
Analysis of Trading Security of Cryptocurrencies: Evidence from the
DAO Hack
Chang Liu
Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, 100044, China
Keywords: Cryptocurrencies, Blockchain, Trading Attack, Computer Technology.
Abstract: Contemporarily, cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin and Ether) gained more public attention in recent years, which
also has financial influences on trading on the blockchain platform. Similar to other emerging digital
technologies, safety especially trading and transaction security becomes a significant issue, with the
increasing number of users. In this article, it will mainly focus on the cryptos trading security on the
blockchain, accompanied by a real attacking case, the DAO hack happened in 2016, to analyze current security
strategies on the blockchain platform and the vulnerabilities within the trading and transaction process.
Although there are many strategies such as hash function used for digital signature and decentralization to
protect the security of users’ privacy and trading’s normal operation, double-spending and multiple
withdrawal attack still happen because of the immature mining technology, caused by a long time for miners
to validation and add blocks onto the blockchain. To address the issue, some new ways, using emerging
computer information technology, to validate transactions can be used to shorten the time and energy
consumption, while the users’ actions still considerably contribute to the trading security on the blockchain.
These results shed light on avoiding and improving the future environment of blockchain and its development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of blockchain can be mainly
divided into three stages, which are blockchain 1.0
from 2008 to 2013, blockchain 2.0 from 2013 to
2015, and blockchain 3.0 from 2015 to 2018. In 2008,
Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper on Bitcoin
(Nakamoto, 2008), and blockchain entered a new
epoch. An electronic payment system was deployed
with cryptographic proof compared with the
traditional transaction strategy based on trust, which
allows no third party to be needed or get involved
when two groups want to transact, leading to a direct
and convenient transaction, solving the decentralized
difficulties on currency and transaction. After that
period, one of the most significant invent was
Ethereum. Vitalik Buterin, a top developer,
recognized the limitation of Bitcoin and brought in
another kind of cryptocurrency which is Ethereum,
making it possible to have a programmable currency
through a smart contract, which can be executed
automatically when the condition is satisfied, without
third parties intervene. When it comes to after 2015,
blockchain and cryptocurrency meet an era of a full
application. Lots of kinds of new implementations of
blockchain appears such as NEO and IOTA, and more
area, e.g., finance, science, and art, uses blockchain
and cryptocurrency to record information and solve
public affairs.
While with the development of blockchain and
cryptocurrency, security becomes a major threat for
users when having transactions with each other.
Research, done by Fröhlich, supported that key
management meets a difficulty for users when
transactions (Fröhlich, 2020). Fröhlich also provided
a model based on CMT, allowing researchers and
developers to understand more users’ actions on the
blockchain with the security issue (Fröhlich, 2020).
Losing currency is a common situation in the
cryptocurrency area, which is always experienced by
holders rather than some freshmen possessing
currency. As Svetlana analyzed in 2021, trying to find
the risk by observing users’ choice of crypto-wallet
and some kinds of security practices used for
protecting crypto-assets, there is some gap between
users in their security perceptions, which affects their
decision on choosing wallet and transaction platform
(Abramova, 2021). While Banerjee, Utsav, and
Anantha developed a new way for encrypting
transactions by a kind of low-power processor for
504
Liu, C.
Analysis of Trading Security of Cryptocurrencies: Evidence from the DAO Hack.
DOI: 10.5220/0012035700003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 504-510
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

secure embedded blockchain, which implemented
elliptic curve pairing (Banerjee, 2021). In addition, a
detailed analysis was developed by Chao Yu on the
security of cryptocurrencies with the domain of
support from blockchain platforms and technology,
suggesting that data authenticity and recording are
used to ensure the security of blockchain technology
(Yu, 2022). However, Baraković, Sabina, and
Jasmina organized some interesting statistics about
what current cryptocurrency meets with security
challenges (Baraković, 2022). Attacks including
network attacks, user wallet attacks, and smart
contract attacks are the most prominent influence on
cryptocurrencies. To summarize, blockchain and
cryptocurrencies are now with security threats on
both users’ side and during the transaction such as
encrypting and various kinds of attacks.
Contemporarily, blockchain has more and more
real use in both people’s daily life and advanced
technologies such as recording important
information, especially personal privacy and ensuring
compulsory consensus with currency transactions.
This article mainly analyzes current trading security
on blockchain and cryptocurrencies with some
evidence. In the beginning, a description of the
blockchain and trading processing for
cryptocurrencies will be given with a simple way and
some flow image to help, followed by security design
for transactions in recent years. Then, the article will
show several possible vulnerabilities in blockchain to
demonstrate the security flaw in the crypto
transaction. In addition, certain cases and examples of
transaction security will be explained for the
happening reason. Finally, the limitation of current
security policies and strategies on the crypto
transaction will be listed, which also includes
possible outlook in the future.
2 BLOCKCHAIN CONCEPTS
AND TRADING PROCESSING
FOR CRYPTOS
2.1 Terms and Concepts
Blockchain is normally known as a chain connecting
lots of blocks, which contains certain information,
sorted by the creation time, which the whole chain
will be saved at all the blockchain servers, standing
for a safety issue that only one server can maintain the
work of the whole blockchain (Eskandari, 2018). It
leads to the two main features of blockchain as temper
(i.e., resistant and decentralization), which account
for difficulties in changing all data in all the servers
of blockchain at one time. A transaction is that when
there is a new block, the owner of the block will use
the former transaction’s hash code and the public key
of the latter owner, which would be added at the end
of the coins, thus, transferring the current coin to the
next owner (Nakamoto, 2008). In this situation, the
ledger, also called blockchain, is maintained and
updated by a decentralized network using a novel
method to reach a consensus that involves
incentivizing nodes in the network with the ability to
generate new Bitcoin and collect transaction fees,
which can be recognized as mining.
Cryptocurrency, an electronic coin, is always used
for a chain of digital signatures, recording the whole
trace for the chain (Fang, 2022). There are three
mainstream cryptocurrencies, which are Bitcoin as
mentioned before, Ethereum, and Litecoin. Bitcoin is
a kind of digital currency described by Nakamoto in
2008 (which also introduces a peer-to-peer electronic
cash system) (Nakamoto, 2008). Different from most
of the currencies, Bitcoin was created by a specific
algorithm with vast computing, handed out to pay
miners’ effort, which supports cryptography as a
design to ensure security in the process of currency
circulation. Ethereum is an open-source common
blockchain platform providing smart contracts, at
which solving by Ethereum Virtual Machine to
support decentralized and peer-to-peer services
(Fang, 2022). Ether is the main transaction coin,
which is also a kind of cryptocurrency used for
trading such as deploying smart contracts and
transactions a with smart contract. In addition,
Litecoin is treated as a leading rival for Bitcoin
currently, which is designed to foster the transaction
of small value on the blockchain. Compared with
Bitcoin, Litecoin needs less energy consumption,
which means that it can be mined by just a normal
computer or laptop (Bhosale, 2018).
2.2 Cryptocurrency Trading Process
The definition of cryptocurrency trading is an activity
in which people buy and sell cryptocurrencies to
make a profit (Fang, 2022). Technical and
fundamental trading are two main trading strategy
categories, with similarity in the reliance on vast
information to verify their performance.
Cryptocurrencies transaction always happens in two
main situations, which are transaction with a smart
contract and transaction with a user.
Analysis of Trading Security of Cryptocurrencies: Evidence from the DAO Hack
505
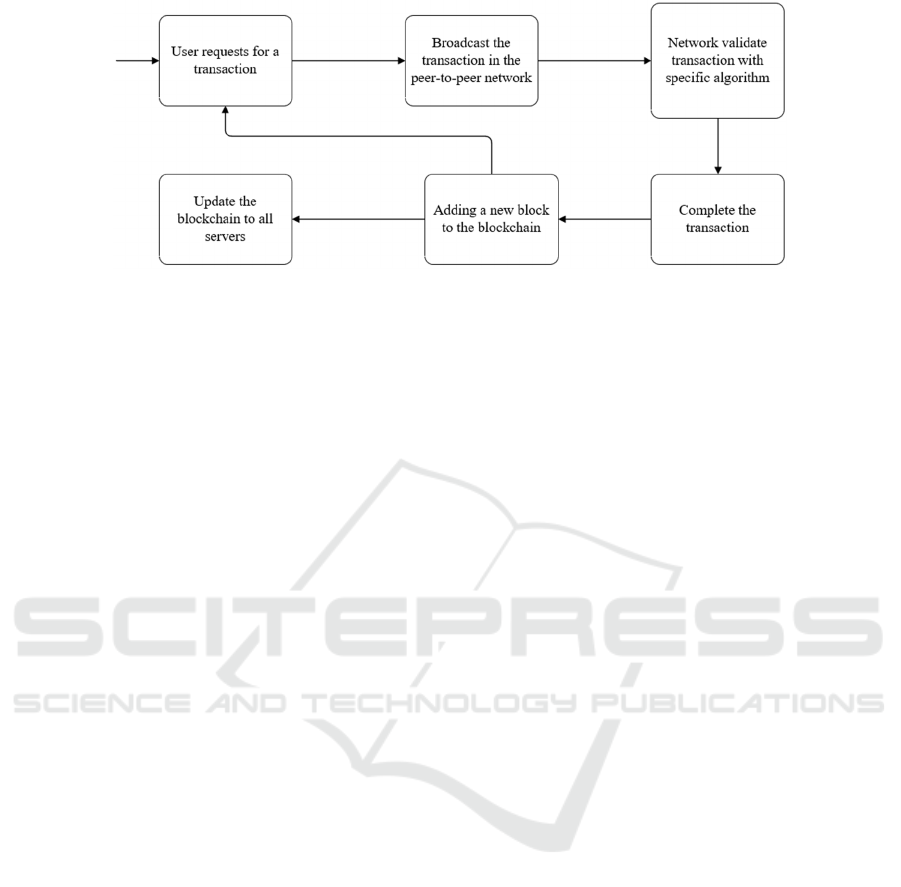
Figure 1: A simple process for transaction validation in the blockchain. [Owner-draw].
As shown in Fig. 1, a flow chart of a cryptos
transaction, the basic trading process for
cryptocurrency begins with users’ requests, followed
by broadcasting the transaction message among the
peer-to-peer network such as Ethereum. After the
miner or smart contract would validate the transaction
with a specific algorithm to compute the correctness.
Then, one comes the final step of the trading and the
new block with the transaction will be added to the
blockchain. This would be a recycle and every time a
user wants to transact will do this process. After all
the update is completed, the whole changes sign in to
the blockchain server.
3 SECURITY DESIGN
In this section, current technologies, and strategies for
protecting transaction security will be demonstrated,
which are based on two main platforms, Bitcoin and
Ethereum.
3.1 Decentralized and Anonymity
In the blockchain, the consensus mechanism is the
precondition of the whole transaction. As Sayeed,
Sarwar, and Hector Marco-Gisbert said that it ensures
that the transaction comes from a legal and correct
resource by informing all participants in the
transaction to have an agreement on the state of
distributed ledger (Sayeed, 2019). Therefore, the
consensus can be seen as a bank in the real world,
with the difference that there are no third parties and
human factors. The trading on the blockchain does
not need a third party, who can control users’
processes and assets leading to huge losses when
being attacked, while all records and transactions are
maintained by the distributed system in each node
participating, and each node has entire transaction
records, which means tiny influences when meets
attacks (Banerjee, 2021). In addition, when two users
transact on the blockchain, what they use is their
public keys, which are unreadable. Moreover, users
can have more than one account, leading to an
unpredictable procession. This increases the privacy
of users enormously, and trading security as well.
3.2 The Hash Function and Digital
Signature
A digital signature is used to validate the accuracy
and security of a data string, which is a mechanism in
the blockchain. Each block contains a string, a unique
digital signature, according to what that block
includes especially information and data stored in the
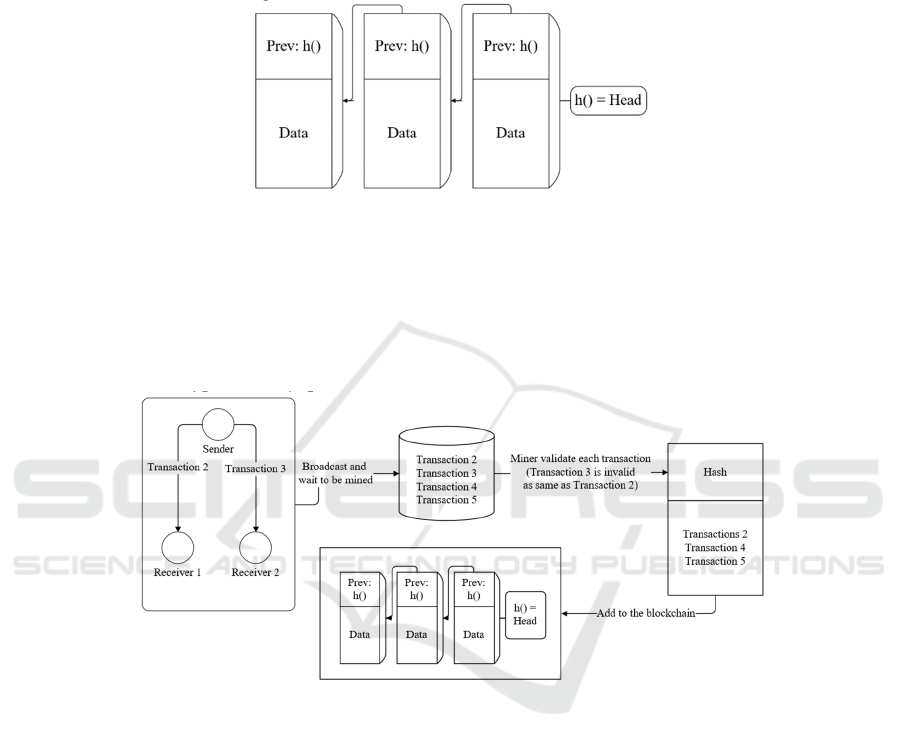
block. Fig. 2 illustrates three blocks that chain
together, which have a hash header, accounting for a
digital signature, e.g., Merkle hash to validate
whether the data is integrated and not changed or not
manipulated. Nevertheless, a digital signature cannot
always represent the next block correctly and validate
it, as is the difficulty of different hash functions. On
this basis, the Bitcoin blockchain sets a level with
certain difficulty for calculating and computing the
creation time for a block. Thus, if there are fewer data
in a block, that does not represent a faster calculation
to create a new block. If the difficulty level requires
that there are exactly sixteen zeros at the front of a
digital signature, the miner should and must satisfy
this requirement to verify one block.
This mechanism protects the data in the block to
some degree, as if there is an attacker who wants to
manipulate information within a block that is in the
middle of the whole blockchain, once the data
changes, leading to a changing of the digital
signature, standing for an error for the validation and
verification of the next block, which is caused by a
not match with the hash value, the attacker needs to
create new digital signatures for each of the following
blocks in the blockchain to solve the unmatching and
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
506
verifying problems, which is expensive and nearly
impossible for either a single person or an attacking
teams (Sun, 2021). Besides, the attacker does not just
need to create new digital signatures for the damaged
blocks but also needs to act for the regular adding
blocks, generating new digital signatures. The reason
is that miners add blocks with digital signatures
according to primary blocks which are not
manipulated by attackers, on the contrary, those
primary blocks have been changed with different
digital signatures.
Figure 2: A sketch to describe the basic structure of how blocks are connected on the blockchain, like a linked list [Owner-
draw].
4 SECURITY FLAW
This section will focus on Ethereum security, which
is the most famous cryptocurrency platform, with
some common attacks happening on Ethereum such
as smart contract leakage.
Figure 3: When a sender sends two same transactions to different receivers during the mining time, double-spending happens
[Owner-draw].
4.1 Double-Spending
In blockchain trading, double-spending is a common
problem, which means using a one-time transaction
two or three times, due to the consensus delay (Saad,
2020). To show this threat, consider a scenario, with
a sender and two receivers in the blockchain. In the
common blockchain, when a sender wants to have
transactions with the receiver, it basically transports
the assert with a sender’s public key to the receiver’s
address, which needs the sender’s private key to sign
for the transaction. Once the transaction is signed, it
will broadcast to the whole blockchain network to
find the receiver. At the time that the receiver gets the
transaction, the receiver would validate the address
and the private key, along with an unspent
transaction, waiting for miners to calculate and put
the block onto the blockchain as a valid block. While
the time for mining cannot be confirmed with
different block computation times. However, when
the receiver is positive and wants to end the
transaction quickly, it would not wait for the
validation and mine of the block by miners, who send
the products back to the sender. On this basis, the
sender can re-sign the transaction and send the same
transaction to another receiver, which means that the
sender sends two same transactions to two different
receivers during the mining time of the transaction
block. In this case, which receivers will get the real
Analysis of Trading Security of Cryptocurrencies: Evidence from the DAO Hack
507

transaction depending on the mining time, as
exhibited in Fig. 3.
4.2 Multiple Withdrawal Attack
An attack that always happens in ERC20 tokens
called a multiple withdrawal attack is also common in
blockchain trading. This attack comes from two
methods in the ERC standard, used for approving and
transferring tokens (Rahimian, 2019). A method
called approve, allows a spender to withdraw a certain
amount of token in the token pool of the approver, and
if the method is called for several times, it will
override the previous modification and update the
newest change of the allowance. In addition, the
method TranferFrom is to transfer tokens from one
user to another without limitation. Imaging a scenario
where there is an approver and a spender, the
approver allows the spender to transfer N tokens on
his balance. Conversely, the approver wants to
change N to M tokens instead, while the new
transaction of this change has not been added to the
blockchain because of the mining time, which is
invalid at that time. The spender transfers N tokens
by front running. When the approver’s transaction is
executed on the blockchain, the spender has another
chance to transfer M tokens to his account, which
means there are (M+N) tokens totally transferring
from the approver. This attack can be avoided by the
approver if he waits for the execution of the first
transaction, compared with what the assumption is
just operated by the spender at one time (Rahimian,
2019).
5 CASES OF SECURITY ISSUES
This section will analyze a smart contract attack
happening in the real world, e.g., the DAO hack
caused huge economic losses and made a big
influence on blockchain development. A famous
attack, the DAO hack, also a kind of reentrancy
attack, leading to a furcation of ETC and ETH, will
be discussed in this section as a case, to show a real
flaw in the blockchain. In June 2016, the DAO hack
happened with more than 3.6 million Ethers stolen by
attackers (Dhillon, 2017). The attacker found a
vulnerability in DAO.sol, which is mainly used for
the deposit and withdrawal balance of users. The
method withdraw was used for having a recursive
withdrawal when a contract calls this function until
the balance of the target contract decreases to zero.
The underlying reason is that the attacker created an
attacking contract with a method fallback, a default
function in Ethereum, which will be called at the time
that the withdraw method was called with payment.
Due to this mechanism, the fallback method can call
the withdraw function within it, which will withdraw
the balance continuously.
Table 1: A target contract and an attacking contract to show how the attack happens [Owner-draw].
contract DAOSam
p
le
{
im
p
ort "./DAOSam
p
le.sol";
mapping(address => uint) public bal; contract Attack {
function de
p
osit
()
p
ublic
p
a
y
able
{
DAOSam
p
le
p
ublic daoAcc;
b
al[ms
g
.sender] += ms
g
.value; constructor
(
address
_
daoAddr
)
{
} daoAcc = DAOSample(_daoAddr);
function withdraw
()
p
ublic
{
}
uint bal = bal[msg.sender]; fallback() external payable {
re
q
uire
(
bal > 0, "Not enou
g
h"
)
; if
(
address
(
daoAcc
)
.bal >= 1 ether
)
(bool send, )=msg.sender.cal}(""); daoAcc.withdraw();
re
q
uire
(
send, "Failed to send"
)
;
}
b
al[msg.sender] = 0; function attack() external payable {
}
re
q
uire
(
ms
g
.value >= 1 ether
)
;
daoAcc.deposit{value: 1 ether}();
daoAcc.withdraw
()
;
}
}
Here is a sample code for the target smart contract
DAOSample.sol and the attack smart contract
Attack.sol (seen from Table. 1) used by the attacker,
which extends the target smart contract. The first step
is to deposit some ethers to the target smart contract
to have a balance in the account by attack method in
the attack contract. Then, the attack begins, with a call
function of withdraw in the target contract, which, as
mentioned before, will execute fallback method in the
attack contract during the action of msg.sender.call in
the target contract after transferring Ethers to the
attack contract. However, here comes a circulation in
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
508

the fallback method, as there is also a call of withdraw
method in the target contract, while the balance of this
account has not been modified from the primary
balance, which leads to another time for withdrawing
balance from the target contract. When the balance
Ether on the target contract comes to zero, the
fallback method ends and begins to return, making no
sense anymore as the Ethers of the target contract has
been transferred to the attack contract.
For solving this attack immediately, the Ethereum
official tried to send plenty of transactions to block
the blockchain and came to the idea that having a soft
branch between the hacked Ethers and the main
blockchain of Ethereum (Dhillon, 2017).
Nonetheless, the reason that users act on the
blockchain is mainly because of the decentralization
and privacy. Whereas, the action of the official
accounts that there is still a third party to supervise
and control the whole blockchain ledgers, and having
the ability to modify users’ transaction and action,
disobeying to the consensus mechanism
(Praitheeshan, 2019). After this soft branch and hard
branch in the next few months, there are two main
blockchains, ETC and ETH, operation by the original
users who believe in and preserve the consensus
mechanism and by the official Ethereum respectively.
6 LIMITATIONS & PROSPECTS
During several years of development of blockchain,
there are some experienced strategies to solve trading
security vulnerabilities. Whereas, the limitations are
also obvious, especially in cryptocurrencies
transaction which is connected with users closely, as
listed in following:
Protocol limitation. Blockchain depends on a
consensus mechanism protocol to keep the platform
working, while this mechanism is quite different on
different blockchain platforms, standing for a weak
consensus (Sayeed, 2020). Therefore, when an attack
happens on the blockchain, the blocks will be
removed, and then, damage the blockchain fully. In
addition, another protocol Pow, Proof of Work, is a
disadvantage in blockchain, which accounts for huge
energy consuming for proofing and validating
transactions, limiting the mining time to add a block
onto the blockchain as a low efficiency on operations.
For this limitation, multiple withdrawal attacks and
also selfish mining attacks were designed to attack
this weakness.
Transaction time limitation. As shown in Fig. 1,
when users want to transact on the blockchain, miners
need to validate the transaction by calculating.
Conversely, this time is always long and depends on
various issues such as the block size and the gas fee
which is used as a reward for miners’ work
(Gebraselase, 2021). Although this long-time
validation provides some security indeed, it leads to
lots of attacks such as double spending and multiple
withdrawal attack, which are caused by the time delta
between sending and validating. The other
disadvantage is that most of the users have no
intention to wait for such a long time, while their time
can also be regarded as money.
Smart contract limitation. This always happens
on an application tier, as after deploying the smart
contract with an application. Once the smart contract
has vulnerabilities, the attackers can make use of
them and steal lots of cryptocurrencies and destroy
the security and also the blockchain. This attack
always occurs when smart contract developers fail to
find and identify the code bugs, and when the smart
contract is deployed, it is static on the blockchain,
which means that the developers cannot modify it
anymore despite deploying a new smart contract,
causing finance loss if the previous threat smart
contract has been used for a long time. Just like the
DAO hack (Dhillon, 2017), the smart contract has
collected lots of Ethers from the blockchain, but, at
that time, the underlying threats appeared, leading to
a huge influence such as the furcation of the two kinds
of cryptocurrencies.
It is undeniable that the appearance of blockchain
and cryptocurrencies makes a significant influence on
trading and finance, while they have not gotten into a
mature way, especially in cryptocurrency trading and
transactions. PoA, Proof of Activity, can be
considered to have wider use in the future to having
less energy consuming by miners and shortening the
time for validating the transaction, which can avoid
some attacks such as multiple withdrawal attacks that
depending on the time difference, and increasing the
enthusiasm on mining (Sayeed, 2020). In addition,
another aspect of the strength of security is that more
work can be done on smart contract. It is obvious that
lots of attacks on the blockchain are caused by some
vulnerabilities on smart contracts, for example, the
DAO hack due to a reentrance attack by contract
threat and the multi-sig wallet attack, which is also an
attack caused by attackers hacking on smart contracts.
It is possible that the blockchain platforms can give
more instructions on smart contract generation and
deployment, together with forbidding unsafe methods
in smart contracts to avoid developers’ misusing
when applying. While the last aspect can be users’
actions. The protection of private keys should be
considered, with more secure ways to use them such
Analysis of Trading Security of Cryptocurrencies: Evidence from the DAO Hack
509

as QR codes or NFC (Saad, 2020). Additionally,
gaining experience from double spending attacks,
users need to ensure their transaction before taking
the following steps.
7 CONCLUSION
In summary, this paper investigates trading security
based on the DAO attack that happened in 2016.
Contemporarily, more people own cryptocurrencies,
such as Bitcoin and Litecoin, on the blockchain,
leading to security issue which is common in every
domain around the world. The safety of blockchain is
mainly protected by the immutability using hash
functions, which cause expensive spending when
attackers change date within one block, and its
decentralization, with no third-parties operation,
while some attacks, like double-spending and
multiple withdrawal, even reentrance, still threat
users trading security currently as the long mining
time for validating transactions and update the
blockchain. In addition, the DAO hack shows an
opposite view, which, to retrieve the loss, the official
of Ethereum changed the blockchain compulsively,
leading to a puzzle on the consensus mechanism with
the basic trust in the blockchain. In the future, new
proof ways such as proof of activity and users’
privacy should be considered more in security
trading. This article only centralized on two main
blockchain platforms, Bitcoin and Ethereum, giving a
simple analysis of current trading security, without
emerging platforms like Cordas. Although threats
still exist, users and developers will have a positive
view of the development of blockchain, to solve
current trading security issues and have a safer way
to store information, especially that sensitive. In the
future, blockchain will provide a more guaranteed
platform for people to trade and save sensitive
information without being supervised. Overall, these
results offer a guideline for learning for blockchain
implementation to realize trading security.
REFERENCES
Abramova, S., et al.: "Bits under the mattress:
Understanding different risk perceptions and security
behaviors of crypto-asset users." Proceedings of the
2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing
Systems. (2021).
Banerjee, U., and Anantha P. C.: "A low-power elliptic
curve pairing crypto-processor for secure embedded
blockchain and functional encryption." 2021 IEEE
Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC). IEEE,
(2021).
Baraković, S., and Jasmina B. H.: "Digital Transformation
Challenges: The Cyber Security Threats of
Cryptocurrency Technology Use." FIRST
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON
ADVANCES IN TRAFFIC AND
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES. (2022).
Bhosale, J., and Sushil M.: "Volatility of select crypto-
currencies: A comparison of Bitcoin, Ethereum and
Litecoin." Annu. Res. J. SCMS, Pune 6 (2018).
Dhillon, V., David M., and Max H.: "The DAO hacked."
Blockchain Enabled Applications. Apress, Berkeley,
CA, 67-78 (2017).
Eskandari, S., et al.: "A first look at the usability of bitcoin
key management." arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.04351
(2018).
Fang, F., et al.: "Cryptocurrency trading: a comprehensive
survey." Financial Innovation 8.1: 1-59 (2022).
Fröhlich, M., Felix G., and Florian A.: "Don't lose your
coin! Investigating Security Practices of
Cryptocurrency Users." Proceedings of the 2020 ACM
Designing Interactive Systems Conference. (2020).
Gebraselase, B. G., Bjarne, E. H., and Jiang, Y.: "Effect of
Miner Incentive on the Confirmation Time of Bitcoin
Transactions." 2021 IEEE International Conference on
Blockchain (Blockchain). IEEE, (2021).
Nakamoto, S.: "Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash
system." Decentralized Business Review: 21260
(2008).
Praitheeshan, P., et al.: "Security analysis methods on
Ethereum smart contract vulnerabilities: a survey."
arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08605 (2019).
Rahimian, R., Shayan E., and Jeremy C.: "Resolving the
multiple withdrawal attack on erc20 tokens." 2019
IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy
Workshops (EuroS&PW). IEEE, (2019).
Sayeed, S., and Hector M. G.: "Assessing blockchain
consensus and security mechanisms against the 51%
attack." Applied sciences 9.9: 1788 (2019).
Sayeed, S., Hector M. G., and Tom C.: "Smart contract:
Attacks and protections." IEEE Access 8: 24416-24427
(2020).
Saad, M., et al.: "Exploring the attack surface of
blockchain: A comprehensive survey." IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials 22.3: 1977-2008
(2020).
Sun, G., et al.: "Research on blockchain transaction
security." Nanjing University of Posts and
Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition)
41.02:36-48 (2021).
Yu, C., et al.: "Technology and Security Analysis of
Cryptocurrency Based on Blockchain." Complexity
2022 (2022).
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
510
