
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through
the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users
Suyu Zhang
1a,*
, Yujun Fang
1b
and Rong Hu
2c
1
Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China
2
Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Keywords: We-Media, Health Dissemination, Middle-Aged and Elderly Groups, TAM.
Abstract: The dissemination of health information through the we-media platform among middle-aged and elderly
users is a critical topic of research. Based on the technology acceptance model (TAM) and in combination
with the characteristics of health we-media, this paper investigated the current trend of middle-aged and
elderly groups using the we-media platform to obtain health information and the factors influencing their
acceptance. The results revealed that the perceived ease of use and usefulness of the platform is
considerably affected by the following: (1) age groups; (2) the trust of the users in the we-media platform;
(3) the technical difficulty of the we-media platform. Moreover, acceptance willingness depends on the
professional level, difficulty of use, and technology. Furthermore, both perceived ease of use and perceived
usefulness of middle-aged and elderly users positively affects their acceptance willingness. Therefore, the
we-media platform needs to continuously improve the user experience and improve the acceptance
willingness of middle-aged and elderly user groups. This paper will be beneficial to enrich the modern life
research of middle-aged and elderly groups, and provide reference for the further improvement of we media
platform.
1 INTRODUCTION
China is a country with a considerable elderly
population. Therefore, population aging and health
literacy of elderly groups are critical concerns. The
Internet age has ushered numerous dissemination
channels, which can rapidly propagate health
information. Therefore, in the current information
era, how middle-aged and elderly groups obtain and
distinguish health knowledge is a critical topic of
research. The all-weather, diversified, and low-cost
information dissemination in the Internet age has
resulted in considerable health information becoming
available. However, middle-aged and elderly groups
cannot discern the authenticity of such information.
Therefore, identifying crucial health information is
key to improving their health literacy among middle-
aged and elderly groups.
Communication of health knowledge among
middle-aged and elderly groups is essential. However,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6934-9065
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8725-3072
people of such age groups do not easily accept new
media, with some elderly people refusing to use we-
media platforms such as Tik Tok, SnackVideo, and
WeChat. Therefore, producing truthful and misleading
information, fine content, and attracting the attention
of middle-aged and elderly groups mainly by service
are problems created by health science we-media. The
current communication strength of health science we-
media among middle-aged and elderly groups, their
communication characteristics, and typical problems
in health science short videos were discussed. This
paper investigated the optimal communication path of
health science short videos to improve the health
literacy of middle-aged and elderly groups and
provided support for building a healthy ageing society.
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3055-8980
*
Chi Corresponding author. E-mail address
654
Zhang, S., Fang, Y. and Hu, R.
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users.
DOI: 10.5220/0012041500003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 654-662
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Health Communication On
We-Media
Reviewing the existing achievements of health
communication under the background of new media
technology, it is found that China's health
communication we media platforms include wechat,
Tiktok and microblog. Most studies focus on the
environmental analysis of new media technology and
current health communication. Most health
communication strategies under new media
technology focus on narrative strategies and
communication methods. The most common method
is to use specific self media short videos for case
studies. Bai Jingjing analyzes the difficulties of
healthy communication in the social media
environment and believes that the concept innovation
and paradigm transformation from one-way publicity
to two-way dialogue are very important. In addition,
this means the transformation from information flow
to well connected networks and from community of
interests to community of values (Hu, 2012). Hai min
analyzed the impact of WeChat official account
"DXY", and summarized the communication
strategies of title, title production, topic selection,
content subdivision and user interaction (Li, Zheng,
2020). Most health communication studies analyze
public health emergencies. Jing and Li show the
advantages of 2019 coronavirus disease transmission
and effectively visualize, simplify and logic
information (Bai, Wu, 2020). Mr. Xi put forward
three common misunderstandings in the content
construction of health science short films: non
professional communicators mislead the audience
and distort the facts; The content is rough and limited;
Excessive commercialization of entertainment leads
to the reduction of public services (Chen, 2021).
2.2 Health Communication Research
on Middle-Aged and Elderly
Groups
Li performed surveys using a questionnaire and in-
depth interviews of retirees in Chunfeng community,
Niujie, Beijing to analyse the spreading and current
trends of health rumours among retirees. The
characteristics of the spread of health rumours among
retirees are as follows: information can be obtained
in numerous method; however, most information is
false; the arrival rate of effective information is low
and information typically changes; retirees have low
information literacy and different media contact
habits. Furthermore, they revealed that the authorities
can play a vital role in preventing and refuting
rumours and improve awareness among retirees (Li,
2021).
Foreign studies on the health communication
among middle-aged and elderly groups have mainly
focused on conventional and social media. Andersen,
Medagalia, and Henriksen conducted a sampling
survey on the middle-aged and elderly people from
China and revealed that the use of conventional
media, digital access, and social media considerably
affects their social participation (Andersen,
Medaglia, et al, 2012). Most studies have analysed
the effect of social media on the executive functions
of middle-aged and elderly groups from the effect
dimension. Tao et al. performed structural equation
model analysis to reveal that the use of social media
by middle-aged and elderly groups can prevent
cognitive decline (He, Huang, et al, 2020).
2.3 Studies on Health Communication
Short Videos
Reviewing existing studies revealed that most
domestic studies on health short videos have used the
qualitative research method focused on content
analysis. Most studies have focused on effects, such
as communication mode, communication subject,
and communication content, resulting from short
videos to identify problems in existing health short
video communication, and recommendations for the
development of the platform. Liru investigated
changes that new media, such as Tik Tok short
videos, has ushered in health communication and
revealed that Tik Tok short videos provided
considerable information supply for health
communication, eased the doctor–patient relationship,
and guided the public to maintain a healthy
mentality[]. Kexian evaluated the forwarding
behaviour of Tik Tok health short video users and the
factors affecting their forwarding in the context of
health communication and summarised influencing
factors as follows: perception of content quality,
information relevance, trust mechanism, opinions
link, social motive, and motive for persuasion
(Zhang, 2021).
3 HYPOTHESES
The technology acceptance model (TAM) based on
Ajzen’s theory of reasoned action (TRA) was first
proposed by DAVIS in 1986. The two primary
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users
655
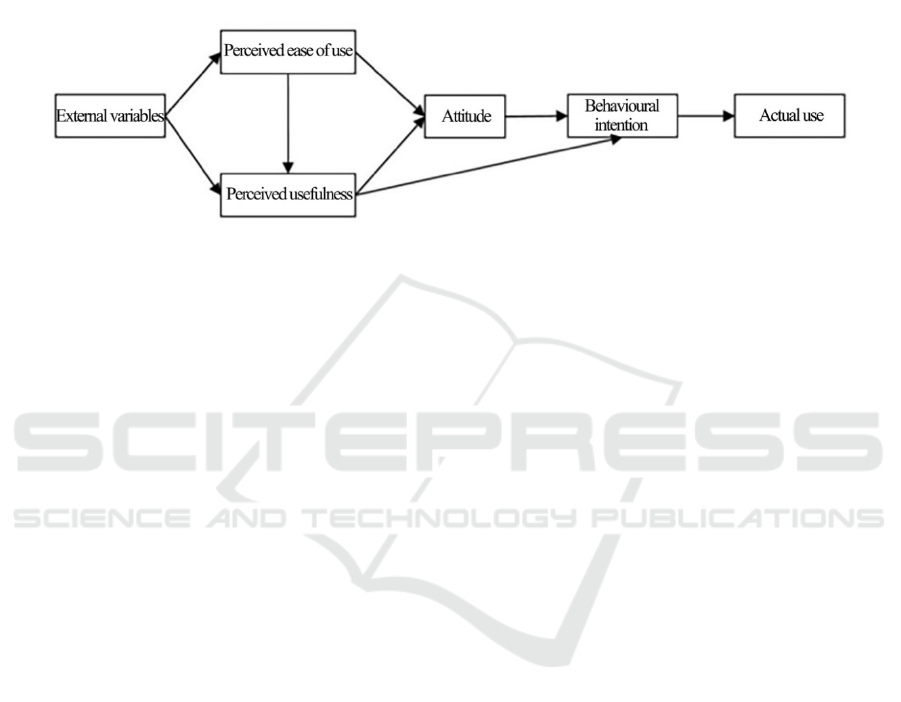
determinants of the TAM, namely perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use, are used to
verify the acceptance of the information system by
the users. The perceived ease of use refers to the
degree to which users believe a technology can
reduce effort by using the system, and perceived
usefulness refers to the degree to which users believe
a technology can improve their work efficiency when
using the system. According to the TAM, external
variables considerably affect the perceived ease of
use, which can indirectly affect the behavioural
intention of users. Both perceived ease of use and
perceived usefulness determine the desire of users to
use the technology. Furthermore, behavioural
intention determines their actual use behaviour. The
TAM developed by DAVIS is displayed in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Technology acceptance model (TAM).
Based on the TAM, this study proposed the
following 18 hypotheses through analyses of the
health we-media platforms and trend of middle-aged
and elderly users.
3.1 Trends of Middle-Aged and Elderly
Users and the TAM
This study investigated the trend of middle-aged and
elderly users from the perspective of age, level of
education, and health literacy, which considerably
affects the perceived ease of use and perceived
usefulness in the TAM. The perceived ease of use
primarily includes three aspects, namely the
difficulty of use, information quality, and level of
service. Perceived usefulness covers three aspects,
namely the efficiency of obtaining information,
convenience of obtaining information, and accuracy
of information. Based on this data, we proposed the
following five specific hypotheses from two
directions, that is, users’ own situation positively
affects their perceived ease of use and perceived
usefulness.
3.1.1 Positive Effects of the Situation of
Middle-Aged and Elderly Users on
Their Perceived Ease of Use
2 specific hypotheses related to this hypotheses are as
follows:
H1: the education level of middle-aged and
elderly groups considerably affects their ability to
identify the truth of health knowledge. The middle-
aged and elderly with higher education could easily
distinguish between real and fake health knowledge.
H2: Considerable differences exists between the
middle-aged and elderly people who have accessed
health information on the Internet and those who
have not. Those who have seen health science
information on we-media platforms are more likely
to identify health rumours than those who have not.
3.1.2 the Situation of Middle-Aged and
Elderly Users Positively Affects Their
Perceived Usefulness
3 specific hypotheses related to this hypotheses are as
follows:
H3: the age of middle-aged and elderly groups
considerably affects their acceptance of health
science we-media. The younger the middle-aged and
elderly users are, the more likely they are to accept
health science we-media.
H4: the gender of middle-aged and elderly groups
considerably affects their acceptance of health
science we-media. Middle-aged and elderly women
are more willing to actively search for health science
knowledge in comparison with men.
H5: the health literacy of middle-aged and elderly
groups considerably affects their acceptance of health
science we-media. The higher the health literacy
level is, the more willing they are to accept health
science we-media.
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
656

3.2 Characteristics of Health Science
We-Media and the TAM
Numerous short video platforms and channels have
emerged for health communication. People can
access various health information through media.
This access is an opportunity and a challenge for we-
media and the health communication industry.
However, verifying the truth of such health
information is difficult. Currently, health we-media
are characterised by various professional levels,
considerable difference in user traffic and diversified
platforms. Therefore, the following eight hypotheses
were proposed from two perspectives: the trust of
middle-aged and elderly users in we-media platform
positively affected their perceived ease of use and
perceived usefulness; the technical difficulty of
health we-media had a negative effect on perceived
ease of use and perceived usefulness of users.
3.2.1 the Trust of Middle-Aged and Elderly
Users in We-Media Platform Has a
Positive Impact on Their Perceived
Usefulness
3 specific hypotheses related to this hypotheses are as
follows:
H6: the wardrobe, props, and makeup of we-
media platform professionals considerably affects the
acceptance of middle-aged and elderly users. These
professionals are more willing to trust short bloggers
who are good at medical care than the health science
short bloggers with casual dressing.
H7: their trust in we-media accounts and
mainstream media accounts: they are more willing to
trust the health information released by the official
mainstream media compared with that released by
we-media bloggers.
H8: the number of followers of we-media
accounts can considerably affect the trust of middle-
aged and elderly users: they prefer to trust the we-
media accounts with high number of followers
compared with those with a small number of fans.
3.2.2 the Difficulty of Health Science
We-Media Has a Positive Effect on
Perceived Ease of Use
5 specific hypotheses related to this hypotheses are as
follows:
H9: the popularity of we-media platforms
considerably affects the acceptance of middle-aged
and elderly users: compared with less popular we-
media platforms, these are more prone to obtain health
information in platforms with popular platforms.
H10: the operating difficulty of we-media
platforms can considerably affect the acceptance of
middle-aged and elderly users: compared with we-
media platforms that require reading text, they prefer
to receive health information through short video
platforms.
H11: the operating difficulty of we-media
platforms can considerably affect the acceptance of
middle-aged and elderly users: compared with the we-
media platforms that require opening a VIP service to
obtain content, middle-aged and elderly users are
more likely to select the we-media platforms through
which they can directly obtain health information.
H12: user interactive experience considerably
affects the acceptance of middle-aged and elderly
users: they prefer to obtain health information in the
platforms with comment areas compared with the
platforms without comment areas.
H13: user interactive experience considerably
affects the acceptance of middle-aged and elderly
users: compared with the platforms that cannot
provide feedback, they are more willing to obtain
health information in the we-media platforms that
allow feedback on complaints.
3.3 TAM and Users’ Willingness to
Adopt
DAVIS in the TAM revealed that the want-to-use
attitude and behavioural intention of users are
determined by their perceived ease of use. Their
perceived usefulness can affect their want-to-use
attitude, whereas their want-to-use attitude directly
affects the behavioural intention of users. Therefore,
we proposed the following five hypotheses:
H14: the perceived ease of use positively affects
the perceived usefulness.
H15: the perceived ease of use positively affects
the want-to-use attitude of users.
H16: the perceived usefulness has a positive
effect on the want-to-use attitude of users.
H17: the perceived ease of use considerably affect
the behavioural intention of users.
H18: the want-to-use attitude of users considerably
affects their behavioural intention.
4 MODEL SPECIFICATION
Based on the TAM developed by DAVIS, we
developed a theoretical model of influencing factors
of middle-aged and elderly groups in health we-
media (see Fig. 2).
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users
657
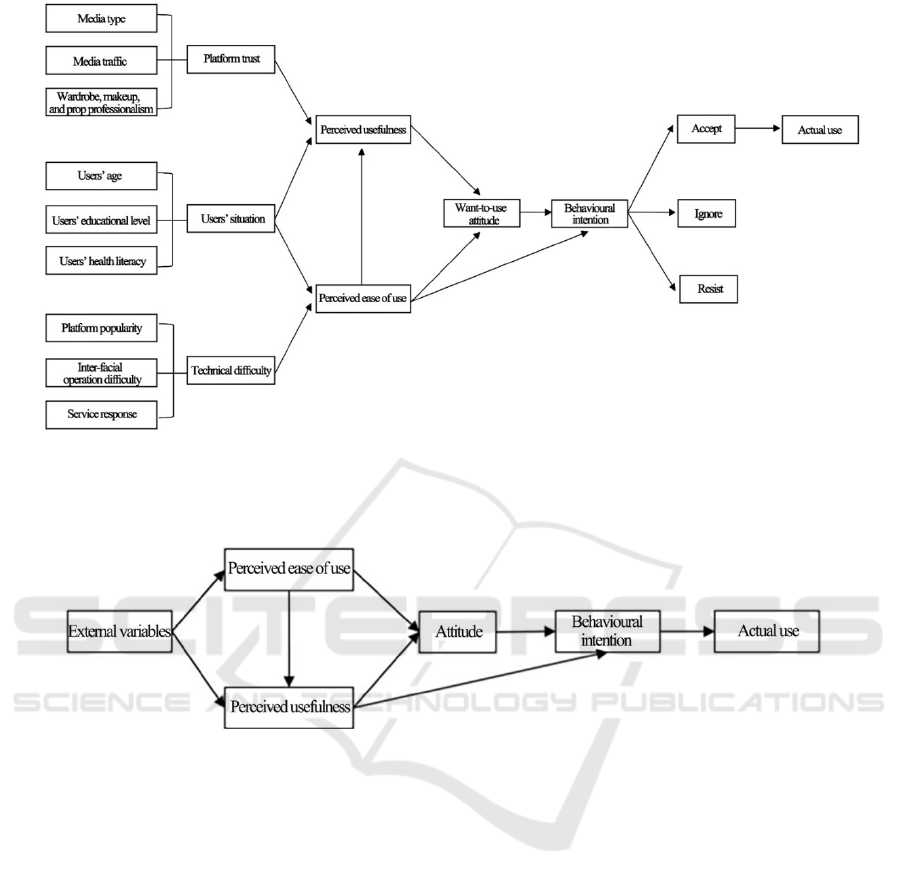
Figure 2: Theoretical model of influencing factors of middle-aged and elderly groups in health we-media.
We developed the original model of the
willingness of middle-aged and elderly users to adopt
health we-media in combination with the
aforementioned model and hypotheses (see Fig. 3).
Figure 3: Original model of the willingness of middle-aged and elderly users to adopt health we-media.
5 METHOD
5.1 Questionnaire Design
The original questionnaire design was performed
according to studies on the situation of middle-aged
and elderly users and the characteristics of health we-
media platforms and their information. Based on the
TAM developed by DAVIS and Venkatesh’s research
on the TAM, we designed 10 questions to measure the
perceived ease of use and the perceived usefulness.
The questionnaire investigated the situation of middle-
aged and elderly users from three directions, including
their age, education level, and health literacy, for
which we designed three relevant questions. Three
relevant questions based on the two hypotheses that the
trust of middle-aged and elderly users has a positive
effect on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of
users. The technical difficulty of the TAM was
performed according to Huaxiao and Li on the
suitability framework analysis of smart care for the
disabled elderly (Chen, Wang, 2021). Five questions
are related to the popularity, operation difficulty, and
service response of we-media platforms. We obtained
the opinions of experts in the field of health and
network to improve the professionalism of the
questionnaire. The questionnaire was distributed for a
pre-survey on a small scale and the content was
adjusted in accordance with the feedback results to
ensure that the language and terms used in the
questionnaire can be comprehensible to the middle-
aged and elderly users. Furthermore, the conceptual
explanation of “health we-media” was added to
facilitate further understanding of the questionnaire
content; subsequently, the final questionnaire was
distributed. All data collected from the simulated
distribution were deleted. The questionnaire was
designed with 28 measurement items including single
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
658
choice, fill-in-the-blank, five-point scale and ten-point
scale.
5.2 Questionnaire Distribution and
Data Collection
Of the 1076 questionnaires were collected in this
survey. 1031 valid responses were obtained, with a
valid questionnaire ratio of 95.8%, after deleting the
invalid questionnaires that did not satisfy the research
age requirements or answered the questionnaire in a
short time. To ensure data accuracy, the results were
obtained through two survey methods. First, 935
questionnaires were distributed through WJX on
November 1, 2021, which were ended and counted
on February 18, 2021. We performed the survey
through leaving words for user comments on the
WeChat official account, sending private messages to
users who follow the health science we-media
accounts on Tik Tok, SnackVideo, MicroBlog and
Zhihu, consulting elderly relatives and friends
through telephones, chat on WeChat and directing
sending messages in the platform, so as to interview
them about their use and opinions of health we-
media. The resulting feedback was mainly in the form
of telephone recordings and chat screenshots.
Among the 935 valid questionnaires distributed
through WJX, 48.4% of respondents were men and
51.6% of respondents were female; the middle-age
and elderly users with access to health information
through the we-media platform were 80.9%. The
respondents mainly graduated from high school and
vocational technical institutes, and the main
platforms they used are WeChat official account and
Tik Tok (see Table 1 and Table 2).
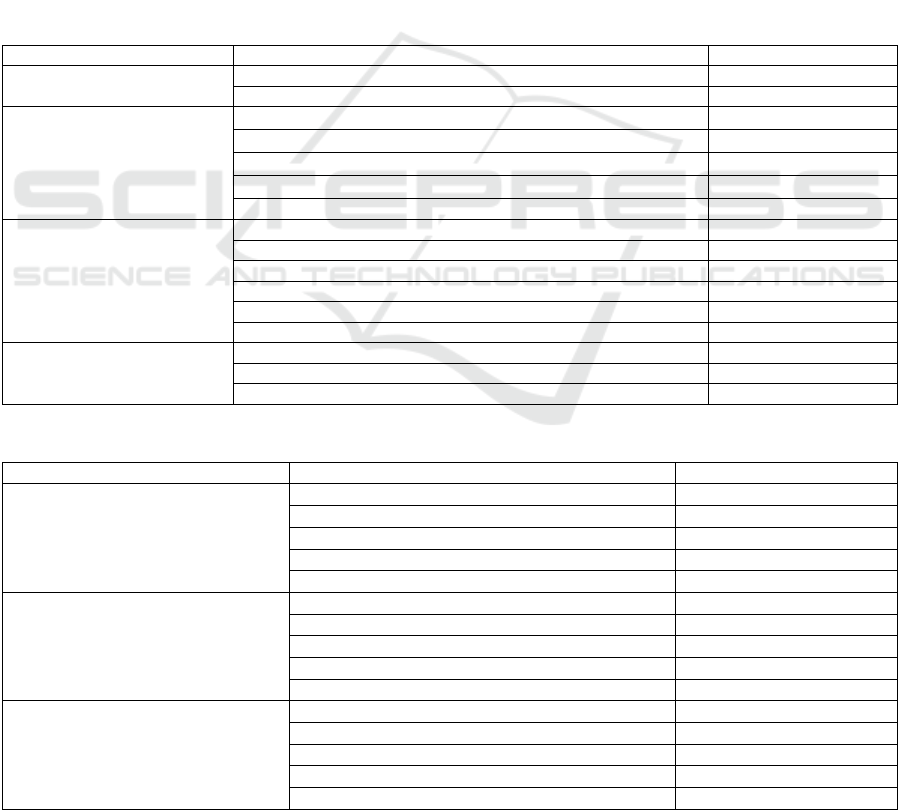
Table 1: Information statistics of health science we-media users.
Classification Options Percentage
Gender
Male 47.7%
Female 52.3%
Age
45~55 17.2%
56~65 51.6%
66~75 21.9%
76~85 9.2%
85 an
d
above 0.1%
Education level
Have no systematic educatio
n
11.2%
Primary education 21.3%
Junio
r
high school educatio
n
18.2%
High school education 20.1%
Vocational technical institute 17.5%
College an
d
above 11.7%
Health literacy
0~33
p
oin
t
32.1%
33~66
p
oin
t
37.5%
67~100
p
oin
t
30.4%
Table 2: Information statistics of the middle-aged and elderly using health science we-media.
Classification O
p
tions %
Understanding level
Neve
r
hear
d
of 9.8%
Only hear
d
of 12.3%
Know a little
b
it 31.1%
Know well 24.3%
Know a lot about 22.5%
Frequency of use (videos)
Almost ever
y
da
y
23.0%
Fre
q
uentl
y
22.2%
Generall
y
27.9%
Occasionall
y
15.1%
Neve
r
11.8%
Frequency of use (non-videos)
Almost ever
y
da
y
21.1%
Fre
q
uentl
y
21.9%
Generall
y
29.9%
Occasionall
y
12.6%
Neve
r
14.5%
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users
659
Based on the data collection results of the
questionnaire, we used SPSS 26 to analyse the data
from three aspects, that is, reliability and validity test,
goodness-of-fit of the model and Pearson correlation,
and finally verified whether the research hypotheses
proposed in the present study are tenable.
6 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
6.1 Test of Validity
Cronbach’s α was used to test the reliability of the scale.
The results revealed that the α values of all variables are
greater than 0.7, including users’ situation, users’ trust
in the platform, technical difficulty of we-media
platform, perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness,
users’ want-to-use attitude and their behavioural
intention. This information indicates that each variable
exhibits internal consistency (see Table 3).
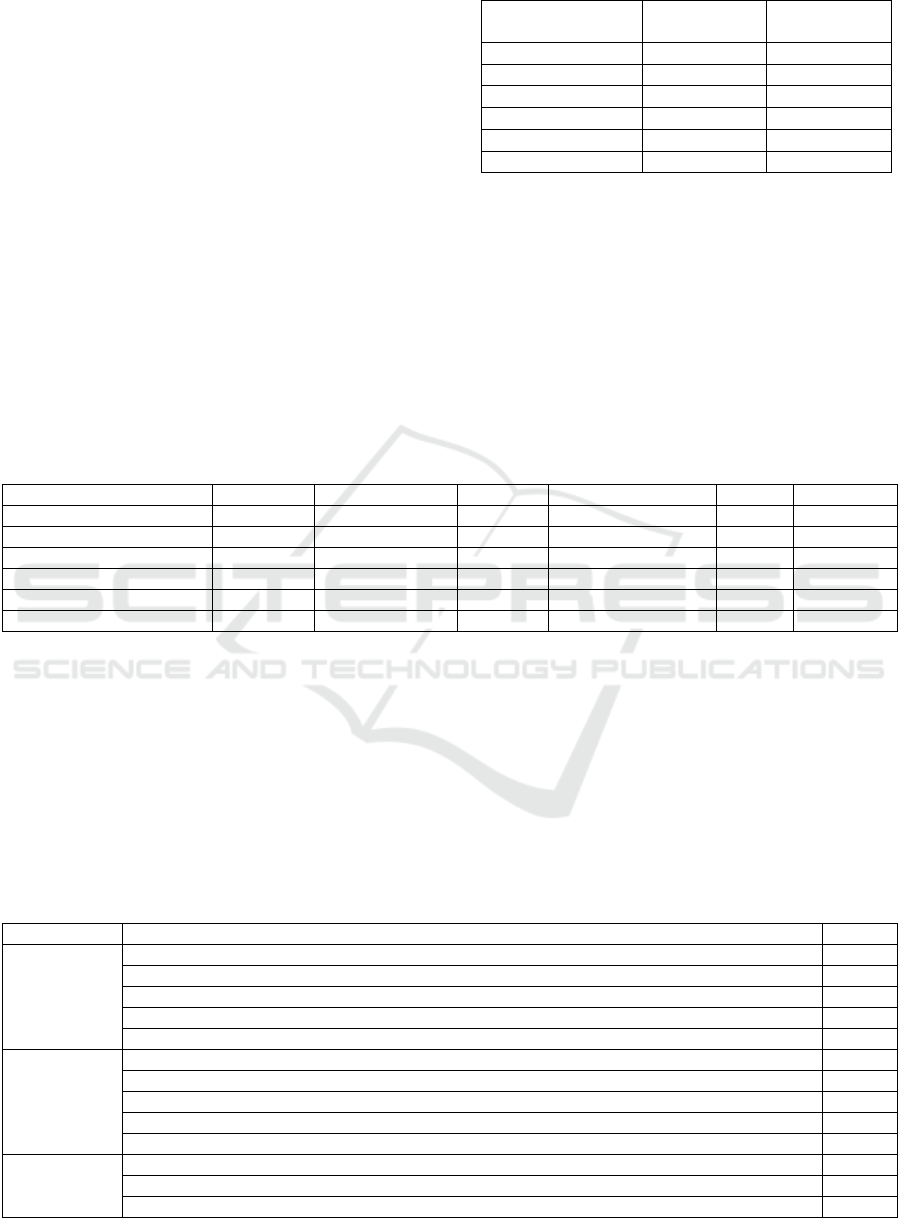
Table 3: Cronbach’s Alpha value of variables in the model.
Latent variables
Number of
items
Cronbach’s
Alpha
Platfor
m
trust 3 0.767
Users’ situation 5 0.778
Technical difficult
y
7 0.808
Perceive
d
ease of use 5 0.918
Perceive
d
usefulness 5 0.918
Want-to-use attitude 3 0.869
Factor analysis and average variance extraction
(AVE) were used to test the validity of the scale. The
factor loads of all latent variables were greater than
0.7, and the AVE value of platform trust, users’
situation, perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness,
and users’ want-to-use attitude were greater than 0.7.
These results indicated that an excellent discriminant
validity existed among variables. We adopt KMO
and performed Bartlett’s spherical test to test the data.
As listed in Table 4, the research model exhibited
discriminant validity.
Table 4: Correlation coefficient between the square root of AVE and latent variables.
Latent variables AVE Facto
r
loads KMO Bartlett's spherical df P
Platfor
m
trust 0.656 0.794 0.722 2680.980 28 0.000
Users’ situation 0.669 0.772 0.869 7331.473 171 0.000
Technical difficulty 0.638 0.743 0.828 10603.635 231 0.000
Perceive
d
ease of use 0.753 0.868 0.901 3294.943 10 0.000
Perceive
d
usefulness 0.754 0.868 0.903 3305.236 10 0.000
Want-to-use attitude 0.792 0.890 0.740 1429.017 3 0.000
6.2 Model Test
The factors influencing the want-to-use attitude of
health we-media were analysed, and the results revealed
that the loads of all variables in the rotational component
matrix were greater than 0.7, and the cumulative
variance explanation rate was 80.165%. Therefore, it is
feasible to use perceived usefulness and perceived ease
of use as the factors influencing users’ want-to-use
attitude toward health we-media. As presented in the
factor analysis of the behavioural intention of health we-
media, the loads of all variables in the rotational
component matrix were higher than 0.8, and the
cumulative variance explanation rate was 73.289%.
This result indicates that want-to-use attitude can better
explain the behavioural intention of middle-aged and
elderly groups on health we-media (see Table 5).
Table 5: The rotational component matrix of want-to-use influence coefficient for health we-media.
Variables Items Factors
Perceived
usefulness
Health science we-media can obtain health information quickl
y
0.867
Health science we-media can obtain comprehensive health information 0.872
Health science we-media can obtain accurate health information 0.903
Health science we-media is more convenient fo
r
me to obtain the health information I nee
d
0.891
It is more reliable to obtain health information from health science we-media. 0.846
Perceived
ease of use
It is easy fo
r
me to fin
d
a health science we-media account 0.806
It is easy to fin
d
the health information I nee
d
0.810
The quality of information obtaine
d
b
y virtue of health we-media is highe
r
than I expecte
d
0.844
The experience an
d
gains of using health we-media are highe
r
than I expecte
d
0.875
The service level of health we-media is highe
r
than I expecte
d
0.802
Attitude
toward using
It is more convenient to use health we-media than othe
r
channels 0.882
It is faste
r
to use health we-media than othe
r
channels 0.834
We can obtain more abundant information fro
m
health we-media than othe
r
channels. 0.889
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
660
We also analysed the four factors influencing the
perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness, that
is, perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, want-
to-use attitude, and behavioural intention, and
regressive analysis was performed to sort out the
paths between variables and obtain the correlation
coefficient values between them (see Table 6). As
listed in Table 6, the correlation coefficients between
perceived ease of use and users’ situation and
technical difficulty are separately 0.802 and −0.645,
respectively, and the correlation coefficients between
perceived usefulness and users’ situation, and
platform trust are 0.771 and 0.847. The correlation
coefficients between want-to-use attitude and
perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness were
0.693 and 0.741, and the correlation coefficients
between behavioural intention and perceived ease of
use and want-to-use attitude were 0.686 and 0.791.
The data revealed that the perceived ease of use
positively affected perceived usefulness; both
perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness
exhibited a positive effect on users’ want-to-use
attitude, and perceived ease of use and want-to-use
attitude have a positive effect on users’ behavioural
intention (see Table 7). The present research results
based on the TAM are further verified.
Table 6: Standardised path coefficients and test values of the modified model.
Hypotheses Paths Correlation coefficients P
H1, H2 Users’ situation - perceived usefulness 0.771 <0.01
H3, H4, H5 Users’ situation - perceived ease of use 0.802 <0.01
H6, H7, H8 Platform trust - perceived usefulness 0.847 <0.01
H9, H10, H11, H12, H13 Technical difficulty - perceived ease of use
-0.645
<0.01
H14 Perceived ease of use - perceived usefulness 0.681 <0.01
H15 Perceived ease of use - want-to-use attitude 0.693 <0.01
H16 Perceived usefulness - perceived usefulness 0.741 <0.01
H17 Perceived ease of use - behavioural intention 0.686 <0.01
H18 Want-to-use attitude - behavioural intention 0.791 <0.01
Table 7: Results summary of hypotheses testing.
No. Research hypotheses Meet the test Fail the test
H1a
The own situation of middle-aged and elderly users has a positive impact
on thei
r
p
erceive
d
ease of use
H1b
The own situation of middle-aged and elderly users has a positive impact
on thei
r
p
erceive
d
usefulness
H2
The trust of middle-aged and elderly users on we-media platform has a
p
ositive impact on thei
r
p
erceive
d
usefulness
H3
The using difficulty of health science we-media has a negative impact on
users’
p
erceive
d
ease of use
H4 Perceived ease of use has a positive impact on perceived usefulness
H5 Perceived ease of use has a positive impact on users’ want-to-use attitude
H6 Perceived usefulness has a positive impact on users’ want-to-use attitude
H7 Perceived ease of use has a positive impact on users’ behavioural intention
7 CONCLUSION AND
ENLIGHTENMENT
7.1 Conclusions and Analyses
The present study investigated the adoption model of
middle-age and elderly users of health we-media, and
a questionnaire survey was conducted in accordance
with the three factors influencing user experience.
Finally, the research hypotheses and theoretical
model were verified through data analysis and
empirical research.
The main conclusions are as follows. Analyses of
information regarding the middle-aged and elderly
groups and health we-media revealed that older users
exhibit a low acceptance health we-media; furthermore,
users with lower education exhibit a low acceptance
rate of health information obtained from health we-
media.
The operating difficulty of we-media platform
negatively affects the perceived ease of use,
A Quantitative Study on Health Information Dissemination Through the We-Media Platform Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Users
661

indicating that the simple the operation interface and
the more convenient the use of we-media are, the
more favoured the middle-aged and elderly users
favour the platform. Data analysis revealed that
middle-aged and elderly users are willing to accept
and use video we-media (e.g., Tik Tok, SnackVideo,
and WeChat video) more frequently than we-media
in the form of picture and texts (e.g., WeChat official
account, MicroBlog and Zhihu), among which Tik
Tok short video exhibited the highest acceptance and
frequency of use.
The trust of middle-aged and elderly users in
health we-media (the professionalism of health we-
media) positively affects their perceived usefulness.
This result indicates that the we-media account with
more professional scene building, wardrobe props,
and literal use results in middle-aged and elderly
users to have a positive attitude toward them.
Both perceived ease of use and perceived
usefulness exhibited a positive effect on want-to-use
attitude of middle-aged and elderly users. Their
perceived ease of use considerably affects their
want-to-use attitude. This result revealed that the
simpler the operation of health we-media is, the
more convenient the access channels, the higher the
acceptance of middle-aged and elderly users are.
The higher the accuracy and professionalism of
health information are in we-media account, the
higher the recognition of middle-aged and elderly
users are.
The want-to-use attitude of middle-aged and
elderly users towards we-media platform has a
positive effect on their use behaviour. As displayed
by the results of empirical research, the more
middle-aged and elderly users want to use health
we-media, the more likely they are to use health
information obtained from health we-media in their
daily life.
7.2 Enlightenment and Limitations
Based on the above conclusions, we proposed the
following suggestions for we-media platforms and
health we-media accounts from the perspective of
technical difficulty and professionalism. We-media
platform owners should consider the requirements of
the middle-aged and elderly users in the design of
interface, simplifying the operation difficulty of the
platform so that they can directly obtain health
information without asking for help. To ensure the
truth and accuracy of health information, we-media
owners should reinforce user trust by improving
shooting environment and the professionalism of
wardrobe, makeup, and props.
REFERENCES
Andersen, K.N., Medaglia, R., Henriksen, H.Z., (2012)
Social media in public health care: Impact domain
propositions, Government Information Quarterly,
29(4): 462-469.
Bai, J., Wu, L. (2020) Visualization in health
communication novel coronavirus pneumonia as an
example, News and writing, (04): 31-36.
Chen, X. (2021) Loss and correction: Analysis on the
creative misunderstanding of short videos of health
science popularization, Contemporary television, (03):
86-89.
Chen, H.X., Wang, L. (2021) Analysis on the suitability
framework of intelligent care for the disabled elderly:
Based on the technology acceptance model, Health
economic research, 38 (11):40-42.
He, T., Huang, C.Q., Ming, L., Zhou, Y.Q., Li, S.H. (2020)
Social participation of the elderly in China: The roles
of conventional media, digital access and social media
engagement, Telematics and Informatics, 48(3).
Hu, B.J. (2012) Innovation of health communication
concept and Paradigm Transformation: on the dilemma
and solution of public communication in the new media
era, International Press, 34 (06): 6-10.
Li H M, Zheng D W. (2020) Research on the operation
strategy of WeChat official account of "Syringa
doctor", Media, (17): 57-59.
Li, H. (2021) A Study on the Phenomenon of Health Rumor
Dissemination among Retirees -- A Case Study of
Chunfeng Community, Niujie, Xicheng District,
Beijing. DOI: 10.27667/d.cnki.gzymu.2021.000086
Shuna, S.K., Hwajin, Y. (2020) Social media use improves
executive functions in middle-aged and older adults: A
structural equation modeling analysis. Computers in
Human Behavior, 111
Zhang, K.X. (2021) Research on Factors Influencing
Forwarding Behavior of Tiktok Healthy Short Video
Users. DOI: 10.27110/d.cnki.ghsfu.2021.000452
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
662
