
Determination of Potassium Iodate in Edible Salt by Potassium
Iodide-Iodine-Starch System
Xinrong Wen
1,2,*
and Changqing Tu
1,2
1
School of Chemistry and Environment, Jiaying University, Meizhou, Guangdong 514015, China
2
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Conservation and Precision Utilization of Characteristic Agricultural Resources
in Mountainous Areas, Jiaying University, Meizhou, Guangdong 514015, China
Keywords: Spectrophotometry, Potassium Iodate, Potassium Iodide, Edible Salt.
Abstract:
In acidic medium, ki can react with kio
3
to form i
2
, then i
2
and starch form i
2
-starch blue complex with a
maximum absorption wavelength of 596 nm. Beer's law is obeyed between the kio
3
content and the absorbance
of i
2
-starch blue complex. Base on this, the kio
3
content can be determined indirectly. A novel method for the
determination of potassium iodate in edible salt by potassium iodide-iodine-starch system has been
established. The various effect factors on the determination of iodide by potassium iodide-iodine-starch
system are investigated in detail. Under optimal conditions, when the mass concentration of kio
3
is
0.4000~1.280 µg/ml, the linear regression equation is a=-0.0649+0.04702c (µg/ml) with the linear correlation
coefficient is 0.9992. this proposed method had been successfully applied to determinate kio
3
in edible salt,
and the results agree well with those by standard method.
1 INTRODUCTION
Iodine is one of the essential microelements for
humans. It can enhance the basic metabolism and
promote the growth and development of human
body. Both iodine deficiency and iodine excess do
harm to the human body. Iodine deficiency can cause
an endemic goiter and potential damage to children's
intellectual growth, and iodine excess can lead to
hypothyroidism, thyroid enlargement and other
clinical manifestations. Eating iodized salt is the most
important and effective way to prevent iodine
deficiency disease. Potassium iodiate is usually added
to the edible salt, which is the iodized salt. Eating
iodized salt can achieve the effect of iodine
supplement. Thus, the determination of iodine
content in iodized salt has great practical significance.
So far, the determination methods for potassium
iodinate in salt are mainly included titration
(Mohammad, 2020), spectrophotometry
(Gavrilenko, 2019), emission spectrometry (Yu,
2013), flow-injection (Kuznetsov, 2007), ICP-OES
(Sager, 2019), CE-ICP-MS (Chen, 2007) HPLC
(Manju, 2010) and so on.
In this paper, a novel method for the
determination of potassium iodate in edible salt by
potassium iodide-iodine-starch system is reported. In
acidic medium, I
-
reacts with KIO
3
to form I
2
, then I
2
and starch form I
2
-starch blue complex with a
maximum absorption wavelength of 596 nm. There is
a good linear relationship between the absorbance of
I
2
-starch blue complex and the KIO
3
dosage, the
linear equation is A=-0.0649+0.04702C(µg/mL)
within the range of 0.4000~1.280 µg/mL KIO
3
concentration. So, by measuring the absorbance of I
2
-
starch blue complex, the content of KIO
3
can be
determined indirectly. This proposed method has
been applied to determinate of KIO
3
in edible salt
with satisfactory result.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Equipment and Reagents
UV-2401 UV-visible spectrophotometer (The
Shimadzu Corporation, japan); 723S
spectrophotometer (Shanghai Precision & Scientific
Instrument Co,. Ltd ).
KIO
3
solution: 10.00 μg·mL
-1
, a 1.000 mg·mL
-1
potassium iodiate solution is prepared and then
Wen, X. and Tu, C.
Determination of Potassium Iodate in Edible Salt by Potassium Iodide-Iodine-Starch System.
DOI: 10.5220/0012012100003633
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine (ICBB 2022), pages 21-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-637-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
21
diluted to 10.00 µg·mL
-1
. KI solution: 1.000 g·L
-1
.
H
3
PO
4
solution: 5.0 mol·L
-1
. Starch solution:5.0 g·L
-1
.
All reagents are of analytical reagent grade.
Bidistilled water is used.
2.2 Method
KI solution 3.00 mL, starch solution 3.00 mL, H
3
PO
4
solution 1.50 mL, a certain volume of KIO
3
solution
or edible salt sample solution are added into a 25 mL
volumetric flask. The solution is diluted to the mark
with bidistilled water, mixed well and placed at room
temperature for 40 minutes in the dark. The
absorbance of I
2
-starch blue complex is measured at
596 nm against the reagent blank.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
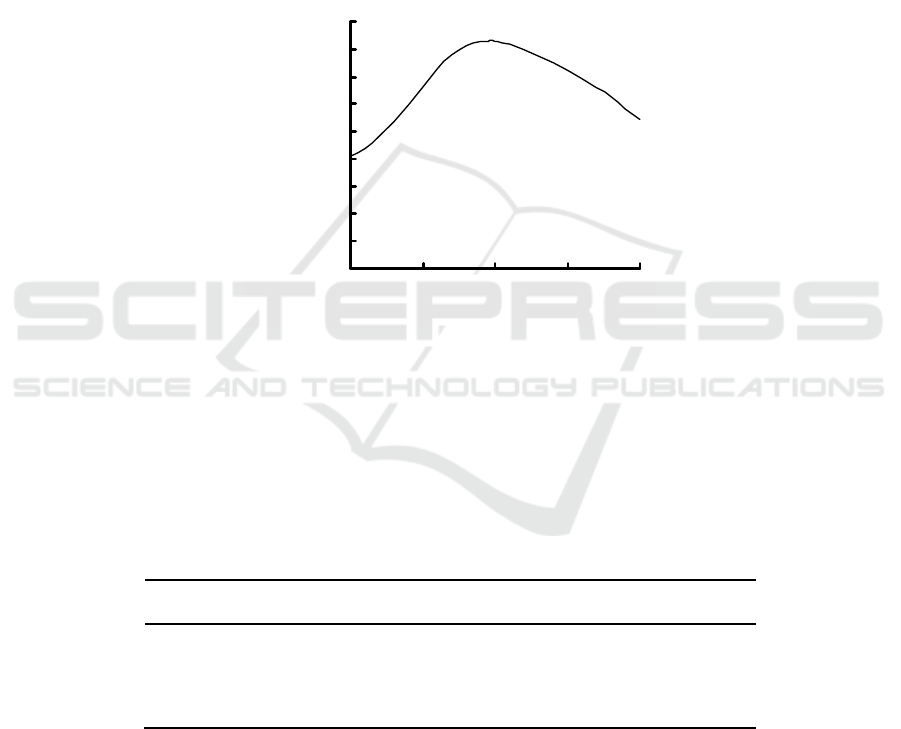
3.1 Maximum Absorption Wavelength
In 500~700 nm, the absorption spectrum of I
2
-starch
blue complex is obtained using UV-2401 UV-visible
spectrophotometer (Fig. 1). Fig. 1 show that the
maximum absorption wavelength of I
2
-starch blue
complex is 596 nm.
KIO
3
:2.00 mL; KI:2.00 mL; H
3
PO
4
:3.00 mL; starch:2.00 mL; reaction time:20 min.
Figure 1: Absorption spectrum.
3.2 Reaction Temperature
The effect of reaction temperature is seen in table 1.
We can sen from table 1 that the absorbance of I
2
-
starch blue complex keep constantly decreasing with
the increase of reaction temperature. Hereby, the
room temperature is used.
Table 1: The effect of reaction temperature on the absorbance.
Temperature /℃
room
tem
p
erature
30 35 40
Absorbance 0.380 0.375 0.374 0.372
Temperature /℃ 45 50 55 60
Absorbance 0.368 0.364 0.353 0.342
Experimental conditions: KIO
3
:2.00 mL; KI:2.00
mL; H
3
PO
4
:3.00 mL; starch:2.00 mL; reaction
time:15 min.
3.3 Reaction Time
The effect of the reaction time is showed in Fig. 2.
It is found that the absorbance of I
2
-starch blue
complex gradually increased with the reaction time, and
the absorbance of I
2
-starch blue complex reaches
greatest when the reaction time is 35 minutes or more.
So, 40 minute is selected.
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
500 550 600 650 700
λ/n
m
A
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
22
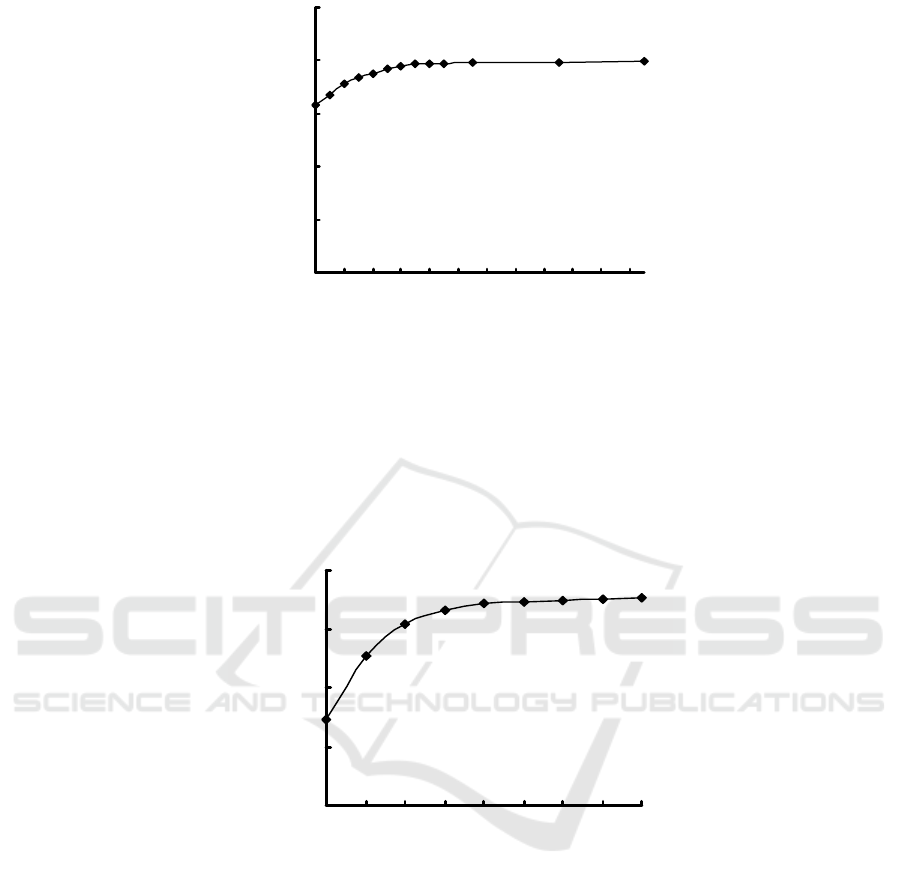
KI:2.00mL; H
3
PO
4
:3.00mL; KIO
3
:2.00mL; starch:2.00mL.
Figure 2: Effect of the reaction time.
3.4 KI Solution Dosage
The effect of KI solution dosage can be seen in fig. 3.
The results showed that as the amount of KI increases,
the absorbance of I
2
-starch blue complex also
gradually increases. The absorbance of I
2
-starch blue
complex reaches the maximum value when KI
solution dosage is 2.50 mL. Thereafter, the
absorbance of I
2
-starch blue is basicly stable as KI
dosage increases. Thus, 3.00 mL KI solution is
chosed.
H
3
PO
4
:3.00mL; KIO
3
:2.00mL; starch:2.00mL; reaction time:40 min.
Figure 3: Effect of KI solution dosage.
3.5 H
3
PO
4
Solution Dosage
The effect of H
3
PO
4
solution dosage is showed in Fig.
4. The results show that the absorbance of I
2
-starch
blue complex gradually increases with the amount of
H
3
PO
4
increases. The absorbances of I
2
-starch blue
complex are essentially constant when the H
3
PO
4
solution dosage is 1.00~2.00 mL. Hence, 1.50 mL
H
3
PO
4
solution is used.
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
5 152535455565758595105115
T
/
min
A
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50
V(KI)/mL
A
Determination of Potassium Iodate in Edible Salt by Potassium Iodide-Iodine-Starch System
23

KI:3.00mL; KIO
3
:2.00mL; starch:2.00mL; reaction time:40 min.
Figure 4: Effect of H3PO4 solution dosage.
3.6 Starch Solution Dosage
The effect of starch solution dosage is showed in
Table 2. The experimental results show that the
absorbance of I
2
-starch blue complex increase with the
increase of starch solution dosage. The absorbance of
I
2
-starch blue complex is maintained at stable values
when the starch solution dosage is 2.50 mL or more.
Therefore, the starch solution dosage is chosen as
3.00 mL.
Table 2: The effect of starch solution dosage on the absorbance.
Starch solution dosage
/mL
0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00
Absorbance 0.292 0.383 0.395 0.407
Starch solution dosage
/mL
2.50 3.00 4.00 5.00
Absorbance 0.413 0.415 0.413 0.414
Experimental conditions: KI:3.00 mL;
H
3
PO
4
:1.50 mL; KIO
3
:2.00mL; reaction time:40 min.
3.7 Calibration Curve
Under the optimum conditions, a series of
determination solutions with different KIO
3
concentrations are prepared, then the absorbances of
these solutions are measured at 596 nm against the
reagent blank. Using concentration as the abscissa
and absorbance as the ordinate, the calibration curve
(Fig. 5) is obtained. In the range of 0.4000-1.280
μg/mL KIO
3
, a good linear relationship between the
KIO
3
concentration and the absorbance of I
2
-starch
blue complex, the linear equation is A=-
0.0649+0.4702C(μg/mL) and the correlation
coefficient is 0.9992.
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50
V( H
3
PO
4
)/mL
A
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
24

KI:3.00 mL; H
3
PO
4
:1.50 mL; starch:3.00 mL; reaction time:40 min.
Figure 5: Calibration curve.
3.8 Sample Analysis
25.0000 g edible salt sample is weighed and dissolved
in proper amounts of bidistilled water, then it is
transferred into a 250 mL volumetric flask and
diluted to the mark with bidistilled water, shaked
well. This is the edible salt sample solution.
According to the experimental method, 5.00 mL
edible salt sample solution is added, then the
absorbance of I
2
-starch blue complex is determined,
and the content of KIO
3
is calculated. Meanwhile, the
recovery tests of standard addition are performed and
the content of KIO
3
is determined by standard method.
The results as show in Table 3.
Table 3: The content of KIO3 in edible salt.
Sample
Proposed
method
(μg·g
-1
)
RSD
(%)
Standard
method
(GB
26402-
2011)
(μg·g
-1
)
Added
(μg·mL
-1
)
Recovered
(μg·mL
-1
)
Recovery
yield
(%)
Natural sea
salt
37.61 0.2 38.82
0.08000
0.1600
0.07614
0.1642
95.2
102.6
Low sodium
salt
36.06 0.6 37.15
0.08000
0.1600
0.07571
0.1510
94.6
94.4
Well cooked
salt
34.40 0.3 35.45
0.08000
0.1600
0.07512
0.1540
93.9
96.2
From Table 3, we can seen that the content of
KIO
3
in edible salt by this proposed method is
consistent with the standard method, and the recovery
yields are 93.9%~102.6%.
4 CONCLUSION
A novel method for the determination of KIO
3
in
edible salt by potassium iodide-iodine-starch system
has been reported in this paper. This method has been
successfully applied to the determination the content
of KIO
3
in different edible salt with satisfactory
results. It is obvious that the determination the content
of KIO
3
by potassium iodide-iodine-starch system
has certain practical significance and foreground of
application.
REFERENCES
Chen J H, Wang K E, Jiang S J. (2007) Determination of
Iodine and Bromine Compounds in Foodstuffs by CE-
Inductively Coupled Plasma MS[J]. Electrophoresis.,
28(22): 4227-4232.
Gavrilenko N A, Fedan D A, Saranchina N V, et al. (2019)
Solid Phase Colorimetric Determination of Iodine in
Food Grade Salt using Polymethacrylate Matrix[J].
Food Chemistry., 280: 15-19.
Kuznetsov V V, Ermolenko Y V, Seffar L. (2007) Amylose
and Amylopectin as Reagents for the Flow-Injection
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.40 0.48 0.56 0.64 0.72 0.80 0.88 0.96 1.04 1.12 1.20 1.28
C/m
g
.mL
-1
A
Determination of Potassium Iodate in Edible Salt by Potassium Iodide-Iodine-Starch System
25

Determination of Elemental Iodine [J]. Journal of
Analytical Chemistry., 62(5): 479-485.
Manju G, Aradhana K.K.V. P, Amrita S, et al. (2010) Salt-
Assisted Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for the
Determination of Iodine in Table Salt by High-
Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array
Detection[J]. Food Chemistry.,124(4):1741-1746.
Mohammad R A, Moumita D, Md K I, et al. (2020)
Determination of Iodine Content of Commercially
Available Table Salts at the Retailer Level in Selected
Areas of Bangladesh[J]. European Journal of Nutrition
& Food Safety., 284-288.
Sager M. (2019) Determination of High Iodine Levels by
ICP-OES after Separation from Excess Phosphate by
Co-precipitation[J]. Journal of Food Science and
Engineering.,9(2):74-80.
The Minister of Health of the People's Republic of China.
(2011) National Food Safety Standards (GB 26402-
2011): Food Additives Potassium Iodate[S]. Standards
Press of China: Beijing. (In Chinese)
Yu Y L, Dou S, Chen M L, et al. (2013) Iodine Excitation
in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Micro-Plasma and its
Determination by Optical Emission Spectrometry[J].
Analyst.,138(6): 1719-1725.
ICBB 2022 - International Conference on Biotechnology and Biomedicine
26
