
Big Data Financial Analysis of BYD Company Profitability Based on
Power BI Software
Tieping Wang
Department of Economics and Management, Taishan University Tai’an, China
Keywords: Big Data, Profitability, Financial Analysis.
Abstract: Big data financial analysis comprehensively considers all the information of the company and can
comprehensively reflect the financial status of the company. This paper uses Power BI software to present
the results of big data financial analysis on BYD's profitability; using industry analysis and trend analysis, it
analyzes BYD's profitability from three aspects: capital profitability, asset profitability and commodity
profitability. The industry analysis method can be used to observe the current level of BYD in the industry,
compare the company's five-year average, judge the company's development status, and study the strengths
and weaknesses of the target company's capabilities; the trend diagram method can be used to observe BYD
in different time periods. Changes in indicators, find out the hidden problems in the company's operation
process, analyze the reasons for changes and put forward optimization suggestions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Big data financial analysis is the fusion of big data
technology and financial analysis. Different from
traditional financial analysis, it adopts big data
technology, comprehensively analyzes the financial
information and non-financial information of the
enterprise, and reflects the financial status of the
enterprise more comprehensively (George, 2014).
Big data financial analysis through PowerBI
software can connect relevant data sources and
generate multi-dimensional financial statements in
real time, which is convenient for accounting
information users to view the company's trend
changes over the years, compare trends with
industry competitors, find the company's
shortcomings and improve them to improve
company achievements (Kaufmann, 2001). The use
of PowerBI software greatly improves the work
efficiency of financial personnel (Fan, 2014).
This paper uses PowerBI software to conduct big
data financial analysis on BYD, which can build
multi-dimensional analysis models and make instant
financial statements. BYD's 2020 operating income
is 156,597,691,000yuan, an increase of
28,859,167,900 yuan compared with the previous
year's operating income, and the operating income
growth rate is 22.59%. The net profit in 2022 will be
6,013,963,000yuan, an increase of 3,895,106,000
yuan compared with the previous year's net profit.
The growth rate was 183.83%. BYD's revenue and
profits have grown, and its overall performance has
been on the rise. In 2020, the operating income
growth rate of BYD's automobile manufacturing
industry is 3.52%, and the net profit growth rate is
22.23%. At present, the overall performance of the
industry is on the rise. This paper takes BYD as the
research object, and analyzes BYD's profitability
from three aspects: capital profitability, asset
profitability and commodity profitability.
2 CAPITAL PROFITABILITY
ANALYSIS
Profitability of capital operation refers to the ability
of the company to obtain profit by investing in
capital operation (Revsine, 2012). ROE is a core
indicator reflecting profitability.
Wang, T.
Big Data Financial Analysis of BYD Company Profitability Based on Power BI Software.
DOI: 10.5220/0012023300003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 49-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
49
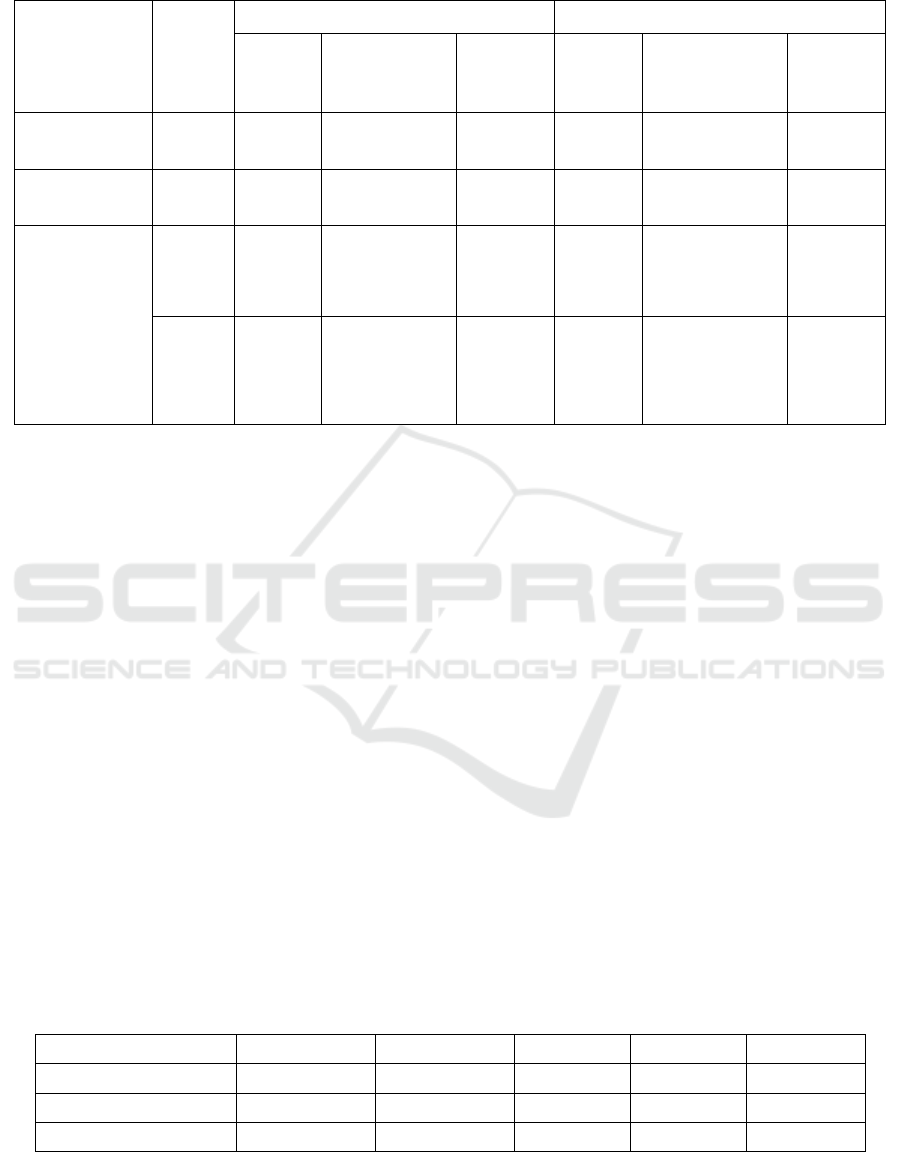
Table 1: Profitability Indicators.
Classification Index
2020 Average 2016-2020
BYD
Automotive
Manufacturing
SAIC BYD
Automotive
Manufacturing
SAIC
Capital
profitability
ROE 9.47% 6.56% 9.55% 7.86% 10.18% 15.46%
Asset
profitability
ROA 3.47% 3.11% 4.06% 4.45% 5.39% 6.92%
Commodity
profitability
Net
sales
margin
3.84% 3.35% 4.04% 3.63% 4.68% 5.03%
Cash to
sales
ratio
88.55% 91.79% 88.19% 85.19% 98.03% 103.03%
2.1 Change Trend of ROE
As shown in Figure 1, BYD's ROE generally
showed a downward trend from 2016 to 2019, from
11.98% to 3.43%. From 2019 to 2020, there was a
substantial growth trend, from 3.43% to 9.46%.
BYD's five-year average is only 7.86%. From 2016
to 2019, the ROE of BYD, the automobile
manufacturing industry and the benchmarking
company SAIC all showed a downward trend. The
average ROE of BYD over the years is 4 percentage
points lower than the average ROE of the industry
over the years, and the average ROE of the
automobile manufacturing industry is nearly 4
percentage points lower than that of the benchmark
company SAIC. In 2020, after BYD's ROE rose, it
was on par with the benchmark company SAIC. The
ROE of the automobile manufacturing industry is in
line with the downward trend of the benchmark
company SAIC, and the profitability of capital is
declining year by year. SAIC's ROE has shown a
downward trend over the years. Its five-year average
ROE is still as high as 15.46%, and the industry's
five-year average ROE is 10.18%.
2.2 BYD's Capital Profitability
ROE is equal to net profit divided by average net
assets, also known as net interest rate on equity
(Gibson, 2013). ROE, as an indicator of capital
profitability, reflects the profitability of all invested
funds. The higher the ROE, the stronger the
profitability of BYD, and vice versa. The ROE
indicator is the core indicator reflecting profitability.
BYD's ROE generally showed a downward trend
from 2016 to 2019, and increased from 2019 to
2020. From 2016 to 2019, ROE dropped
significantly to 3.43%, and BYD's capital
profitability was relatively weak. In 2020, BYD's
capital profitability has been greatly improved, and
the utilization efficiency of shareholders' invested
capital has been significantly improved.
Table 2: Change trend of ROE.
ROE 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD 11.98% 8.52% 5.89% 3.43% 9.46%
Industry 15.18% 13.72% 9.79% 5.64% 6.56%
SAIC 19.71% 18.57% 17.38% 12.05% 9.55%
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
50
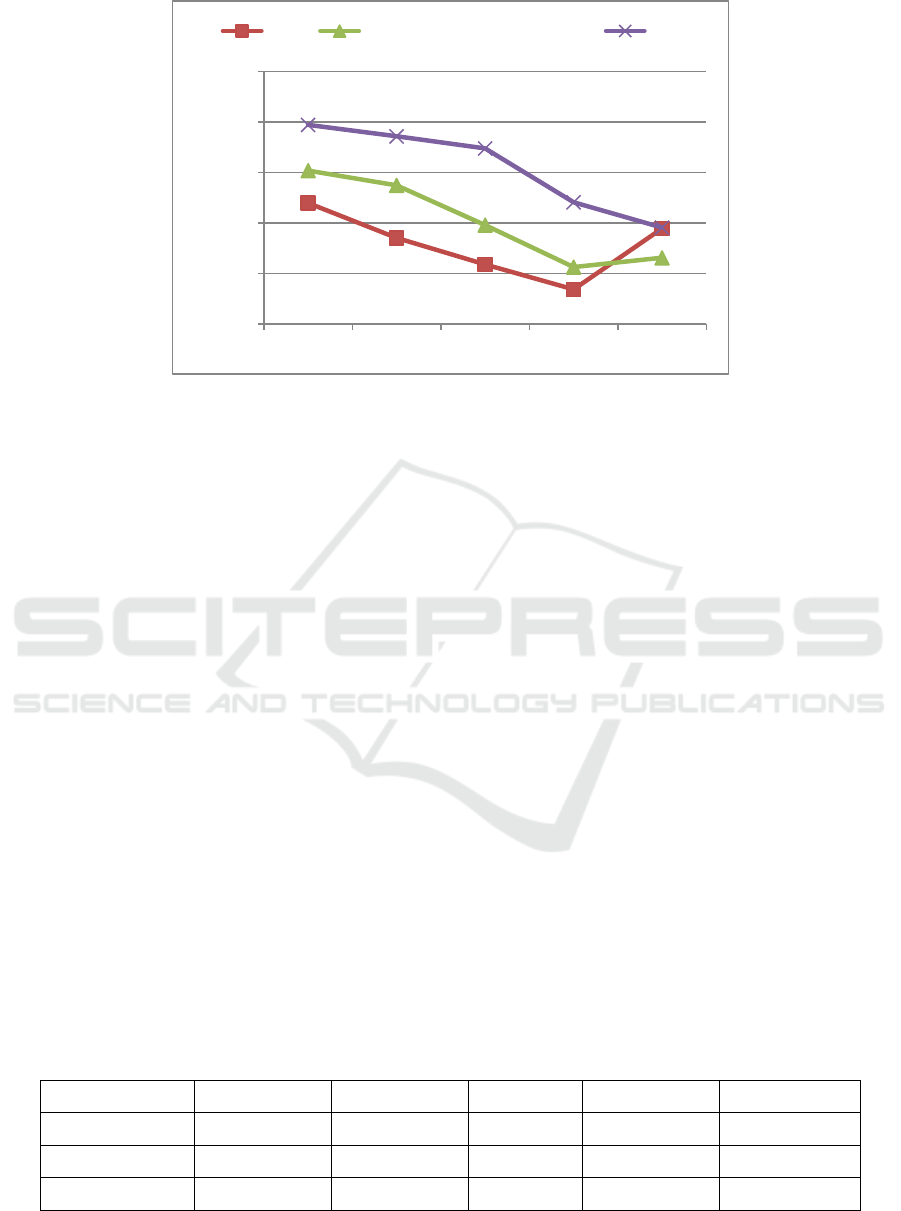
Figure 1: Change trend of ROE.
3 ASSET PROFITABILITY
ANALYSIS
Asset management capability refers to the ability of
the company to operate assets and generate profits.
ROA reflects the profitability of asset management.
3.1 The Changing Trend of ROA
As shown in Figure 2, BYD's ROA generally
showed a downward trend from 2016 to 2019, and
the decline in five years was relatively obvious,
from 6.52% in 2016 to 3.13% in 2019, and ROA
increased slightly from 2019 to 2020, rising to
3.47 %. BYD's five-year average ROA is 4.45%.
From 2016 to 2020, the industry ROA of BYD's
auto manufacturing industry showed a downward
trend, from 7.90% in 2016 to 3.11% in 2020. The
five-year average ROA of the automobile
manufacturing industry is 5.39%. The change trend
of ROA of the benchmark enterprise SAIC is in line
with the industry, from 9.29% in 2016 to 4.06% in
2020. The five-year average ROA of SAIC is
6.92%.
3.2 BYD's Asset Profitability
ROA is equal to EBIT divided by average total
assets. The higher the ROA, the stronger the asset
profitability of the company, and vice versa. When
only operating conditions are considered, ROA
reflects the benefits of management's management
of all assets, that is, management's ability to create
value from the company's existing resources.
Although the ROA trend of BYD, the automobile
manufacturing industry and SAIC is in the same
downward trend, the decline rate of BYD is
significantly slower than that of the other two
parties. At the same time, BYD achieved a slight
increase in ROA in 2020 (3.47%), which is higher
than the industry ROA of 3.11%, and the gap with
SAIC is also small (4.06%). The asset profitability
of the auto manufacturing industry is generally low.
The profitability of BYD's assets in the last five
years is not strong, although there will be a slight
rebound in 2020, which needs the attention of
BYD's management.
Table 3: Change trend of ROA.
ROA 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD 6.52% 4.97% 4.15% 3.13% 3.47%
Industry 7.90% 7.15% 5.43% 3.41% 3.11%
SAIC 9.29% 8.47% 7.47% 5.27% 4.06%
0,00%
5,00%
10,00%
15,00%
20,00%
25,00%
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD Automotive Manufacturing SAIC
Big Data Financial Analysis of BYD Company Profitability Based on Power BI Software
51
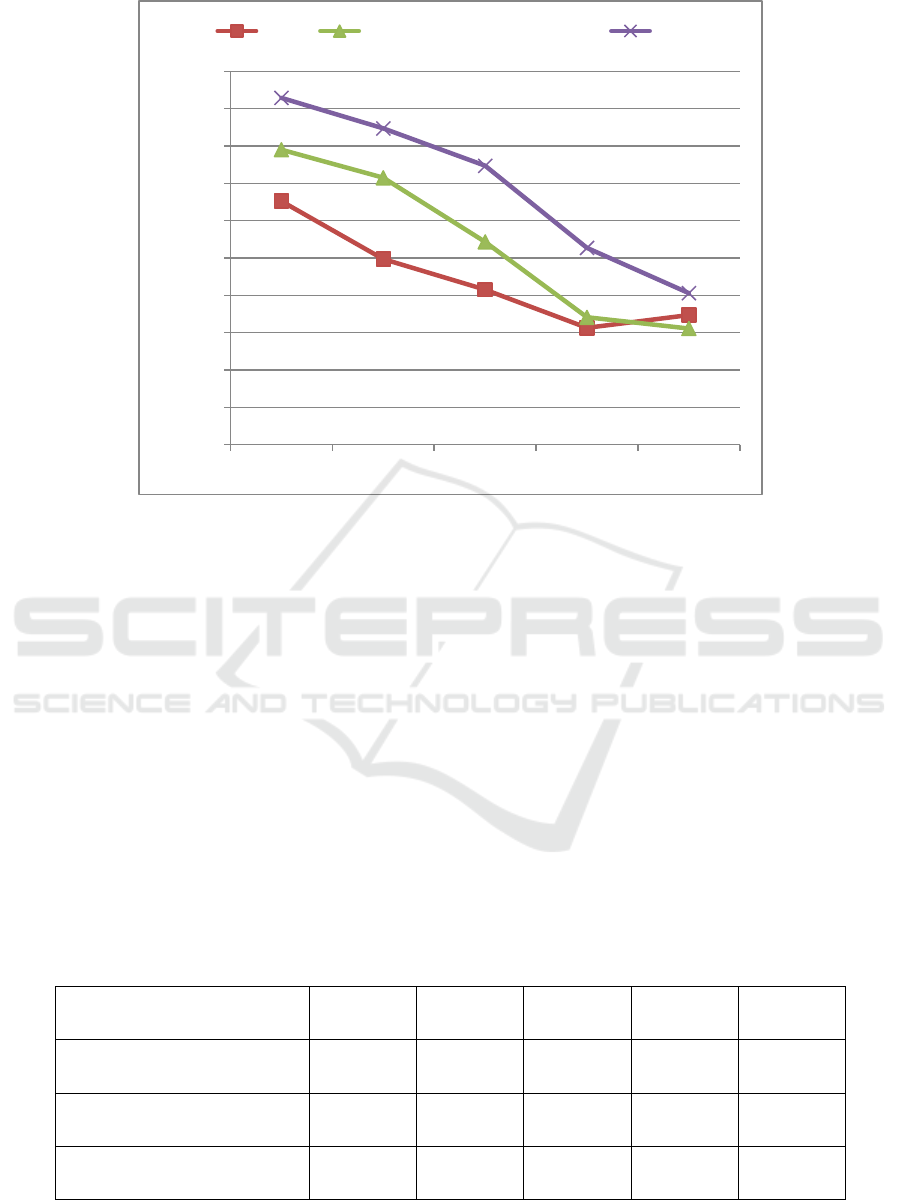
Figure 2: Change trend of ROA.
4 PRODUCT PROFITABILITY
The profitability of commodity operation does not
consider the financing or investment of the
enterprise, and only studies the ratio between profit
and income or cost. In this paper, the net profit ratio
of sales and the ratio of cash sales are used to reflect
the profitability of commodities.
4.1 Change Trend of Net Sales Margin
As shown in Figure 3, BYD's net sales margin from
2016 to 2019 generally showed a downward trend,
and the decline in the five years was relatively
obvious, from 5.29% in 2016 to 1.66% in 2019, and
the net sales margin from 2019 to 2020. It increased
slightly to 3.84%. The five-year average of BYD's
net sales margin is 3.63%. From 2016 to 2019, the
net sales margin of BYD's auto manufacturing
industry showed a downward trend, from 6.53% in
2016 to 2.84% in 2020. From 2019 to 2020, the net
sales margin in the automobile manufacturing
industry increased slightly to 3.35%. The average
five-year sales net sales margin of the automobile
manufacturing industry is 4.68%. The net sales
margin of benchmark company SAIC showed a
gradual downward trend, from 5.89% in 2016 to
4.04% in 2020. The five-year average of SAIC's net
sales margin is 5.03%.
Table 4: Change trend of Net sales margin.
Net sales margin 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD 5.29% 4.64% 2.73% 1.66% 3.84%
Industry 6.53% 6.01% 4.66% 2.84% 3.35%
SAIC 5.89% 5.49% 5.45% 4.27% 4.04%
0,00%
1,00%
2,00%
3,00%
4,00%
5,00%
6,00%
7,00%
8,00%
9,00%
10,00%
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD Automotive Manufacturing SAIC
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
52

Figure 3: Change trend of Net sales margin.
4.2 Change Trend of the Cash-to-Sales
Ratio
As shown in Figure 4, BYD's cash-to-sales ratio was
generally stable from 2016 to 2020, fluctuating
within the range of 79.82% to 88.55%. The five-year
average of BYD's cash-to-sales ratio is 85.19%.
From 2016 to 2018, the cash-to-sales ratio of BYD's
auto manufacturing industry was relatively stable,
fluctuating between 100.34% and 103.84%. The
average five-year cash-to-sales ratio of the
automobile manufacturing industry is 98.03%. The
cash-to-sales ratio of the benchmark company SAIC
has shown a downward trend, from 119.48% in
2016 to 88.19% in 2020. The five-year average of
SAIC's cash-to-sales ratio is 103.03%.
Table 5: Trends in Cash to Sales Ratio.
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD 86.44% 89.07% 79.82% 83.89% 88.55%
Industry 103.84% 100.34% 102.92% 91.27% 91.79%
SAIC 119.48% 111.89% 111.50% 84.07% 88.19%
Figure 4: Trend of Cash to Sales Ratio.
0,00%
2,00%
4,00%
6,00%
8,00%
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD Automotive Manufacturing SAIC
0,00%
20,00%
40,00%
60,00%
80,00%
100,00%
120,00%
140,00%
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
BYD Automotive Manufacturing SAIC
Big Data Financial Analysis of BYD Company Profitability Based on Power BI Software
53

4.3 BYD's Commodity Profitability
The net profit rate of sales is equal to the ratio of net
profit to operating income. From 2016 to 2019, the
sales net profit margin of BYD and the automobile
manufacturing industry showed a similar downward
trend. BYD's sales net profit margin was always 1%
lower than the industry average, and SAIC's sales
net profit margin was generally better than the
industry average. In 2019, the inflection point of
BYD's sales net profit margin appeared, rising to
3.84% in 2020, basically the same as SAIC's 4.04%,
and higher than the industry average of 3.35%.
Although BYD is comparable to benchmark
companies, BYD's sales net profit margin is still
low, and the overall profitability of goods in the auto
manufacturing industry has declined.
The cash-to-sales ratio is equal to the cash
received from the sale of goods and services,
divided by the operating income. The higher the
cash-to-sales ratio, the stronger the company's
ability to obtain cash through sales, the good sales
situation of the company's products, the reasonable
credit policy, the timely recovery of payment for
goods, and the effective collection of payments.
From 2016 to 2020, BYD's cash-to-sales ratio has a
relatively stable change trend, and the fluctuation
range is also relatively flat, which is generally lower
than the industry average and SAIC. BYD's
commodity profitability indicator was little changed.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The paper uses Power BI software to carry out big
data financial analysis of Vanke's solvency. The
conclusions are as below. This paper uses industry
analysis and trend analysis to analyze BYD's
profitability. Compared with SAIC, a benchmark
company in the automobile manufacturing industry,
BYD's performance in 2020 is very good, and its
profitability has risen sharply, which is basically the
same as SAIC and higher than the industry average.
But at the same time, it should be noted that the
overall profitability of the automobile manufacturing
industry is on a downward trend, and even the
profitability of SAIC, the leading enterprise, is not
high. The increase in the cost of automobile
manufacturing has led to a decline in profits. It is
necessary to strengthen cost management, reduce
expenses, and increase corporate profits.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The thesis is the result of the Taishan University
Introduced Talents Scientific Research Start-up
Fund Project.
REFERENCES
Fan, J., F. Han and H. Liu, Challenges of big data
analysis. National science review, 2014. 1(2): p.
293-314.
George, G., M.R. Haas and A. Pentland, Big data and
management. 2014, Academy of Management
Briarcliff Manor, NY. p. 321-326.
Gibson, C.H. and P.A. Boyer, Financial statement
analysis. 2013.
Kaufmann, R., A. Gadmer and R. Klett, Introduction to
dynamic financial analysis. ASTIN Bulletin: The
Journal of the IAA, 2001. 31(1): p. 213-249.
Revsine, L., et al., Financial reporting and analysis. 2012:
McGraw Hill.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
54
