
Connotation Analysis of Corporate Value Creation Based on ESG
Perspective
Qianzi Kong and Gang Fang
*
Business School, Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology, Beijing, China
Keywords: The Sustainable Development, Stakeholder Supremacy, Environment-Social-Governance, Corporate Value
Creation.
Abstract: As the concept of the sustainable development and other goodness-oriented ideas take root, the connotation
of corporate value creation has been transformed accordingly. Stakeholder Supremacy enriches the single
connotation of traditional economic value creation. Based on the ESG theoretical framework, this paper
integrates the three perspectives of social, environmental, and corporate governance to explore the feasibility
of corporate value creation under the new scope. By analysing the data of the selected sample with the help
of Multiple Regression model by the SPSS software, the study concluded that the realization of integrated
value creation by will promote the realization of single value creation, as well as the achievement of long-
term development goals of Chinese enterprises and the sustainable development of society as a whole.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ESG concept was formally proposed by United
Nations in 2005, and the ESG disclosure framework
was also formally established in The Code on
Governance of Listed Enterprises revised by China
Securities Regulatory Commission in 2018. ESG is a
value concept that encompasses environmental,
social, and corporate governance and provides a
comprehensive assessment of a company's
sustainability from a non-financial perspective. ESG
is a value concept that encompasses Environment,
Social, and Governance to provides a comprehensive
assessment of an enterprise's sustainability from a
non-financial perspective (HUANG 2021). With the
establishment of the peak carbon dioxide emissions
and carbon neutrality goals, The Fourteenth Five-
Year Plan, and Vision 2035, China is paying more
and more attention to ESG, encouraging enterprises
to improve their economic, social and environmental
values through the application of ESG concepts, and
promoting their sustainable and healthy development.
More and more enterprise management matters such
as the choice of value creation choice require positive
analysis. And with the support of various economic
models by data analytics technology and software,
such as Stata, SPSS, EViews, and so on, the
*
Corresponding author
enterprises management behaviour is becoming more
efficiently and accurately.
2 CURRENT STATUS OF
RESEARCH ON CORPORATE
VALUE CREATION
The emergence of the ESG concept has accelerated
the impact on the shareholder supremacy's
mainstream of the long dominant. The Shareholder
Supremacy insists on the view that administrator only
needs to be accountable to its shareholders, to
generate residual income for them and thus achieve
the goal of profit maximization. Then the Stakeholder
Supremacy has further captured the discourse on the
meaning of enterprise value creation.
Stakeholder Supremacy didn't deny the former
view, and it thought the traditional scope of enterprise
value creation is too superficial and narrow. In
addition to ESG, Triple Bottom Line also provides a
solid theoretical basis for the broadening of the scope
of this doctrine, which believes that only the
enterprise that create economic, social, and
environmental values (HUANG 2021) and contribute
to social progress in this way are sustainable
282
Kong, Q. and Fang, G.
Connotation Analysis of Corporate Value Creation Based on ESG Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0012029600003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 282-287
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

enterprises. Therefore, in order to respond to the
development of the times, what enterprise have to do
today is to let their hidden social and environmental
value creation requirements come to the surface, and
not only the pursuit of economic value.
However, there is still disagreement among
academics on the scope of enterprise value creation
enriched by Stakeholder Supremacy, and the point of
contention that prevents full agreement is whether the
new scope of corporate value creation is a
complement or an addition to the traditional
economic value creation, and the findings can be
summarized into two broad categories.
One type of conclusion is that cost is a factor that
must be taken into account when an enterprise creates
value, and that value creation under the new category
may result in a significant increase in the costs and an
increase in resource consumption of the enterprise,
which, on the contrary, has a negative impact on the
long-term profits of the enterprise and damages the
economic value originally created to obstacle the
sustainable development of the enterprise. Another
type of conclusion says, while realizing value
creation under the new category, the enterprise also
builds a positive image for itself, which can increase
its visibility and obtain policy support in the long run,
thus contributing to increased profits and further
realization of value creation in the traditional
economy.
As the quest for the sustainable development
grows, the above-mentioned controversial point is the
impact of the new scope of enterprise value creation
on the traditional economic value creation, that needs
to be clarified. After analysing the points of
contention, this paper argues that the difference in the
quality of the indicators chosen to measure corporate
value creation is the key point of disagreement in the
research findings and the reason why corporate value
creation under the new scope is not yet universally
accepted.
Based on the ESG concept framework and Triple
Bottom Line, this paper will select representative
indicators based on the nature of corporate value
creation under the new scope, and further prove that
the realization of corporate value creation under the
new scope does not conflict with the connotation of
corporate value creation, but brings positive analysis
to it, thus promoting the long-term sustainable
development of enterprises.
3 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
At this stage, with the development of the concept of
the sustainable development and the peak carbon
dioxide emissions and carbon neutrality goals, the
new scope of corporate value creation is attracting
more and more attention, and the demand of various
stakeholders for such information is gradually
expanding, which makes enterprises pay more and
more attention to the disclosure of their own
comprehensive value realization. In order to measure
this integrated value, various new types of integrated
indicators have emerged to evaluate the creation of
economic, social, and environmental values of
enterprises.
However, due to the diversity of the connotation
of corporate value creation under the new scope, the
lack of common and unified standards for the
measurement of indicators by rating agencies, and the
considerable discretion of administrators in
disclosing such information, there are a lot of
greenwashing in many new comprehensive
indicators.
Based on the above analysis, this study uses the
ESG concept framework for measuring corporate
value creation under the new scope, and selects
relevant raw factors data from three perspectives
respectively, social, environmental and corporate
governance, to show its comprehensive value
creation.
3.1 Corporate Social Responsibility
and Financial Performance
From the social point of view, enterprises can
accumulate a good reputation and gain the trust of
relevant stakeholders through the long-term
performance of social responsibility, while
effectively reducing the instability and uncertainty of
their future development, enterprise-wide risk and
idiosyncratic risk, and also has a stabilizing effect on
stock market prices. This not only helps to reduce the
economic losses caused by the volatility of the
enterprise, but can further lead to an increase in
financial performance. According to the above
analysis, this research proposes hypothesis 1:
H1: Corporate social responsibility
performance and corporate financial
p
erformance has s positive correlation.
Connotation Analysis of Corporate Value Creation Based on ESG Perspective
283

3.2 Corporate Environmental
Protection and Financial
Performance
From an environmental perspective, based on
Michael Porter's Porter Hypothesis, appropriate
environmental regulation can effectively improve the
productivity of enterprises, and the increase can be
fully offset by the cost of doing for this. Enterprises
to establish the concept of environmental protection
to increase environmental protection behaviours (LI
2022), which helps to save resources consumption in
operations, green technology innovation capabilities
and the economic transformation of ecological
benefits, and all this will lead to an increase in the
economic efficiency of the enterprise. According to
the above analysis, this research proposes hypothesis
2:
H2: Corporate environmental protection
performance and corporate financial
p
erformance has s positive correlation.
3.3 Corporate Governance and
Financial Performance
From a corporate perspective, corporate governance
is a series of institutional arrangements that serve the
creation of corporate value, and good corporate
governance can promote the standardization of its
operations (YANG 2020). On the one hand, it helps
to improve the quality of internal and external
controls and the accuracy and efficiency of decision-
making; on the other hand, effective management and
balance between stakeholders can reduce transaction
costs and thus increase the economic gains of the
enterprise. In order to realize the role of corporate
governance in promoting value creation, it is
necessary to change to a shared governance model, so
that ownership of the enterprise can be dispersed to
all stakeholders in an orderly manner and avoid the
Tunnel Effect caused by the concentration of large
areas of equity. According to the above analysis, this
research proposes hypothesis 3:
H3: Corporate equity concentration and
corporate financial performance has s
ne
g
ative correlation.
4 RESEARCH DESIGN
4.1 Sample Selection and Processing
In March 2021, World Economic Forum released a
white paper called ESG Report: Helping China Take
Off to Gather Momentum and Win Together with
PwC China. ESG Practice Roadmap under The Peak
Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Carbon Neutrality
Goals and Evaluation Report on the Development of
Chinese Listed Enterprises (2021) has published by
Southern International Forum of Finance and
Economics in December. Both of them studied the
ESG performance of listed enterprises in China and
gave evaluation and suggestions on their current
development status and future development direction.
The release of successive heavyweight ESG
documents signifies that the concept and its
framework have become a signpost for the
sustainable development path of Chinese companies,
as well as a guide for enterprises to achieve value
creation under the new scope.
According to the above reports Secondary Sector
of Economy is more perfect in disclosing information
related to ESG concept. And industries of that area
are all heavyweight players in achieving the peak
carbon dioxide emissions and carbon neutrality goals,
so starting them can provides a relatively abundant
data base for this study on the one hand, and it will
has practical significance for Chinese enterprises to
promote sustainable development on the other.
Therefore, this research selects the 2014-2020
data of listed enterprises from the above industries
Shenzhen A- Main-Board share market as the
research sample using the CSRC's Industry
Classification Guidelines for Listed Enterprises
(2012) as the standard. This research also takes the
following treatments on the data: firstly, the sample
of enterprises with ST status in the year interval is
excluded; secondly, the sample of enterprises with
missing observations is excluded, and finally 208
enterprises with a total of 1,456 sample values are
obtained.
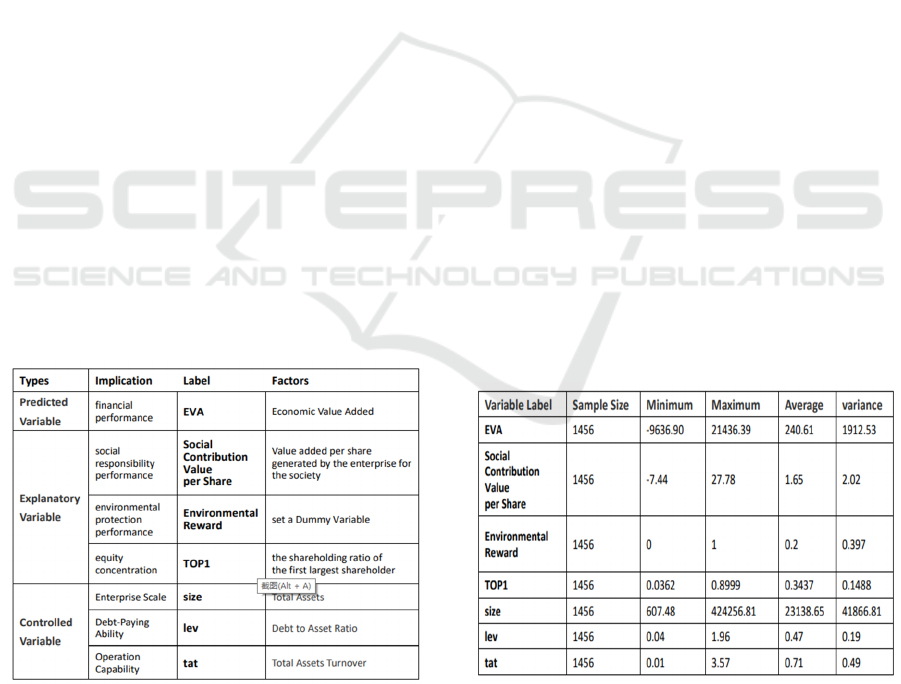
4.2 Variable Definition
4.2.1 Predicted Variable
Domestic and foreign scholars have taken a multi-
industry sample of enterprises, and through research
and analysis of common indicators such as ROA and
ROE, it has been demonstrated that Economic Value
Added (EVA) can reflect a more realistic and
effective corporate financial performance compared
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
284
to traditional financial performance measures (LI
2022). Therefore, this research adopts EVA as
predicted variable to measure corporate financial
performance based on the CSMAR database.
4.2.2 Explanatory Variable
In 2008, the Shanghai Stock Exchange issued The
Notice on Strengthening the Social Responsibility of
Listed Enterprises, in which the concept of Social
Contribution Value per Share was introduced for the
first time, and this indicator integrates the
contribution of enterprises to various interest groups
in society. Therefore, this research adopts Social
Contribution Value per Share as an explanatory
variable to measure the performance of corporate
social responsibility based on the CSMAR database.
The annual environmental performance of an
enterprise can be clearly and intuitively reflected by
whether the enterprise receives annual environmental
honours or reward or not, and this can be used as a
variable to represent the environmental protection
performance of the enterprise. Therefore, this
research sets a dummy variable to represent the
enterprise got an honour or a reward or not as a
measure of environmental protection performance
based on the CSMAR database.
In this research, based on the CSMAR database,
the shareholding ratio of the first largest shareholder
is selected as an explanatory variable to measure the
concentration of corporate equity.
In addition, total corporate assets, gearing ratio,
and total asset turnover ratio were selected as
controlled variables based on the CSMAR database.
Figure 1: Variable Definition.
4.3 Research Model
This research builds up the following model (1) based
on the above analytical theoretical analysis and
assumptions:
EVA=α
0
+α
1*
(Social Contribution per
Share) +α
2*
(Environmental Rewards) +α
3*
(TOP1) +α
4*
(size) +α
5*
(lev) +α
6*
(tat) +ε1
(1)
α
0
is the constant term; α
i
(i =1 to 6) is the
coefficient of each variable; and ε
1
is the error term.
In this research, the sample data were standardized
before further positive analysis.
The following positive analysis will be conducted
using Multiple Regression model by SPSS software.
5 POSITIVE ANALYSIS
5.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Figure 2 shows the results of the descriptive
statistical analysis. the maximum value of EVA is
21436.39, the minimum value is -9639.90, and the
variance is 1912.53, indicating that there are
significant differences in the level of financial
performance of the companies within the selected
sample, and the development of each industry is very
different. Among the explanatory variables, the
shareholding ratio of the first largest shareholder is
89.99% at the maximum and 3.62% at the minimum,
with the average of 34.37%, which shows that the
concentration of equity among corporates is not
uniform.
Figure 2: Descriptive Statistical.
5.2 Correlation Analysis
The correlation matrix in Figure 3 shows that EVA is
significantly and positively correlated with Social
Connotation Analysis of Corporate Value Creation Based on ESG Perspective
285
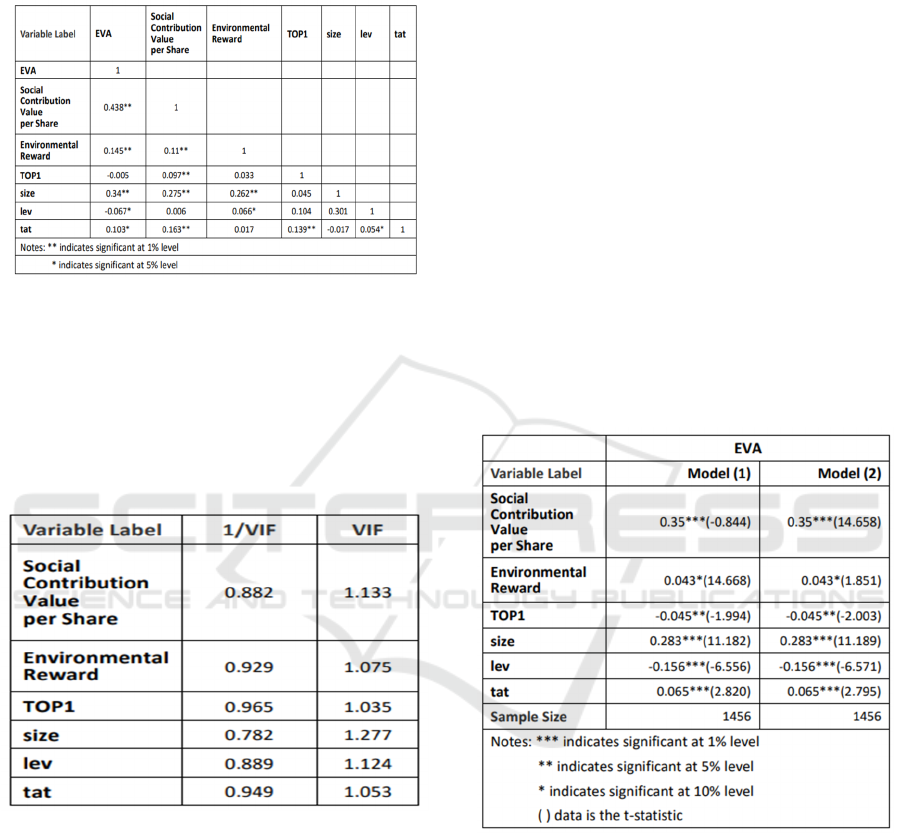
Contribution per Share at the 1% level, and EVA is
also significantly and positively correlated with
Environmental Rewards at the 1% level, tentatively
verifying hypotheses 1 and 2.
Figure 3: Correlation Matrix.
5.3 Multicollinearity Analysis
The samples were tested for multicollinearity, and as
shown in Table 4, the mean the average of VIF were
much less than 10 and the 1/VIF were all close to 1,
indicating that there was no multicollinearity between
the explanatory variables.
Figure 4: Multicollinearity Test.
5.4 Multiple Regression Analysis
By multiple regression analysis of the samples
yielded Figure 5, the coefficients of Social
Contribution Value per Share, Environmental
Reward and TOP1 were significant at the 1%, 10%,
and 5% levels respectively. The coefficient α
1
was
positive for Social Contribution Value per Share, α
2
was positive for Environmental Reward, and α
3
was
negative for TOP1. As well as it demonstrated the
social responsibility performance and environmental
protection performance both have a positive
correlation with financial performance in an
enterprise. And the corporate equity concentration
and its financial performance has s negative
correlation. Therefore, hypotheses 1, 2, and 3 were all
valid.
5.5 Robustness Analysis
To ensure the robustness and reliability of the study
results, the control variable of operating income
growth rate is added to model (1), and turned to model
(2) for testing. As can be seen from Figure 5, the
coefficients of the predicted variable EVA and the
explanatory variables Social Contribution Value per
Share, Environmental Reward, and TOP1 in the
model (1) are still significant at the 1%, 10%, and 5%
levels. The original hypotheses remain valid through
the robustness test.
EVA=β
0
+β
1*
(Social Contribution Value
per Share) +β
2*
(Environmental Rewards)
+β
3*
(TOP1) +β
4*
(size) +β
5*
(lev) +β
6*
(tat)
+β
7*
(income
g
rowth rate) +ε
2
(2)
Figure 5: Multiple Regression & Robustness Test.
5.6 Results and Discussions
Based on the ESG concept framework, the following
conclusions and suggestions are drawn from the
above research conducted by SPSS software.
Enterprise managers should be good at building
appropriate economic models to control the business
and development situation before and after the event,
and have a global grasp of it, so as to achieve efficient
and accurate management.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
286

Corporate social performance and financial
performance are positively correlated, and good
social performance can improve corporate economic
performance to a certain extent. Corporate
environmental performance is positively related to
corporate financial performance. Environmental
protection behaviour recognized by the policy will
bring considerable economic value-added to
enterprises. The higher the concentration of equity,
the lower the level of financial performance.
Diversification of equity can effectively avoid
undesirable governance performance.
Enterprises should actively assume social
responsibility so as to promote the achievement of
their economic goals and enhance corporate value.
Enterprises should actively participate in
environmental protection and establish a positive
image of low carbon and environmental protection,
which in turn will get the policy support and
positively influence their financial performance. A
reasonable degree of standardization of the
governance system will effectively reduce non-
systematic risks of enterprises, avoid internal
fluctuations and achieve smooth long-term operation
of enterprises. Enterprises should make reasonable
allocations of assets, liabilities, and related equity,
and regularly evaluate their debt-paying ability,
profitability, operating ability, development level,
and risk level to reduce uncertainty and enhance their
coping capacity.
Through the three perspectives of social,
environmental, and corporate governance, and with
the help of a large number of representative raw
factors data we have conducted research and analysis
on corporate value creation under the new scope, and
confirmed that the comprehensive realization of
economic, social, and environmental values is not a
substitute for the traditional value creation, but an
addition to the maximization of profits. The
integrated value creation connotation of the current
stage of enterprises proposed by Stakeholder
Supremacy which contains the economic value, social
value, and environmental value is feasible.
6 CONCLUSIONS
With the support of various data analysis technologies
and software for various economic models, the
enterprise stakeholders become more accurate in
grasping the overall situation, administrators become
more disciplined in their behaviours, and the
enterprise operations become more efficient.
Nowadays, the realization of integrated value creation
by Chinese enterprises can not only promote their
long-term pursuit of sustainable development, but
also promote the achievement of China's the peak
carbon dioxide emissions and carbon neutrality goals,
and then move towards the direction of the
sustainable development of the whole society.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Support by: The construction program of innovation
team at Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology
(BIFTTD201901); “The first batch of new liberal arts
research and reform practice projects of the Ministry
of Education” project (Project No.: 2021140009).
REFERENCES
HUANG, S. Z. (2021). Three theoretical pillars supporting
ESG. J. Finance and Accounting Monthly. 19, 3–10.
HUANG, S. Z. (2021). Three major changes in value
creation from ESG perspective. J. Finance Research. 6,
3–14.
LI, J. T. (2022). The Impact of ESG performance on
corporate financial performance from a media focus
perspective. J. Scientific and Technological
Management of Land and Resource. 39(1), 96–104.
LI, J. (2022). Environmental information disclosure and
business performance of firms - A test of mediating
effects based on investor concerns. J. Technology
Economics. 41(5), 85–96.
YANG, J. (2020). The relationship between corporate
governance, social responsibility and financial
performance. J. Commercial Accounting. 21, 85–88.
Connotation Analysis of Corporate Value Creation Based on ESG Perspective
287
