
Effects of Different Feed Additives on Growth and Water Quality
of Koi Carp
Dongjie Shi
1,2
, Wei Gao
3
, Jiguo Xie
3
, Qiang Zhang
4
, Wentong Li
1,2
, Jufeng Jiang
5
, Dong Wei
6
,
Saisai Wang
1,2
, Yansheng Sun
1
and Yan Lu
7*
1
Fisheries Research Institute, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Beijing 100068, China
2
Key Laboratory of Urban Agriculture (North China), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing 100097, China
3
Beijing Daxing District Animal Husbandry and Aquatic Products Technology Extension Office, Beijing 102699, China
4
Beijing Tongzhou District Animal Epidemic Disease Prevention and Control Center, Beijing 101101, China
5
Tianjin Fisheries Research Institute, Tianjin Ornamental Fish Technology and Engineering Centre, Tianjin 300221, China
6
Tianjin Agricultural University Fisheries College, Tianjin 300380, China
7
Beijing Hepingli Hospital, Beijing 100013, China
Keywords:
Feed Additives, Fish Growth, Water Quality, Koi Carp.
Abstract: In this experiment, koi carp was used as the experimental object. The effects of the 2% Guar gum (GG), 2%
sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and 2% sodium polyacrylate (SP) on the growth performance and
aquaculture water quality of Koi carp were studied by adding additives to the basic feed. The results showed
as follows: Compared with the control group, the final body weight (W
t
), weight gain rate (WGR) and specific
growth rate (SGR) were significantly increased after adding 2%GG, 2%CMC, and 2%SP (P < 0.05). In
addition, all three additives can reduce the FCR value. The concentrations of nitrite and ammonia in the
experimental group supplemented with 2% Guar gum, 2%CMC and 2% SP were significantly lower than
those in the control group (P < 0.05). The concentrations of nitrite and ammonia in the 2% Guar gum group
were the lowest (P < 0.05). At the late stage of the experiment, the concentrations of nitrite and ammonia in
the 2% GG group were significantly lower than those of 2% CMC (P < 0.05). The results showed that adding
2% GG to the diet was more beneficial to the growth of Koi carp and the regulation of aquaculture water
quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Koi is favored by consumers because of its bright
body color, body shape and varied pattern. With the
rapid development of the ornamental koi breeding
industry, a new breeding model of factory production
has been formed. In order to achieve economic
efficiency, farmers usually use the efficient feeding
method. However, a large amount of feed is put into
the breeding tank, so that the feed is dissolved in the
water, which will cause eutrophication of the water
body. In addition, high-frequency feeding will
increase the excrement of fish, causing pollution of
aquaculture water bodies, prone to diseases, not only
causing economic losses but also seriously affecting
the ecological environment. Therefore, efficient
feeding should not only meet the requirements of
increasing the growth rate of koi, but also reduce the
pollution of the water body by the feed itself and the
excrement of the fish.
Guar gum, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and
sodium polyacrylate are three additives which have
the functions of thickening, emulsifying, bonding,
stabilization, and improving adhesion. These three
additives are non-toxic and harmless and have a wide
range of uses in food processing, factory production,
medical and pharmaceutical, and many other aspects
(Gu, 2010; Li, 2018). However, there is less research
on the application of these three additives in aquatic
animal feed (Shen, 2017; Shen, 2019). Therefore, this
experiment studied the effects of these three additives
on the growth of koi and the quality of aquaculture
water by adding these three additives to the feed, in
order to provide a theoretical basis for solving the
problem of water pollution caused by bait residues
and provide a reference for the research and
development of low-pollution feed for koi.
Shi, D., Gao, W., Xie, J., Zhang, Q., Li, W., Jiang, J., Wei, D., Wang, S., Sun, Y. and Lu, Y.
Effects of Different Feed Additives on Growth and Water Quality of Koi Carp.
DOI: 10.5220/0012001300003625
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology (FSB 2022), pages 47-51
ISBN: 978-989-758-638-5
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
47

2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Experimental Design
The koi used in this experiment were from Beijing
Yashi Koi Culture Technology Co., Ltd. In this
experiment, 360 koi carps with the same
specifications and healthy and harmless were
selected. The experiment was carried out in
Xiaotangshan Breeding Base of Beijing Fisheries
Science Institute. The koi were divided into 4 groups,
each group was set up with three parallels, and 30 fish
were placed in each parallel. The composition of the
experimental diet is shown in Tab. 1. Three different
binders were added to the basal feed: 2% GG, 2%
CMC and 2% SP. Guar gum, respectively, to study
the effect of seed adhesive on the growth
performance and aquaculture water quality of koi
carp.
Table 1: Ingredient composition of experimental diets %.
Ingredients additive amount
Fish meal 15
Soybean meal 30
Rapeseed meal 15
Wheat flou
r
20
Wheat bran 5.4
Soybean oil 2
Fish oil 2
Premix 1.3
Choline oxide 0.3
Rapeseed meal 9
2.2 Indicator Measurement Method
Determination of fish body weight, body length,
specific growth rate (SGR), weight gain rate (WGR),
feed coefficient (FCR) and Survival rate (SR) and
other indicators were listed as follows. A portable
water quality monitor was used to monitor dissolved
oxygen, water temperature and pH, Ammonia
nitrogen and nitrite in aquaculture water were
measured in the laboratory.
SR = 100% × S
t
/S
0
(1)
WGR = 100% × (W
t
-W
o
)/ W
o
(2)
SGR = 100 × [Ln(W
t
)-Ln(W
o
)]/ t
(3)
FCR = C/ (W
t
+W
d
-W
o
) (4)
In the above formula: S
t
is the number of
surviving fish at the end of the experiment, S
o
is the
number of initial fish; W
o
is the initial body weight of
the fish, W
t
is the final body weight, W
d
is the total
weight of the dead fish (g); t is the number of days of
experiment (d); C is food intake.
2.3 Data Processing and Analysis
One-way ANOVA was conducted on the
experimental data using STATISTIC 7.0 statistical
software, and Duncan's method was used to test the
significance of difference, and the significance level
was P<0.05.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Effects of Three Additives on The
Growth Performance of Koi Carp
As can be seen from Tab. 2, the average initial body
weight of experimental fish was 75.47-79.33 g, and
there was no significant difference among all groups
(P > 0.05). The W
t
, WGR and SGR of the
experimental group were significantly higher than
those of the control group after adding 2% GG, 2%
CMC and 2% SP. The WGR and SGR indexes of
2%CMC and 2%GG were significantly higher than
those of 2% SP group. All three adhesive groups can
reduce the FCR value.
Table 2: Survival and growth performance of different groups for Koi carp.
Index Control group 2%GG 2%CMC 2%SP
W
o
78.64±3.22
a
75.47±5.43
a
76.49±7.28
a
79.33±5.24
a
W
t
167.22±8.99
d
189.58±10.22
b
194.83±13.57
a
174.89±18.27
c
WGR 112.69±9.42
c
151.27±12.45
a
154.78±10.03
a
120.49±15.23
b
SGR 1.27±0.58
c
1.53±0.31
a
1.55±0.07
a
1.32±0.36
b
FCR 1.38±0.14
a
1.33±0.21
a
1.35±0.24
a
1.35±0.33
a
SR 100 100 100 100
FSB 2022 - The International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology
48
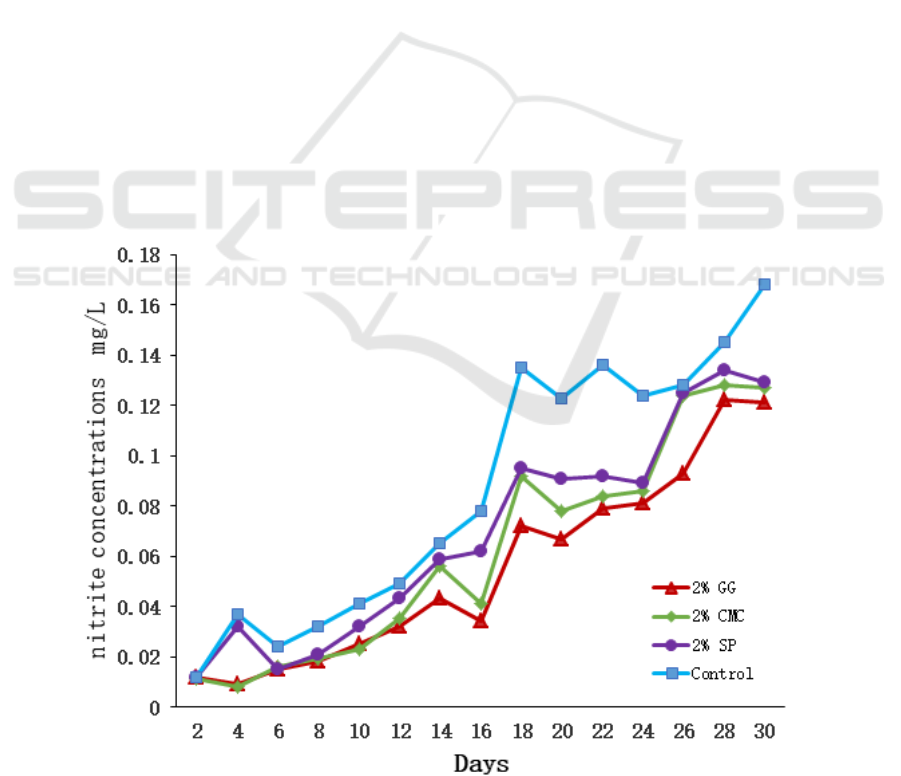
3.2 Effects of Three Adhesives on
Nitrite Content in Aquaculture
Water
As can be seen from Fig. 1, the nitrite concentrations
in the experimental group supplemented with 2%GG,
2%CMC and 2% SP were significantly lower than
those in the control group (P < 0.05). In the first 10
days of experiment, the 2% GG and 2% CMC groups
had no significant effect on the concentration of
nitrite in aquaculture water (P > 0.05). After 12 days,
the concentration of nitrite in 2% GG supplemental
group was significantly lower than that in 2% CMC
supplemental group (P < 0.05).
3.3 Effects of Three Additives on
Ammonia in Aquaculture Water
As can be seen from Fig. 2, the ammonia
concentration in the experimental group
supplemented with 2% GG, 2% CMC and 2% SP
were significantly lower than that in the control group
(P < 0.05), and the ammonia concentration in the 2%
GG supplemental level group was the lowest (P <
0.05). In the first 10 days of the experiment, there was
no significant difference in ammonia concentration
between the experimental treatment groups and the
control group (P > 0.05). After 24 days, the ammonia
concentration of the 2% GG group tended to
decrease.
4 DISCUSSION
The main feed of koi carp is pelleted. In the
production of pelleted feed, its stability in water has
been a wide concern. If the adhesion of feed is
improved, a certain proportion of adhesive can be
added in the process of making the feed to increase
the viscosity of feed, which is helpful to feed molding
and reduce the dissolution of feed in the water. In fish
feed, adhesive plays an important role in water
stability of fish feed. There are two main types of
adhesives: synthetic chemicals and natural
substances. The natural substances are mainly
derived from extracts of animals, land plants, and
seaweed. GG is a feed additive extracted from Guar
bean by special processing technology, which is
relatively mature in domestic and foreign research
and application (Zhu, 2002; Muna-Ahmed M M,
2000). CMC is a chemically synthesized adhesive,
which has developed rapidly in recent years. CMC is
also a kind of water-soluble polymer cellulose ether,
which is granular powder or white fiber, odorless and
tasteless, and its aqueous solution is extremely
unstable to heat. In addition, CMC has no nutritional
Figure 1: Effects of three additives on nitrite content of the water body.
Effects of Different Feed Additives on Growth and Water Quality of Koi Carp
49
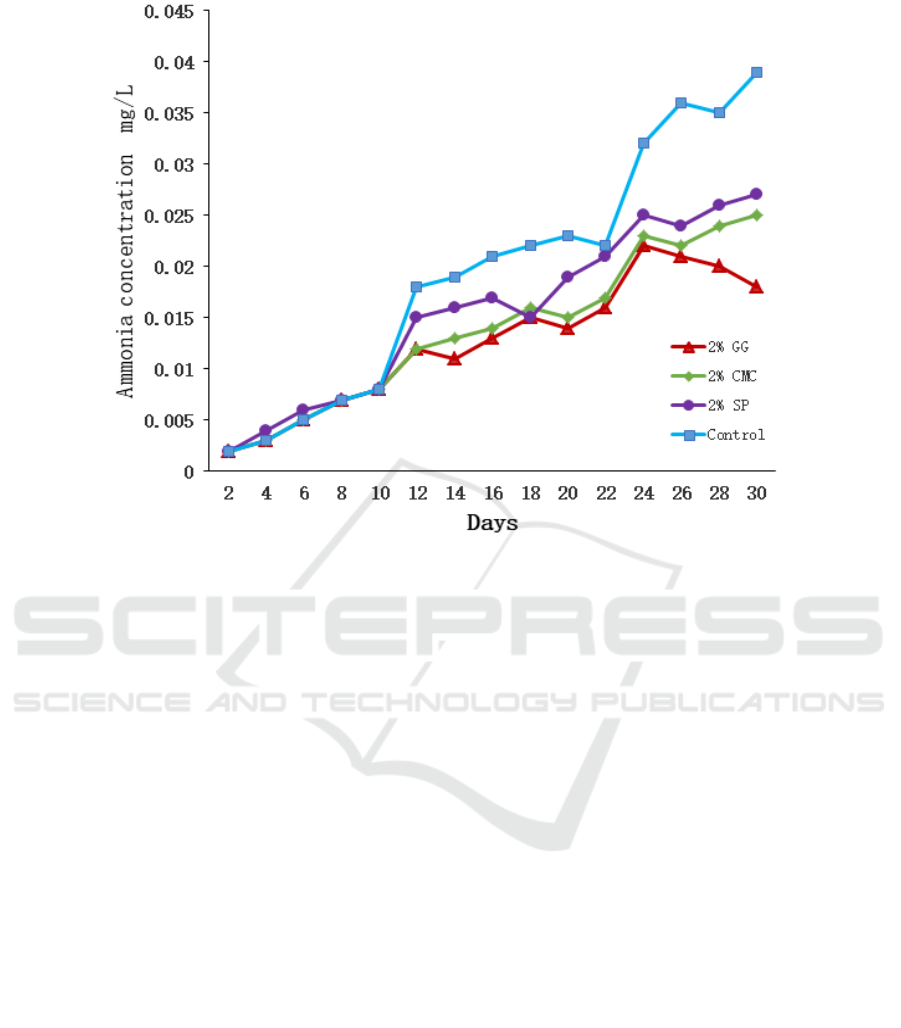
Figure 2: Effects of three additives on ammonia content of the water body.
components, and mainly plays the role of adhesion.
Previous studies have proved that the addition amount
of CMC in fish feed should not be more than 2%
(Xiao, 2016). Therefore, in this study, 2% was also
selected for CMC. It has been proved by experiments
that CMC has similar properties to sodium alginate,
good water holdup and certain ductility resistance
(Luo, 1998). SP is a high polymer electrolyte,
colorless water-soluble transparent resin, which can
be used as food additives and widely used in animal
feed. Xue et al. (Xu, 2005) reported that it can
effectively prevent gastric ulcer disease in pig feed. It
can be seen that sodium polyacrylate as a feed
additive in livestock and poultry feed also has an
effect on disease prevention.
In this experiment, 2% CMC addition had the
most significant effect on the final body weight of
koi, indicating that the addition of CMC adhesive
could promote the weight gain of koi and play an
important role in promoting the feed digestion and
transformation of koi. Li et al. (Li, 2008) reported that
adding CMC could improve the nitrification ability of
post-weaning piglets. It has been shown that the
addition of CMC adhesive facilitates the digestion of
protein in piglets, and similar favourable results were
obtained in this study. CMC adhesives are rarely used
in livestock and poultry feeds, mainly due to the
increased lignification of the CMC cell wall. Long-
term feeding will affect the digestive system of
livestock and poultry, thus affecting the ability of
digestion and absorption. However, no adverse
effects of CMC on the fish digestive system have
been reported in aquatic feeds. In addition, CMC is
usually weakly alkaline, which can regulate the pH
value of fish to a certain extent.
In aquaculture, the main source of nitrogen input
is feed. Previous studies have shown that the
proportion of nitrogen input from feed that can be
stored and utilized by fish generally does not exceed
50% (Chai, 2013; Penczak T, 1982), and the
remaining 50% or more nitrogen is released into the
aquaculture system as aquaculture waste, resulting in
the deterioration of water bodies. The study of Krom
et al. (Krom M D, 1989) on brackish and Marine fish
farming with different densities (6 fish /m
2
and 10 fish
/m
2
) proved that the proportion of nitrogen input due
to feed was 88% and 99%, respectively. Daniels et al.
(Daniels H V, 1989) showed that the nitrogen brought
in by feed accounted for 84.3%~92.7% of the total
nitrogen input in the pond in the common soil culture
system. It can be seen that feed contributes a higher
proportion of nitrogen content to the aquaculture
system. Ammonia nitrogen in aquaculture water may
be harmful to fish, and higher concentrations of
ammonia nitrogen may even lead to fish death. Some
scholars believe that when the concentration of non-
ionic ammonia accumulated in water reaches a certain
concentration, it will cause damage to fish epidermal
FSB 2022 - The International Conference on Food Science and Biotechnology
50

cells, thereby reducing the immunity of fish (Xu,
2015). In this experiment, the ammonia concentration
of the experimental group supplemented with 2%
GG, 2% CMC and 2% SP are significantly lower than
that of the control group, and the ammonia
concentration of the 2% GG addition group has a
tendency to decrease significantly after 24 days. In
addition, the concentration of nitrate in the treatment
group supplemented with 2% GG, 2% CMC and 2%
SP were significantly lower than that in the control
group.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the effects of the 2% Guar gum (GG),
2% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and 2%
sodium polyacrylate (SP) on the growth performance
and aquaculture water quality of Koi carp were
studied. Our results showed that the GG has a good
bonding effect on feed, reduces the dissolution rate of
feed in the water, and also has the effect of reducing
nitrite in water.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Supported by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of
Agriculture and Rural Affairs ,Beijing Municipal
Finance Bureau and Beijing Municipal Forestry and
Parks Bureau “Beijing Joint Research Program for
Germplasm Innovation and New Variety Breeding”
(G20220628009); Beijing Academy of Agriculture
and Forestry Sciences “Preservation of Beijing
Freshwater Fish Germplasm Resources”; Tianjing
Municipal Finance Bureau and Tianjing Municipal
Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs “The project
for the Ornamental Fish Innovation Team of Tianjin
Mariculture Research System (ITTMRS2021004)”;
Tianjin Fisheries Research Institute “The project for
the Ornamental Fish Innovation Team”
(scyjs201902)
REFERENCES
Chai X J, Ji W X, Han H, et al.(2013) Growth, feed
utilization, body composition and swimming
performance of giant croaker, Nibea japonica
Temminck and Schlegel, fed at different dietary protein
and lipid levels. Aquaculture Nutrition,19(6): 928
–
935.
Daniels H V, Boyd C E. (1989) Chemical budgets for
polyethylene lined, brackish water ponds. Journal of the
World Aquaculture Society,20(2):53
–
60.
Gu Z D, Liu X Y.
(2010) Research progress on production
and application of guar gum. Guangxi Journal of
Light Industry,07:
11
–
13+34.
Krom M D, Neori A. (1989) A total nutrient budget for an
experimental intensive fishpond with circularly moving
seawater. Aquaculture,01:185
–
193.
Li B B. (2018). Effect of Carboxymethylcellulose Adhesive
on the Granular Feed Quality and Feeding Effect in
Growing Meat Rabbits. Shenyang Agricultural
University, 6
–
9.
Luo L, Lin S M, Ye Y T, Li Q. (1998) Determination of
adhesive properties of common adhesives for aquatic
products. Feed Industry,19(9):18
–
19.
Li X X, J. Fledderus, P. Bikker, J.W. Kluess. (2008)
Increasingdiet viscosityusing carboxymethyl-cellulose
inweaned piglets stimulates protein digestibility.
Animal Science Abroad (Pigs and Poultry), 04: 40-41.
Muna-Ahmed M M, El-Hag F M.Mananil M A.(2000) The
use of guar meal in the diet of sheep.J Anim Feed
Sci(Poland), 09:91
–
98.
Penczak T, Galicka W, Molinski M, et al. (1982) The
enrichment of a mesotrophic lake by carbon,
phosphorus and nitrogen from the cage aquaculture of
rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Journal of Applied
Ecology,19 (2): 371
–
393.
Shen Q Y, Chen Y, He C, Huang W. (2017) Effects of guar
gum on growth and water stability of excreta of Songpu
mirror carp. China Feed,18:24
–
37.
Shen Q Y, Chen Y, Zhao L, Huang W, Li Sen. (2019)
Budget of nitrogen and phosphorus of guar gum as a
feed additive under the water-pushing aquaculture
mode. China Feed,03:77
–
82.
Xiao Y, Wang Z J, Sun T, Sun R J, Liu F. (2016)
Application and prospect of aquatic adhesive.
Shandong Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary
Medicine,05:56
–
57.
Xu F L. (2005) Sodium polyacrylate feed additive. Hunan
Feed,05:33+27.
Xu Y. (2015) Physiological Response to Stress of
Ammonia and Nitrite in tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus.
Nanjing Agricultural University,22-27.
Zhu X Y, Du Y F. (2002) Exotic Legume Species in China.
Bulletin of Botanical Research, 22:2.
Effects of Different Feed Additives on Growth and Water Quality of Koi Carp
51
