Materials, 118, 180–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.conbuildmat.2016.04.142
Bashir, J., Kathwari, I., Tiwary, A., & Singh, K. (2016). Bio
Concrete- The Self-Healing Concrete. Indian Journal
of Science and Technology, 9(47). https://doi.
org/10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i1/105252
Ghodke, P., & Mote, S. (2018). THE SELF-HEALING
CONCRETE – A REVIEW. International Journal of
Advances in Engineering & Technology, 11(1), 29–34.
Jayanti rusyda. (2014). Abstrak uji kemampuan bakteri. Iii.
https://repository.its.ac.id/82007/1/3310100024-Under
graduate_Thesis.pdf
Mauludin, Luthfi M., Zhuang, X., & Rabczuk, T. (2018).
Computational modeling of fracture in encapsulation-
based self-healing concrete using cohesive elements.
iCAST-ES 2022 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
990

Composite Structures, 196(April), 63–75. https://doi.
org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.04.066
Mauludin, Luthfi Muhammad, & Rabczuk, T. (2021).
Computational modeling of fracture in capsule-based
self-healing concrete: A 3D study. Frontiers of
Structural and Civil Engineering, 15(6), 1337–1346.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-021-0781-1
Mauludin, Luthfi Muhammad, & Rendragraha, A. P.
(2022). The Effect of Inclusion on Crack Propagation
Using Extended Finite Element Method. Current
Journal: International Journal Applied Technology
Research, 3(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.35313/
ijatr.v3i1.78
Rizal, F., Syahyadi, R., & Jaya, Z. (2020). Viabilitas
Bakteri Bacillus Subtilis sebagai Self Healing Agent
pada Mortar Geopolimer. Seminar Nasional Politeknik
Negeri Lhokseumawe, 4(1), 6–12.
Stanaszek-Tomal, E. (2020). Bacterial concrete as a
sustainable building material? Sustainability
(Switzerland), 12(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020
696
Tiwary, A. K. (2021). Behaviour of Incorporation of
Bacteria in Concrete. IOP Conference Series: Earth
and Environmental Science, 889(1), 012022.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/889/1/012022
Tziviloglou, E., Wiktor, V., Jonkers, H. M., & Schlangen,
E. (2016). Bacteria-based self-healing concrete to
increase liquid tightness of cracks. Construction and
Building Materials, 122, 118–125. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.080.
.
The Flexural Strength of Bacteria-Based Concrete for Sustainable Materials
991
