
Study on Relationship between Regional Environment, High-Tech
Zones Entrepreneurship and Regional Economic Growth:
A Perspective of Direct Effect and Moderating Effect
Liang Fang
School of Economics and Management, Huangshan University, Huangshan, China
Keywords: National High-Tech Zones, Entrepreneurship, Regional Economic Growth, SEM, CFA.
Abstract: In order to explore the relationship between regional environment, entrepreneurship in national high-tech
zones and regional economic growth, the paper analyzes that national high-tech zones entrepreneurship’s
direct effect on regional economic growth and moderating effect of economic environment, cultural
environment, political environment, open environment and infrastructures by confirmatory factor analysis
and structural equation moderating effect analysis by the method of CFA Analysis and SEM Analysis, the
concludes is that national high-tech zones entrepreneurship promotes regional economy growth significantly,
and cultural environment, political environment, open environment and infrastructures have significant
moderating effect, then the paper puts forward suggestions: strengthen high-tech zones entrepreneurship
management, strengthen cultural environment construction, strengthen support for entrepreneurship, create
an open business environment, improve infrastructures and so on.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past few decades, the economic situation has
experienced severe tests such as oil crisis, debt crisis,
financial crisis and inflation. However, this has given
birth to entrepreneurial activities all over the world,
and entrepreneurship has become a beautiful
landscape under the economic wave.
Entrepreneurship has become an engine to promote
the growth of business sectors and the rapid
expansion of social sectors. In China, entrepreneurial
activities are active. Entrepreneurs has increased year
by year since 2000, the total number of entrepreneurs
ranked first in the world by 2014. The high-tech
industry has developed rapidly. The number of
entrepreneurs and entrepreneurial service institutions
is increasing day by day, and new enterprises emerge
one after another. Entrepreneurship has become a
powerful driving force to promote regional economic
growth. The emergence of entrepreneurial activities
is not only a sign of economic development, but also
an important force to promote economic
development, Guiso and schivardi (2011) believed
that lower entry costs, the external effects were
higher, the entrepreneurship rate was higher, and the
impact on the regional economy was greater.
Therefore, a high entrepreneurship rate was more
conducive to promoting the growth of the regional
economy. Moreover, entrepreneurship was closely
related to employment. Lumpkin et al.(2009)
believed entrepreneurial output was also conducive to
promoting economic growth.
Many researchers also believe that
entrepreneurial behavior occurs in a certain social
environment and is inevitably affected by the external
environment, such as economic environment, tax
system and market competition, which have an
important impact on entrepreneurship. So the
research on entrepreneurship should be incorporated
into the overall framework of the environment for
exploration. Timmons et al. put forward the influence
and regulation of economic environment on
entrepreneurship, the economic effect of
entrepreneurship is closely related to environmental
factors such as government support and financial
investment. The success rate of entrepreneurship is
higher in areas with strong cultural atmosphere.
Minguzzi and Passaro(2001) pointed out that
entrepreneurs in areas with backward cultural level
often showed avoidance and resistance to
entrepreneurship.
However, so far, there are few studies on the
42
Fang, L.
Study on Relationship Between Regional Environment, High-Tech Zones Entrepreneurship and Regional Economic Growth: A Perspective of Direct Effect and Moderating Effect.
DOI: 10.5220/0012023200003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 42-48
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

impact of entrepreneurship in national high-tech zones
on regional economic growth, especially the relevant
empirical research results are very underdeveloped.
Entrepreneurship is an important economic activity of
the national high-tech zones. In fact, entrepreneurship
plays a positive role not only in the economic output
of the high-tech zonse, but also in regional economic
growth. Moreover, the process of entrepreneurship
affecting regional economic growth will be moderated
by the regional environment, and the unused
environmental conditions will have different effects.
Therefore, this study will analyze the impact of
entrepreneurship in national high-tech zones on
regional economic growth and moderating effect of
different regional environments.
2 INDEX DESIGN
Regional environment is important external condition
and influencing factor of entrepreneurship. The
environment affects every link of entrepreneurship.
How to adapt to and make use of the regional
environment is important for entrepreneurship. The
entrepreneurial environment mainly includes politics,
economy, population, culture, globalization and so
on. This study measures the regional environment
and moderating effect of the regional environment
based on the content of this environmental dimension
theory.
The variables and indexes are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Index System.
Variables Index and Codes
Entrepreneurship(EA)
Total Income of National Incubators in National High-tech Zones (1000 yuan) (EA1);
Number of Incubated Enterprises in National High-tech Zone National Science and
Technology Enterprise Incubator (persons) (EA2); Number of National Science and
Technology Plan Projects Undertaken by Incubated Enterprises of National High-tech
Zone National Science and Technology Enterprise Incubators (EA3); Total Number of
Personnel of National Demonstration Productivity Promotion Center of National High-
tech Zone (persons) (EA4); Government Investment of National Demonstration
Productivit
y
Promotion Center of National Hi
g
h-tech Zone
(
1000
y
uan
)
(
EA5
)
Regional Economic Growth
(RE)
Per Capita GDP of the City where the High-tech Zone is Located (100 million yuan)
(RE)
Economic Environment
(JJHJ)
Total Amount of Venture Capital Received by Incubating Enterprises per Capita in
High-tech Zone (1000 yuan per person) (EE1); Added Value of Secondary Production
per Capita (yuan per person) (EE2); Per Capita Disposable Income of Urban Residents
(y
uan
)
(
EE3
)
; Per Ca
p
ita Net Income of Rural Residents
(y
uan
)
(
EE4
)
Cultural Environment
(
WHHJ
)
Proportion of Personnel with College Degree or Above in Total Employment in
National Hi
g
h-tech Zones
(
EE5
)
Political Environment
(ZZHJ)
Per capita Financial Expenditure (yuan per person) (EE6); Annual per Capita
Investment in Fixed Assets of the Whole Society (yuan per person) (EE7); Investment
Amount of Government Public Technology Service Platform Obtained by Enterprises
in High-tech Zones per Capita (1000 yuan per person) (EE8)
Open Environment
(KFHJ)
Proportion of Total Import and Export to GDP (EE9)
Infrastructures (JCSS)
Highway Passenger Turnover (100 million person kilometers) (EE10); Per Capita Total
Income of Communication Business (10000 yuan per person) (EE11); Incubator Area
p
er Capita in National High-tech Zones (square meters per person) (EE12)
The data of the index mainly comes from the
statistical yearbook of China torch, region science
and technology yearbooks, region high-tech industry
development yearbooks, region statistical bulletin of
national economic and social development, and
statistical data obtained from market survey
conducted by national high-tech zones. Some missing
data is supplemented by interpolation.
3 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
3.1 CFA Analysis of Structural
Equation
CFA analysis is performed by amos20.0, parameter
estimates and model suitability indicators are shown
in Table 2. All index standardization coefficients are
greater than 0.5, 𝑋
/DF 3 , GFI 0.9 , AGFI
0.9, RMSEA 0.08.
Study on Relationship Between Regional Environment, High-Tech Zones Entrepreneurship and Regional Economic Growth: A Perspective
of Direct Effect and Moderating Effect
43

Table 2: Summary of CFA.
Model Parameter Estimation Model Matching Index Convergence Validity
Variables Index Non-SFL
t
P X
2
/DF GFI
AGFI e SFL SMC CR AVE
Entreprene
urship
EA1 1
1.815 0.967 0.901 0.089
0.96 0.922
0.939 0.757
EA2 0.150 23.054 *** 0.96 0.922
EA3 0.000 14.925 *** 0.86 0.740
EA4 0.001 11.669 *** 0.78 0.608
EA5 0.214 11.223 *** 0.77 0.593
Economic
Environme
nt
EE1 1
0.328 0.997 0.984 0.000
0.49 0.240
0.822 0.545
EE2 75430.6 4.708 *** 0.77 0.593
EE3 21773.5 4.776 *** 0.80 0.640
EE4 20338.2 4.840 *** 0.84 0.706
Political
Environme
nt
EE6 1
— 1 — —
0.88 0.774
0.762 0.523
EE7 3.170 4.649 *** 0.61 0.372
EE8 0.000 4.766 *** 0.65 0.423
Infrastructu
res
EE10 1
— 1 — —
0.91 0.828
0.821 0.608
EE11 0.001 6.296 *** 0.67 0.449
EE12 0.006 6.698 *** 0.74 0.548
Note: * * * stands for P<0.001.
3.2 Reliability Analysis
The index of Entrepreneurship, Economic
Environment, Political Environment and
Infrastructures are tested for composition reliability
and convergence validity. According to the condition
of CFA Analysis, Convergence validity (𝐶𝑅 0.7),
the formula of CR is as follows:
𝐶𝑅
∑
∑
∑
(1)
𝛽
is standardization factor loading(SFL), 𝑒
i s
error of index, the formula of Average variation
extraction (AVE≥0.36)is as follows:
𝐴𝑉𝐸
∑
'
∑
'
∑
(2)
𝛽
' is non-standardization factor loading(non-
SFL), 𝑒
is error of index, the results are shown in
Table 2. The values of CR and AVE meet the CFA
condition, the indexes have good reliability and
convergence effect.
3.3 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
The results of descriptive statistical analysis of
variables are shown in Table3. It can be seen that
there is a significant positive correlation between the
indexes of entrepreneurship, also there is a significant
positive correlation between the indexes of
entrepreneurship and regional economic growth.
Table 3: Descriptive Statistical Analysis.
Index Mean SD EA1 EA2 EA3 EA4 EA5 RE
EA1 40912.08 71647.55 1
EA2 8062.10 10673.82 0.921** 1
EA3 14.35 32.76 0.837** 0.821** 1
EA4 51.90 53.25 0.730** 0.772** 0.690** 1
EA5 10251.72 19165.22 0.746** 0.749** 0.621** 0.536** 1
RE 59419.32 27753.60 0.433** 0.459** 0.235* 0.258** 0.398** 1
Note: * * represents significant correlation at 0.01 level, * represents significant correlation at 0.05 level.
3.4 Direct Effect of Entrepreneurship
on Regional Economic Growth
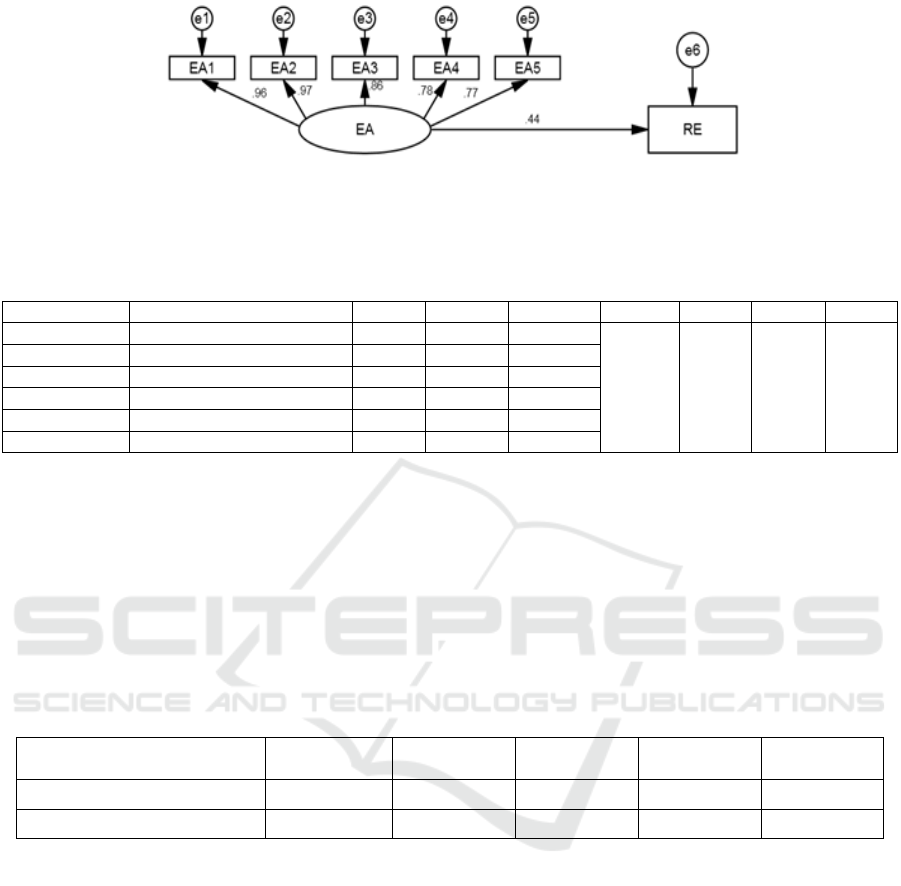
The analysis results are shown in Figure 1 and table
4. The standardized regression coefficient of
entrepreneurship on regional economic growth is
0.44, t is 4.912, 𝑝 0.001, SD is 0.037, the value of
entrepreneurship index meets the model conditions,
and the model fitness meets the SEM conditions. This
shows that entrepreneurship has a very significant
impact on regional economic growth.
Entrepreneurship in high-tech zones can positively
promote regional economic growth, and the higher
the entrepreneurship level of high-tech zones, the
greater the growth of regional economy.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
44
X
2
=24.948 df=9; X
2
/df=2.772; GFI=0.926; AGFI=0.828; RMSEA=0.131
Figure 1: Effect Model of Entrepreneurship on Regional Economic Growth.
Table 4: Regression Results of Entrepreneurship on Regional Economic Growth.
Index Non standardized value SD T P X
2
/df GFI AGFI e
EA1←EA 1
2.772 0.926 0.828 0.131
EA2←EA 0.151 0.006 23.326 ***
EA3←EA 0 0 14.688 ***
EA4←EA 0.001 0 11.62 ***
EA5←EA 0.215 0.019 11.254 ***
RE←EA 0.18 0.037 4.912 ***
Note: * * * stands for P ≤ 0.001, * * stands for P ≤ 0.01, * stands for P ≤ 0.05.
3.5 Moderating Effect of Environment
3.5.1 Group Division
The moderating variables are divided into two
groups: excellent group and inferior group according
to the comprehensive factor score in order to explore
the moderating effect of economic environment,
cultural environment, political environment, open
environment and infrastructures environment. The
excellent group represents the group with larger
value, and the inferior group represents the group
with smaller value, then the differences between the
two groups are compared. The division of index
values are shown in Table5.
Table 5: Division Points of Regional Environment.
Infrastructures
Economic
Environment
Political
Environment
Cultural
Environment
Open
Environment
Upper limit of inferior group -0.1625 -0.4365 -0.3885 0.3991 0.0989
Lower limit of excellent group -0.3073 0.2635 0.1913 0.4210 0.2882
3.5.2 Moderating Effect of Economic
Environment
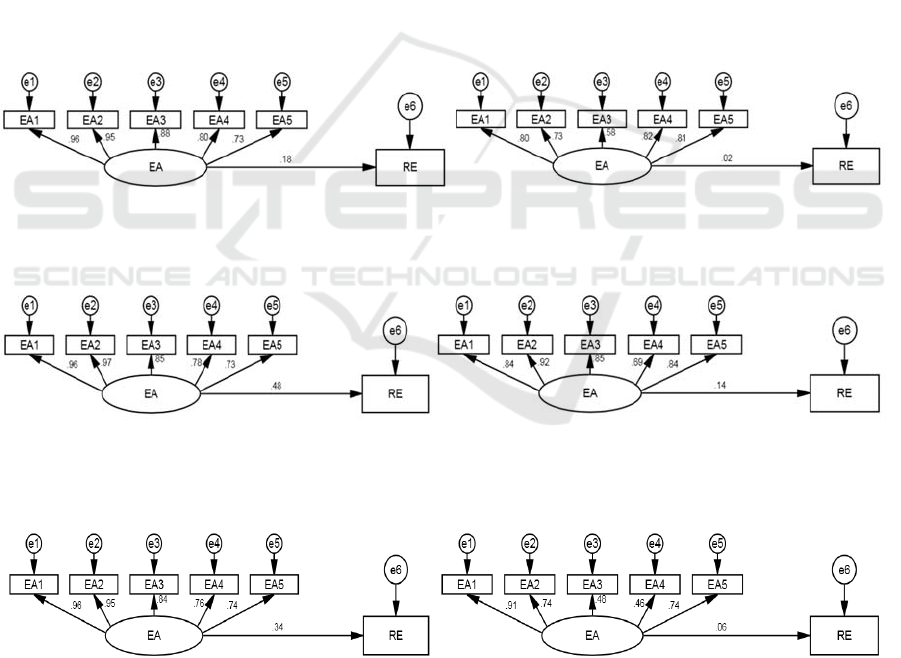
The analysis results of moderating effect of
Economic Environment are shown in Figure 2 (1) and
Figure 2 (2). Entrepreneurship regression coefficient
on regional economic growth of excellent group is
0.18, The coefficient of inferior group is 0.02. The
significance of moderating variables is tested, the
results are shown in Table 6. p=0.38˃0.1, It is
considered that the Economic Environment does not
play a significant moderating effect between
entrepreneurship and regional economic growth in
national high-tech zones.
3.5.3 Moderating Effect of Cultural
Environment
The analysis results of Cultural Environment are
shown in Figure3 (1) and Figure3 (2).
Entrepreneurship regression coefficient on regional
economic growth of excellent group is 0.48, the
coefficient of inferior group is 0.14. It is considered
that high-tech zones located in areas with better
cultural environment are more conducive to
entrepreneurship and promote regional economic
growth. The significance of moderating variables is
tested, the results are shown in Table 6.𝑝 0.028
0.05, it is considered that the Cultural Environment
in high-tech zones plays a significant moderating role
between entrepreneurship and regional economic
growth.
Study on Relationship Between Regional Environment, High-Tech Zones Entrepreneurship and Regional Economic Growth: A Perspective
of Direct Effect and Moderating Effect
45
3.5.4 Moderating Effect of Political
Environment
The analysis results of Political Environment are
shown in Figure4 (1) and Figure4 (2). The regression
coefficient of the excellent group is 0.34 and that of
the inferior group is 0.06. It is believed that
Entrepreneurship in high-tech zones with better
political environment is more conducive to
promoting regional economic growth. The test results
are shown in Table 6, 𝑝 0.091 0.1 , it is
considered that the Political Environment in high-
tech zones plays a significant moderating role
between entrepreneurship and regional economic
growth.
3.5.5 Moderating Effect of Open
Environment
The analysis results of Open Environment are shown
in Figure5 (1) and Figure5(2). The regression
coefficient of the excellent group was 0.42, and that
of the inferior group is 0.08. The test results are
shown in Table 6, 𝑝 0.034 0.05 , it is
considered that Open Environment in high-tech zones
plays a significant moderating role between
entrepreneurship and regional economic growth.
3.5.6 Moderating Effect of Infrastructures
The analysis results of Infrastructures are shown in
Figure6 (1) and Figure6 (2). The regression
coefficient of the excellent group was 0.51, and that
of the inferior group is 0.02. The test results are
shown in Table 6, 𝑝 0.036 0.05 , it is
considered that Infrastructures in high-tech zones
plays a significant moderating role between
entrepreneurship and regional economic growth.
(1) Excellent Group Regression Results (2) Inferior Group Regression Results
Figure 2: Moderating Effect of Economic Environment.
(1) Excellent Group Regression Results (2) Inferior Group Regression Results
Figure 3: Moderating Effect of Cultural Environment.
(1) Excellent Group Regression Results (2) Inferior Group Regression Results
Figure 4: Moderating Effect of Political Environment.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
46
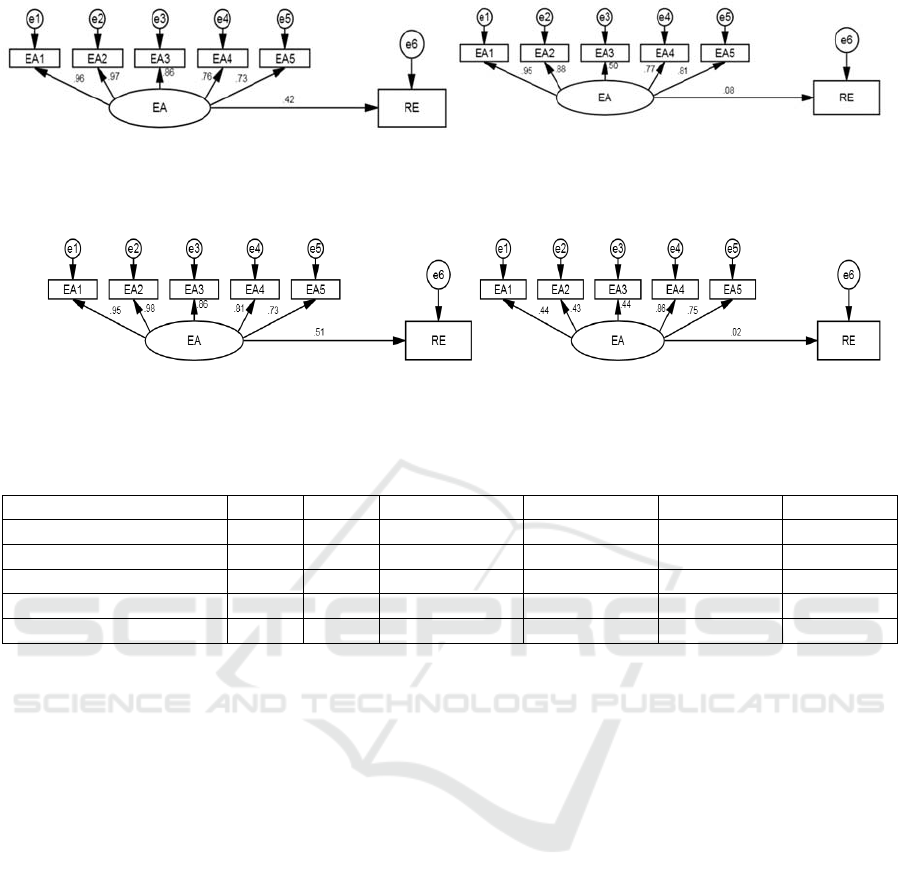
(1) Excellent Group Regression Results (2) Inferior Group Regression Results
Figure 5: Moderating Effect of Open Environment.
(1) Excellent Group Regression Results (2) Inferior Group Regression Results
Figure 6: Moderating Effect of Infrastructures.
Table 6: the Significance of Moderating Variables.
Statistic X
2
P NFI Delta-1 IFI Delta-2 RFI rho-1 TLI rho2
Economic Environment 0.770 0.380 0.003 0.003 -0.008 -0.009
Cultural Environment 4.858 0.028 0.010 0.010 0.005 0.005
Political Environment 2.707 0.091 0.009 0.010 -0.005 -0.005
O
p
en Environment 4.515 0.034 0.013 0.014 0.013 0.014
Infrastructures 4.409 0.036 0.013 0.013 0.003 0.004
4 CONCLUSIONS
ased on the current analysis and research results, this
paper discusses the paper analyzed that national high-
tech zones entrepreneurship’s direct effect on
regional economic growth and moderating effect of
economic environment, cultural environment,
political environment, open environment and
infrastructures by confirmatory factor analysis and
structural equation moderating effect.
The following
conclusions are drawn: (1) national high-tech zones
entrepreneurship promotes regional economy growth
significantly, (2) the Cultural Environment in high-
tech zones plays a significant moderating role
between entrepreneurship and regional economic
growth; (3)
Political Environment in high-tech zones
plays a significant moderating role between
entrepreneurship and regional economic growth; (4)
Open Environment in high-tech zones plays a
significant moderating role between entrepreneurship
and regional economic growth; (5)
Infrastructures in
high-tech zones plays a significant moderating role
between entrepreneurship and regional economic
growth.
5 SUGGESTIONS AND
COUNTERMEASURES
Strengthen entrepreneurship management in high-
tech zones, encourage all kinds of entrepreneurial
explorations and experimentations, encourage the
entrepreneurial behaviors of large enterprises. The
government and administrative departments should
also support the development of incubators and
support incubated enterprises and newly established
small enterprises. Set up special funds for incubator
development, strengthen the service function of the
Productivity Promotion Center, develop the driving
role of entrepreneurship in regional economic
growth.
Strengthen the construction of entrepreneurial
culture environment in high-tech zones, strengthen
talents training and education, improve the
entrepreneurial ability and quality of talents in high-
tech zones, create entrepreneurial teams and learning
organizations actively, and strengthen the
performance managements of entrepreneurs. Local
government departments should build education
Study on Relationship Between Regional Environment, High-Tech Zones Entrepreneurship and Regional Economic Growth: A Perspective
of Direct Effect and Moderating Effect
47

platforms for entrepreneurial talents in high-tech
zones, guide cooperation and exchanges between
enterprises and education training institutions, and
encourage cooperation of industries, universities and
research institutions.
Strengthen support for entrepreneurship,
especially entrepreneurial activities with good market
prospects and great market value. Encourage the
commercialization and marketization of
entrepreneurial projects. Build special policies such
as entrepreneurship fund and entrepreneurship
support fund, expand entrepreneurship loans and
financing channels, and implement entrepreneurship
tax incentives to improve the performance of
entrepreneurship effectively.
Create open entrepreneurial environment,
increase regional openness, strengthen cross regional
exchanges and cooperation, and encourage foreign
investments in science and technology
entrepreneurship.
Improve infrastructure conditions, improve the
comprehensive transportation network, especially
promote the constructions of entrepreneurship
network, improve the constructions of information
and communication facilities, and improve the
service capacity of information facilities, especially
in the central and western regions with relatively low
economic development level.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research is supported by research project of
Anhui Province Special Project of Science and
Technology Innovation Strategy and Soft Science
Research (project number: 202006f01050044);
Humanities and social sciences research project of the
Ministry of Education (project number:
20YJCZH028); Huangshan University National Fund
cultivation project (project number: 2021GJYY006);
Anhui social science innovation and development
research project (project number: 2021CX047);
Anhui Province University Excellent Top Talent
Cultivation Project (project number:
gxbjZD2022062); Anhui University Humanities
Research Project (project number: SK2021A0641);
Scientific Research and Innovation Team of
Huangshan University (project number:
2021XCXTDPY04); National Undergraduate
Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program
(project number: 202110375034).
REFERENCES
Austin J, Stevenson H, Wei‐Skillern J. Social and
Commercial Entrepreneurship: Same, Different, or
Both?[J]. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 2006,
30(1)
Yuli Zhang. A Review of Classical Literature on
Entrepreneurship[M]. Tianjin: Nankai University
Press, 2010
Guiso L, Schivardi F. What Determines Entrepreneurial
Clusters?[J]. Journal of the European Economic
Association, 2011, 9(1)
Lumpkin GT, Cogliser C C, Schneider D R. Understanding
and Measuring Autonomy: An Entrepreneurial
Orientation Perspective[J]. Entrepreneurship Theory &
Practice, 2009, volume 33(1):47-69(23).
Qiong Qiu, Jian Gao. A Summary of Research Trends on
the Relationship Between Entrepreneurship and
Economic Growth [J]. Foreign economy and
management, 2004, 26(1)
Song Lin. Entrepreneurship: Principle and
Practice[M].Shanghai: Shanghai University of Finance
and Economics Press,2008
Shivani S, Mukherjee S K, Sharan R. Socio-cultural
influences on Indian entrepreneurs: The need for
appropriate structural interventions[J]. Journal of Asian
Economics, 2006, 17(1)
Minguzzi A, Passaro R. The network of relationships
between the economic environment and the
entrepreneurial culture in small firms[J]. Journal of
Business Venturing, 2001, 16(2): 181-207.
Xiaobo Wu, Weihua Zhou, Jian Du. Entrepreneurship
Management [M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2011
Nicholls-Nixon C L, Cooper A C, Woo C Y. Strategic
experimentation: understanding change and
performance in new ventures [J]. Journal of Business
Venturing, 2000, 15(5):493-521.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
48
