
Analysis of Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Construction
Enterprises Based on Combination Empowerment Method
Yinghui Xiang
a
, Zheng Liu
*b
and Weiwei Zhu
c
School of Management, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang 110168, China
Keywords: Overseas Construction Enterprises, Social Responsibility, Combination Weighting Method, Index of
Evaluation.
Abstract: In the context of the development of the "Belt and Road Initiative", in order to ensure that Chinese overseas
construction enterprises can better fulfill their corresponding social responsibilities in the international market,
this paper, from the perspective of stakeholders, constructs a social responsibility evaluation index system of
Chinese overseas construction enterprises, including 5 first-level indexes such as customers, employees,
environment, community and local government responsibilities, and 21 second-level indexes. Using AHP and
entropy weight method to determine the weight of each relevant evaluation index, then taking the PKM project
in Pakistan undertaken by the overseas division of Chinese construction company as a practical case, and
using the extreme value method to conduct dimensionless processing of some indexes. In addition, the
relevant indexes of the enterprise are analyzed and classified, so as to obtain the grade of the enterprise's social
responsibility, and then encourage the relevant similar enterprises in China to better fulfill their social
responsibility in the construction process.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of the "Belt and Road
Initiative" policy, Chinese construction and
engineering enterprises are playing an increasingly
important role around the world. Under the current
situation, the issue of green development and social
stability have gradually attracted attention, especially
in the countries along the "Belt and Road Initiative".
As an important factor to improve the sustainability
of major projects, social responsibility has gradually
attracted the attention of overseas construction
enterprises.
In recent years, domestic scholars have conducted
extensive research on the social responsibility of
construction enterprises. Wang Xuetong et al. (2020)
conducted an empirical analysis of different types of
CSR expectations of construction enterprises in
countries along the "Belt and Road Initiative" and
found that Chinese construction enterprises should
fully consider their CSR expectations in these
countries. Xie Linlin et al.(2018) believe that
construction enterprises have a one-sided
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-23338-4444
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2377-4000
understanding of social responsibility, pay too much
attention to the construction process and ignore the
completion, and have insufficient understanding of
community public welfare and weak awareness of
information disclosure. Pang Yongshi et al. (2012)
calculated the importance of each attribute of the
most reduced set according to the existing disclosure
of the social responsibility of construction
enterprises, converted the importance of each
attribute into the weight of the index through
normalization processing, and obtained the weight
distribution of the first-level index and the second-
level index of the evaluation. From the perspective of
stakeholders, Wan Dongjun et al. (2020) combined
with the characteristics and current situation of
international projects, adopted the empirical
determination method to construct the CSR
performance evaluation index system of international
construction enterprises, and then determined the
direction that should be paid attention to in the CSR
performance of international enterprises.
At present, foreign countries, especially European
and American countries, have a good overall
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2387-4020
Xiang, Y., Liu, Z. and Zhu, W.
Analysis of Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Construction Enterprises Based on Combination Empowerment Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0012027900003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 191-197
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
191
awareness and implementation of social
responsibility of construction enterprises, and the
research results are relatively rich. Liao et al. (2017)
conducted a comparative study on the CSR reports of
international project contractors and Chinese
construction enterprises and found that the CSR
awareness and overall implementation in Europe are
better, while the CSR construction of Chinese
overseas construction enterprises is relatively low.
Based on the research of existing literature at home
and abroad, Jiang(2015) compared the research status
of the social responsibility of construction industry
and corporate social responsibility, and proposed that
the research on the social responsibility of
construction enterprises is in the preliminary stage.
Existing studies have proved that the
implementation of social responsibility of
construction enterprises is conducive to improving
the competitiveness of enterprises and creating a good
image and reputation for enterprises, but there is still
a lack of research on the definition of social
responsibility content and how to effectively
implement it. Therefore, this paper aims to: (1)
understand the social responsibility awareness and
current situation of Chinese overseas construction
enterprises through the text analysis of social
responsibility report; (2) establish a set of scientific
evaluation index system by reviewing literature and
consulting experts' opinions, and determine the index
weight to make the evaluation more objective and
reasonable, so as to help Chinese overseas
construction enterprises to clarify their social
responsibilities and better guide the construction of
corporate social responsibility in the process of the
"Belt and Road Initiative".
2 TO ESTABLISH A SOCIAL
RESPONSIBILITY
EVALUATION INDEX SYSTEM
OF CHINESE OVERSEAS
CONSTRUCTION
ENTERPRISES
2.1 Identification of Risk Factors
Due to the differences between overseas and domestic
construction projects, this paper selects the relevant
responsibilities of overseas construction enterprises
in full life cycle as customers, employees,
environment, community and local government,
which based on the analysis of existing literature and
combined with the general implementation process
and characteristics of international construction
projects.
2.2 Selection of Evaluation Indexes
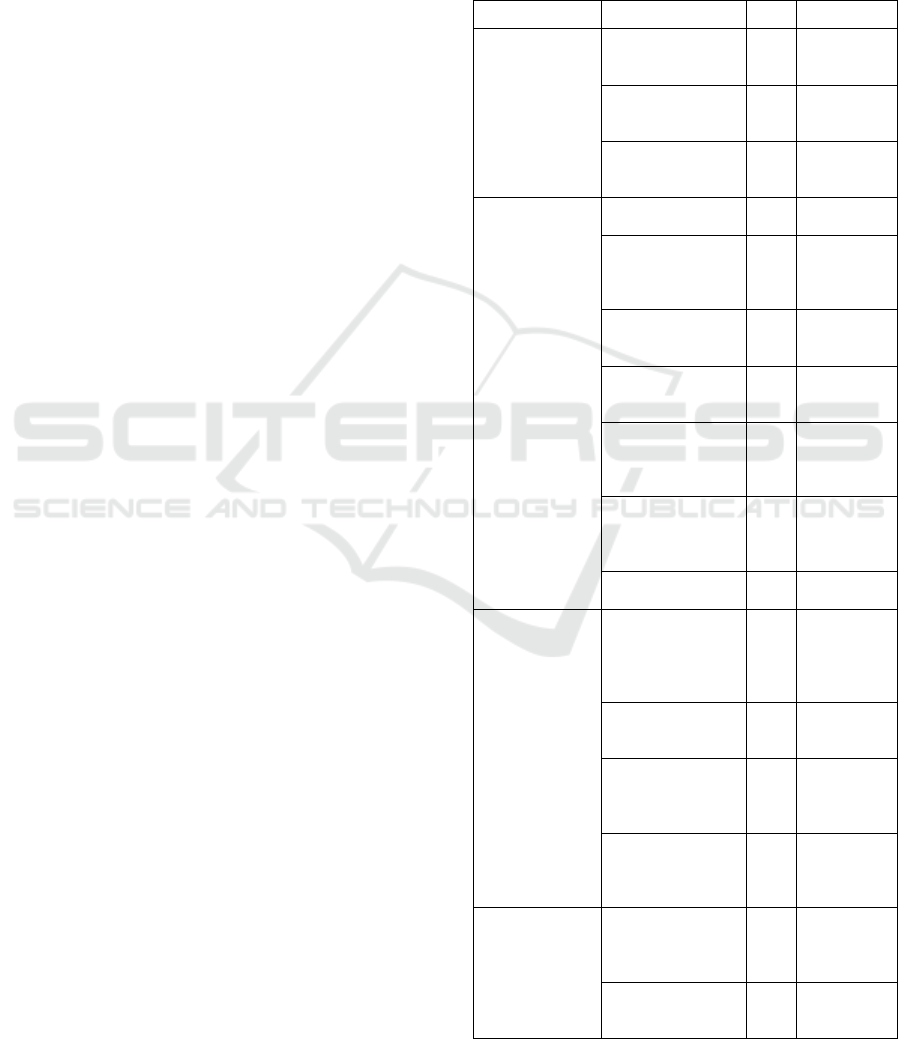
Table 1: Social responsibility evaluation index system of
Chinese overseas construction enterprises.
First-level index Second-level index Unit Nature
Responsibilities
of
Customers(A
1
)
Quality acceptance
rate of overseas
project (
A
11
)
% Quantitative
Quality
management
system(
A
12
)
Qualitative
Customer
satisfaction
rate(
A
13
)
% Quantitative
Responsibilities
of
Employees(A
2
)
Rate of wage
paymen
t
(
A
21
)
% Quantitative
Labor contract
signing rate of
overseas
employees(
A
22
)
% Quantitative
Overseas
employee
satisfaction(
A
23
)
% Quantitative
Injury death rate of
overseas
employees(
A
24
)
‰ Quantitative
Situation of
production and
safety protection
for employees(
A
25
)
Qualitative
Annual per capita
training funds for
overseas
employees(
A
26
)
yua
n
Quantitative
Care of female
employees(
A
27
)
Qualitative
Responsibilities
of
Environment(A
3
)
Environmental
acceptance rate of
construction
project
completion(
A
31
)
% Quantitative
Green building
construction
system(
A
32
)
Qualitative
Disposal
utilization rate of
construction
waste(
A
33
)
% Quantitative
Processing
compliance rate of
construction noise
and dus
t
(
A
34
)
% Quantitative
Responsibilities
of
Community(A
4
)
Promote the
construction of
local
infrastructure(
A
41
)
Qualitative
Whether to respect
local customs and
culture(
A
42
)
Qualitative
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
192

Degree of
participation in
community
activities(
A
43
)
Qualitative
Resource
investment in
materials
purchasing(
A
44
)
yua
n
Quantitative
Responsibilities
of Local
government(A
5
)
Promote the
development of
local enterprise
system(
A
51
)
Qualitative
Tax rate on
assets(
A
52
)
% Quantitative
Local employment
contribution
rate(
A
53
)
% Quantitative
At present, in addition to domestic or foreign
standards, there are also CSR reports issued by large
construction enterprises every year for the social
responsibility indexes screening of Chinese overseas
construction enterprises, so the representative indexes
can be selected as the research indexes (Zhu Jigao et
al., 2019). Finally, 5 first-level evaluation indexes and
21 second-level evaluation indexes of Chinese
overseas construction enterprises' social
responsibility are obtained, as shown in Table 1.
3 DETERMINING INDEXES
WEIGHTS
In this paper, the subjective and objective methods are
combined to determine the weight of indexes. Firstly,
AHP and entropy weight method are used to calculate
the weight, and then the required combined weight
value is calculated according to the principle of
minimum information entropy.
3.1 Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
to Determine the Indexes Weights
The AHP method is used to compare each index of
the same dimension, construct the judgment matrix
between them, and finally determine the weight of the
indexes through the consistency test. In order to make
the scoring results objective enough, we invited 20
experts working in different positions in overseas
construction companies, among which 40% were
engaged in Party A management, 30% were engaged
in third-party consulting services such as project
supervision, and 30% were from local management
personnel of the host country. The work experience
of these experts in the field of construction is more
than 10 years, and they are very familiar with the
characteristics of overseas construction industry. The
relevant discriminant matrix formed by the above
evaluation indexes can be constructed, and the
eigenvector of the matrix, namely the weight of each
factor, can be calculated by the root method. Multiply
each row of elements in the matrix to get the product
of each row of elements "K
i
":
∏
=
=
n
j
iji
bK
1
(1)
Using square root method to calculate the weight
of evaluation indexes, and calculating the NTH root
of "K
i
" to get "V
*
":
n
i
KV =
*
(2)
After the normalization of "V*", "V
i
" representing
the weight of each index is obtained:
=
=
n
i
i
V
V
V
1
*
*
(3)
3.2 Entropy Weight Method to
Determine the Indexes Weights
When determining the weight of each quantitative
index, the entropy weight method should be used to
confirm (Da Kening et al., 2018), in order to avoid the
error caused by human subjective factors affecting the
difference size of objective samples. The specific
processing process is as follows: suppose there are n
indexes, and define X
i
={X
1
, X
2
, ..., X
n
}. Through the
standardization of each index data, the value is
obtained as "Y
1
, Y
2
, ..., Y
n
", and then the normalization
process is carried out.
(
)
() ()
ijij
ijij
ij
xx
xx
y
minmax
min
−
−
=
(4)
Then the normalized matrix is obtained:
nm
yyy
yyy
yyy
Y
mnmm
n
n
*
21
22221
11211
=
(5)
According to the above standardized matrix, the
entropy of risk index is calculated:
ij
m
i
ijj
ppke
−= ln
(6)
In the formula, k>0,
m
k
ln
1
=
. The difference
degree of the JTH index is defined as "d
j
=1-e
j
", and
the defined weight of the evaluation index is obtained
as "
=
=
n
j
j
j
j
d
d
w
1
".
Analysis of Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Construction Enterprises Based on Combination Empowerment Method
193

3.3 Combination Weighting Method to
Determine the Comprehensive
Indexes Weights
In the weight distribution of indexes, the internal
statistical rules and authoritative values between
index data should be considered. In order to make up
for the deficiency caused by single weighting, this
paper adopts the combination weighting method to
determine the weight, that is, the subjective weight is
calculated by AHP, and the objective weight is
calculated by the entropy weighting method.
The comprehensive weight coefficient "Q
j
" of
each index is:
=
=
n
j
jj
jj
j
wv
wv
Q
1
(7)
"V
j
" is the weight coefficient calculated by AHP,
"W
j
" is the weight coefficient calculated by entropy
weight method. The final calculated combination
weights are shown in Table 2.
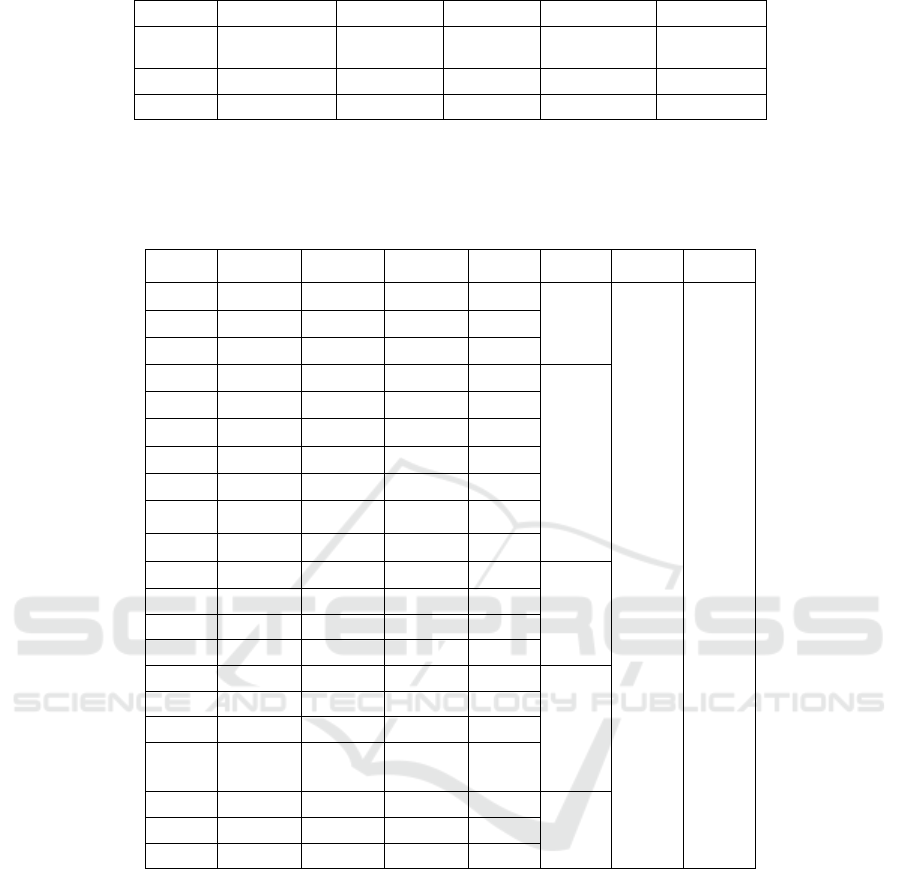
Table 2: Index weights based on AHP-entropy weight combination weighting method.
First-level index Weight Second-level index Weight Combination weight
Responsibilities of
Customers(A
1
)
0.3257
Quality acceptance rate of
overseas project (
A
11
)
0.4216 0.1373
Quality management
system(
A
12
)
0.3125 0.1018
Customer satisfaction
rate(
A
13
)
0.2659 0.0866
Responsibilities of
Employees(A
2
)
0.2762
Rate of wage payment(A
21
) 0.1467 0.0405
Labor contract signing rate
of overseas employees(
A
22
)
0.1127 0.0311
Overseas employee
satisfaction(
A
23
)
0.1413 0.0390
Injury death rate of
overseas employees(
A
24
)
0.1749 0.0483
Situation of production and
safety protection for
employees(
A
25
)
0.2682 0.0741
Annual per capita training
funds for overseas
employees(
A
26
)
0.0827 0.0228
Care of female
employees(
A
27
)
0.0735 0.0203
Responsibilities of
Environment(A
3
)
0.1048
Environmental acceptance
rate of construction project
completion(
A
31
)
0.2578 0.0270
Green building
construction system(
A
32
)
0.1737 0.0182
Disposal utilization rate of
construction waste(
A
33
)
0.4326 0.0453
Processing compliance rate
of construction noise and
dus
t
(
A
34
)
0.1359 0.0142
Responsibilities of
Community(A
4
)
0.1279
Promote the construction
of local infrastructure(
A
41
)
0.3577 0.0457
Whether to respect local
customs and culture(
A
42
)
0.1726 0.0221
Degree of participation in
community activities(
A
43
)
0.1852 0.0237
Resource investment in
materials purchasing(
A
44
)
0.2845 0.0364
Responsibilities of
Local government(A
5
)
0.1654
Promote the development
of local enterprise
system(
A
51
)
0.2187 0.0362
Tax rate on assets(A
52
)
0.3579 0.0592
Local employment
contribution rate(
A
53
)
0.4234 0.0700
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
194

4 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Introduction to Case
This paper takes the PKM project undertaken by
China State Construction Group Co., Ltd. in Pakistan
as the case, and makes an empirical analysis of the
social responsibilities undertaken by Chinese
overseas construction enterprises in the construction
process, so as to test the fulfillment of the social
responsibilities of the enterprises in the construction
process.
The PKM project (Sukkur-Multan section) starts
from Sukkur City of Sindh Province in the south and
ends in Multan, the economic center of Punjab
Province in the north, with a total length of 392km. It
is designed as a two-way 6-lane highway with ITS
(Intelligent Transportation System) and access
control. It is the first highway in Pakistan adopting
ITS, with a contract value of $2.889 billion. EPC
contract mode is adopted, and the contract period is
36 months. In the process of construction, there are
difficulties in project organization, design
communication and coordination, technical
difficulties, construction resources organization,
severe security situation and other engineering
construction difficulties.
4.2 Treatment of Standardization
Part of the data selected in this paper are from the
social responsibility reports released by enterprises,
such as the quality acceptance rate of overseas project
and tax rate on assets, etc. Some of them come from
within the enterprise and are obtained through
communication with the enterprise, such as the
customer satisfaction rate and labor contract signing
rate of overseas employees. And we choose expert
scoring to identify some unavailable data, qualitative
indexes and indexes requiring comprehensive
analysis. According to the rating value of the
evaluation factors, the comment set is adopted
accordingly, and the evaluation set is established
according to the evaluation index system. Finally, the
comment set is quantified and expressed by the
hundred-mark system interval, that is, "excellent,
good, general, poor, very poor" corresponds to the
ideal score of each evaluation level, which is
[100,90], (90,80], (80,70], (70,60], (60,0]
respectively.
Since the dimensions of each evaluation index
data is different, it is necessary to carry out
dimensionless processing. In this paper, extreme
value method is selected, and the specific method is
as follows:
(1) Processing of positive indexes. Set the index
standardized score corresponding to the maximum
value of each index of social responsibility of
overseas construction enterprises to 100 points, and
the index standardized score corresponding to the
minimum value to 60 points. And the standardized
scores of other indexes corresponding to the value of
this index are obtained with the linear difference
between 60 and 100 points.
()
()
ii
ii
i
CB
BX
E
−
−
+=
*40
60
(8)
(2) Processing of negative indexes. Set the index
standardized score corresponding to the minimum
value of each index of social responsibility of
overseas construction enterprises to 100 points, and
the index standardized score corresponding to the
maximum value to 60 points. And the standardized
scores of other indexes corresponding to the value of
this index are obtained with the linear difference
between 60 and 100 points.
()
()
ii
ii
i
CB
XB
E
−
−
+=
*40
60
(9)
Finally, the comprehensive evaluation value of
social responsibility of this case is obtained by
summing up the product of the standardized score of
each index and its weight.
=
=
21
1
*
i
ii
WEF
(10)
(3) Standardization of qualitative indexes.
Qualitative indexes are difficult to be processed by
quantitative standards, so the qualitative indexes are
scored according to the opinions of relevant experts,
as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Evaluation criteria of qualitative indexes.
Index [0,60) [60,70) [70,80) [80,90) [90,100]
A
12
very
imperfect
less perfect general
relatively
p
erfect
perfect
A
25
very poor poor general good excellent
A
27
very poor poor general good excellent
A
32
very
imperfect
less perfect general
relatively
p
erfect
perfect
Analysis of Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Construction Enterprises Based on Combination Empowerment Method
195
A
41
very poor poor general good excellent
A
42
very
disrespectful
less
respectful
general
relatively
respectful
respectful
A
43
very poor poor general good excellent
A
51
very poor poor general good excellent
4.3 Comprehensive Value of Case
Social Responsibility Evaluation
Table 4: Comprehensive score table of social responsibility indexes.
Index
B
i
(max)
C
i
(min)
X
i
E
i
W
i
F
Level of
case
A
11
100% 80% 96% 92.00
89.45
87.33 good
A
12
100 60 90.32 90.32
A
13
100% 85.46% 94.32% 84.37
A
21
100% 80% 93% 86.00
91.33
A
22
98.27% 85.33% 94.30% 87.72
A
23
100 60 89.82 89.82
A
24
0.15‰ 0 0.01‰ 97.33
A
25
100 60 93.47 93.47
A
26
2200
yuan
1300
yuan
1945.9yua
n
88.71
A
27
100 60 91.26 91.26
A
31
99.3% 91.5% 92.8% 66.67
78.22
A
32
100 60 81.26 81.26
A
33
95% 73% 87% 85.45
A
34
80% 46.2% 57.4% 73.25
A
41
100 60 91.35 91.35
85.08
A
42
100 60 77.23 77.23
A
43
0.95 0.65 0.82 82.67
A
44
874
million
yuan
456
million
yuan
699.3milli
on yuan
83.28
A
51
100 60 86.41 86.41
84.00
A
52
7.02% 2.53% 4.97% 81.73
A
53
30% 10% 22.34% 84.68
Note: The data in the table are based on China Construction Annual Social Responsibility Report, statistical yearbook, Belt
and Road Portal, relevant literature, questionnaire, etc.
Combined with each index and weight, the
standardized scores of 21 indexes were calculated
respectively, and the comprehensive value of the
social responsibility evaluation indexes of this case
was further calculated, so as to determine the grade of
the corporate social responsibility. The specific
results are shown in Table 4.
As can be seen from Table 4, the overall index
comprehensive score of the case is 87.33, indicating
that the overseas branches of China Construction
Group Co., Ltd. perform well in their overall social
responsibilities. Among the first-level indexes, the
score of "Responsibilities of Employees" is 91.33
points, indicating excellent performance. Meanwhile,
among the second-level indexes, the "Injury death
rate of overseas employees" has the highest score,
indicating that Chinese overseas construction
enterprises attach great importance to construction
safety, people-oriented, and pay attention to the
training and care of employees in the construction
process. The score of "Responsibilities of
Environment" is 78.22 points, which is relatively low.
The performance of environmental acceptance rate of
construction project completion is poor, which
indicates that the overseas construction enterprises in
China should strengthen environmental management
in the process of construction and protect the
surrounding environment at the same time. In terms
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
196

of customers, communities and local government, the
score of "Responsibilities of Local government" is
84.00, indicating that Chinese construction
enterprises should abide by the laws and regulations
of the host country, actively cooperate with the
relevant policies of the host country government, and
promote the better development of local enterprises in
the process of undertaking overseas project
construction. In the process of fulfilling social
responsibilities in local communities, the awareness
of social responsibility should be strengthened, and
sufficient attention should be paid to community
voluntary service, local market employment and
enterprise cooperation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the construction of the social responsibility
evaluation index system of overseas construction
enterprises under the background of the "Belt and
Road Initiative" and the adoption of reasonable
evaluation methods, this paper makes a detailed
analysis of their social responsibility construction
according to the actual situation of Chinese overseas
construction enterprises. From the theoretical level, it
is clear that the content orientation of overseas
construction enterprises should include 21 indexes
from 5 dimensions of "customers, employees,
environment, community and local government", and
the problems existing in the fulfillment of social
responsibilities of Chinese overseas construction
enterprises are analyzed. It also points out that
enterprises should pay attention to the cultivation of
employees, environment, community public welfare
and other dimensions in the process of cultivating
social responsibility, which can help enterprises
understand social responsibility more
comprehensively and provide theoretical basis for
their choice of social responsibility behavior.
REFERENCES
Da Kening, Peng Yifeng, Guo Baorong(2018). Research on
Urban Business environment based on entropy weight
method -- A case study of Shenyang City. J. Journal of
Shenyang Jianzhu University (Social Science Edition).
20(03): 250-255.
Jiang W, Wong J KW. Corporate Social Responsibility in
Construction: A Critical Review on Research
[C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium
on Advancement of Construction Management and
Real Estate. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2015: 1195-
1206.
Liao P, Xia N, Wu C, etal(2017). Communicating the
corporate social responsibility (CSR) of international
contractors: Content analysis of CSR reporting. J.
Journal of Cleaner Production. 156: 327-336.
Pang Yongshi, Wang Ying (2012). Evaluation index weight
determination of construction enterprises' social
responsibility based on Rough set. J. Journal of
Engineering Management. 26(03):109-113.
Wang Xuetong, Zhang Guanqiao, Song Xiangnan, Xian
Dixi (2020). Research on the social responsibility
expectations of construction enterprises in countries
along the "Belt and Road Initiative". J. Journal of
Engineering Management. 34(04): 16-21.
Wan Dongjun, Ma Xuerui, Sun Chengshuang (2020).
Research on CSR Performance Evaluation Index
System of international engineering contractors. J.
Journal of Beijing University of Civil Engineering and
Architecture. 36(01):91-98.
Xie Linlin, Han Ting, Hu Yi, Le Yun (2018). Chinese
construction enterprise social responsibility index
system. J. Journal of Civil Engineering and
Management. 35(06):36-42.
Zhu Jigao, Wang Yi, Tang Guliang(2019). Research on
Central Enterprises' Fulfillment of social responsibility
under the "Belt and Road Initiative": from the
perspective of strategic social responsibility and
reactive social responsibility. J. China Industrial
Economics. (09):174-192.
Analysis of Social Responsibility of Chinese Overseas Construction Enterprises Based on Combination Empowerment Method
197
