
Performance of Delta-Neutral Hedging Strategy on Moderna Inc
Stock
Beibei Liu
College of Literature, Science, and Arts, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, State of Michigan, U.S.A.
Keywords: Hedging Strategy, Option Contract, Delta-Neutral Hedging Strategy, The Black-Scholes Model, Binomial
Tree Model, Historical Return Model.
Abstract: This paper investigates the effectiveness of delta-neutral hedging strategy. The goal of this paper is to hedge
an option contract on Moderna Inc stock. The result of this paper is useful for investors, especially beginners,
to use as a reference when building a portfolio. This study is divided into two parts. The first one is to calibrate
volatility of stock using three different models: the Black-Scholes model, binomial tree model, and historical
return model. With implied volatility in hand, a delta-neutral portfolio is built to hedge a put option on
Moderna Inc stock. The performance of the hedging strategy can be observed by comparing portfolio return
with the return of the option contract alone. The result of this study indicates that delta-neutral hedging
strategy does reduce loss in investment. Such result is beneficial for individual investors in formulating a
simple portfolio.
1 INTRODUCTION
Option pricing calculates implied value of option
contract with the aid of mathematical models. Two
commonly used derivative pricing models are the
binomial tree model and the Black-Scholes model.
The Black-Scholes model is a well-known derivative
pricing strategy. The significance of the Black-
Scholes model is it lays a foundation for a new field of
finance called the continent-claims analysis (Gilster,
1997), which is useful in pricing complex financial
securities. The binomial tree model values options at
a discrete set of nodes. Binomial tree model has more
applications than the Black-Scholes model because it
works for both American options, European options,
and options with dividend-paying underlying stock.
Hedging strategy is a risk management strategy,
and it generates value for investors by reducing loss of
portfolio. Investments like options, futures, and other
derivatives are most used by investors when
formulating a hedging strategy. Delta hedging is a
commonly used strategy, where delta measures the
fluctuation in portfolio value with respect to the
change in the underlying asset price (Ajay, 1997). The
goal of delta-neutral hedging strategy is that value of
portfolio does not vary much as stock price changes.
Such a goal can be achieved by building a portfolio
that has zero value for delta (Capinski, 2003). One
problem with delta-neutral hedging strategy is that it
requires constant rebalance to ensure delta is equal to
zero (Robins, 1994). However, in the real world,
market is not frictionless. Rebalance results in
transaction cost, which is not taken into consideration
by delta-neutral strategy. Even though delta hedging
might not be an optimal strategy, it’s still commonly
used due to its simplicity.
Within the field of financial engineering, much
research has been done on different hedging strategy
and option pricing strategy. For example, Hauser and
Eales analyzed option hedging strategies (Hauser,
1987); Schweizer researched on mean-variance
hedging (Schweizer, 1992); Wang, Wu, and Yang
studied hedging with futures (Wang, 2015); Schied
and Staje wrote about the robustness of delta hedging
(Schweizer, 1992). Moreover, for option pricing,
Merton analyzed the theory of rational option pricing
(Merton, 1973); Kremer and Roenfeldt compared
jump-diffusion pricing model with the Black-Scholes
model (Kremer, 1993); Schaefer investigated the
development of derivative pricing method (Schaefer,
1998) etc. As the topics are of interests in the financial
field, this paper also focuses on the issue.
This paper combines option pricing and risk
hedging and specifically looks into the implied
volatility by three different methods on the same stock
412
Liu, B.
Performance of Delta-Neutral Hedging Strategy on Moderna Inc Stock.
DOI: 10.5220/0012033900003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 412-416
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
during the same time period, and compares return with
and without hedging.
The paper is divided into four sections: section 2
organizes data and explains method used; section 3
displays results and discuss; section 4 concludes the
discussion.
2 DATA
In this paper, Moderna stock is chosen because
Moderna is a dominant player in the field of mRNA
vaccine (Dolgin, 2021). During the Covid-19
pandemic, it was the second pharmaceutical company
to develop a mRNA vaccine for Covid-19. Moderna’s
vaccine reduces the chance of getting infected by
Covid-19, and many countries around the globe have
adopted Moderna’s mRNA vaccine during the
pandemic. For example, British had ordered around 17
million doses of Moderna before January 2021 (BBC,
2021).
Stock open price and option contract price is
collected from Yahoo Finance
(www.yahoo.com/finance). Open price of Moderna
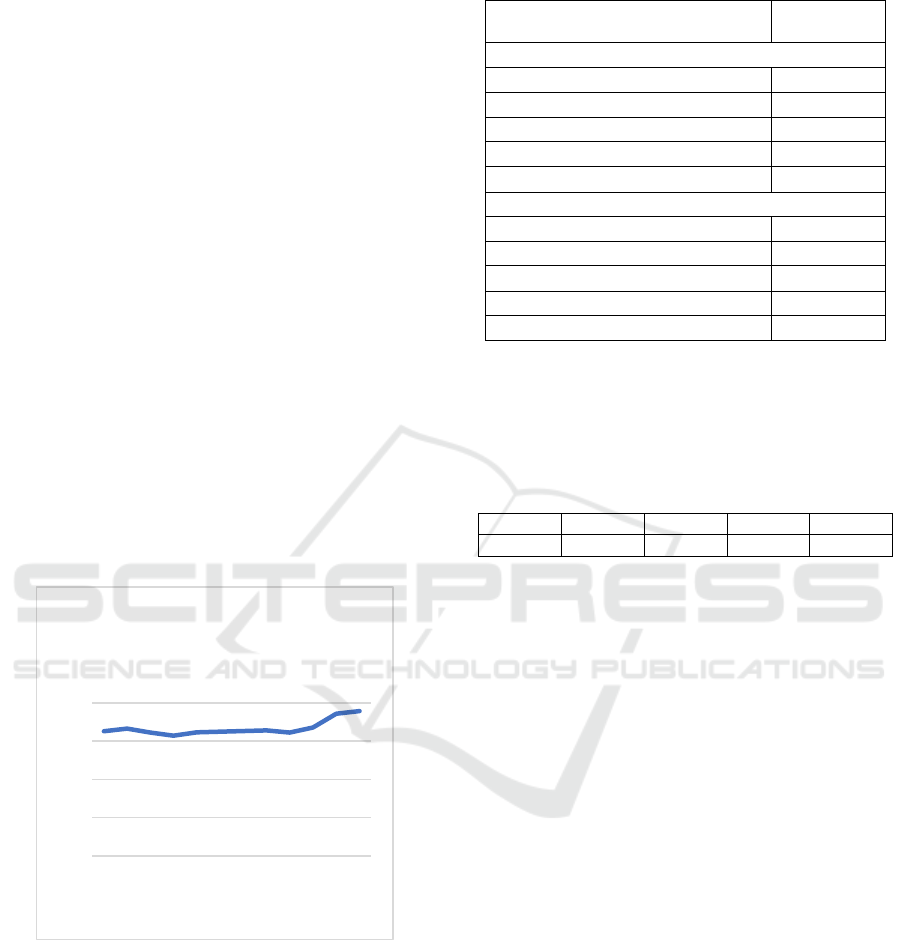
Inc stock from July 25th, 2022, to Aug 5th, 2022, is
recorded and shown in the graph below.
Figure 1. The stock price trend
In order to calibrate volatility, price of 5 call
options and 5 put options on July 25th, 2022, is
recorded. Each option has Moderna Inc stock as the
underlying asset. Option contracts chosen are shown
in the table below.
Table 1: 10 Options chosen.
Contrast Name Option
Price
Call Option
MRNA220729C00160000 5.15
MRNA220729C00157500 7.87
MRNA220729C00155000 8.76
MRNA220729C00152500 11.75
MRNA220729C00150000 11.50
Put Option
MRNA220729P00160000 3.70
MRNA220729P00162500 5.00
MRNA220729P00165000 8.00
MRNA220729P00167500 10.04
MRNA220729P00170000 11.69
After acquiring calibrated volatility, a delta
hedging strategy is formulated to hedge a new put
option, MRNA220805P00170000, from Aug 1st,
2022, to Aug 5th, 2022. Market put option price, from
Aug 1st to Aug 5th, is shown in the table below.
Table 2: Put option price.
08/01 08/02 08/03 08/04 08/05
10.07 10.20 3.21 0.36 0.07
3 METHOD
In this paper, the hedging strategy is made up of two
parts. The first one is to calibrate volatility using three
different models: Black-Scholes model, binomial
model, and historical return model. The reasons are
shown below. First, the Black-Scholes model is shown
to be a highly accurate prediction of future volatility;
Second, the binomial tree model suits the discrete-
time case. Next, this paper builds a delta-neutral
portfolio to hedge a new option using delta hedging
strategy.
3.1 The Black-Scholes Model
The Black-Scholes model, a derivative pricing model,
measures the price of European put and call option.
The Black-Sholes model assumes that price of
European option is a function of strike price, time to
maturity, underlying stock price, volatility, and
interest rate of the return of the underlying stock. First
developed by Fischer Black, Robert Merton, and
Myron Scholes in 1973 (Manaster, 1982), the Black-
Scholes model is still widely used today to price
option contract. Although Black-Scholes model is an
easy method to calculate option price, this method has
0
50
100
150
200
7/25/22
7/26/22
7/27/22
7/28/22
7/29/22
7/30/22
7/31/22
8/1/22
8/2/22
8/3/22
8/4/22
8/5/22
Moderna Inc Open
Stock Price
Performance of Delta-Neutral Hedging Strategy on Moderna Inc Stock
413

some limitations. First, the Black-Scholes model only
works for European options since one assumption is
options can only be exercised at their maturity date.
Second, this model assumes that stocks do not pay
dividends and no interest is paid. Third, it assumes a
frictionless market, which means this model does not
take various transaction cost, like commissions and
taxes, into consideration. Fourth, it assumes that the
risk-free interest rate remains constant. However,
above assumptions are hardly ever the case in reality.
Details of the Black-Scholes model is shown below.
Time to maturity (t), strike price (K), interest rate
(r), and stock spot price (S(t)), are all known for each
of the ten options. The only unknown variable is
volatility ( σ). To calculate option price using the
Black-Scholes model, first assume that volatility
equals to 0.3. With above information, implied prices
of ten options are calculated using the below
equations. For clarification, 𝐶(𝑡) and 𝑃(𝑡) denote
price of European call and put option, and 𝑁
(
𝑑
)
represents the cumulative standard normal probability
of the value 𝑑
.
c𝑑
=
√()
ln
(
)
+
𝑟+
𝑡
(1)
𝑑
=
1
σ
√
(t)
ln
𝑆
(
𝑡
)
𝐾
+𝑟−
σ
2
𝑡
(2)
𝐶
(
𝑡
)
=𝑆
(
𝑡
)
𝑁
(
𝑑
)
−𝐾𝑒
𝑁(𝑑
)
(3)
𝑃
(
𝑡
)
=𝐾𝑒
𝑁
(
−𝑑
)
−𝑆
(
𝑡
)
𝑁
(
−𝑑
)
(4)
Then, the sum of squared errors (SSE) is used to
measure the discrepancy between the implied prices
and the market option prices. Equation (5) is the
formula for calculating SSE. In equation (5), 𝑃
stands for actual option price in the market. 𝑃
stands
for the theoretical option price. Lastly, minimize SSE
by plugging in different values for volatility, and mark
the value that yields minimum SSE.
𝑆𝑆𝑅=
(
)
+
(
)
+⋯+
(
)
(5)
3.2 Binomial Tree Model
Binomial tree model is a simple discrete-time model
used to determine value of option. Under the binomial
tree model, the lifetime of one option contract is
divided into discrete many intervals (Breen, 1991).
During each interval, the value of underlying asset
either goes up or goes down. The multiplicative
parameters of the movements are denoted by u and d,
and p denotes the probability of price of underlying
asset going up. Mechanism of binomial tree model is
that the value of option at certain node relies on the
possibility of stock price moving up or down. One
advantage of binomial tree model is that it works for
both American and European options. Also, it is
appliable for dividend paying options. However, one
fundamental assumption of binomial tree model is that
the underlying asset can only take one of the two
suggested values, which is more than idealized.
Binomial tree model is similar to the Black-
Scholes model when time interval is small enough
(Cvitanić, 2004). Use below equations to find
theoretical option price. Similarly, calculate SSE and
mark the volatility that yields minimum SSE. Detailed
model specifications are shown by the follow
equations.
𝑢=𝑒
√
∆
(6)
𝑑=
1
𝑢
(7)
𝑝=
𝑒
−𝑑
𝑢
−
𝑑
(8)
3.3 Historical Return Model
The historical return model utilizes historical stock
returns to predict sigma. Among the three models,
volatility calibrated by the historical return model, in
theory, deviates most from the actual volatility.
Because stock price is highly volatile and follows no
discernible trend. Past return is not a good indicator of
return in the future.
For the historical return model, plug stock prices
from July 25th to July 29th into equation (9).
𝜎=
251𝑉𝑎𝑟[ln
(
𝑆
)
−ln
(
𝑆
)
]
(9)
3.4 Delta-neutral Hedging Strategy
Delta-neutral hedging strategy is a commonly used
risk managing option trading strategy. Delta measures
the fluctuation in the value of portfolio as the
underlying asset price moves. Mathematically, delta
can be expressed as the partial derivative of the
portfolio value with respect to the underlying asset
price. The purpose of the hedging strategy is to build
a portfolio that reaches a delta neutral position, which
means the delta of the portfolio is zero. Following
equations shows how to calculate the overall profit or
loss of a delta neutral portfolio. Lastly, calculate loss
without using hedging and compare the loss with
hedging and loss without hedging. This step verifies
that delta hedging strategy reduce the loss in option
trading.
The goal of the paper is to hedge one share of put
option, MRNA220805P00170000, with some shares
of stock. Equation (10) gives the delta of option, ΔP.
The delta-neutral portfolio consists of one share of put
option and -ΔP shares of stock. In addition, equation
(11) and equation (12) calculate the loss with and
without hedging strategy at maturity (T).
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
414
∆𝑃=−𝑁
(
−𝑑
)
(10)
𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ ℎ𝑒𝑑𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑔
=𝑀𝑎𝑥
0,𝐾− 𝑆(𝑇)
−ΔP
[
S
(
𝑇
)
−S
(
0
)
]
−P(t)
(11)
𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑡 ℎ𝑒𝑑𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑔
=𝑀𝑎𝑥
0,𝐾− 𝑆(𝑇)
−𝑃(𝑡)
(12)
4 RESULT
The below chart shows three parameters of the Black-
Scholes model. Interest rate, 0.028, is collected from
Federal Reserve website. Because there is 251 trading
days in 2022, time to maturity (t) is
.
Table 3: Parameters of black-scholes model.
Parameter r t S(t)
Value 0.028 0.020 162.75
The volatility calibrated, and the return from three
different methods are shown in the table III. The return
of delta-neutral hedging is calculated using three
different volatilities.
Table 4: Result using three different models.
Method SSE volatility
Black-Scholes 8.162 0.389
Binomial 1.706 0.481
Historical Return - 0.493
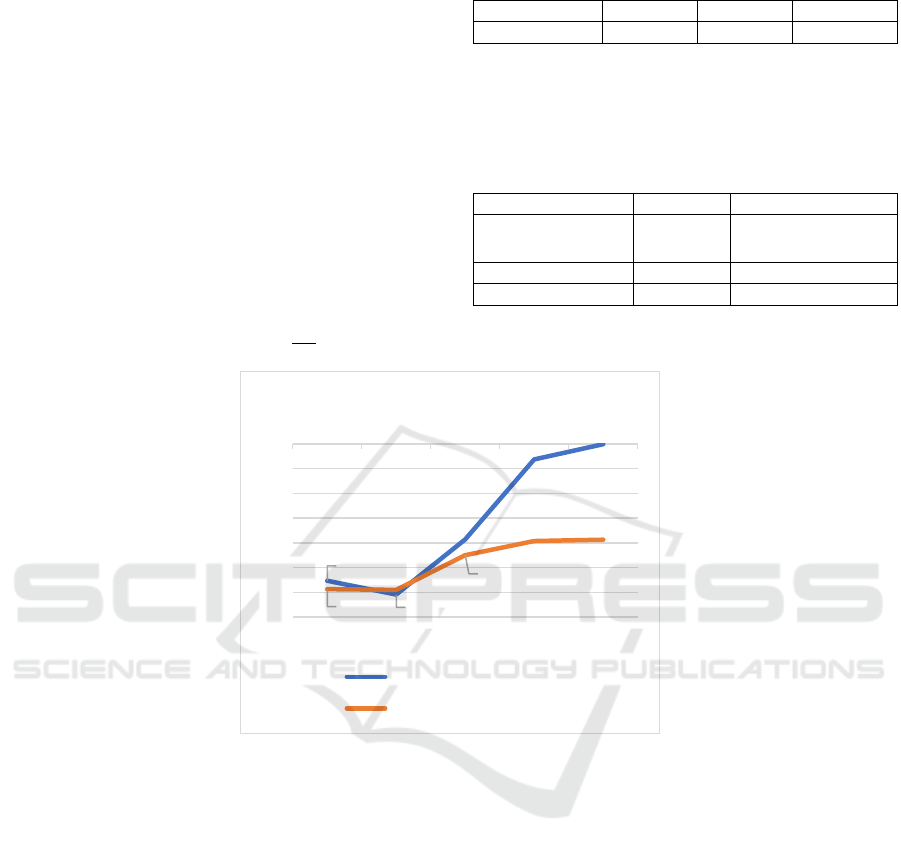
Figure 2: Trends of return with and without heding.
5 DISCUSSION
As shown in the previous section, the volatilities
calibrated ranges from 0.389 to 0.493, which means
Moderna stock is volatile. Price of security is closely
related to the value of the firm. Modern belongs to the
healthcare sector, and its firm value is closely related
to the change in sales, and the launch of new product.
Moderna specializes in developing mRNA vaccine.
Because, before a vaccine got approved by the FDA,
its research process is highly costly. Currently, mRNA
vaccine for COVID-19 is the only type of mRNA
vaccine in the market, and Pfizer is a strong
competitor in the Covid-19 mRNA vaccine market.
Due to these factors, it’s reasonable that Moderna
stock is highly volatile.
In figure (2), there is only one curve showing the
return with hedging. Because the difference between
the returns calculated using three different volatility is
too small that it’s reasonable to ignore the difference.
The Result section also shows that the loss with
hedging is lower than the loss without hedging on
every day except for Aug 2nd. The most significance
difference between the two approach is 19.27. In this
case, the hedging strategy indeed reduces the overall
risk of the portfolio. On Aug 2nd, the loss without
hedging is lower than the loss with hedging, because
the goal of delta-neutral hedging strategy is to reduce
the fluctuation in overall portfolio value with respect
to variation in stock price. But in some cases, change
in stock price leads to a larger increase in option return
than increase in overall portfolio return. To avoid
having lower return with hedging strategy, when
-27,65
-30,41
-19,31
-3,17
-0,07
-29,34
-29,47
-22,48
-19,63
-19,34
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
8/1/22 8/2/22 8/3/22 8/4/22 8/5/22
Return
Return with hedging
Return without hedging
Performance of Delta-Neutral Hedging Strategy on Moderna Inc Stock
415

trading with delta-neutral strategy, it’s necessary for
traders to closely monitor and constantly rebalance the
portfolio.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper examines the performance of delta-neutral
hedging strategy using three different implied
volatility. Because the limitations of each model the
implied volatility might deviate from the actual
volatility of the stock. No transaction cost is taken into
consideration, and very option studied in paper is
treated as European option. Moreover, despite the
actual interest rate futurates daily, for simplicity of this
paper, 0.028 is chosen to be the interest rate.
Therefore, the implied volatility might deviate from
the actual volatility of the stock, and the results shown
in this paper might not be perfectly accurate. Another
potential problem is that calibration using the Black-
Scholes model and binomial tree model only uses 10
options; calibration using the historical return method
only collects historical open price for five consecutive
trading days. For improvement, more data should be
used in the process of calibration. Further study is
needed for a more accurate result.
REFRENCES
BBC. Covid-19: England gets third jab as Moderna rollout
begins, 2021
E. Dolgin. The tangled history of mRNA vaccines. Nature
News, 2021
J. Cvitanić, F. Zapatero. Introduction to the Economics and
Mathematics of Financial Markets. The MIT Press,
2004
J.E. Gilster. Option Pricing Theory: Is “Risk-Free” Hedging
Feasible Financial Management, 1997, 26(1), 91–105.
J. W. Kremer, R. L.Roenfeldt. Warrant Pricing: Jump-
Diffusion vs. Black-Scholes. The Journal of Financial
and Quantitative Analysis, 1993, 28(2), 255–272.
M. Capinski, T. Zastawniak. (2003). Mathematics for
Finance: An Introduction to Financial Engineering.
Springer, 2003.
M. Schweizer. Mean-Variance Hedging for General
Claims. The Annals of Applied Probability, 1992, 2(1),
171–179.
M. Schweizer. Mean-Variance Hedging for General
Claims. The Annals of Applied Probability, 1992, 2(1),
171–179.
R. Breen. The Accelerated Binomial Option Pricing Model.
The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis,
1991, 26(2), 153–164.
R.P. Robins, B. Schachter. An Analysis of the Risk in
Discretely Rebalanced Option Hedges and Delta-
Based Techniques. Management Science, 1994, 40(6),
798–808.
R.J. Hauser, J. S. Eales. Option Hedging Strategies. North
Central Journal of Agricultural Economics,1987, 9(1),
123–134.
R.C. Merton. Theory of Rational Option Pricing. The Bell
Journal of Economics and Management Science, 1973,
4(1), 141–183.
S. Ajay. Black, Merton and Scholes: Their Work and Its
Consequences. Economic and Political Weekly, 1997,
32(52), 3337–3342.
S. M. Schaefer. Robert Merton, Myron Scholes and the
Development of Derivative Pricing. The Scandinavian
Journal of Economics, 1998, 100(2), 425–445.
S. Manaster, G. Koehler. The Calculation of Implied
Variances from the Black-Scholes Model: A Note. The
Journal of Finance, 1982, 37(1), 227–230.
Y. Wang, C. Wu, L. Yang. Hedging with Futures: Does
Anything Beat the Naïve Hedging Strategy?
Management Science, 2015, 61(12), 2870–2889.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
416
