
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial
Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method:
Opportunity-Resource Integration as Intermediary
Zhenying Xu
School of Business Administration, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, China
Keywords: Entrepreneurial Orientation, Market Orientation, Opportunity-Resource Integration, Entrepreneurial Perfor-
mance, SPSS Statistical Method.
Abstract: Start-ups need to take reasonable strategic orientation to deal with the turbulent and complex environment
and fierce market competition, so as to obtain resources to break through the dilemma of resource constraints.
Entrepreneurial orientation and market orientation play a key role in entrepreneurial performance, but there
is a lack of research based on the perspective of opportunity-resource integration. Therefore, based on dy-
namic capability theory and opportunity-resource integration theory, this paper constructs a 'orientation-pro-
cess-performance' model to explore the mechanism of the interaction between entrepreneurial orientation and
market orientation affecting the entrepreneurial performance of start-ups through opportunity-resource inte-
gration behavior.
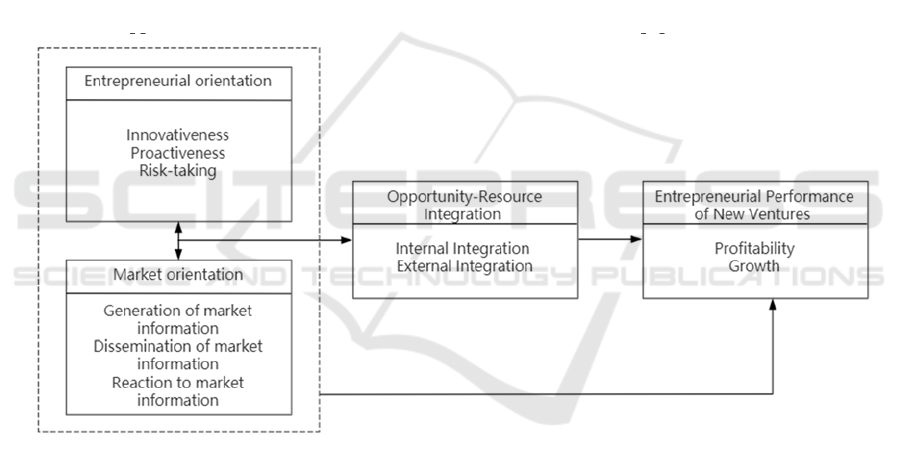
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, China is in a new stage of economic trans-
formation and social development. The state attaches
great importance to industrial upgrading and inde-
pendent innovation. Small and medium-sized enter-
prises have become the backbone of promoting eco-
nomic development. However, the failure rate of en-
trepreneurship is still very high. In the process of car-
rying out independent innovation activities, start-ups
are faced with the problem of how to improve entre-
preneurial performance through innovation. Studies
have shown that strategic orientation will have an im-
pact on entrepreneurial performance, especially en-
trepreneurial orientation and market orientation as the
key to independent innovation of new ventures. En-
trepreneurial orientation and market orientation are
not mutually exclusive.
They affect the competitiveness and performance
of enterprises from different perspectives. There are
more and more studies on the effective combination
of the two. Foreign scholars have realized the im-
portance of combining entrepreneurial orientation
and market orientation earlier. Both have their limita-
tions, and the combination can bring higher value.
Some studies have pointed out that the interaction be-
tween entrepreneurial orientation and market orienta-
tion has a positive effect on corporate performance,
but there is a lack of research on the mechanism of
entrepreneurial performance of start-ups.
Most of the research on entrepreneurial behavior
is based on the opportunity perspective or resource
perspective. However, the development and utiliza-
tion of opportunities and resources are two mutually
influential behaviors of enterprises in the entrepre-
neurial process, and the two are closely related. For
SMEs, continuous innovation and meeting customer
needs are the key to improving entrepreneurial per-
formance. Enterprises are driven by both technology
and market, and their entrepreneurial process is
driven by both opportunities and resources (Ge,
2020). In summary, based on dynamic capability the-
ory and opportunity-resource integration theory, this
paper constructs a 'orientation-process-performance'
model to explore the mechanism by which the inter-
action between entrepreneurial orientation and mar-
ket orientation affects the entrepreneurial perfor-
mance of start-ups through opportunity-resource inte-
gration behavior.
108
Xu, Z.
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method: Opportunity-Resource Integration as Intermediary.
DOI: 10.5220/0012026600003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 108-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
AND RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
2.1 Interaction Between
Entrepreneurial Orientation and
Market Orientation and
Opportunity-Resource Integration
There have been many studies on the impact of the
interaction between entrepreneurial orientation and
market orientation on corporate performance. How-
ever, there is a lack of research on the interaction be-
tween the two for the opportunity-resource integra-
tion entrepreneurial process. Opportunity-resource
integration entrepreneurial process is divided into op-
portunity-resource internal integration and oppor-
tunity-resource external integration. According to the
opportunity-resource integration theory, opportuni-
ties and resources are closely related and indispensa-
ble in the process of enterprise entrepreneurship. The
dynamic balance between the two has a profound im-
pact on the development of start-ups. Entrepreneurial
success depends on the high level of internal and ex-
ternal integration.
Entrepreneurial orientation reflects the attitude of
enterprises to cope with changes and risks, and is a
key strategic measure for start-ups to survive in a
fierce competitive environment (Hu, 2012). Enter-
prises with entrepreneurial orientation have higher in-
novation awareness than other enterprises. Most of
these enterprises pursue innovation, actively develop
new products and technologies, dare to face risks, and
actively influence and change the surrounding envi-
ronment. In a turbulent market environment, entre-
preneurial firms grasp new opportunities by identify-
ing and utilizing external scarce resources to achieve
external opportunity-resource integration, and inte-
grate and utilize internal resources to create new op-
portunities and achieve internal opportunity-resource
integration. Market orientation is reflected in the stra-
tegic behavior of enterprises to obtain customer and
market information. In the stage of information gen-
eration, enterprises can identify potential changes in
the market, discover and utilize new external oppor-
tunities and resources, and realize the external inte-
gration of opportunities and resources. In the stage of
information dissemination and response, enterprises
obtain new opportunities by deploying existing inter-
nal resources, and realize the internal integration of
opportunity-resources. Making full use of the role of
market orientation is reflected in the process of iden-
tifying market opportunities, which helps to enhance
the dynamic capabilities of enterprises (Zahra, 2008),
thus promoting the entrepreneurial process of oppor-
tunity-resource integration.
The study of Kumar et al. (2011) (Kumar, 2011)
shows that the interaction of multiple strategic orien-
tations is the key to the success of start-ups, and a sin-
gle orientation is difficult to maintain long-term ad-
vantages. This shows that the interaction effect of en-
trepreneurial orientation and market orientation is
better than single orientation on the opportunity-re-
source integration process. In summary, this paper
proposes the following hypothesis:
H1: The interaction between entrepreneurial ori-
entation and market orientation has a positive impact
on opportunity-resource integration.
2.2 The Interaction Between
Entrepreneurial Orientation and
Market Orientation and
Entrepreneurial Performance
The interaction between entrepreneurial orientation
and market orientation plays different roles in the de-
velopment of start-ups and affects entrepreneurial
performance from different aspects. Zahra (2008)
be-
lieves that entrepreneurial orientation and market ori-
entation reflect the complementarity of organiza-
tional capabilities, and the emphasis on market orien-
tation will strengthen the relationship between entre-
preneurial orientation and financial performance. Ah-
madi (2016) (Ahmadi, 2016) conducted an empirical
study on new technology enterprises. The results
show that the combination of entrepreneurial orienta-
tion and market orientation can produce greater utility
and improve product performance. The combination
of market orientation and entrepreneurial orientation
plays a positive role in the overall development of en-
terprises, reflected in product innovation, profitability
and customer response (González‐Benito Ó, 2009).
Entrepreneurial orientation is closely related to
the behavior of enterprises to seize market opportuni-
ties. Innovation, initiative and risk-taking are the
three main aspects of entrepreneurial orientation.
Highly entrepreneurial-oriented companies often pur-
sue progress, break through the old framework con-
straints to adapt to the new environment, and base
themselves on long-term future development (Zhu,
2018). However, too much emphasis on innovation
will bring high uncertainty and risk to enterprises.
Sun (2019) (Sun, 2019) believed that enterprises need
to combine market orientation and balance the poten-
tial risks in entrepreneurship by paying close attention
to changes in the market environment. Market orien-
tation reflects the attitude of enterprises to external
factors such as customers and government (Kohli,
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method: Opportunity-Resource
Integration as Intermediary
109

1990), which is mainly reflected in the behavior of
enterprises to generate, transmit and respond to mar-
ket information. Enterprises that attach importance to
market orientation are more sensitive to potential
risks in market operation, and the pursuit of certainty
can reduce the uncertainty risk generated by entrepre-
neurial orientation. The comprehensive consideration
of the two is conducive to improving entrepreneurial
performance.
According to the dynamic capability theory, start-
ups need to rationally allocate and utilize various in-
ternal and external resources to cope with the rapidly
changing market to ensure their dominant position.
Market orientation can improve enterprises ' under-
standing of the market, clarify the direction of enter-
prises ' efforts, reduce enterprises ' excessive risk-tak-
ing behavior, and reduce the possibility of risks
caused by wrong decisions. Firms that adhere to en-
trepreneurial orientation actively identify potential
opportunities in the environment and promote busi-
ness change through innovative behavior can avoid
the lag and structural inertia of market orientation.
The interaction between the two is conducive to im-
proving entrepreneurial performance. In summary,
this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
H2: The interaction between entrepreneurial ori-
entation and market orientation has a positive impact
on entrepreneurial performance.
2.3 Opportunity-Resource Integration
and Entrepreneurial Performance
Entrepreneurship is a complex process. Start-ups
want to gain a foothold in the market, need to interact
with the internal and external environment, and adapt
to environmental changes by constantly learning to
actively adjust their behavior (Day, 2011). Enter-
prises want to gain a competitive advantage in a com-
petitive business environment to win long-term de-
velopment, is inseparable from the efficient develop-
ment of opportunities and resources. Some scholars
explain the relationship between the two from the per-
spective of opportunity recognition. They believe that
the identification of opportunities is the beginning of
entrepreneurship, enterprises in the process of entre-
preneurship demand for resources. When they obtain
resources, they will screen them and explore new op-
portunities (Cai, 2011; Eckhardt, 2003). The organi-
zation ' s internal resources flow with the opportunity
to selectively attract external resources, especially
some scarce resources (Ardichvili, 2003). Therefore,
the identification of opportunities and resource iden-
tification of mutual coordination, together contrib-
uted to new business opportunities for product devel-
opment or service upgrade laid the foundation. Some
scholars have studied from the perspective of the re-
lationship between opportunity utilization and re-
sources, and concluded that opportunity utilization
requires effective resource matching. Hills et al.
(1995) (Hills, 1995) consider the use of opportunities
and resources as a process of matching needs and re-
sources between unnoticed opportunities and un-
derutilized resources. Opportunity utilization and re-
source allocation at the same time, in order to realize
the opportunity, the integration of existing resources,
while the development of new resources, promote the
development of opportunities, and ultimately the out-
put of new products and new services, enhance entre-
preneurial performance. In Gaoyang et al. (2019)
(Gao, 2019), through research, it is concluded that op-
portunity-resource integration will have a positive ef-
fect on corporate entrepreneurial performance. The
internal integration and external integration of oppor-
tunity-resource are not independent of each other.
The two are complementary and both are conducive
to improving corporate performance. Li et al. (2021)
(Li, 2021) conducted an empirical study on 274 new
ventures, and concluded that the interaction of oppor-
tunity-resources internal integration and opportunity-
resources external integration has a positive effect on
entrepreneurial performance. The flexible allocation
of resources is conducive to opportunity develop-
ment, enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises
and bringing higher entrepreneurial performance
(Hitt, 2001). Previous studies have confirmed that
there is a positive correlation between opportunity-re-
source integration and corporate performance. Sys-
tematically balancing opportunities and resources is
conducive to start-ups to cope with risks in entrepre-
neurship and improve entrepreneurial performance
more comprehensively. When the enterprise imple-
ments the opportunity-resource integration strategy,
the internal and external integration reaches a high
level. The two can promote each other and comple-
ment each other, and work together to improve the
entrepreneurial performance of the enterprise. In
summary, this paper proposes the following hypothe-
sis:
H3: Opportunity-resource integration has a posi-
tive impact on entrepreneurial performance.
2.4 The Mediating Role of
Opportunity-Resource Integration
There are many studies on the impact of the interac-
tion between entrepreneurial orientation and market
orientation on corporate performance, but there are
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
110
few studies on the mediating role of opportunity-re-
source integration. The strategic orientation of enter-
prise capability will not automatically bring better
performance, but through the enterprise internal val-
ues and beliefs cause behavior change and then affect
the performance of enterprises (Zhou, 2005). Sarkar
et al. (2016) (Sarkar, 2016) found through research
that strategic orientation is a necessary condition for
long-term success of enterprises, but it is not a suffi-
cient condition, and it needs to be combined with
other behaviors or capabilities to play a role. Boso
(2018) (Boso, 2018) believes that entrepreneurial ori-
entation and market orientation do not have a direct
impact on corporate performance alone or together.
They must first recombine corporate resources and
processes to improve performance. Shane (2000)
(Shane, 2000) studied the relationship between op-
portunities and resources, and found that the develop-
ment of enterprises depends on the acquisition and
utilization of opportunities and resources, and the
continuous integration of resources is a necessary
condition for mining new opportunities. Facing the
complex and changeable market environment, start-
ups need to do their best to integrate opportunity-re-
sources to achieve higher entrepreneurial perfor-
mance. Therefore, the opportunity-resource integra-
tion theory will affect the interaction between entre-
preneurial orientation and market orientation on en-
trepreneurial performance. Therefore, this paper pro-
poses the following hypothesis:
H4: Opportunity-resource integration plays an in-
termediary role between entrepreneurial orientation,
market orientation interaction and entrepreneurial
performance.
In summary, the mechanism between the interac-
tion of entrepreneurial orientation and market orien-
tation and the entrepreneurial performance of start-
ups is basically determined, in which opportunity-re-
source integration is a mediating variable. The re-
search model of this paper is as follows:
Figure 1: Theoretical model of the study.
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
3.1 Sample and Data
Affected by the local epidemic situation, this study
mainly collects data from the respondents by sending
WeChat links and filling in questionnaires. The re-
search objects are start-ups with a history of no more
than 8 years. A total of 235 questionnaires were dis-
tributed in this study. After filtering and screening,
215 valid questionnaires were obtained, with an ef-
fective recovery rate of 91%. The personnel of the
surveyed enterprises are mainly concentrated in the
Yangtze River Delta region of China with relatively
high entrepreneurial activity.
3.2 Variable Measurement
The questionnaire on the impact of entrepreneurial
orientation, market orientation and opportunity-re-
source integration on entrepreneurial performance of
start-ups has 28 items, including entrepreneurial ori-
entation, market orientation, opportunity-resource in-
tegration and entrepreneurial performance. The ques-
tionnaire uses the Likert 5-level scale, and the re-
spondents choose to score from 1 to 5 according to
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method: Opportunity-Resource
Integration as Intermediary
111
the actual situation. Among them, 1 means very disa-
gree and 5 means very agree. The design of various
items is based on literature research and pre-analysis
data, which has been modified and improved. The en-
trepreneurial orientation scale adopts the three-di-
mensional scale of entrepreneurial orientation of
Covin and Slevin (1989) (Covin, 1989) and Li Xuel-
ing et al. (2010) (Li, 2010), which is measured from
three aspects: innovation, initiative and risk-taking,
with a total of 9 items. The market orientation scale
refers to the market-oriented behavior scale of Jawor-
ski and Kohli (1993) (Jaworski, 1993) and Zhou et al.
(2008) (Zhou, 2008). It is measured from three as-
pects: the generation, dissemination and response of
market information. There are 7 items. According to
the research scale of Gao Yang et al. (2019), the de-
gree of opportunity-resource integration is measured
from two aspects of internal and external integration,
with a total of 6 items. In addition, based on the scale
of Spanjer and Van (2017) (Spanjer, 2017), the entre-
preneurial performance of start-ups is measured from
the two aspects of profitability and growth, with a to-
tal of 6 items. In terms of control variables, it is con-
sidered that enterprise age and enterprise size are the
influencing factors of entrepreneurial performance of
start-ups, as variables to control organizational sce-
narios, in order to obtain stable research conclusions.
3.3 Reliability and Validity Analysis
This study used SPSS25.0 software to measure relia-
bility and validity. This paper tests the reliability of
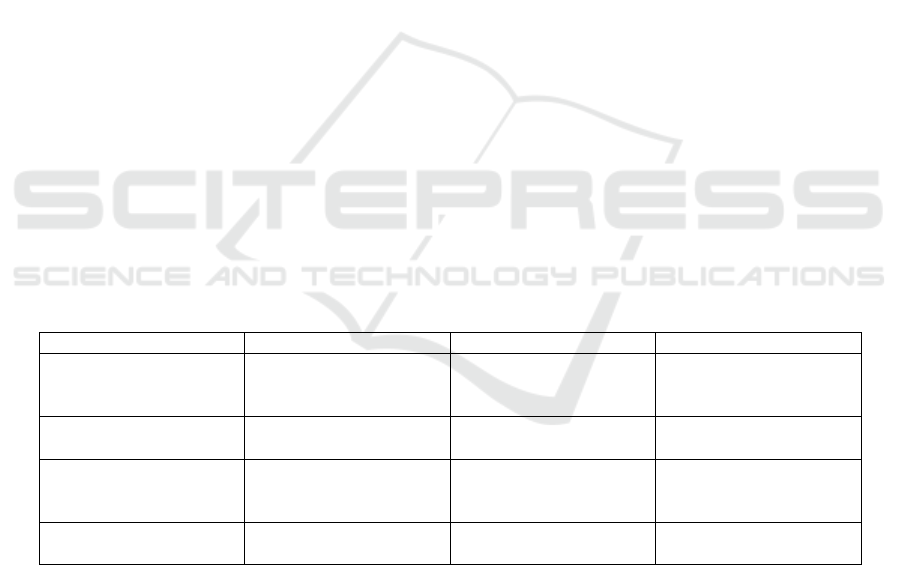
each scale by Cronbach's α coefficient test. As shown
in Table 1, the α values of each variable and its di-
mensions are greater than 0.7, indicating that the sta-
bility and internal consistency of the scale are good.
In terms of validity, many scholars have tested the
content validity of the scale for many times, so the
measurement scales used in this paper are relatively
mature, so the content validity of the scale is good. In
view of the structural validity, this paper uses the fac-
tor analysis method to test. Through the calculation of
SPSS25.0 data analysis software, the KMO values of
the measurement scale are all greater than 0.7. The
Bartlett spherical test sig values of the three variables
were all equal to 0.000, indicating that the signifi-
cance level was reached. Thus, the study sample data
is suitable for factor analysis, the variable measured
items have common factors and can be extracted. In
this paper, the principal component method is used to
extract the common factors of the pre-test data varia-
bles by setting the eigenvalue range of the extracted
factors to be greater than 1, and the factors are orthog-
onally rotated by the maximum variance method.
Then by observing the rotated factor loading matrix,
the number of common factors extracted from each
scale is consistent with the division of each variable
dimension in this study. Therefore, the structural va-
lidity of each scale is also good. The specific values
of the reliability and validity test are shown in Table
1.
Table 1: Reliability and validity analysis.
Variable Cronbach'sα Sig value KMO value
Entrepreneurial orienta-
tion
0.841
0.000
0.904
Market orientation
0.815 0.000 0.857
Opportunity-resource in-
tegration
0.770
0.000
0.843
Entrepreneurial perfor-
mance
0.752
0.000
0.758
4 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Main Effect Test
In this study, the hierarchical regression analysis
method is used to test the research hypothesis, and the
regression model shown in Table 2 is obtained. The
specific analysis is as follows: model 1 is the regres-
sion model of control variables on opportunity-re-
source integration, and model 2 is the interaction be-
tween entrepreneurial orientation and market orienta-
tion on opportunity-resource integration. The results
show that the regression coefficient of entrepreneurial
orientation*market orientation to opportunity-re-
source integration is 0.620 (p<0.01), hypothesis 1 is
verified. Model 3 is the regression model of control
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
112

variables on entrepreneurial performance. Model 4
adds the impact of entrepreneurial orientation*market
orientation on entrepreneurial performance on the ba-
sis of model 3. The results show that the interaction
between entrepreneurial orientation and market ori-
entation has a positive impact on entrepreneurial per-
formance (β=0.590, p<0.01), and hypothesis 2 is es-
tablished. The results of Model 5 show that oppor-
tunity-resource integration has a significant impact on
entrepreneurial performance of new ventures
(β=0.609, p<0.01), and Hypothesis 3 is verified.
4.2 Mediation Effect Test
By comparing the data of Model 4-6 and combining
the analysis results of Model 2, it can be seen that the
preconditions for the establishment of the mediating
effect have been met. According to model 6, when the
independent variables and mediating variables are
added to the regression equation, the interaction be-
tween entrepreneurial orientation and market orienta-
tion is still positively correlated with the innovation
performance of new ventures (β=0.347, p<0.01), and
the opportunity-resource integration positively af-
fects the entrepreneurial performance of new ventures
(β=0.392, p<0.01). This shows that opportunity re-
source-integration plays a partial mediating role be-
tween the interaction of entrepreneurial orientation
and market orientation and the entrepreneurial perfor-
mance of new ventures. According to the above anal-
ysis hypothesis 4 is verified.
Table 2. Regression model and results
Variable
Opportunity-resource integration Entrepreneurial performance
Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5 Model 6
Enterprise age 0.075 0.034 0.164
*
0.124
*
00.118
*
0.111
*
Enterprise
scale
0.093 0.049 -0.061 -0.103
*
-0.118
**
-0.122
**
EO*MO 0.620
**
0.590
**
0.347
**
Opportunity-
resource inte-
g
ration
0.609
**
0.392
**
R
2
0.020 0.399 0.033 0.377 0.396 0.469
Ad
j
.R
2
0.010 0.391 0.024 0.368 0.388 0.459
F-value 2.122 46.781
***
3.619
*
42.506
***
46.182
***
46.384
***
Note:
*
p<0.05,
**
p<0.01,
***
p<0.001.
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Research Conclusions
Due to the large number of small and medium-sized
enterprises, they have become the main driving force
of our country 's economic development. However,
due to the new weakness, new enterprises are con-
strained in terms of resources, capabilities and so on.
Therefore, new ventures need to pay close attention
to market changes and adopt a variety of strategic ori-
entations to efficiently develop and utilize opportuni-
ties and resources, so as to improve entrepreneurial
performance. This paper reveals the mechanism of
the interaction between entrepreneurial orientation
and market orientation on entrepreneurial perfor-
mance of start-ups, and explores the mediating role of
opportunity-resource integration. Through empirical
analysis, the following conclusions are drawn: First,
the interaction between entrepreneurial orientation
and market orientation has a positive and significant
impact on entrepreneurial performance and oppor-
tunity-resource integration of start-ups. Therefore,
new enterprises need to combine the two strategic ori-
entations to promote the efficient development of op-
portunities and resources, and give full play to the
complementary role of the two on business perfor-
mance. Secondly, opportunity-resource integration
has a significant positive impact on entrepreneurial
performance of start-ups. It shows that in the context
of resource constraints, new enterprises need to coor-
dinate and integrate opportunities and resources, cob-
ble together internal resources to create new opportu-
nities, identify external resources to find new oppor-
tunities, and bring higher performance to enterprises
through high integration of internal and external.
Third, opportunity-resource integration plays an in-
termediary role between the interaction of entrepre-
neurial orientation and market orientation and entre-
preneurial performance of start-ups. This conclusion
shows that, on the one hand, start-ups enhance their
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method: Opportunity-Resource
Integration as Intermediary
113

awareness of the environment and promote the devel-
opment and utilization of opportunities and resources
by combining entrepreneurial orientation and market
orientation. On the other hand, the improvement of
opportunity-resource integration of start-ups helps to
improve entrepreneurial performance.
5.2 Research Significance
From the perspective of academic research, firstly,
this paper enriches the research on opportunity-re-
source integration. Most of the existing studies on op-
portunities and resources are based on a single per-
spective of opportunities or resources (Fan, 2021).
The existing research on opportunity-resource inte-
gration is mainly based on concept and dimension
discussion, and lacks in-depth research on oppor-
tunity-resource integration entrepreneurial behavior.
Secondly, it enriches the existing theoretical system
of entrepreneurship research. By sorting out the exist-
ing literature and analyzing the actual situation of
start-ups, this paper studies the impact of strategic ori-
entation interaction on start-up entrepreneurial per-
formance through opportunity-resource integration
by constructing the theoretical model of ' orientation-
process-performance ' of start-ups.
From a practical point of view, through the study
of the impact of the interaction between entrepreneur-
ial orientation and market orientation on the entrepre-
neurial performance of start-ups, start-ups are guided
to make strategic choices. Secondly, through the
study of the mediating effect of opportunity-resource
integration, this paper explores the mechanism of the
interaction between entrepreneurial orientation and
market orientation on the entrepreneurial perfor-
mance of start-ups, guides start-ups to pay attention
to the characteristics of dual channels of opportunities
and resources, and coordinates and integrates the two,
so as to win competitive advantages and achieve
high-quality development of enterprises.
5.3 Research Limitations
Although this study reveals the mechanism of the in-
teraction between entrepreneurial orientation and
market orientation, opportunity-resource integration
on the relationship between entrepreneurial perfor-
mance of start-ups, the proposition is novel and inno-
vative, but there are still some shortcomings.
First, the nature of data is limited. This paper is a
study of cross-sectional data, and the sample size is
relatively small, there are some defects in the support
of causality. If longitudinal large sample data can be
obtained, it can provide more powerful empirical sup-
port for the interaction between entrepreneurial orien-
tation and market orientation, the relationship be-
tween opportunity-resource integration and entrepre-
neurial performance of start-ups; second, the limita-
tions of research variables. This paper only focuses
on enterprise-level factors such as strategic orienta-
tion and opportunity-resource integration behavior,
and does not examine the impact of external environ-
mental dynamic factors such as market volatility,
competition intensity, and technological changes.
Therefore, the determinants of entrepreneurial perfor-
mance cannot be completely excluded.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China under Grant
(72172142).
REFERENCES
Ahmadi H, O'Cass A. The role of entrepreneurial marketing
in new technology ventures first product commerciali-
zation[J]. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 2016, 24(1):
47-60.
Ardichvili A, Cardozo R, Ray S. “A theory of entrepreneur-
ial opportunity identification and development”, Jour-
nal of Business Venturing, 2003, 18(1): 105-123.
Boso N, Annan J, Adeleye I, et al. Examining the paths
from export strategic orientations to export perfor-
mance: The mediating role of export resource transfor-
mation capability[J]. Thunderbird International Busi-
ness Review, 2018, 60(2): 207-230.
Cai L, Zhu X M. Liu Y. “The impact of entrepreneurship
orientation on new firms’ resource obtainment”, [J].
Studies in Science of Science, 2011, 4 (5): 601-609.
Covin J G, Slevin D P. Strategic management of small firms
in hostile and benign environments[J]. Strategic man-
agement journal, 1989, 10(1): 75-87.
Day G S. Closing the marketing capabilities gap[J]. Journal
of marketing, 2011, 75(4): 183-195.
Eckhardt J T, Shane S A. Opportunities and entrepreneur-
ship[J]. Journal of management, 2003, 29(3): 333-349.
Fan Xu, Liang Bichan. The evolution of innovation mode
of small and medium technology enterprises under the
synergy of opportunity identification and ambidextrous
strategy combinations[J]. Chinese Journal of manage-
ment,2021,18(06):873-883.
Gao Yang, Xue Xingqun, Ge Baoshan. An empirical re-
search on impacts of the integration of opportunity and
resource and social network on entrepreneurial perfor-
mance [J]. Studies in Science of Science,2019,37(12):
2211-2221. DOI: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-
2053.2019.12.011.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
114

Ge Baoshan, Wang Zhiguo. A review of the research on
hidden champion entrepreneurship and prospects [J]
Foreign Economics & Management, 2020, 42(11):20-
32. DOI: 10.16538/j.cnki.fem.20200904.401.
González‐Benito Ó, González‐Benito J, Muñoz‐Gallego P
A. Role of entrepreneurship and market orientation in
firms' success[J]. European Journal of Marketing, 2009.
Hitt M A, Ireland R D, Camp S M, et al. Strategic entrepre-
neurship: Entrepreneurial strategies for wealth crea-
tion[J]. Strategic management journal, 2001, 22(6‐7):
479-491.
Hills G E, Hansen D J, Merrilees B. Research at the Mar-
keting/Entrepreneurship Interface[J]. International
Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 1995.
Hu Wangbing, Zhang Yuli. Measuring and functions of
new venture’s entrepreneurial orientation: an empirical
study in China [J]. Management Review, 2012, 24(03):
40-48+57. DOI: 10.14120/j.cnki.cn11-
5057/f.2012.03.015.
Jaworski B J, Kohli A K. Market orientation: antecedents
and consequences[J]. Journal of marketing, 1993,
57(3): 53-70.
Kohli A K, Jaworski B J. Market orientation: the construct,
research propositions, and managerial implications[J].
Journal of marketing, 1990, 54(2): 1-18.
Kumar V, Jones E, Venkatesan R, et al. Is market orienta-
tion a source of sustainable competitive advantage or
simply the cost of competing? [J]. Journal of marketing,
2011, 75(1): 16-30.
Li N, Sun Y, Jiang D, et al. Exploring the moderating effect
of interpersonal emotion regulation between the inte-
gration of opportunity and resource and entrepreneurial
performance[J]. Frontiers in Psychology, 2021, 12:
756767.
Li Xueling, Yao Yiwei, Wang Lijun. Research on the rela-
tionship between new venture entrepreneurial orienta-
tion and innovative performance: proactive market ori-
entation as a mediator[J]. China Industrial Economics,
2010 (6): 116-125.
Sarkar S, Coelho D M, Maroco J. Strategic orientations, dy-
namic capabilities, and firm performance: An analysis
for knowledge intensive business services[J]. Journal of
the Knowledge Economy, 2016, 7(4): 1000-1020.
Shane S, Venkataraman S. The promise of entrepreneurship
as a field of research[J]. Academy of management re-
view, 2000, 25(1): 217-226.
Spanjer A, van Witteloostuijn A. The entrepreneur’s expe-
riential diversity and entrepreneurial performance[J].
Small Business Economics, 2017, 49(1): 141-161.
Sun W, Price J, Ding Y. The longitudinal effects of interna-
tionalization on firm performance: The moderating role
of marketing capability[J]. Journal of Business Re-
search, 2019, 95: 326-337.
Zahra S A. Being entrepreneurial and market driven: impli-
cations for company performance[J]. Journal of strat-
egy and management, 2008.
Zhu C, Liu A, Chen G. High performance work systems and
corporate performance: the influence of entrepreneurial
orientation and organizational learning[J]. Frontiers of
Business Research in China, 2018, 12(1): 1-22.
Zhou K Z, Yim C K, Tse D K. The effects of strategic ori-
entations on technology-and market-based break-
through innovations[J]. Journal of marketing, 2005,
69(2): 42-60.
Zhou K Z, Li J J, Zhou N, et al. Market orientation, job sat-
isfaction, product quality, and firm performance: evi-
dence from China[J]. Strategic management journal,
2008, 29(9): 985-1000.
Analysis of the Influence of Strategic Orientation on Entrepreneurial Performance Based on SPSS Statistical Method: Opportunity-Resource
Integration as Intermediary
115
