
Research and Application of Big Data Analysis on the Winning Rules
in the Men's Singles Final of 2021 French Open
Jianjian Lin
1
, Jie Song
2,*
, Wenjing Zhang
3
and Xiaoyan Li
4
1
University of International Relations, Beijing, 100091, China
2
Beijing University of Agriculture, Beijing,102206, China
3
Beijing National Day School • Jinyuan, Beijing,100143, China
4
Yuxin School Attached to Capital Normal University, Beijing,100096, China
Keywords: Big Data, Tennis, 2021 French Open, Winning Rules.
Abstract: This paper aims to through the practical application of big data in tennis events; the research on big data
analysis of tennis events can accurately obtain the winning rules of athletes. This paper makes big data
statistics on the matches between Djokovic and Sisipas in the men's singles final of the 2021 French Open,
and uses Excel to process and analyze the data.The results show that Djokovic's number of Aces is less than
that of Tsitsipas, and the number of Double Faults of the two is similar. Tsitsipas's First Serve Percentage,
First Serve Winning Rate and Second Serve Winning Rate are lower than Djokovic's, Djokovic's Fastest Serve
Speed, Average First Serve Speed and Average Second Serve Speed are slower than Tsitsipas's, and
Tsitsipas's Receiving Service Winning Rate is lower than Djokovic's. In AD Court, Djokovic's first and second
serve are mainly in the wide. In Deuce Court, Djokovic's first serve is mainly in the wide and the second serve
is mainly middle; In AD Court, the first serve of Tsitsipas is mainly in the middle and the second serve is
mainly in the body. In AD Court, the first serve of Tsitsipas is mainly in the wide and the second serve is
mainly in the body. Djokovic is less than Tsitsipas in Short Rallies Points, and Tsitsipas is less than Djokovic
in Medium Rallies Points, Long Rallies Points, and Total Points Won. Tsitsipas has more Total Winners than
Djokovic in number, but it is lower than Djokovic in Winners Height above Ground, Djokovic has higher
speed in Winners Average Spin than Tsitsipas, and the two men have the same speed in the fastest Winners.
In terms of impacting points, Djokovic and Tsitsipas' Winners are mainly distributed near the singles sideline,
and Djokovic's Winners are closer to the baseline than Tsitsipas. It draws the conclusion that through the
analysis of the big data of the men's singles final of the 2021 French Open, it is pointed out that the rules of
the athletes' winning in the competition are: high Serve Success Rate and Winning Rate; It has a high Rate of
Receive and Serve; In the stalemate stage, it is necessary to have a stable and continuous offensive ability to
obtain more Medium Rallies Points and Long Rallies Points; The impacting points are closer to the sideline
and baseline of singles.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with the rapid development of the
Internet, big data analysis has been applied in many
fields such as medicine, education, industry and
agriculture. The progress of science and technology
has also brought vitality to the sports field. In the
previous broadcast of sports events, we can only see
some statistics about the events, sometimes it needs
manual statistics, and the statistics also have a great
lag. In the live broadcast of the event in recent two
*
Corresponding author
years, we can intuitively feel the surprise brought to
us by the age of big data. For example, we can see a
variety of statistical data from live events, and we can
also see a number of statistical data immediately
between events. The accuracy and breadth of the data
bring another wonderful visual feast to the audience
when watching live events (Zan, 2021; Liu, 2022).
742
Lin, J., Song, J., Zhang, W. and Li, X.
Research and Application of Big Data Analysis on the Winning Rules in the Men’s Singles Final of 2021 French Open.
DOI: 10.5220/0012043300003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 742-747
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
2 METHODS
2.1 Object
The research object is the video of Djokovic vs
Tsitsipas in the men's singles final of the 2021 French
Open. The result was Djokovic's victory over
Tsitsipas. The score is 3-2 (6-76, 2-6, 6-3, 6-2, 6-4).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Expert Interview
Before the research, through video connection and
on-site visits, we consulted excellent tennis coaches
and professional athletes at home and abroad, as well
as famous experts and scholars at home and abroad
on the relevant content, research ideas, research
methods and other related issues of this research. At
the same time, the division method and scope of
service area and hitting area, the definition of hitting
line and the determination of hitting point are jointly
formulated.
2.2.2 Observation Method
Through repeated observation of the video of the
men's singles final of the 2021 French Open, the
statistics and analysis of relevant indicators were
carried out. The competition was conducted in 5
rounds, totaling 48 rounds. This paper takes the
competitive process of each basic hitting unit as the
observation unit, records the number of shots and
scores or points lost in the competitive process of
each basic hitting unit of each player, and conducts
big data statistics and analysis on each stroke in each
round. Select experienced competition statisticians in
the statistics, and conduct statistics after strict
training. At the same time, organize another group of
people to proofread to ensure the accuracy and
consistency of statistical data.
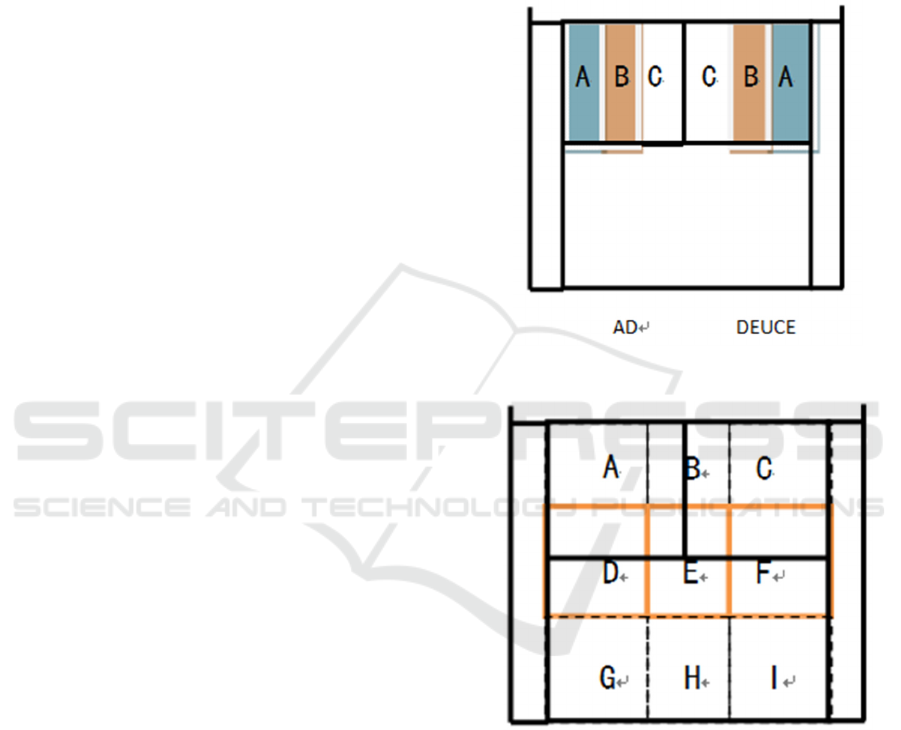
a) The division of the service area (Tao, 2002)
In this paper, AD and DEUCE are divided into three
parts with equal area, namely, Area A is the wide,
Area B is the body, and Area C is the middle
(Figure.1).
b) The division of impacting area (Tao, 2002)
In this paper, the two sides' respective impacting
fields are divided into 9 parts, each part of the area is
basically equal, and the statistics of the impacting
area are carried out. In the statistics, record the
impact area of each impact.
The impacting area of the competition site is
marked with the following signs: A is Backhand
Forecourt; B is Front Court of Middle; C is Forehand
Forecourt; D is Backhand Midfield; E is Middle
Court; F is Forehand Midfield; G is Backhand
Backcourt; H is Middle Back Court; I is Forehand
Backcourt. A, B, C are the Front Court; D, E ,F are
the Middle Court, and G, H , I are the Back Court; In
addition, A, D, G are Backhand, B, E, H are Middle,
and C, F, I are Forehand (Figure.2).
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of serve area division.
Figure.2: Schematic diagram of the division of the
impacting area.
In the actual statistical work, there will be some
special cases. In order to ensure the consistency of
the statistical data, the following provisions will be
made for the special cases: (a) When the landing
point is located at the junction of the front court and
the middle court, the landing point statistics will be
divided into the middle court; (b) When the landing
point is located at the junction of midcourt and
backcourt, the landing point statistics will be divided
into backcourt; (c) When the landing point is located
at the junction of forehand and middle, the landing
Research and Application of Big Data Analysis on the Winning Rules in the Men’s Singles Final of 2021 French Open
743
point statistics will be divided into forehand; (4)
When the landing point is located at the junction of
backhand and middle, the landing point statistics will
be divided into backhand.
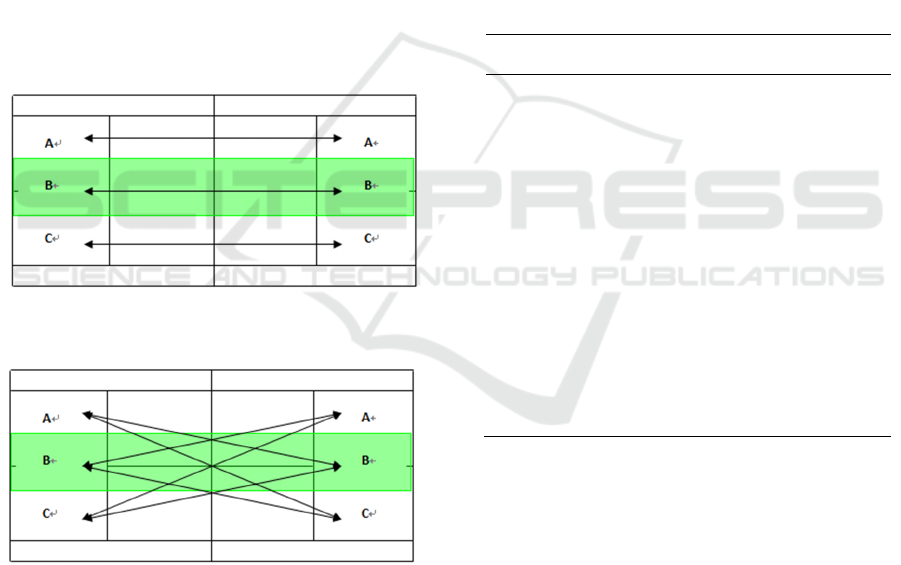
c) The division of impacting line area (Tao, 2002)
In this paper, the impacting line is specified as
follows: The tennis court is vertically divided into
three equal areas, which are respectively represented
by Area A, Area B and Area C (forehand, middle and
backhand) (Figure.3).
Straight stroke statistics: In the stroke process,
any two adjacent strokes that fall in the same area
(without distinction between the front court, the
middle court and the back court) are recognized as
straight strokes in the line statistics. If any two
adjacent shots fall on different edges of the same area,
they are considered as straight shots in line statistics.
Statistics of oblique strokes: Any two adjacent
strokes in different areas (without distinction
between the front court, the middle court and the
back court) during the stroke are identified as oblique
strokes in the line statistics (Figure.4).
Figure. 3: The division diagram of straight line impacting
area.
Figure. 4: The division diagram of diagonal line impacting
area.
2.2.3 Mathematical Statistics
This paper first filters and classifies the relevant raw
data of the game video statistics, then further
processes the filtered data using the formula, and
finally uses Microsoft Excel to statistically process
the corresponding data. In the statistics, part of the
original data comes from the official website of the
French Open (https://www.r-olandgarros.com).
3 RESULTS
3.1 Serve and Receive
Djokovic's number of Aces is less than that of
Tsitsipas, and the number of Double Faults of the two
is similar. Tsitsipas's First Serve Percentage, First
Serve Winning Rate and Second Serve Winning Rate
are lower than Djokovic's, Djokovic's Fastest Serve
Speed, Average First Serve Speed and Average
Second Serve Speed are slower than Tsitsipas's, and
Tsitsipas's Receiving Service Winning Rate is lower
than Djokovic's. (Table 1).
Table 1: Statistical table of serving and receiving ability.
Djokovic Tsitsipas
Aces 5 14
Double Faults 3 4
1
st
Serve Percentage 68% 62%
Win on 1
st
Serve 78% 67%
Win on 2
nd
Serve 53% 50%
Max Speed(mph) 123 127
1
st
Serve Average
S
p
eed
(
m
p
h
)
108 115
2
nd
Serve Average
S
p
eed
(
m
p
h
)
86 94
Receiving Points Won 40% 30%
In AD Court, Djokovic's first and second serve
are mainly in the wide. In Deuce Court, Djokovic's
first serve is mainly in the wide and the second serve
is mainly middle; In AD Court, the first serve of
Tsitsipas is mainly in the middle and the second serve
is mainly in the body. In AD Court, the first serve of
Tsitsipas is mainly in the wide and the second serve
is mainly in the body. (Table 2).
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
744

Table 2: Statistical table of serve point.
AD Court Deuce Court
Middle Boby Wide Middle Boby Wide
Djokovic
1
st
Serve 43% 0% 57% 40% 0% 60%
2
nd
Serve 28% 11% 61% 59% 9% 32%
Tsitsipas
1
st
Serve 48% 10% 42% 38% 9% 53%
2
nd
Serve 18% 66% 16% 31% 63% 6%
3.2 Stalemate Stage
Infosys Rally Analysis represents the performance of
the players in short, medium and long rally lengths
with an option to deep dive further to each shot-level.
Djokovic is less than Tsitsipas in Short Rallies
Points, and Tsitsipas is less than Djokovic in Medium
Rallies Points, Long Rallies Points, and Total Points
Won. (Table 3).
Table 3: Statistical table of rally lengths points.
Short
Rallies
Points
(
0-4
)
Medium
Rallies
Points
(
5-8
)
Long
Rallies
Points
(
9+
)
Total
Points
Won
Djokovic 82 49 33 164
Tsitsipas 85 37 25 147
Note: points won by a player on opponent’s errors are
considered as a legal shot.
Tsitsipas has more Total Winners than Djokovic
in number, but it is lower than Djokovic in Winners
Height above Ground, Djokovic has higher speed in
Winners Average Spin than Tsitsipas, and the two
men have the same speed in the fastest Winners.
(Table 4).
Table 4: Statistical table of winners.
Height
Above
Ground
(
feet
)
Average
Spin
(rpm)
Fastest
Speed
(mph)
Total
Winners
Djokovic 5.9 3018 123 56
Tsitsipas 5.5 2756 122 61
In terms of impacting points, Djokovic and
Tsitsipas' Winners are mainly distributed near the
singles sideline, and Djokovic's Winners are closer to
the baseline than Tsitsipas. (Figure.5).
Note: ball bounce location is not available for some points.
Figure. 5: The diagram of the winners positions of djokovic
and tsitsipas.
4 DISCUSSION
Every point of a tennis match and every stroke of a
player can be regarded as data. When these huge data
are gathered together, they can be treated as an
unusually effective method for athletes and coaches
to evaluate the game, analyse opponents and
summarize themselves. By marking the line, impact
point and position of each shot as special data, we
will more intuitively and clearly summarize the
winning rules of tennis matches. (Zeng, 2019; Guo,
2019; Liu, 2019)
The first data mark of tennis match is serving.
Although serve seems to be independent, it is the
beginning of the whole tactical system in a point. It
is purposeful and planned. To a large extent, the
quality of serve will affect the outcome of this point.
In the serve, players can improve the quality of serve
through strength, speed, rotation, angle, depth,
placement and other elements, but there are also great
constraints between these elements. For example,
increasing the speed of serve will increase the threat
of serve, but the Success Rate will also decrease; On
the contrary, if you reduce the speed of serve in order
to improve the Success Rate of Serve, it is bound to
affect the threat of serve. Therefore, when serving,
players will seek a dynamic balance between the
Research and Application of Big Data Analysis on the Winning Rules in the Men’s Singles Final of 2021 French Open
745

threat and Success Rate of Serve. For example,
players will focus on the threat of serve through
tricky angle and extremely fast speed at the first
serve; in the second serve, it will focus on the
stability of the serve and strengthen its
aggressiveness through the change of rotation and
placement (Fu, 2015; Jiang, 2014).
The big data analysis of Djokovic and Tsitsipas
in the game also confirmed the previous view.
Djokovic and Tsitsipas also increase the threat of
serve to attack the opponent's weak links, increase
the difficulty of the opponent's receiving the serve,
and further expand the advantages brought by the
serve through tricky angles. In the French Open, the
clay court has brought trouble to the players who
serve fast. The players who serve slowly and fast on
the clay court do not have the advantage. The players
can only achieve the goal of serve score through the
coordination of angle rotation. Big data analysis
points out that their serve points are mainly external
corners, which are mainly aimed at increasing the
angle of serve, making it more difficult for opponents
to return the ball, and further expanding the
advantages of serve for subsequent attacks (Li, 2014;
Liu, 2014).
When the athletes serve the second time, they pay
more attention to the stability of the serve and attack
on the basis of ensuring the stability. The big data
analysis points out that the athletes of both sides
avoid the forehand position of the opponent in the
choice of the placement of the second round and
attack the relative weak links of the opponent.
Djokovic's second serve in the AD court is mainly in
the wide, mainly serving to the opponent's forehand.
Its purpose is to pull the opponent out of the court by
increasing the angle of the serve line, so that the
opponent can expose a greater gap and pave the way
for the next attack. The second serve point in the
bisection area is mainly in the middle. The middle
point is the line with the shortest serve distance. Due
to the shortening of the distance, the reaction time of
the opponent is relatively shortened. In addition,
when the opponent returns the ball at the middle
point, it is not easy to hit the ball from a large angle.
In a certain sense, it limits the opponent's attack. In
AD court and Deuce court, Tsitsipas's second serve
placement is mainly based on body, which is
consistent with Djokovic's tactical thinking, and lays
the groundwork for the next attack by restricting the
opponent's advantage.
From the data, Tsitsipas' first serve and second
serve are faster than Djokovic in speed, but the First
Serve Winning Rate and the Second Serve Winning
Rate are lower than Djokovic's. It is not difficult to
see that Fast Serve Speed is not the decisive factor
for winning. In order to win the score, it is also
necessary to cooperate with the placement, angle and
rotation when serve, or to establish the advantage of
attack by serve. According to the data in Rally
Lengths Points, the advantage of Tsitsipas in serve
fast is reflected in Short Rallies Points. The
advantage established through fast serve is easily
realized in Short Rallies Points.
The level of serve reception will affect the
outcome of the game to a certain extent. The opposite
side of the server is the receiver. To a certain extent,
the server has the advantage of this point, while the
receiver is at a disadvantage. The receiver can only
resolve the disadvantage of the receiver through
high-quality receive. In receiving serve, the emphasis
of receiving the first serve and the second serve will
be different. Due to the fast speed, large angle and
tricky placement of the first serve, the success rate
and stability are usually emphasized when receiving
the first serve; however, the second serve is relatively
slow and the angle is relatively small, which gives
the receiver more time to prepare. Usually, when
receiving the second serve, the receiver pays more
attention to the offensive, and resolves the
disadvantage of receiving the serve through a strong
attack, so as to create scoring opportunities for the
next step as much as possible. Big data analysis
points out that Djokovic scored higher than Tsitsipas
on Receiving Points Won, which reflects Djokovic's
excellent receive ability. He can quickly and
accurately judge the direction and location of the
serve through the opponent's throwing action when
serving, and make correct coping strategies to
eliminate the disadvantages of the receive as much as
possible to create scoring opportunities for the next
step.
The game went through the stages of serving and
receiving, and then entered the stalemate stage. In the
stalemate stage, the players switched attack and
defend through the cooperation of angle, placement,
speed and other factors, waiting for opportunities to
expand their advantages and win the score. In the
stalemate stage, physical reserves are also a great test
for athletes. During the confrontation in the stalemate
stage, the number of strokes and the moving distance
of both players increased, so the physical strength
required increased. Big data points out that Djokovic
and Tsitsipas have hit a lot of Winners in the game.
Among these Winners, the Height Above Group is
higher than that of Tsitsipas, and the Average Spin is
higher than that of Tsitsipas. From another angle,
Djokovic's hitting quality is higher than that of
Tsitsipas. In different venues, athletes will use
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
746

different types of venues to formulate the most
effective competition strategy. The playing field of
the French Open belongs to the clay court. The ball
speed is slow and the bounce is high, so that the
players have enough time to prepare before
impacting. For those players who rely on the ball
speed to win, the clay court will limit their
advantages. Compared with speed, a strong topspin
ball can make players gain greater advantages in the
process of stalemate. Big data analysis points out that
Djokovic's Height Above Group and Average Spin
are higher than those of Tsitsipas in the stalemate.
The high bouncing stroke limits Tsitsipas, who is
good at fast attack. Compared with Medium Rallies
Points, Long Rallies Points and Total Points Won,
Djokovic has a greater advantage. We can find out
from the big data analysis that once the match is in
the stalemate stage on the clay court with slow speed
and high bounce, the effective scoring means of the
players can be summarized as follows: use the high
bounce topspin to impact the ball, mobilize the
opponent through a wide angle of impact, attack
continuously and stably, and force the opponent to
make mistakes. Big data analysis points out that
Djokovic's impacting points are closer to the baseline
and the singles sideline in the distribution of
Winners' impacting points. Only continuous and
stable attack can win the score (Tan, 2016; Yang,
2020; Zhang, 2011).
5 CONCLUSION
This paper analyses the big data of the men's singles
final of the 2021 French Open and points out that the
rules of the athletes' winning in the competition are:
high Serve Success Rate and Winning Rate; It has a
high Rate of Receive and Serve; In the stalemate
stage, it is necessary to have a stable and continuous
offensive ability to obtain more Medium Rallies
Points and Long Rallies Points; The impacting points
are closer to the sideline and baseline of singles.
6 SUGGESTION
It is suggested that speed, strength, placement, angle
and other factors should be added to the serve
training to strengthen the aggressiveness and stability
of stalemate and improve the accuracy of impacting.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is supported by Fundamental Research
Funds for Central Universities, University of
International Relations
REFERENCES
Fu Jian. Analysis on Technical Characteristics of Men's
Singles Final in 2014 French Open [J]. Hubei Sports
Science and technology, 2015, 34 (01).
Guo Jian, Wang Wenlong. Comparative Analysis of
Techniques and Tactics between Djokovic and Nadal
in the Men's Singles Final of the Australian Open in
2019[J]. Modern sports science and technology, 2019,
9(15).
Jiang Bin. Analysis on Scoring Characteristics of Different
Types of Men's Tennis Players in Different Stages of
Competition [J]. Liaoning Sports Science and
technology, 2014, 36 (05).
Li Guoxiang, Peng Shasha, Hu Baiping. Analysis of Main
Techniques and Tactics of 2014 French Open Men's
Singles Champion Nadal [J]. Liaoning Sports Science
and technology, 2014, 36 (06).
Liu Shukai The application status and prospect of big data
in China's football field [J]. Contemporary sports
science and technology 2022, 12(10):169-172.
Liu Yue, Peng Jie. Technical and Tactical Analysis of
Djokovic vs. Nadal in the Men's Singles Semifinal of
Wimbledon in 2018[J]. Anhui Sports Science and
technology, 2019, 40 (01).
Liu Yuzheng. Technical and Tactical Analysis of Men's
Singles Final in 2014 French Open [J]. Liaoning Sports
Science and technology, 2014, 36 (04).
Tao Zhixiang. Research on the basic unit competitive
process of men's single event of holding rackets and
fighting with nets [D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport
University, 2002.
Tan Xiaoqiang, Luo Sheng. Technical and Tactical
Analysis of Nadal in 2013 US Open Men's Singles
Final [J]. Shang, 2016, (10).
Yang Chuntao. Statistics and Analysis of Tactics and
Techniques of Nadal Vs Djokovic in the Men's Singles
Final of the Australian Open in 2019 [J]. Sports science
and technology literature Bulletin, 2020, 28(06).
Zan Dengliang Research on the application of big data to
the tactical analysis of high-level football matches [J].
Engineering technology research 2021, 6(17):140-142.
Zeng lingbiao. Technical Analysis and Comparison
between Djokovic and Nadal in the Men's Singles Final
of the Australian Open in 2019[J]. Modern sports
science and technology, 2019, 9(33).
Zhang Zhi, Li Mao. Technical Analysis of Djokovic and
Nadal in 2011 Australian Open Men's Singles [J].
Sports, 2011, (13).
Research and Application of Big Data Analysis on the Winning Rules in the Men’s Singles Final of 2021 French Open
747
