
Design of P-RAN Business Model
Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production
Fanrong Meng, Hua Liu, Weimin Li, Xin Chen, Qingfeng Yang, Jiasi Jiang and Zhao Zou
China Telecom Research Institute, China
yangqf6@chinatelecom.cn, jiangjs@chinatelecom.cn, zouz1@chinatelecom.cn
Keywords: Decentralization, Value Co-Production, Web 3.0, Business Model.
Abstract: Based on the value co-production theory, this paper summarizes three key issues of value co-production:
resource coordination, operation governance and risk management. Then, this paper constructs a decentralized
value co-production model by combining with the characteristics of decentralized products. Based on this
model, this paper analyzes how to realize value co-production in decentralized network P-RAN, and finds
that users in decentralized network can independently control sharing and use according to their own network
resources, thus forming an “Online to Earn” operation mode. The decentralized network still faces many risks,
which need to be solved by technological and operational innovation in the future.
1 INTRODUCTION
The era of decentralized Web 3.0 has arrived. Web
3.0 is the next generation of “Read+Write+Own” net-
work compared to Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. Web 1.0,
where users can only read what the website provides,
is a typical centralized product. Web 2.0 realizes the
interaction between users and the network, and urges
enterprises to shift from the typical product-led logic
based on product cost performance to the typical ser-
vice-led logic based on providing a full set of service
solutions (Vargo, 2020; Yoo, 2010), thus leading to
the development of centralized products. Under the
operation and management of the centralized plat-
form, enterprises, users, suppliers and other roles can
jointly obtain value promotion (Heidenreich, 2015;
Prahalad, 2000), which accordingly realize value co-
production. In this case, some users can serve as re-
source delivery nodes. For example, social media us-
ers are both content creators and readers, which has
already had the initial prototype of decentralization.
With the development of blockchain technology and
the improvement of computing power, as well as the
urgent needs of users for personalized services and
data controls in their own hands, Web3.0 comes into
being.
In the Web 3.0 era, decentralized products empha-
size returning control of the internet to users. At pre-
sent, many decentralized products, such as Bitcoin
and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) products, have
been accepted and recognized by governments. It is
foreseeable that decentralized Web 3.0 will become a
new focus of international competition in the future.
Therefore, based on the three breakthrough points of
the value co-production theory and the characteristics
of decentralized products, this paper analyzes and
constructs the decentralized operation model. By ap-
plying the decentralized operation model, this paper
focuses on how mobile network operators (MNOs)
can innovate products and services in the 5G+/6G era
and then puts forward business proposals for them.
2 RESEARCH ON
DECENTRALIZED VALUE
CO-PRODUCTION MODEL
2.1 Value Co-Production
Value co-production was first proposed by scholar
Ramirez R (1999) (Ramirez,, 1999), which is jointly
created by two or more participants, including mutual
value and value created for other participants. Value
co-production theory has developed rapidly in the era
of internet economy. With the progress of Internet
technology, enterprises have been liberated from the
constraints of the concept and model of value creation
(Hirschhorn, 1984; Trist, 1981). It is believed that
484
Meng, F., Liu, H., Li, W., Chen, X., Yang, Q., Jiang, J. and Zou, Z.
Design of P-RAN Business Model Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production.
DOI: 10.5220/0012035400003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 484-491
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

consumers hope to Interact with professionals, ser-
vice providers and other consumer groups to achieve
value co-production (Prahalad, 2004), and it is be-
lieved that intangible resources such as services will
also promote the improvement of value (Vargo,
2014). Some scholars have studied how enterprises
coordinate to achieve value co-production from the
aspects of resource coordination (Bharti, 2015; Lavie,
2006), operation governance (Dhanaraj, 2004;
Gawer, 2002) and risk management (Prahalad, 2004).
It can be seen from the existing research that value
co-production is the process of value maximization in
economic exchange of various production factors
(human factors, material factors and their combina-
tion factors). To achieve value co-production, enter-
prises or products need to focus on three break-
through directions: resource coordination, operation
governance and risk management.
2.2 Decentralization Value
Co-Production
Decentralization is initiated by the idea of Web3.0
network. Every node is the center, which can connect
and influence other nodes. It has the characteristics of
flat, open source and equality. A decentralized prod-
uct replicates the corresponding functions of central-
ized products in a decentralized manner (flat, open
source, equality, etc.). In order to find out how to re-
alize value co-production of decentralized products,
this paper will conduct a detailed analysis from three
breakthrough directions of value co-production: re-
source coordination, operation governance and risk
management.
(1) Resource coordination: from centralized man-
agement to spontaneous management, thus improving
quality and efficiency
The resource coordination and integration of de-
centralized products is spontaneous. The value is
mainly generated from the common authentication of
each node. The traditional centralized products real-
ize value promotion by coordinating the resources of
the upstream and downstream of the whole industry
and form a chain structure. Traditional centralized
products review the qualifications of suppliers, dis-
tributors and other users who provide known re-
sources, and adjust supply and demand by means of
automatic algorithm matching, big data recommenda-
tion matching or stakeholder interference matching.
Since the evaluation of resources in the later stage
mainly depends on user evaluation, paid posters and
advertisement can easily have a negative impact on
the merchant platform, which will reduce the effi-
ciency of information searching for users. For exam-
ple, search engines such as Google distort search
rankings for their own benefits.
Decentralized products are managed by individual
nodes in coordination with each other to form a net-
work ecosystem, so the resource management has
spontaneity. Nodes identify and judge the value of re-
sources by voting. Based on the consideration of their
own benefits, nodes will make careful judgments to
reduce the adverse influence caused by false infor-
mation. Taking the decentralized search product To-
ken Curated Registries (TCRs) as an example.
Through the voting judgment of nodes and optimizing
the screening mechanism of resources, TCRs can ef-
fectively select the candidate content with the best
quality, and puts it into TCR (Asgaonkar, 2018),
which is convenient for users to find valuable infor-
mation.
(2) Operation governance: build X to Earn incen-
tive mechanism to stimulate user initiative
Decentralized products emphasize the improve-
ment of data autonomy and algorithm autonomy of
users, weaken the centralized management ability of
products, and enhance user activity through incentive
mechanism. With the help of the control of produc-
tion factors such as channels and data, the centralized
products have the innate control and supervision
power over users. Centralized products coordinate
user behaviors through various rules, and achieve
platform profits increase through flow realization,
commission sharing, value-added services and
charged services. The operation of the centralized
products depends on the data privacy rights and con-
tent selection rights given by users. If data abuse oc-
curs, it is difficult for users to ensure the security of
their account data. For example, Facebook and Twit-
ter blocked Trump’s account.
Decentralized products do not have such central-
ized rights. To achieve similar operational and regu-
latory capabilities as centralized products, decentral-
ized products must rely on incentive mechanism de-
sign to provide power for the flow of production fac-
tors. Therefore, decentralized products try to combine
smart contracts, Decentralized Autonomous Organi-
zation (DAO), DeFi and other tools to relate user rev-
enue to user behavior, which create a new profit
model “X to Earn (X2E) (X represents user behavior,
such as learn, write, play, etc.)”. In the metaverse
game Axie Infinity, users can earn SLP tokens to feed
NFT pet Axie through pvp, pve and completing daily
tasks, which realizes a new profit model of Play to
Earn (P2E). Through this incentive method, rights are
reserved at each node as much as possible. Even if
harmful information appears, it will be recorded in the
Design of P-RAN Business Model Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production
485
product to facilitate supervision and governance. For
example, the decentralized social media Steemit will
not delete the content of low quality, but will only
hide it.
In short, decentralized products use blockchain to
reduce or eliminate reliance on third-party institu-
tions, and enhance user choice. At the same time, de-
centralized products connect behavior with profit to
form a more and richer X2E incentive mechanism in
the future, which will promote the value flow of pro-
duction factors.
(3) Risk management: decentralization reduces
risks by operational means such as limiting transac-
tions, establishing third-party neutral institutions, and
technical means such as blockchain technology
Decentralized products present a network opera-
tion because nodes do not interfere with each other.
Compared with centralized products, the risk degree
is higher and the risk spreads faster. Therefore, it is
necessary to explore new risk management methods.
Traditional centralized products can use centralized
platforms to supervise or block fraudulent transac-
tions, harmful information, data leakage, etc.
In order to solve the above risks, decentralized
products, on the one hand, take advantage of techno-
logical innovation, and based on blockchain, propose
Decentralized ID (DID) and smart contract to solve
the issues of identity verification and property rights
clarification, so as to reduce the risk of data leakage
and reduce the memory cost caused by account non-
communication of centralized products. On the other
hand, decentralized products use certain operational
innovations to reduce transaction risks. For example,
Steemit reduces the risks of illegal transactions by
limiting the time and frequency of transactions. In ad-
dition, third-party neutral institutions also provide
support for decentralized products to reduce fraudu-
lent transactions by providing trusts.
Based on the above analysis, this paper summa-
rizes the comparison of operation models of decen-
tralized products and centralized products as shown
in the following Table 1:
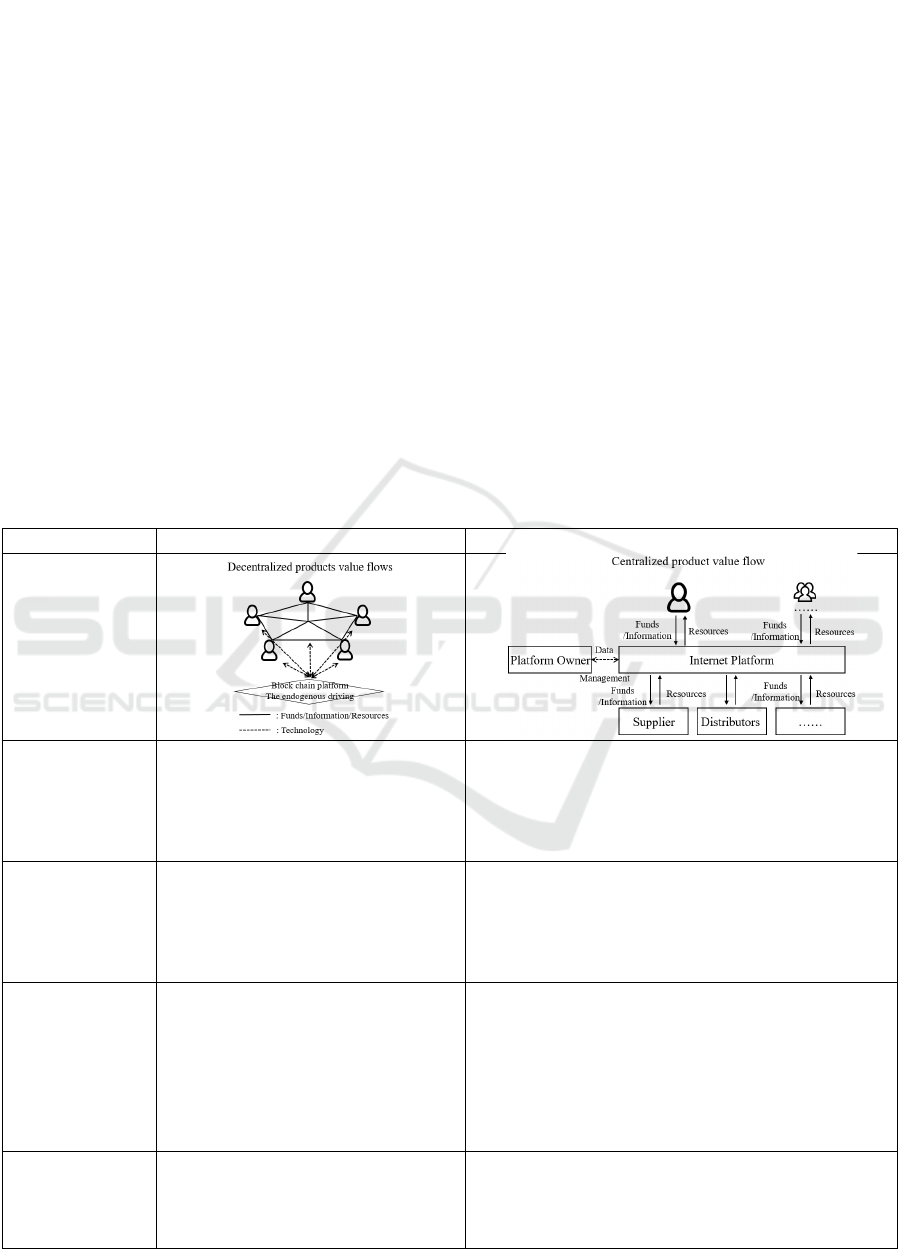
Table 1. Comparison of value co-production models between decentralized products and centralized products.
Web3.0 decentralize
d
p
roducts Web2.0 centralize
d
p
roducts
Schematic dia-
gram
Value co-produc-
tion subject
• Individual user nodes constitute a de-
centralized product ecology
• Connection mode: node-node
• Rights: user rights > decentralized
p
roducts
• Users, suppliers, distributors and third-party organiza-
tions constitute the industrial chain
• Connection method: supplier-platform; distributors -
platform; user-platform
• Ri
g
hts: centralize
d
p
roducts > use
r
ri
g
hts
Value Co-produc-
tion resource gov-
ernance
• Resource source: node creation
• Value judgment criteria: node voting,
subjective judgment, etc
• Management mode: based on block-
chain technolo
gy
• Source of resources: provided by suppliers
• Value judgment criteria: the central platform is based on
objective criteria
• Management mode: platform management, algorithm
im
p
lementation
Value Co-produc-
tion operation
management
• Product profit: commission sharing,
etc
• Incentives: X2E
• Data management: data and computing
power are stored in individual nodes
• Operation structure: network operation
• Product profit methods: flow realization, commission
sharing, value-added services, charged services, etc
• Incentives: promotions, discount activities, etc
• Data management: data and computing power are stored
on the platform, and the platform can optimize opera-
tions through big data analysis
• O
p
eration structure: chain o
p
eration
Value Co-produc-
tion risk manage-
ment
• A higher risk level than centralized
products
• Adopt technology, operation and other
means
• Rely on a centralized platform to manage risk
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
486

2.3 Design of Decentralized Value
Co-Production Model
Based on the summary of value co-production theory
and the characteristics of decentralized products, this
paper constructs a decentralized value co-production
model as shown in the Figure 1 below. Decentralized
product value co-production model solves the prob-
lems of resource coordination, operation governance
and risk management of production factors through
flattening, open source and equalization, so as to
achieve value growth. Decentralized value co-pro-
duction is reflected in the spontaneous management
of resources. Under the promotion of the “X2E” in-
centive mechanism, nodes automatically create value
and judge value. It has the characteristics of endoge-
nous autonomy, which reduces the memory cost of
users, gives users real data autonomy, improves us-
ers’ autonomy in front of algorithms, and establishes
a new trust and collaboration relationship.
Figure 1: Decentralized value co-production model
3 APPLICATION OF P-RAN
OPERATION MODEL BASED
ON DECENTRALIZED VALUE
CO-PRODUCTION
3.1 Introduction of P-RAN
The development of decentralization is evolving in
stages, from products to services. At present, experts
and scholars have put forward many products and
ideas for the decentralized transformation of organiza-
tional and financial services. Similarly, web services,
as the foundation to support decentralized products,
have also received attention. Among them, Qi Bi (Bi,
2022), from China Telecom, proposed the idea of
Web3.0 decentralized network P-RAN (as shown in
the Figure 2) from the perspective of network archi-
tecture, which uses idle mobile terminals of users as
mobile relay and provides network coverage services
for users in areas with weak coverage or even no cov-
erage through multi-hop connection to cellular net-
works. It solves the problem of decentralized infra-
structure from the fundamental level of network ac-
cess. From the distribution form of the network, it can
be seen that P-RAN is a decentralized network. Users
can use the network and share the network with others.
Each person is both a terminal and a relay. This way
of network implementation provides a thinking direc-
tion for exploring decentralized network services.
This paper analyzes the business value model of de-
centralized P-RAN according to the current decentral-
ized product value co-production operation model,
which is helpful to judge the value of decentralized
network service development in the future.
Figure 2: P-RAN Schematic Diagram.
Design of P-RAN Business Model Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production
487

3.2 Application of P-RAN in
Decentralization Value
Co-Production
Resource Coordination
Compared with the traditional network, P-RAN users
have greater control over network resources. Users
play a dual role in the network, not only as users but
also as sharers. Traditional network resource alloca-
tion requires MNOs to build network base stations ac-
cording to the demand through network planning.
With the continuous update of technology, network
coverage will inevitably develop towards higher fre-
quency. However, the high-frequency signal has a
low barrier-breaking ability, so more base stations are
needed to achieve full coverage, and the cost of net-
work construction will increase gradually. Further-
more, with the continuous development of mobile ap-
plications, users’ demand for data usage is also very
different. Although the existing data usage packages
are graded according to the amount of data usage,
they can’t realize targeted package design according
to the preferences of each user.
To solve the above problems, the P-RAN network
is connected by intelligent terminals, and each net-
work user is regarded as a node. By encouraging
nodes to share the idle data usage in the package, the
P-RAN network provides network for users in weak
coverage areas, thus, realizing resource matching and
improves the utilization rate of network resources.
Through the coordination between nodes, the original
network dominated by MNOs has been upgraded to a
decentralized network jointly built by MNOs and us-
ers, and users can control the sharing and use of net-
work resources independently according to their own
needs.
Operation Governance
According to the network architecture of P-RAN, it
can be seen that in the early stage of P-RAN, node
users need to join quickly, and the rapid increase of
relay nodes can form a mesh connection relationship
and promote the whole network construction. Tradi-
tional MNOs have mostly used two approaches to
promote network construction. One is to provide a
good network experience through technical means to
attract users to join, such as Deutsche Telekom’s suc-
cessful test of stratospheric base stations designed to
help achieve mobile signal coverage in remote areas
where terrestrial connecting networks are difficult to
reach. The other is through marketing strategy, by
promoting web application development and thus at-
tracting users. For example, South Korea Telecom
uses synergistic development with the edge cloud to
build 5G clusters/communities to enable direct com-
munication and interaction with users in the region
with large bandwidth. It can be seen that P-RAN is
different from the traditional way of providing high-
quality network to attract users for promotion. There-
fore, the incentive mechanism of P-RAN network op-
eration is especially important.
According to the previous analysis, the incentive
mechanism of decentralized products trend to use the
X2E approach to manage users. P-RAN can also use
“token” as an incentive method to build “Online to
Earn (O2E)”, thus attracting users to share. Firstly,
MNOs can rely on a combination of objective and
subjective network performance characteristics, such
as QoS, network speed, user connection times, user
ratings, etc., so as to provide a fair and objective value
judgment criteria for identifying user contributions.
Secondly, MNOs can also refer to the form of Tiktok
topic challenge for network weak coverage areas to
identify and issue rewarding “token” rewards to at-
tract nearby users to share the network. Finally, the
establishment of “token” also provides support for
MNOs to supervise the traceability of illegal infor-
mation, which is helpful to purify the network envi-
ronment.
Traditional networks rely on connecting B-side
and C-side users to gain profits. In contrast, P-RAN
uses a distributed network architecture, which can ex-
pand this con-nectivity capability and incubate more
business scenarios. The trend of next-generation net-
work is the integration of space and earth, and the
combination of reality and virtual reality. The decen-
tralized network will promote the formation of full-
coverage network and provide a faster and more con-
venient way of network coverage compared to base
stations for daily weak coverage network supplement,
global network roaming, emergency network con-
struction and other scenarios. P-RAN through device-
to-device (D2D) connectivity is also helpful to iden-
tify proximity connection relationships, which can be
utilized to drive proximity service model innovation
such as accurately identifying potential COVID-19
infected persons, accurately placing promotional in-
formation in shopping centers and etc.
Risk Management
Compared with traditional networks, decentralized
networks will face more risk issues, such as technical
implementation risks, identity security risks, and risks
brought by “O2E” operation mode. From the current
stage, it is necessary for MNOs to lead the establish-
ment of P-RAN networks; MNOs can provide credit
endorsement and legal supervision for network secu-
rity issues.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
488

To solve these problems, apart from the risk man-
agement methods of existing networks, decentralized
networks can also verify users’ identity through the
dual method of “physical SIM card + virtual account
password”. When users share data usage or connect
to other sharers’ hotspots, their identity information
will also be recorded on the blockchain along with
data usage changes, thus ensuring network security
from a technical perspective. In the process of asset
trading, MNOs can use methods such as limiting the
time and frequency of transactions to reduce the op-
erational risks that may be associated with O2E.
Besides the risk management of the decentralized
network itself, P-RAN, as a decentralized infrastruc-
ture, can provide authentication at network access
level for other decentralized products. MNOs can
even serve as third-party organizations to provide risk
management support in other decentralized products,
such as tracking illegal information or even blocking
it from network access level, thus improving the net-
work security of users at application level.
3.3 Discussion
Combined with the previous analysis, a comparison
of decentralized network operation and traditional
network operation is summarized as shown in Table2:
Table 2: Comparison between Decentralized P-RAN Network and Traditional Network Based on Value Co- Production.
Decentralize
d
Networ
k
P-RAN Traditional Networ
k
The main
body of the
network
• MNOs and users jointly build and
own decentralized network
• Network connection mode: user-
user; use
r
-
b
ase station
• MNOs build and own networks
• Network connection mode: user-
user-base station
Network re-
source man-
agement
• Source of Network Resource:
MNOs and user
• Network Judgment Criteria: QoS,
network coverage time, user con-
nection times and user ratings, etc.
• Data usage management: users pur-
chase a fixed package, and the re-
maining data usage can be shared
with othe
r
users
• Source of Network Resource:
MNOs
• Network Judgment Criteria: QoS,
etc.
• Data usage management: users
purchase a fixed package
Network Op-
eration Gov-
ernance
• Incentive Mechanism: O2E
• Data management: user and MNO
• Potential expansion strategies: full
coverage scenarios, proximity ser-
vice scenarios, other decentralized
applications
• Incentive Mechanism: combina-
tion of Technological innovation
(improving network coverage)
and marketing innovation (pack-
age discounts, etc.) to attract user
to join
• Data management: MNO
• Potential expansion strategies:
ex
p
an
d
users with 2B2C mode
Network
Risk Man-
agement
• Identity authentication through the
dual method of “physical SIM card
+ virtual account password”
• Limiting transaction time or fre-
quency
• Potential Expansion Service: pro-
vide risk management support for
othe
r
decentralize
d
p
roducts
• Identity authentication through
“Account + Password”
According to the above table, it can be seen that
P-RAN decentralized network is a practice in decen-
tralized value co-production operation model, which
is reflected in the following three aspects.
First, P-RAN is a network infrastructure jointly
owned by users and MNOs. P-RAN is a decentralized
network dominated by MNOs and deeply involved by
users.
Design of P-RAN Business Model Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production
489

Second, P-RAN is a new economic system which
is jointly built and shared by users and MNOs. The
value to MNOs is reflected in the more personalized
network resources allocation. Taking advantage of
the inherent network resources and user, MNOs save
investment in base station construction, and expand
to achieve full network coverage of Web 3.0. The
value to users is reflected in the self-control of net-
work resources; users can even make profits through
the “O2E” model. For other enterprises, the value is
reflected in the incubation of more Web3.0 applica-
tions and the landing of proximity service scenarios
under the support of P-RAN network.
Third, in terms of network risk management,
MNOs solve the risk of P-RAN network technology
implementation, identity security and the risk brought
by the “O2E” operation mode through technical and
operational means, and build a safe, credible and val-
uable network. With the dual support of MNOs’
credit endorsement and immutability of blockchain,
P-RAN’s security is fully guaranteed and provides
risk management support for other decentralized
products.
The relationship between decentralization value
co-production and decentralized network P-RAN
value co-production is shown in the following Figure
3:
Figure 3: Decentralized network P-RAN value co- production positioning
4 CONCLUSION
In the era of Web 3.0, the rapid development of block-
chain technology has promoted the birth of various
decentralized products. In this paper, the decentral-
ized product value co-production model is con-
structed from three breakthrough directions of value
co-production (resource, operation, and risk). The
value of decentralized products is reflected in the
spontaneity of coordinated resource allocation. Under
the incentive mechanism of “X2E”, nodes have the
autonomy of data and algorithm, thus realizing the
real “Read+Write+Own”.
On the basis of defining the value points of exist-
ing decentralized products, this paper analyzes the
business model of decentralized network P-RAN. It
is found that in terms of network resource allocation,
decentralized networks are more autonomous and
personalized than traditional networks. On the one
hand, MNOs can use the 5G/6G investment savings
as the fund source for the decentralized network’s re-
wards pool, incentivizing users to share and use the
network through the “O2E” model. On the other
hand, users can use idle terminals to share excess data
usage within their packages to gain revenue on the
basis of ensuring their own network quality, while
providing support for MNOs to achieve full coverage.
Compared with traditional networks, risk manage-
ment in decentralized networks is more difficult. In
addition to technological innovation, MNOs can also
reduce risk by means of authentication, limiting trans-
action time or frequency, etc. Ultimately, with the
participation of users and MNOs, the decentralized
network will become a secure and valuable network
infrastructure and economic system.
On the basis of traditional network 2B2C busi-
ness, the decentralized network is expected to incu-
bate more new business and bring more potential
value to other en-terprises. Driven by the decentral-
ized network, new decentralized products will drive
the rapid growth of users and data usage across the
network, and finally form a value growth cycle. At
the same time, the decentralized network can also
promote the innovation of proximity service mode by
virtue of the connection characteristics of intelligent
terminals, such as providing support for precise epi-
demic prevention and control, merchant information
promotion, etc. In the future, the decentralized net-
work can be expanded into a global Web 3.0 network,
and users traveling abroad will not need to open in-
ternational roaming. Combining the above factors,
the construction of a decentralized network can
achieve growth in the overall value of MNOs, enter-
prises and users, and drive the birth of more decen-
tralized products.
Due to limited time and energy, the vision of de-
centralized infrastructure con-struction in this paper
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
490

is summarized according to the characteristics of ex-
isting decentralized products. In the future, more re-
search is needed to solve problems such as how to re-
alize the compatibility between decentralized net-
works and existing networks, and how to achieve net-
work interface among MNOs. Meanwhile, in the pro-
cess of decentralized operation, the supervision of de-
centralized network still needs legal support; how to
quickly block illegal information and how to coordi-
nate the property rights system of network sharing are
also issues that need to be addressed. These problems
require not only the technical innovation by MNOs
and enterprises, but also the support of government
regulatory authorities. Currently, decentralized infra-
structure is in its envisioned stage, but with the pro-
gress of technology, more applications will emerge.
REFERENCES
Asgaonkar, A., Krishnamachari, B.: Token curated regis-
tries-a game theoretic approach. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1809.01756(2018).
https://arxiv.53yu.com/pdf/1809.01756.pdf
Bharti, K., Agrawal, R., Sharma, V.: Value co-creation: Lit-
erature review and proposed conceptual framework. Int
J Market Res, 57(4), 571-604(2015). doi:10.2501/ijmr-
2015-012
Bi, Q.: The Proximity Radio Access Network for 5G and
6G. IEEE Communications Magazine, 60(1), 67-
73(2022). doi: 10.1109/mcom.001.21494
Dhanaraj, C., Lyles, M. A., Steensma, H. K., Tihanyi, L.:
Managing tacit and explicit knowledge transfer in IJVs:
the role of relational embeddedness and the impact on
performance. J INT BUS STUD, 35(5), 428-442(2004).
doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400098
Gawer, A., Cusumano, M. A.: Platform leadership: How In-
tel, Microsoft, and Cisco drive industry innovation
(Vol. 5, pp. 29-30). Boston: Harvard Business School
Press (2002). doi:10.5172/impp.2003.5.1.91
Heidenreich, S., Handrich, M.: Adoption of technology-
based services: the role of customers’ willingness to co-
create. J SERV MANAGE, 26(1), 44-71(2015).
doi:10.1108/josm-03-2014-0079
Hirschhorn L. Beyond Mechanization. MIT Press, Boston,
MA,1984.
Lavie, D.: Capability reconfiguration: An analysis of in-
cumbent responses to technological change. AMR,
31(1), 153-174(2006).
doi:10.5465/amr.2006.19379629
Prahalad, C. K., Ramaswamy, V.: Co-opting customer
competence. HBR, 78(1), 79-90(2000).
https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A59023943/AONE?u=
anon~185c9bd6&sid=googleScholar&xid=08ca2fb8
Prahalad, C. K., Ramaswamy, V.: Co-creating unique value
with Customers. Strategy & Leadership, 32(3), 4-
9(2004). doi: 10.1108/10878570410699249
Ramirez, R.: Value co‐production: intellectual origins and
implications for practice and research. Strateg. Manag.
J., 20(1), 49-65(1999). doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-
0266(199901)20:1<49::aid-smj20>3.0.co;2-2
Trist, E. L.: The evolution of socio-technical systems (Vol.
2). Toronto: Ontario Quality of Working Life Centre
(1981).
Vargo, S. L., Lusch, R. F.: Evolving to a new dominant
logic for marketing. In: The service-dominant logic of
marketing (pp. 21-46). Routledge (2014).
doi:10.4324/9781315699035-9
Vargo, S. L.: From Promise to Perspective: Reconsidering
Value Propositions from a Service-dominant Logic Ori-
entation, IND MARKET MANAG, 87(5), 309-
311(2020). doi:10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.10.013
Yoo, Y., Henfridsson, O., Lyytinen, K.: Research commen-
tary—the new organizing logic of digital innovation: an
agenda for information systems research. INFORM
SYST RES, 21(4), 724-735(2010).
doi:10.1287/isre.1100.0322
Design of P-RAN Business Model Based on Decentralized Value Co-Production
491
