
Design and Development of Esp32-Based Non-Invasive Blood Sugar
Level Measurement Equipment
Dika Ari Saputra and J. Rajes Khana
Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta Podomoro, Jl. Sunter Permai Raya Sunter Agung, Kec. Tj. Priok, Kota Jkt Utara,
Daerah Khusus Ibukota, 14350, Jakarta
Keywords: Photodiode, Blood Sugar Level, and Non-Intrusive.
Abstract: This research was conducted to produce a non-invasive blood sugar measuring device, which is a device that
can measure blood sugar levels without having to test and examine the blood directly but using a finger
attached to the sensor as a specimen, the Photoplethysmography (PPG) method is used in the design of the
device system in this work is to measure blood sugar levels. The architecture of this system uses an easy-to-
use and low-cost optical measurement technique. The ILI9488 LCD module also functions to display, in this
study the results of the calculation of the average percentage error of the tool are 3.52% with a calculation
that has an accuracy value of 95.48% from the actual tool. Judging from the calculation results, the percentage
experienced a measurement error of 0% - 3.52% in 16 trials. Thus, this GlucoTest tool can only be used as a
comparison of the sugar content of a glucometer in general. And it takes a lag time of 1 to 3 minutes for the
same patient or respondent to take measurements again.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease in which the
amount of sugar in the blood is too high
(hyperglycemia) due to the inability of the pancreas
to produce insulin. When the pancreas cannot
produce insulin, the body has difficulty maintaining
blood sugar levels, resulting in high blood sugar
levels or hyperglycemia. Diabetes is divided into type
I diabetes and type II diabetes. Type I diabetes occurs
when the body is unable to produce insulin, while
type II diabetes occurs when the body is unable to
receive and process insulin efficiently. This second
can lead to obesity and lack of physical activity (F. Z.
Kamilah et al.,2021).
In blood or serum there is a concentration of
glucose called blood glucose, a normal limit for a
person who has not eaten for 3 or 4 hours and then
close to 90 milligrams or dl. Even though the
consumption of foods that contain lots of
carbohydrates, this focus does not often increase
above 140 milligrams or dl, but the person has
Diabetes Mellitus. Glucose that flows through the
blood is an important base of energy for the body's
cells. Blood glucose is sugar in the blood that is
created from carbohydrate metabolism. Checking
blood glucose is one of the checks in clinical trials (N.
F. Fahmi et al., 2021)
Currently, the most commonly used tool to
measure blood sugar levels is a blood glucose meter.
Measurement of blood glucose levels was carried out
using a glucometer which works enzymatically based
on the glucose oxidase reaction. The glucose meter
works on the principle of a biosensor. A biosensor is
a combination of a biological receptor and a
transducer. Bioreceptors are devices used to sense the
concentration of biological elements, such as
enzymes, antibodies, living cells, and other tissues.
The function of the sensor is to convert biochemical
signals into electrical signals, which then appear on
the blood glucose meter screen (J Fine et al., 2021).
However, in taking blood samples, it is necessary
to use a tool in the form of a syringe, although the
process is carried out quickly but there are still many
patients who are afraid of needles for taking blood
samples. Therefore, an accurate blood glucose meter
is needed without injuring the body first (non-
invasive).
In this study, a tool was made to measure blood
sugar levels without injuring the body. The device
does not require urine as a test material to measure the
patient's blood sugar level. This tool works on the
principle that the photodiode sensor will capture light
Saputra, D. and Khana, J.
Design and Development of Esp32-Based Non-Invasive Blood Sugar Level Measurement Equipment.
DOI: 10.5220/0012026300003582
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP) UTA â
˘
A
´
Z45 Jakarta (ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022), pages 381-385
ISBN: 978-989-758-654-5; ISSN: 2828-853X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
381
from a light source. used are LEDs. When the tool is
turned on, the light from the LED will radiate and
pass through the finger before reaching the
photodiode. The intensity of light received by the
photodiode changes from a factor of changes in the
number of blood sugar molecules. The photodiode
output signal will be processed on the ESP32. After
the signal is processed by esp32, the patient's blood
sugar value can be known. This blood sugar value is
shown on the TFT LCD screen attached to Glucotest.
The output of the tool includes the value of blood
glucose levels and a description (low/normal/high) in
units (mg/dl).
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research was conducted in several locations, the
place is in the electrical laboratory at the University
of 17 August 1945, Jakarta to design a non-invasive
blood sugar level measuring device based on esp32.
And for sampling, the trial was carried out in the
author's home area.
2.1 System Block Diagram Design Tool
The overall planning of the hardware block diagram
made in this research is as follows:
Figure 1. System Block Diagram.
In the block diagram, the output system of the
photodiode will enter the microcontroller for
processing and display
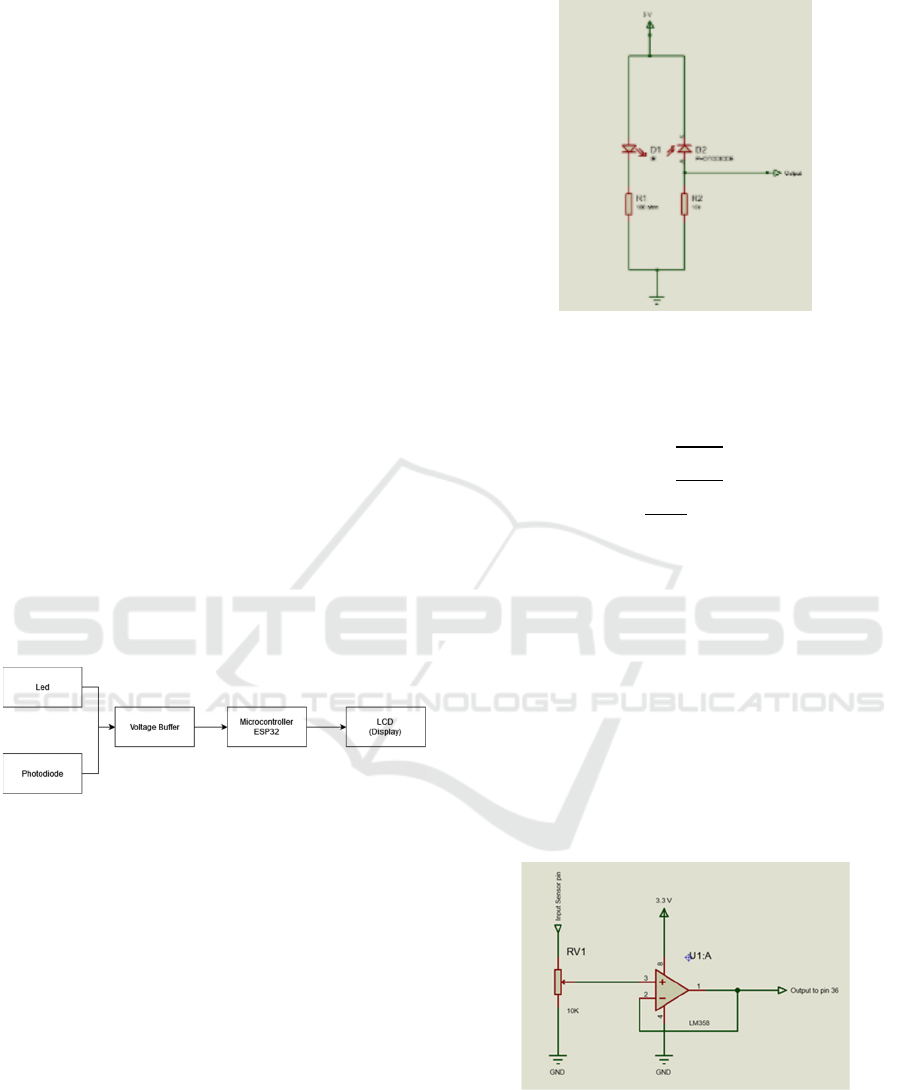
2.2 Sensor System Design
The design of this sensor system circuit uses a red
LED as a light source and a Photodiode sensor as a
receiver. With a schematic of the circuit as shown in
Figure 2
.
Figure 2: Sensor Circuit.
The resistance value of the resistor can be
calculated using the formula:
R =
R =
R =
= 100Ω
(1
)
So the value of the resistor is considered to be
100Ω
where
R = current limiting resistor
𝑣
= 5v (tegangan Input)
𝑣
= 2v (Input voltage)
I = 50 mA = 0,05 A
2.3 Voltage Buffer Design
The voltage buffer circuit design stage is needed to
stabilize the sensor reading value. In this circuit the
components used are 538 op-amp and 10kΩ trimmer
Figure 3. Voltage buffer Circuit.
This arrangement is very profitable because we can
get an amplifier with very large input resistance
(input impedance) and with very small output
resistance (output impedance), which is close to
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
382
perfect conditions. As a result, an operational
amplifier with a shape like the one in the picture
above acts as a buffer with a gain = 1. The application
of a good buffer arrangement made of a transistor
amplifier or operational amplifier (Op-Amp) is
usually used as a signal stabilizer.
2.4 Program Design
The software design stage begins with making a
flowchart followed by making a lasting program
using Arduino Uno. The software design flowchart is
as follows:
Figure 4: Flowchart Program.
When the start button is pressed, the program will
start port initialization, if the sensor detects a finger,
the program will read the sensor value, if the sensor
does not detect a finger, the program will again ask
for finger input, then if the value is obtained, the value
will be converted and determined whether the blood
sugar level is low, normal or height is then displayed
on the LCD.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This chapter discusses the results and systems that
have been designed and built. It is designed to
determine if the system meets the standards the author
wants. Each block is tested with the aim of Knowing
the work of each circuit block, making it possible to
know whether each circuit module performs its
function properly. Proceed with the overall test. The
test of this tool consists of 7 main parts, namely:
1. Sensor
Testing
2. Measurement Condition Testing
3. LCD
Testing
4. Overall Tool Testing
5. Reading Value
6. Research Results.
7. Error Percentage.
3.1 Sensor Testing
In sensor testing, it is done by measuring the output
voltage of the sensor when it is not blocked by a
finger and when the sensor is blocked by a finger. The
sensor measurement results can be seen in table 1.
Table 1: Sensor Measurement Results.
No Condition ADC Out
p
ut Volta
g
e
1 Not blocked by
fingers
470 1,51 V
2 Blocked b
y
fin
g
e
r
878 2,83 V
In this test, the adc value is 470 when the sensor
is not blocked by a finger and will produce an adc
value of more than 470 when the sensor is blocked by
a finger. This shows the sensor is functioning
properly. According to the way the photodiode sensor
works, the brighter the light, the smaller the sensor
reading value. Conversely, the darker the light, the
greater the sensor reading value.
3.2 Measurement Condition Testing
In this test, it is carried out by simulating two
measurement conditions, namely when measuring in
the dark (the instrument is in a closed condition) and
when the instrument is in a light condition (the
instrument is in an open condition). The results of this
test can be seen from table 2.
Table 2. Testing Measurement Conditions
Condition ADC LUX Tool
Results
Glukometer
Results
Dark
conditions
788 281 94 mg/dL
98 mg/dl
Light
Condition
920 680
165
mg/dL
The results of these tests show that the darker the
measurement conditions, the more accurate the
measurement results, on the contrary, the brighter the
measurement conditions, the more error the reading
value will be.
Design and Development of Esp32-Based Non-Invasive Blood Sugar Level Measurement Equipment
383

3.3 LCD Testing
The ILI9488 TFT LCD test aims to find out whether
the lcd can function properly. The use of pins on the
ILI9488 TFT LCD, there are several pins that are
used as data sender and data receiver pins, namely
CS, RESET, DC/RS, SDI(MOSI), SCK pins. For the
touchscreen pins, namely T_CLK, T_CS, T_DIN,
TDO. and for power use the VCC, GND, and LED
pins as the backlight power which is connected
directly to the esp32 pin.
Figure 5: Tool Preview.
3.4 Overall Tool Testing
Overall system testing is carried out after testing in
each part of the tool. The purpose of this test is to
understand how the esp32-based non-invasive blood
glucose meter works as shown in Figure 5. The whole
system of the whole system
Figure 6: Overall System Circuit.
Block diagram A shows the sensor network, the
output from the photodiode sensor is passed to pin A0
on the esp32,. Block B shows the overall picture of
the esp32 network and input from the tft lcd module,
.In block C there is a battery as a voltage source, and
in block D is the power supply network.suplay.
Figure 7: Overall View of the Tool.
Figure 6 shows the overall shape of the finished
tool, where all the components needed have been
assembled into a single unit and the tool is ready to
be used.
3.5 Reading Value Converter
The test between the 3 in 1 autocheck medical device
and the tool made has a different display of
measurement results so that conversion must be done
in order to get good results, the adc value is obtained
when taking measurements and then converted so that
the measurement results displayed show the mg/dl
value. this conversion is done withdengan
Nilai Gula Darah =
– 295
(2)
The test results after conversion are obtained
that are close to the 3 in 1 autocheck comparison tool.
As shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Measurement results.
3.6 Research Result
In this study, it was carried out by measuring ten
respondents who would be measured using a tool that
was made and simultaneously it would also be
measured with a 3-in autocheck tool, the
measurement data would be written into a table to
find out the measurement error between the tool made
and the tool used as a comparison. shown in table 3.
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
384
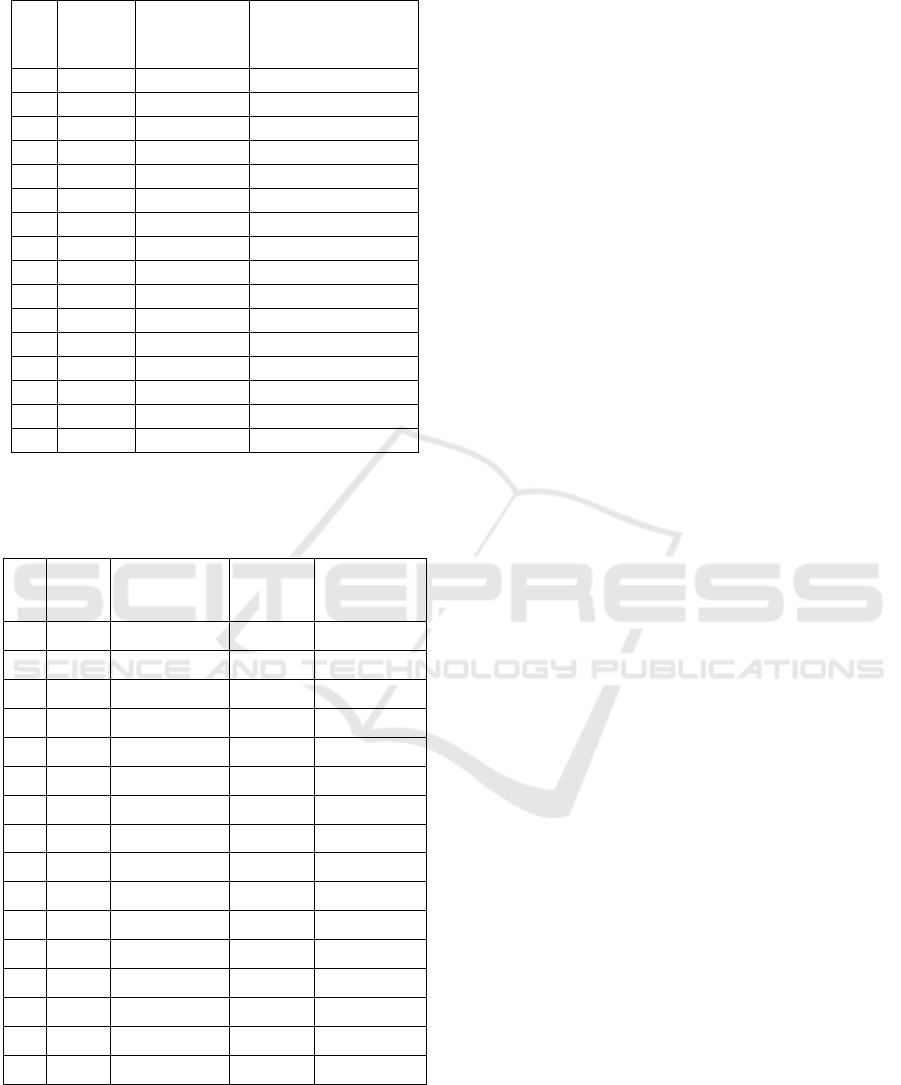
Table 3: Blood Sugar Level Measurement Results
No ADC
Conversion
Value
(mg/dL)
Standard Value
(mg/dL)
1
776 93 96
2
740 75 78
3
765 87,5 91
4
779 94,5 97
5
810 110 113
6
706 58 62
7
768 89 91
8
804 107 110
9
713 61,5 65
10
780 95 99
11
878 144 148
12
868 139 147
13
847 128,5 135
14
770 90 93
15
720 65 69
16
790 100 103
3.7 Persentasi Error
Table 4: Presentation Error.
No ADC
Nilai Konversi
(mg/ dL)
Nilai
Standart
(mg/dL)
Keakurasian
1 776 93 96 3,13%
2 740 75 78 3,13%
3 765 87,5 91 3,65%
4 779 94,5 97 2,60%
5 810 110 113 3,13%
6 706 58 62 4,17%
7 768 89 91 2,08%
8 804 107 110 3,13%
9 713 61,5 65 3,65%
10 780 95 99 4,17%
11 878 144 148 4,17%
12 868 139 147 4,17%
13 847 128,5 135 4,69%
14 770 90 93 3,13%
15 720 65 69 4,17%
16 790 100 103 3,13%
The results obtained from the overall instrument
testing will be compared with the results obtained
from the invasive blood sugar measuring instrument
namely the glucometer so that the percentage error is
obtained using the equation.
4 CONCLUSIONS
After carrying out the design and manufacture of the
tool, which is then followed by the testing and
analysis phase, the following conclusions can be
drawn: Measurable blood sugar levels of 25-
300mg/dLd, The resistance sensor used is sensitive to
the state of the blood when it is fresh and accurate.
reading persists 30 seconds after sensor reading,
Judging from the results of the calculation of the
percentage experienced a measurement error of 0% -
4.62% in 16 trials. Thus the tool cannot be used as a
reference for measuring blood sugar values in the
body. Judging from the results of the research, the
tools made show that the 11th to 16th measurements
show a decreasing accuracy. It takes a lag time of 1 to
3 minutes for the same patient or respondent to take
measurements again.
REFERENCES
F. Z. Kamilah et al., “Analysis of the Determinants of
Diabetes Mellitus in Indonesia: A Case Study of the
2014 Indonesian Family Life Survey,” Disease
Prevention and Public Health Journal, vol. 15, no. 2,
2021, doi: 10.12928/dpphj.v15i2.3079.
N. F. Fahmi, N. Firdaus, and N. Putri, “Article
PENGARUH WAKTU PENUNDAAN TERHADAP
KADAR GLUKOSA DARAH SEWAKTU DENGAN
METODE POCT PADA MAHASISWA.”
J. Fine et al., “Sources of inaccuracy in
photoplethysmography for continuous cardiovascular
monitoring,” Biosensors, vol. 11, no. 4. 2021. doi:
10.3390/bios11040126.
Design and Development of Esp32-Based Non-Invasive Blood Sugar Level Measurement Equipment
385
