
Research on the Application of Blockchain Technology in the
Innovative Development of Agricultural Supply Chain Finance
Chunhua Li
Xi'an eurasia university, China
Keywords: Blockchain, Supply Chain Finance, Distribution of Benefits, "Agriculture, Rural Areas and Farmers".
Abstract: Supply chain finance can provide high-quality financing channels for agriculture, rural areas and farmers to
support the development of agricultural industry chain, but agricultural supply chain finance has not reached
the maturity in the industrial field, the agricultural supply chain structure is loose, the enterprise
qualification is quite different, the agricultural industry itself has a special attribute determines the
agricultural and industrial supply chain finance innovation mechanism is significantly different. This paper
analyzes the construction method of embedding the key technology of blockchain into agricultural supply
chain finance to solve the problems of "difficult financing, expensive financing and slow financing" of
agriculture-related smes from the technical level. Combined with the characteristics of agricultural
cooperatives, a "1+1+N" supply chain finance architecture was proposed to solve the problem of loose
structure of agricultural supply chain from the management level, and the agricultural supply chain finance
model was innovated on a sub-basis by combining blockchain technology. Shapley value method was used
to construct the financial benefit distribution model of agricultural supply chain, and the incentive
mechanism of participating enterprises in supply chain finance was discussed by means of the benefit
distribution model. The research results enrich the application of blockchain in the fields related to
agricultural supply chain finance, and contribute to the establishment of supply chain financing environment
for small, medium and micro agriculture-related enterprises based on cooperatives, thus contributing to rural
revitalization.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the data from the Blue Book of Internet
Finance for "Agriculture, Countryside and Farmers"
released by the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences,
the financial gap for "agriculture, countryside and
farmers" in China has reached 3.05 trillion yuan, and
there is still much room for improvement in the
revitalization of financial services for rural industries.
At present, China's rural financial resources are
seriously deficient. The systems of rural homestead
mortgage, agricultural product mortgage, rural land
contractual management right mortgage, and
agricultural product insurance are not perfect. Small,
medium-sized and micro agricultural enterprises and
farmers have limited financing channels, large
financing difficulties, long financing cycle, and high
financing costs. These problems are closely related to
the existing supply chain status of agricultural
enterprises.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Ahluwalia Saurabh et al. (2020) analyzed how to use
blockchain technology for start-up financing, and
proposed a model based on the theory of transaction
cost economics and the transaction nature of
blockchain technology to demonstrate how to use
blockchain technology to overcome many problems
inherent in start-up financing of enterprises
(Ahluwalia, 2020). Feng Bao et al. (2022) takes the
platform-type supply chain finance financing
business as the research object, analyzes the factors
that affect the decision-making of participants, builds
a tripartitic evolutionary game model of smes, core
enterprises and financial institutions under traditional
circumstances and under the drive of blockchain,
respectively, and explores the balanced choice of
each participant (Feng, 2022). Huo Hong et al.
(2022) aiming at the agricultural supply chain
composed of e-commerce, farmers and leading
enterprises, took into account the bankruptcy risk of
Li, C.
Research on the Application of Blockchain Technology in the Innovative Development of Agricultural Supply Chain Finance.
DOI: 10.5220/0012036300003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 529-534
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
529

farmers and the output randomness of agricultural
products, respectively built the income model of
e-commerce, farmers and leading enterprises under
the insurance and risk sharing mode, and proposed
the optimal decision of e-commerce, farmers and
leading enterprises and the influencing factors of the
optimal decision (Huo, 2022). Sun Zhonghe and Xu
Xiaoyan et al. (2021) selected 11 risk assessment
indicators of agricultural supply chain finance
business, built an agricultural supply chain risk
assessment model based on GA-BP neural network,
and verified the proposed risk assessment model with
case analysis (Sun, 2021). Wang Y. (2021) Combined
blockchain and fuzzy neural network algorithm,
studied the credit risk of SME financing from the
perspective of SME financing, built the supply chain
financial information module by integrating the
financial system with blockchain technology, adopted
fuzzy neural network algorithm for financial data
processing and risk assessment, and effectively
solved and improved the risk handling level of
financial enterprises (Wang, 2021). Based on the
current development status of agricultural supply
chain finance in China, Zheng Yi (2022) analyzed the
main models and development difficulties of supply
chain finance and proposed innovative strategies of
agricultural supply chain finance (Zheng, 2022).
To sum up, domestic and foreign scholars'
research on supply chain finance has combined
financial technologies such as blockchain, and some
literatures have studied the profit distribution and
balanced selection of various participants in supply
chain finance. It rarely discusses the promotion and
promotion of the internal drive of the agricultural
supply chain financial model in combination with the
characteristics of the agricultural supply chain. This
paper uses the research experience of domestic and
foreign scholars for reference, relies on the
agricultural supply chain financial model innovation
and benefit distribution model, solves the problems
of loose and difficult management of the agricultural
supply chain structure, and relies on the blockchain
technology to solve the key problems in the
implementation of supply chain finance.
3 METHODS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Analysis of Key Issues in the
Implementation of Agricultural
Supply Chain Finance
First, Cause analysis of financing difficulties. The
supply chain finance relies on the core enterprise's
ability to control goods and adjust sales. For the sake
of risk control, the capital end is generally willing to
provide financial services only to the core enterprise's
upstream and downstream primary suppliers and
dealers, which leads to the failure to meet the needs of
secondary and tertiary suppliers/dealers with huge
financing needs. In addition, bills cannot be separated
during the financing process, and the flexibility of use
is very limited. Therefore, the main problems in
financing are credit multi-level transmission, bill
splitting and trust consensus.
Second, the characteristics of supply chain
finance require participants to have a very detailed
and full understanding of the whole industry chain,
and have high requirements on the control ability and
technical ability of underlying assets. In order to
reduce risks, it is difficult to reduce the operating
costs of supply chain finance. In addition, the supply
chain financing business lacks a regulatory body in
the implementation process. In order to obtain
financing, SMEs make unlimited concessions in the
discount rate, which makes the overall financing cost
of the supply chain rise. Therefore, the problem of
expensive financing mainly lies in the consensus of
trust, the achievement of risk management and
control, and the cooperation of enterprises in the
agricultural supply chain.
Third, agriculture itself has a long production
input cycle, and there is a serious problem of
information islands in the agricultural supply chain
system. Pledged goods are stored in third-party
logistics companies, and it is difficult to verify the
authenticity, quality, status, transaction and other
storage information of goods, which increases the
difficulty of information audit and lengthens the audit
cycle. Therefore, the problem of slow financing is
mainly the difficulty of preventing bill fraud and the
achievement of the efficiency of bill information
review.
Therefore, the key issues of agricultural supply
chain financial development can be summarized as
trust consensus, bill splitting, credit transmission, risk
control, bill cost, slow information review, etc.
3.2 Construction Method of New
Model of Agricultural Supply
Chain Finance Implanted with
Blockchain Technology
3.2.1 Construction of Agricultural Supply
Chain Financial Data System
Based on blockchain and big data technology, build a
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
530
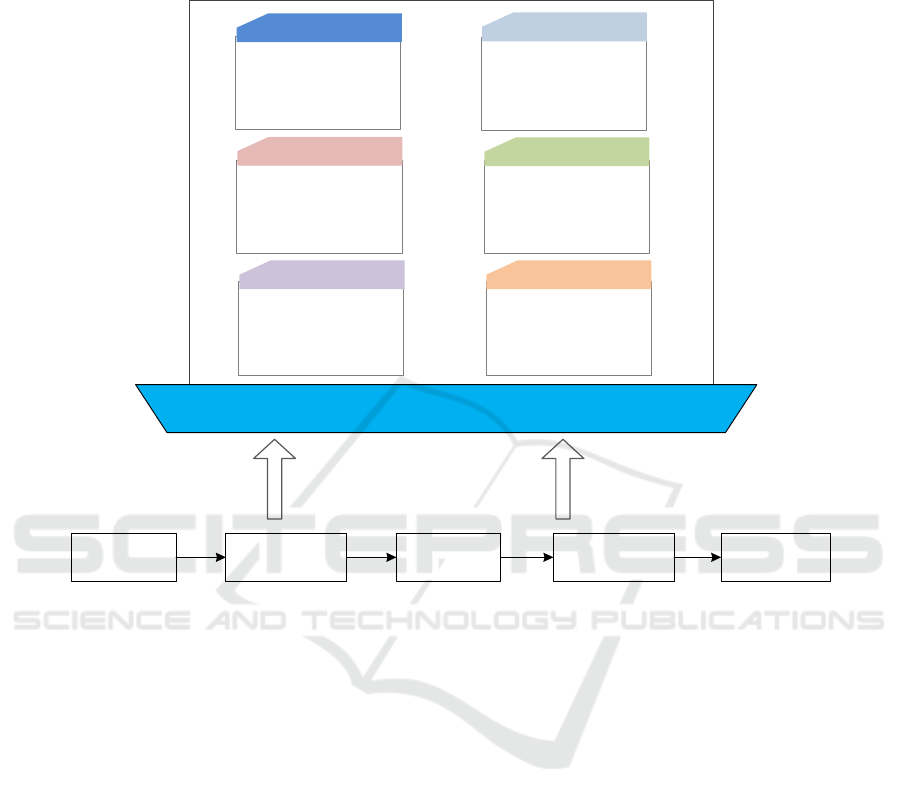
visual, tamper proof, non replicable and traceable
agricultural supply chain financial data platform, and
rely on this platform to achieve online data storage
and business online operation on the agricultural
supply chain., as shown in Figure 1.
Core
Enterprise
Downstream
enterprises
Upstream
enterprise
On-chain
data store
On-chain
business operations
Data read, data write,
data authorization, time
stamp
Logistics, information
flow, capital flow,
business flow data
storage, financing data
storage
Encryption of trade
information and supply
chain financing
information
Voucher split, voucher
transfer, voucher
financing
Contract online
automatic execution,
voucher automatic
review, automatic
lending, automatic
repayment
Record the transaction
information of each link
of enterprises and
implement the right
confirmation
Agricultural supply chain finance platform
Block management
Smart contract
Distributed data
storage
certificate
consensus
Encryption of
information
Third party
logistics
Third party
logistics
Figure 1: Core module of agricultural supply chain finance platform
Suppliers, core enterprises, distributors, retailers,
third-party logistics companies, banks and other
financial institutions in the supply chain create
blockchain users. Block users record logistics, capital
flow, information flow, business flow and other
information related to their own business, and upload
them to the agricultural supply chain financial
platform. These data are recorded synchronously in
each enterprise with the occurrence of business in the
supply chain, A decentralized database of the whole
supply chain process has been formed. Of course, it is
not safe to disclose all these information. Therefore,
the asymmetric encryption algorithm is used to
encrypt the data uploaded by enterprises with public
keys, and different users are given different download
permissions. When enterprises download the data
they need, they use the private key to decrypt it.
3.2.2 Implementation Logic of Trust
Consensus
Under the blockchain framework, the upstream and
downstream enterprises and financial institutions of
the supply chain, as node enterprises, can obtain
system data at any time. The decentralized distributed
structure can solve the problem of information
asymmetry. Node enterprises do not need to trust a
single node in a centralized way, and also save a lot of
intermediate costs. In addition, due to the tamper
proof, non replicable and traceability of blockchain
technology, the reliability of transaction information
has been improved, thus establishing the trust
consensus of all participants in the supply chain.
3.2.3 Implementation Logic of Bill and
Transaction Information Fraud
Prevention
The ledger distribution feature of the blockchain
enables the supply chain system to automatically
form data that cannot be tampered with, and these
data will be confirmed in real time by the blockchain
technology, which not only reduces the delay, but also
solves the problem of information audit. The tamper
proof timestamp can solve the problem of data
tracking and information anti-counterfeiting. In
Research on the Application of Blockchain Technology in the Innovative Development of Agricultural Supply Chain Finance
531

addition, the data blocks in the blockchain are
connected in order and form an tamper proof data
chain. Timestamps attach a set of real data that cannot
be forged to all transactions, which can effectively
prevent bill forgery, information distortion and other
problems.
3.2.4 Information Audit Efficiency
Improvement
Since the system stores reliable and tamper proof
data, as a computer execution language, smart
contracts can eliminate all artificial obstacles to the
execution of the contract and realize the automatic
transfer of capital, goods, claims and other assets
under the condition that the set conditions are met. It
is mandatory and solves the problem of low
efficiency and high cost of labor.
3.2.5 Implementation Logic of Credit
Transfer and Bill Disassembly
Under the traditional supply chain finance mode, only
enterprises with direct transaction relationship with
core enterprises can be supported to finance. The
credit of core enterprises cannot be transferred, and
the accounts receivable vouchers cannot be
disassembled. Under the blockchain structure, the
token disassembles the credit of the detachable core
enterprises and transfers the credit level by level, so
that the upstream and downstream remote enterprises
of the supply chain can enjoy the credit guarantee of
the core enterprises, expand the financial benefit
coverage of the supply chain, and meet the financing
needs of all SMEs in the supply chain.
3.3 Basic Principle of “Shapley” Value
Method
In the supply chain finance business, core enterprises,
agriculture-related smes and financial institutions
form an alliance to pursue the effect of 1+1>2. The
prerequisite for the long-term, sustainable and stable
cooperation of such an alliance is that all parties can
obtain their due share of income in the income
distribution. In this paper, the benefits of alliance
members are distributed based on the "Shapley"
value method, which can reflect the contribution
degree of each participating enterprise to the overall
goal of supply chain finance, and has good rationality
and fairness. Specific assumptions are as follows:
Let I be the enterprise set of the cooperative
alliance of n participants, expressed as I:{1,2... , n},
participants set S is a subset of the I (S ⊆ I), expressed
in V (S) each of the participants set S corresponding
revenue function, meet:
()
()()()
ISSSSSVSVSSV
V
⊆=∩+≥∪
=
21212121
,,,
0
φ
φ
(1)
Formula (1) indicates that the revenue of any two
disjoint enterprise sets in the case of cooperation is no
less than the revenue of non-cooperation. Therefore,
when all the participants cooperate, the maximum
revenue will be reached, which is denoted as V(I).At
this time, X
i
is used to represent the income
distribution quota obtained by members i of the
largest aggregate I from the maximum cooperation
income V(I) according to their contribution degree,
forming an n-dimensional vector X=(X
1
, X
2
,..., X
n
),
which meets the following conditions:
(1) Meet the individual rationality, that is, the
income of an enterprise when it joins the alliance and
chooses to cooperate must not be less than the income
of its own independent operation, otherwise the
enterprise will not choose to join, so X
i
≥ V (i).
(2) Meet the overall rational condition, that is, the
total income obtained by the alliance must be fully
distributed, otherwise all member enterprises will not
agree to this distribution scheme, so
n
I
VX
,...,2,1i,
n
1i
i
=
=
=
According to the "Shapley" value method, the
income distribution amount X
i
of participating
enterprise i is called the "Shapley" value, which is
recorded as φ
i
(E). The calculation formula is as
follows:
()
()
() ()
[]
()
!
其中
n
1)!-()!-(n
i
SS
SW
ISVSVSWE
IS
=
−=
⊆
ϕ
(2)
N is the number of all participants in set I, |s| is the
number of cooperative enterprises in subset S, V(S) is
the overall income of subset S, V (S/I) is the income
obtained when member i does not participate in
cooperation in subset S, and W(|s|) is the weighting
factor.
4 RESULTS
4.1 "1+1+N" Financial Model of
Agricultural Supply Chain
The "1+1+N" agricultural supply chain financial
model is a new agricultural supply chain financial
model operated by one leading enterprise and one
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
532

rural cooperative. N refers to small and medium-sized
agricultural enterprises, logistics companies,
commercial banks, etc. Leading enterprises have
market influence and good qualifications, which are
suitable for endorsing all links of supply chain
financing, and can play a leading and promoting role
in the development of supply chain finance; As a
special organization, the cooperative has a deep
foundation of farmers and financial support from the
state. It has natural advantages in the collection of
supply chain financial data. Therefore, the rural
cooperative is most suitable for the operation of the
agricultural supply chain financial data platform, and
is responsible for the specific business of the supply
chain financial data platform, such as platform
building, daily operation, data maintenance, etc. The
agricultural supply chain financial platform operated
by cooperatives has the objectivity and timeliness of
information. The addition of blockchain technology
makes the data tamper proof and open, and enables
the bill to be disassembled and the transaction
efficiency to be improved. In this way, an open
platform jointly recognized by enterprises has been
formed. All small and medium-sized agricultural
enterprises, financial institutions and logistics
companies that are interested in participating in the
supply chain financial business can register on the
platform, Participate in it and make profits
respectively. This mode is applicable to most types of
agricultural supply chains, and the overall
architecture is shown in Figure 2.
Rural cooperatives
Small and medium-sized
agricultural enterprises,
logistics companies,
commercial banks, etc
1
Leading
enterprise
1 N
Figure 2: Financial structure of agricultural supply chain.
4.2 Construction of Financial Benefit
Distribution Model in Agricultural
Supply Chain
The existence of rural cooperatives is to improve the
level of farmers' organization, promote the
development of agricultural production and increase
farmers' income. It is an important window for
farmers to talk with the government. The primary
purpose of the establishment of cooperatives is not to
earn excess profits, and there are national financial
subsidies. From the perspective of model
construction, cooperatives maintain the platform and
do not directly create benefits for the supply chain
alliance. According to the nominal representative
axiom of the "Shaley" value method, those who have
not made contributions to the system should not share
the benefits, which is called nominal representatives.
Therefore, in combination with the "1+1+N"
agricultural supply chain financial model, the interest
distribution among financing enterprises (i.e.
agricultural SMEs), commercial banks and leading
enterprises is mainly considered.
Suppose the financing enterprise is X, the
commercial bank is Y, and the leading enterprise is Z,
then I={X, Y, Z}, the cooperation between X and Y is
XY, the cooperation between X and Z is XZ, the
cooperation between Y and Z is YZ, and the supply
chain alliance formed by X, Y, and Z is XYZ. Set the
annual profits of financing enterprises, commercial
banks and leading enterprises when they operate
alone and do not participate in cooperation as x, y and
z respectively, and the expected income of X and Y
cooperation is a; the expected income of X and Z
cooperation is b; the expected income of Y and Z
cooperation is c. If X Y and Z cooperate to form a
supply chain alliance, and the expected income is d.
According to formula (2), calculate the benefit
distribution table of each participating enterprise, as
shown in Table 1:
Table 1: φ
i
(E) value solution table
S
X
V(S) V(S/X) V(S)-V(S/X)
X x 0 x 1/3 x/3
XY a y a-y 1/6 (a-y)/6
XZ b z b-z 1/6 (b-z)/6
XYZ d c d-c 1/3 (d-c)/3
()
SW
()
() ()
[]
ISVSVSW −
Research on the Application of Blockchain Technology in the Innovative Development of Agricultural Supply Chain Finance
533

Therefore, the profit distribution of financing
enterprise X is:
()
()
() ()
[]
6/)d2cba2z2yx(
3/cd6/zb6/yax/3
i
+++−+−−=
−+−+−+=
−=
⊆
)()()(
ISVSVSWE
IS
ϕ
Similarly, the profit distribution of commercial
banks is (- x+2y-z+a-2b+c+2d)/6, and that of leading
enterprises is (- x-y+2z-2a+b+c+2d)/6.
5 DISCUSSION
When studying the benefits of each participant in the
supply chain, the "Shapley" value method mainly
distributes the total benefits of the supply chain
according to the contribution of each participant to
the supply chain. In the actual supply chain financial
business, according to the different risks undertaken
by the participating enterprises, on the basis of the
benefit distribution model, the participating
enterprises with large risks can allocate relatively
more benefits, so as to urge the supply chain related
enterprises to actively participate in the supply chain
financial business. In future research, risk correction
factors can be introduced to modify the Shapley
value, thus forming an improved supply chain
financial benefit allocation model.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research enriches the relevant theories of
blockchain enabled supply chain finance. Through
the application of blockchain, the risk of "1+1+N"
agricultural supply chain financial model has been
greatly reduced. From the perspective of commercial
banks, the problems of trust consensus, risk
management and control, and bill cost of all
participating enterprises have been well solved; For
financing enterprises, problems such as bill splitting,
credit transmission and slow information review have
been solved; For leading enterprises, while helping
SMEs solve the capital problem, it has improved the
management and control ability of the agricultural
supply chain and the stickiness between enterprises,
thus boosting the development of the agricultural
industry chain.
FUNDING
This research is funded by the university level
scientific research of Xi'an Eurasian University
(Project No.: 2022XCZX04)
REFERENCES
Ahluwalia Saurabh, Mahto Raj V, Guerrero Maribel.
Blockchain technology and startup financing: A
transaction cost economics perspective[J].
Technological Forecasting and Social
Change,2020,151(2):119854~119863
Feng Bao, Zhang Zuo Minyang. Blockchain empowerment
and financial optimization of platform based supply
chain - game analysis based on cost perspective [J].
Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Social
Sciences), 2022,36 (10): 110-121
Huo Hong, Jia Xuelian, Jiang Man, Xu Lingling. Research
on Decision making of Agricultural Product Supply
Chain under Different Risk Prevention Modes [J].
Computer Application and Software, 2022,39 (02):
68-74
Sun Zhongye, Xu Xiaoyan. Research on Financial Risk
Assessment of Agricultural Supply Chain -- Based on
GA-BP Neural Network Model [J]. Technical Economy
and Management Research, 2021 (08): 78-82
Wang Y. Research on supply chain financial risk
assessment based on blockchain and fuzzy neural
networks[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile
Computing, 2021(2021)124~128
Zheng Yi. Innovative Development of Agricultural Supply
Chain Finance in the Transformation of Rural
Production Mode [J]. Agricultural Economy, 2022
(01): 115-117
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
534
